Suppositories for adnexitis are one of the most used methods of treating the disease. There can be many reasons for it: infection with sexually transmitted pathogens not associated with sexual intercourse - after surgical interventions, hypothermia, installation (or removal) of the uterine device, and others. Whatever the cause of the disease, it is necessary to diagnose and treat it in a timely manner, since the transition of adnexitis to a chronic form is fraught with the occurrence of adhesions in the pelvic organs and, as a result, infertility.
In this article we will look at all types of suppositories that are used to treat adnexitis (salpingoophoritis), their pros and cons.
Treatment methods for adnexitis
Treatment of inflammation of the appendages should be based on an integrated approach and include drug therapy, physiotherapy, spa treatment and various methods of further prevention.
The main place in the treatment of the disease is drug therapy, which includes taking antibacterial, antiviral and antifungal drugs (depending on the type of pathogen identified), which are available in various forms - tablets, injections, suppositories, sprays for irrigating the external genitalia and preparing anti-inflammatory bath
To achieve the best result, gynecologists prescribe several medications at the same time, since taking only oral medications is not enough to quickly stop the inflammatory process, nor is using exclusively local remedies.
Suppositories for adnexitis are prescribed in almost 100% of cases, since no treatment method can replace the effect of suppositories.
Treatment: antibiotics and drugs for inflammation of the appendages
In the acute period of the disease - bed rest. After the diagnosis is established, painkillers (analgin, tempalgin, nurofen), antispasmodics (no-shpu, papaverine), antibiotics (azithromycin, ampiox, cefazolin, ceftriaxone and others) are prescribed. A 10% calcium chloride solution of 10 ml is administered intravenously, ice is placed on the stomach during the day for 1.5 hours with a break of 1 hour.
In the subacute period , light thermal procedures on the abdomen (warming compresses, heating pad, UHF), local administration of antibiotics (by puncture of the posterior vaginal fornix after preliminary suction of the contents) are indicated, if this is successful (the puncture is carried out once every three to four days, a total of 5– 6 procedures).
Autohemotherapy may be effective.
As the general condition improves, physiotherapy is added to speed up resorption - paraffin on the lower abdomen (but not “pants”!) and ionogalvanization with calcium chloride.
Recently, adrenal cortex hormones have been used to treat adnexitis in acute and subacute forms: prednisolone 0.005 g three times a day for the first three days; twice a day for the next three days and once a day for another three days.
In chronic cases, physiotherapy (UHF, paraffin, mud, ozokerite, ion-galvanization with potassium iodide) is indicated. Hydrotherapy, exercise therapy, and gynecological massage are also used.
Spa treatment is indicated no earlier than 6 months after the acute period.
Pros and cons of candle therapy
Suppositories for the treatment of adnexitis have a number of positive and negative aspects of use.
| No. | pros | Minuses |
| 1. | Does not require special skills to use, such as injections | During treatment with suppositories, it is necessary to abstain from sexual intercourse. |
| 2. | Direct effect on inflamed tissues | Should be used in combination with other forms of drugs, for example, tablets or injections, since local treatment alone will not produce the expected therapeutic effect |
| 3. | Quick relief of pain and relief of the inflammatory process at the local level | Some drugs cause local reactions in the form of itching, burning, allergies |
| 4. | Unlike tablets, they do not irritate the mucous membranes of the gastrointestinal tract | During treatment, it is necessary to use sanitary pads intended for daily use, since suppositories, after dissolving in the mucous membranes, may leak slightly and stain the laundry |
| 5. | Do not have a negative effect on the liver, like most antibiotic tablets | , |
| 6. | Wide range of drugs, both in terms of pharmacological effects and price | , |
| 7. | A number of drugs can be used during pregnancy and lactation | , |
As can be seen from the comparative table, there are fewer disadvantages of using vaginal suppositories than advantages; they are very conditional and associated with temporary inconvenience.
general description
Another name for adnexitis is salpingoophoritis. This difficult-to-pronounce medical term is formed by the fusion of two simpler ones - salpingitis, which is an inflammatory process in the fallopian tubes, and oophoritis, which is an inflammation of the ovaries. Thus, salpingoophoritis covers problems with both the fallopian tubes and the ovaries. But this term is rarely used. Most authors and medical publications prefer the shorter name of the disease - adnexitis.
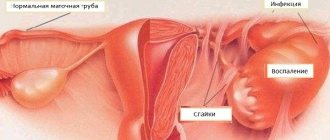
The symptoms of this disease, which occurs on the left and right of the uterus, may differ slightly. They can also be regarded as signs of completely different diseases not related to gynecology. Only a doctor can make an accurate diagnosis. Without treatment, adnexitis is fraught with infertility, and in some cases, the development of peritonitis.
Many women know this disease as inflammation of the appendages. It should be noted that there are appendages of the uterus (fallopian or fallopian tubes and ovaries) and ovaries (including rudimentary remains of the primary kidney and its ducts). When they talk about salpingoophoritis, they mean pathological processes in the fallopian tubes and in the ovaries with all their appendages.
Rules for using candles
For adnexitis, not only vaginal medications can be prescribed, but also rectal ones. The latter usually refer to anti-inflammatory drugs.
There is a certain algorithm for using suppositories for adnexitis.
- It is necessary to insert the suppository after all hygiene procedures and only with clean hands. If rectal medications are used, you must have a bowel movement before using them.
- The administration is carried out in a lying position. If treatment is carried out with a vaginal drug, then lie on your back, if rectal, then lie on your side. Immediately after administration, it is recommended to lie down for at least half an hour so that the drug is distributed throughout the mucous membranes.
- Unless otherwise indicated, suppositories are administered at night, before bedtime.
- Throughout the entire course of treatment, it is necessary to abstain from sexual intercourse and also use sanitary pads.
Treatment of acute form
The doctor prescribes treatment for adnexitis based on test results and symptoms. At home, a woman will have to follow all the recommendations of her gynecologist. Often, the course of therapy includes intramuscular and intravenous injections, for which the patient will have to visit the manipulation room in the clinic. In many cases, adnexitis is treated in a hospital. This applies primarily to pregnant women who undergo therapy only in a hospital.
Since the disease is caused by the penetration of microbes into the appendages, the main direction of treatment is antimicrobial therapy. To prescribe an effective drug, it is necessary to test for bacterial resistance to antibiotics, but in practice this is not always done. Basically, treatment follows a well-established scheme. For antibacterial therapy the following drugs are used:
- Penicillins (“Oxacillin”, “Ampicillin”).
- Tetracyclines (“Doxycycline”, “Tetracycline”).
- Fluoroquinolones (Oflaxacin and analogues).
- Macrolides (“Erythromycin”, “Azithromycin”).
Anti-inflammatory drugs and biogenic stimulants are also prescribed:
- "Sulfadimethoxine".
- "Biseptol".
- "Plasmol."
- "Vitreous body."
Homeopathy treatment for adnexitis, the symptoms and course of which indicate an acute form, is not carried out, since the very concept of “homeopathy” means therapy in small doses, that is, very moderate.
As an integrated approach to treatment, patients are prescribed physiotherapeutic procedures (electrophoresis, UHF, mud therapy).
Types of candles
Suppositories for adnexitis can be grouped into several categories.
Antibacterial, antiviral and antifungal
These are vaginal medications that kill pathogens. The advantages of these remedies include the rapid elimination of painful sensations and stopping the spread of the inflammatory process to nearby organs. The disadvantages are the negative impact on the vaginal microflora, since along with harmful bacteria, antibiotics also destroy natural representatives of the microflora. Therefore, after treatment with antibacterial suppositories, it is necessary to take probiotics (Bifidumbacterin, Linex, Bifiform, etc.). Also, on the last day of antibiotic treatment, it would be a good idea to take a Flucostat capsule (a cheaper analogue, Fluconazole) to prevent the occurrence of thrush.
The most effective suppositories with antibiotics for inflammation of the appendages are Polygynax, Clindacin, Klion D, Hexicon, Terzhinan, Betadine.
Most antibacterial drugs are mixed in nature, that is, they are effective not only against pathogenic bacteria, but also against some viruses and fungi.
Ichthyol suppositories for adnexitis deserve special attention. This is a complex drug that has anti-inflammatory, antibacterial and reparative properties. That is, these suppositories not only destroy pathogenic flora and relieve inflammation, but also restore mucous membranes damaged by bacteria.
A specific drug is prescribed by a doctor depending on the pathogen identified and whether the patient has any contraindications. The duration of treatment is also determined individually depending on the severity of the disease and other indications.
Anti-inflammatory suppositories for adnexitis
As a rule, they are prescribed rectally and simultaneously with suppositories of the previous group. The most popular and effective drugs are Indomethacin, Diclofenac, Movalis.
Indomethacin is the most effective drug among those mentioned, it relieves pain after the first injection, however, it has a number of side effects and contraindications, so it is not suitable for everyone.
Diclofenac can be considered an analogue of Indomethacin, however, its pharmacological properties are less effective, and it is also not prescribed to persons with a history of hypertension or a tendency to increase blood pressure.
Movalis is a non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drug that is effective for inflammation of the appendages, but cannot be used with all antibiotics.
Suppositories for restoring vaginal microflora (probiotics)
You can use vaginal suppositories Bifidumbacterin or Acelact. Both drugs have an affordable price, are effective and have virtually no contraindications. But suppositories of this group are not always prescribed, but only in cases where very strong antibiotics were used for an extensive inflammatory process, as well as for long-term treatment with them. If adnexitis occurs for the first time, and the inflammation was stopped in the early stages of the disease, then it is not necessary to use probiotics.
Pathogenesis of acute adnexitis
This form of the disease develops immediately after infection of the appendages by microorganisms. The manifestation may not begin suddenly, as with some other diseases (for example, appendicitis, shigellosis, influenza). Often the acute form lasts several months. A woman observes a disturbance in her menstrual cycle, the appearance of signs of cystitis (frequent and painful urination), pain in the lower abdomen that appears after performing heavy physical exertion, after hypothermia. If inflammation is observed on one side of the uterus, it is called unilateral adnexitis. The symptoms on the left side and on the right are slightly different. Very often, bilateral adnexitis is observed when the fallopian tubes and ovaries are affected on both the left and the right. In this case, the woman feels pain in the lower abdomen, radiating to the anus and vagina. On palpation, the abdominal muscles below the navel tense, discharge increases, and increased leukocytosis is detected in the blood.
If adnexitis is on the right, symptoms expressed in pain on the right side, which can be mistaken for attacks of appendicitis. These two diseases can be distinguished by additional signs. So, with appendicitis, in most cases, vomiting and nausea are observed. This is not typical for inflammation of the appendages, but with adnexitis, women almost always experience pain during sexual intercourse and discharge (profuse leucorrhoea mixed with pus and sometimes blood). The surgeon must rule out appendicitis.
With adnexitis on the left, women experience nagging painful sensations, respectively, on the left side of the navel. They almost always intensify during sexual intercourse, menstruation, and ovulation.
In addition to pain and discharge, the symptoms of acute adnexitis are as follows:
- Prostration.
- Heat.
- Headache.
- Lack of appetite.
- Brokenness.
These signs are not leading in determining adnexitis and may indicate dozens of other diseases. However, they worsen the patient’s general condition and complicate diagnosis. If women experience such symptoms, especially pain in the lower part of the peritoneum on either side and profuse purulent discharge, they should immediately consult a gynecologist.
Video on the topic
Adnexitis acute and chronic
Barto Ruslan Aleksandrovich, ultrasound diagnostics doctor, Moscow Regional Scientific Research Institute of Obstetrics and Gynecology (MONIIAG) answers the most troubling questions.
Exacerbation of chronic salpingoophoritis with swelling of the fallopian tube and accumulation of inflammatory exudate in it (formation of hydrosalpinx). The walls of the fallopian tube are swollen and thickened. Noteworthy is the good visualization of the fimbrial part of the fallopian tube and fimbriae (normally not visible on ultrasound) against the background of free fluid in the pelvis.
It should be noted that ultrasound diagnosis of inflammatory diseases of the pelvic organs (PID, acute, subacute adnexitis, exacerbation of chronic adnexitis, salpingo-oophoritis, endometritis) already in the early stages of these diseases, when clinical manifestations are still minimal, in most cases allows the doctor to , assess the situation, establish a true diagnosis and begin treatment. As you know, a correct diagnosis is the key to proper treatment, and timely treatment is the right path to recovery.
Salpingo-oophoritis, or adnexitis - inflammation of the appendages
Homeopathy as a method of treating chronic adnexitis.
Inflammation of the appendages: causes and treatment
Inflammation of the appendages can lead to infertility, so it is necessary to promptly treat and prevent this disease.
Chronic adnexitis: symptoms, adhesions
Source
The information presented in this article is based on official authoritative sources:
- Video on the topic.
- Home medical encyclopedia. Ch. ed. V. I. Pokrovsky. In one volume. Abortion - Foot and mouth disease. – M.: “Medicine”, 1993. – 496 p. from illus. NPO "Medical Encyclopedia" 1993.
- Tarasov E. A. Self-help from A to Z: Complete reference book / Tarasov E. A. - M.: LLC Publishing House Eksmo, 2009. - 352 p. – (Complete medical reference for the whole family).
- Fragment of a page from the site: https://www.ja-zdorov.ru/blog/svechi-pri-adneksite-7-effektivnyx-lekarstvennyx-preparatov/
- Uzhegov G.N. People's medical book. The best recipes of traditional medicine. – M.: Arnadiya, 1998. – 352 p. /Medicine for everyone.
- Uzhegov G. N. Official and traditional medicine. The most detailed encyclopedia. – M.: Eksmo Publishing House, 2012.
Description of the disease and the reasons for its development
Adnexitis is an inflammatory disease of the uterine appendages. The pathological process involves the ovaries and fallopian tubes, and the inflammation can be unilateral or bilateral. The disease is considered one of the most common and frequently diagnosed and develops due to the activity of pathogenic microorganisms, such as streptococci, gonococci, Trichomonas, chlamydia, enterococci, and some types of fungi.
A specialist briefly talks about the causes of adnexitis and its consequences:
Inflammation can develop in several ways. Most often, the pathological process spreads through the uterus from the cervical canal, but can directly affect the ovaries or fallopian tubes. The following pathways for the development of inflammation are distinguished: ascending (from the vagina to the cervix, then the body of the uterus, and then to its appendages), descending (through the peritoneum from the cecum or sigmoid colon), lymphogenous (with lymphatic fluid) and hematogenous (with blood flow).
The main cause of adnexitis is the activity of pathogenic organisms, and the following factors can provoke its development:
- Promiscuous sexual intercourse, unprotected sexual contacts, multiple sexual partners.
- Failure to comply with personal hygiene rules, which can provoke the penetration of pathogenic microorganisms into the vagina from the anus.
- Sexually transmitted sexually transmitted diseases and infections: gonorrhea, chlamydia.
- Early resumption of intimate life after an abortion or childbirth. At these stages, the cervix remains slightly open, and bacteria, viruses or fungi can penetrate through it.
- Mechanical damage to the mucous membranes of the appendages or uterus as a result of abortions or other surgical interventions, or improper installation of the intrauterine device.
- The presence of sources of chronic infection in the body. By lymphogenous and hematogenous routes, pathogenic microorganisms can penetrate into the appendages with pyelonephritis, colitis, appendicitis, tonsillitis or otitis media.
- Inflammatory diseases of the internal genital organs, such as endocervicitis, colpitis, endometritis.
- Weakening of the body's natural defenses. When immunity decreases, the vaginal microflora is disrupted: bacteria begin to multiply at a rapid pace and spread throughout the uterus and appendages. Hypothermia, stress, irregular daily routine or nutrition, vitamin deficiencies, pregnancy, and hormonal disorders can weaken the protection.