| Astrocyte | |
| Catalogs | |
| |
| Media files on Wikimedia Commons |
Astrocyte
(Latin astrocytus; from Greek άστρον - star; and
κύτος
- cell [2]) - a type of stellate-shaped neuroglial cell with numerous processes [3].
The collection of astrocytes is called astroglia
.
Functions of astroglia[edit | edit code]
- Supportive and delimiting function - support neurons and divide them into groups (compartments) with their bodies. This function is enabled by the presence of dense bundles of microtubules in the cytoplasm of astrocytes.
- Trophic function - regulation of the composition of intercellular fluid, supply of nutrients (glycogen). Astrocytes also mediate the movement of substances from the capillary wall to the plasma membrane of neurons.
- Participation in the growth of nervous tissue: astrocytes are capable of secreting substances, the distribution of which sets the direction of neuronal growth during embryonic development. The growth of neurons is possible as a rare exception [ source not specified 2712 days
] and in the adult body in the olfactory epithelium, where nerve cells are renewed every 40 days. - Reparative function - when nerve tissue is damaged, for example due to a stroke, astrocytes can be converted into neurons.[4]
- Participation in neuronal migration: in the rostral migratory tract, astrocytes form glial tubes
, along which neuroblasts formed during adult neurogenesis move into the olfactory bulb. - Homeostatic function - formation of glymphatic flow. Extraction of glutamate and potassium ions from the synaptic cleft after signal transmission between neurons.
- The blood-brain barrier protects nervous tissue from harmful substances that can penetrate from the circulatory system. Astrocytes serve as a specific “gateway” between the bloodstream and nervous tissue, preventing their direct contact.
- Modulation of blood flow and blood vessel diameter - astrocytes are capable of generating calcium signals in response to neuronal activity. Astroglia is involved in the control of blood flow, regulates the release of certain specific substances,
- The hypothesis is that memory and IQ are the only things that distinguished Einstein's brain - the number of astrocytes.[5]
- Regulation of neuronal activity - astroglia are capable of releasing neurotransmitters. Regulation of slow wave activity during sleep[6].
Diagnostics
To make a diagnosis, a neurologist must collect an accurate history and check what neurological symptoms the patient has. For this purpose, special tests and tests are carried out that allow us to identify motor and sensory disorders, the functioning of reflexes, etc. It is also necessary to check your vision and hearing. The combination of certain symptoms may indicate the presence of a tumor in a certain part of the brain.
To confirm the diagnosis of brain cancer, the following methods are used:
- X-ray of the skull or craniography. Can be used in the initial stages. The photographs will show various changes in the bones that are caused by the tumor process (dehiscence of the sutures, thinning of the bones, deepening of the pits, atrophy, destruction, etc.) and displacement of the cerebral vessels and pineal gland.
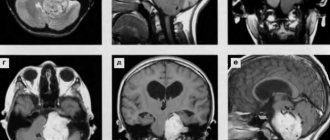
- Computed tomography (CT). Its accuracy is greater than that of a simple x-ray, since scanning occurs from several angles, which allows you to obtain a cross-sectional image of the brain. In this way, you can determine the extent of the tumor and its nature, distinguish areas of cysts and edematous tissue, and see compression and displacement of brain structures. On CT, pilocytic astrocytomas appear as soft, small lesions without mass effect.
- Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI). This is a more sensitive method for diagnosing brain astrocytoma, which allows you to detect even the smallest nodes that are not recognized on CT. In this way, a three-dimensional image of the brain can be obtained. An MRI does not use harmful radiation, so it is safer. MRI with piloid astrocytoma shows a low signal in the T1 mode and a high signal in the T2 mode.
- Positron emission tomography (PET). A relatively new method that involves the intravenous administration of a radiopharmaceutical that mixes with the blood and is absorbed by all organs. After this, a scan is carried out in a special tomograph. Tumor cells are distinguished by the fact that metabolic processes in them occur faster. This will be visible in the scan results. All areas of the GM that have any violations will be marked in blue and blue. This way you can determine not only the prevalence of cancer, but also the functional activity of the brain or even the entire organism as a whole.
- Stereotactic biopsy. To accurately establish the histology of the tumor, it is necessary to study its structure under a microscope. To do this, a small piece of tumor tissue is taken through a hole drilled in the skull with a special thin needle. To correctly guide the needle, CT or MRI machines are used, as well as a stereotactic frame that fixes the patient’s head.
Read here: Lymphoma of the pancreas: developmental features
Additional tests for piloid astrocytoma that may be needed include:
- Encephalogram (allows you to assess the severity of neurological disorders and identify displacement of brain structures, which indicates the presence of a formation);
- Angiography (necessary to assess the state of the circulatory system of the brain).
Modulation of blood flow and blood vessel diameter[edit | edit code]
In response to neuronal activation, astrocytes are capable of releasing vasoactive substances (substances that can dilate or contract blood vessels) prostaglandins, nitric oxide (NO), cyclooxygenase COX1 and others. The mechanism for releasing these substances is different.
- The main factor in the release of these substances is the absorption of glutamate from the synaptic cleft. Glutamate can be delivered to astrocytes by specialized glutamate transporters and can also act on astrocyte metabotropic receptors. The effect on astrocyte receptors leads to an increase in the concentration of calcium ions Ca2+ in them, which subsequently leads to the release of vasoactive substances COX1. The mechanism of regulation of vascular diameter during glutamate transport by glutamate transporters is still unknown.
- In addition to glutamate receptors, astrocytes also possess ATP receptors. Activation of ATP receptors also leads to an increase in the concentration of calcium ions in astrocytes and the release of vasoactive substances.
- The absorption of potassium ions from the synaptic cleft by astrocytes also leads to the release of substances that affect blood vessels.
Causes of pilocytic astrocytoma of the brain
What are the causes of piloid astrocytoma of the brain? Scientists do not know the exact answer to this question.
Read here: What is colon adenocarcinoma?
Presumably the occurrence of cancer is influenced by:
- heredity (if your closest relative had cancer, then there is a chance that this disease will be inherited from you);
- genetic disorders. Also, piloid astrocytoma can occur in people with chromosomal abnormalities and diseases such as Li-Fraumeni syndrome, neurofibromatosis;
- radiation;
- chemicals;
- bad habits;
- weakened immunity.
Regulation of neuronal activity[edit | edit code]
Metabolic interactions between neuron and astrocyte, from Çakιr et al., 2007
For a long time, astrocytes were considered the supporting cells of neurons, providing their nutrition and physical support. Recent research has led to the creation of a model of a tripartite synapse (presynaptic neuron, astrocyte, postsynaptic neuron). Astrocytes are capable of releasing neurotransmitters ATP, GABA, serine and others. This allows them to directly participate in the process of transmitting and processing information in nervous tissue.
Treatment of pilocytic astrocytoma of the brain
Piloid astrocytoma: treatment
The best treatment for piloid astrocytoma of the brain is considered to be radical removal, after which a complete recovery of the patient is possible. Such an operation may not even require subsequent chemotherapy and radiation therapy, but it is not always possible. Total resection is available for small tumor sizes, localization in the cerebral hemispheres or cerebellum, and if the patient’s condition is satisfactory.
First, a craniotomy is performed, that is, the required area of the skull is opened. Then the neoplasm is excised, the cut tissues are sutured, and a titanium plate is placed in place of the bone defect. Of course, such manipulations must be carried out under the control of high-precision microscopes and computerized MRI or CT systems, which will allow the boundaries of the tumor to be determined. This tactic is necessary, since when operating on the brain, the surgeon cannot touch healthy tissue, because this can lead to serious neurological disorders, hemorrhages, swelling and even death of the patient.
Total removal of pilocytic astrocytoma of the brain is not always available. Then the doctor’s task is to excise as much of the formation as possible. This treatment helps prevent the development of intracranial pressure, occlusion of the cerebrospinal fluid pathways and eliminate the neurological symptoms that arise as a result of compression. In some cases, in patients after subtotal removal of piloid astrocytoma, the tumor stopped growing.
The exact volume of residual tumor can only be determined by MRI with contrast, which is performed within 48 hours after surgery. If the resection was incomplete, then it is additionally necessary to undergo a course of chemotherapy or radiation to destroy the remaining cells. There are also methods of intraoperative destruction, which include radiation therapy and cryofreezing. But even after complex treatment, there is always a possibility that the tumor will return again. Recurrent brain cancer is also treated comprehensively (if possible).
Read here: Non-Hodgkin lymphomas, what is it?
Sometimes the operation cannot be performed, for example, when located in the area of the visual pathways or in the trunk. Moreover, with pilocytic astrocytoma this happens very often. In this case, chemotherapy or radiation is used as the main treatment. For small tumors without a significant mass effect, a stereotactic biopsy is performed (which can replace surgery) in order to select the best treatment option based on the diagnosis.
Chemotherapy for piloid astrocytoma of the brain in childhood remains preferable, due to the fact that radiation therapy can cause negative consequences in the future that are associated with the influence of radiation. Moreover, such tumors grow very slowly and chemotherapy is often sufficient. The drugs are prescribed one at a time or in combination. For the treatment of piloid astrocytoma, Lomustine, Vincristine and Procarbazine, Cisplatin, Carboplatin are used. Some of them are administered intravenously, others orally.
Radiation therapy for pilocytic astrocytoma of the brain is often prescribed for relapses. The total focal dose for highly differentiated tumors is 45-54 Gy.
Radiosurgery can be used as an alternative to surgical treatment or in addition to it. Its essence lies in a one-time irradiation of the tumor with a maximum dose of radiation, as a result of which its cells die. In this case, the healthy part of the brain is not affected. The Gamma Knife and Cyber Knife devices operate on this principle.
Surgery for small pilocytic astrocytoma that does not cause neurological damage and grows very slowly may be delayed. Such patients are prescribed symptomatic therapy and regular monitoring. Further decisions are made based on the MRI results. This tactic is more suitable for elderly patients, in whom the tumor may not have time to develop to alarming proportions. After undergoing treatment, to control the recurrence of the tumor, the patient must undergo regular examinations, which also makes it possible to find out in time about the malignant degeneration of the tumor.
Notes[edit | edit code]
- ↑ 12
Foundational Model of Anatomy - Astrocyte // TSB
- Large medical dictionary. 2000.
- Lenta.ru: Science and technology: Science: The mechanism for restoring nerve cells after a stroke has been discovered for the first time
- Creating Meaningful Groups and the Memory Palace Technique - Procrastination and Memory | Coursera (English). Coursera. Retrieved March 8, 2020.
- Publication, popular synopsis:
- Fellin, T. et al. Endogenous nonneuronal modulators of synaptic transmission control cortical slow oscillations in vivo. Proc. Natl Acad. Sci. USA 106, 15037-15042 (2009) PMID 19706442`
Neuron-glia interactions: Glia make waves - Leonie Welberg; Nature Reviews Neuroscience, advance online publication, Published online 9 September 2009 | doi:10.1038/nrn2724 (Freely available after free registration).
Symptoms of astrocytoma
The development of astrocytoma may be accompanied by the following symptoms:
- unmotivated headache;
- nausea and vomiting;
- dizziness;
- fluctuations in blood pressure;
- visual impairment;
- impaired balance and coordination of movements.
With the development of a tumor such as astrocytoma, the symptoms of the tumor process may vary depending on the location of the tumor:
- occipital lobe – characterized by decreased visual acuity and the appearance of visual hallucinations;
- frontal lobe – as the tumor progresses, personality changes, mood swings, hemiparesis, hemiplegia appear;
- parietal lobe – impairments in writing, fine motor skills, and tactile sensations develop;
- temporal lobe – memory, speech, coordination of movements are impaired.
⇓ Applying for Treatment | Top ⇑