Under the influence of various toxic substances and toxic damage to the nervous system, the white matter of the human brain suffers. Dystrophic changes in the structure of an organ are called encephalopathy in medicine. The pathological condition develops as a result of external and internal influences, poses a threat to the life and health of the patient and is difficult to treat.
General information about the disease
Regular exposure to toxins of various origins has a detrimental effect on brain cells - neurons, leading to their death. Each group of neurons is responsible for performing certain functions in the body, so the death of individual sections disrupts the functioning of all organs and systems.
Some toxic substances act gradually, others more rapidly. Toxic damage to the brain leads to disruption of the nutrition of cells and blood vessels, which provokes the appearance of foci of necrosis.
The disease most often occurs in a chronic form. There are cases of acute poisoning.
Causes of intoxication
Often the person himself is to blame for brain intoxication. Symptoms of poisoning appear due to several factors:
- Regular consumption of large doses of alcoholic beverages.
- Smoking abuse for many years.
- Professional activity that involves constant contact with harmful chemical compounds.
- Difficult ecological situation in the populated area.
- Violation of instructions for use of household chemicals.
- Various emergency situations in hazardous industries.
- Systematic use of narcotic substances.
- Drug abuse.
There are also some diseases that cause internal intoxication:
- Diseases of the urinary system and thyroid gland.
- Metabolic disorders leading to the development of diabetes mellitus.
- Coronary heart disease, which causes constant oxygen starvation of brain cells.
- Severe liver diseases that cause the release of ketone compounds into the blood.
Such reasons provoke serious complications from all organs, often leading to death.
Read also: Types of facial piercings and the consequences of using them
General symptoms of toxic damage
There are several signs that clearly indicate the initial stage of brain intoxication. Symptoms of the pathology are manifested as follows:
- Nervous excitement of the patient, inability to sit still, feeling of euphoria.
- Unreasonable aggression.
- Loss of coordination, sudden movements.
- Involuntary contractions of the muscles of the upper and lower extremities, reminiscent of cramps.
- Dyspeptic disorders.
- Excessive drowsiness that occurs after an emotional upsurge.
- Hallucinations, delusions.
- Speech dysfunction.
- Fainting state.
In severe cases, the patient falls into a toxic coma, which is a dangerous sign and significantly complicates treatment.
Types of pathological condition
Depending on what type of toxin acts on the brain, several types of intoxication are distinguished. Each of them has its own characteristics and clinical picture:
- Alcohol intoxication is the most common form of brain poisoning. Develops as a result of long-term abuse of drinks based on methyl alcohol. Taking methyl alcohol often leads to the death of the patient. The pathological condition can occur in several forms: acute methigirated, Korsakoff's psychosis, Gaye-Wernicke syndrome, alcoholic pseudoparalysis. All these forms have common symptoms. In addition to the main signs of intoxication, the patient experiences progressive memory impairment, digestive system disorders, weight loss, sweating, low-grade fever, and epileptic seizures.
- Manganese encephalopathy most often develops in people with drug addiction who inject homemade drugs. The pathology is characterized by the patient's lethargy, speech disorder and the disappearance of the ability to write, deterioration of memory and the ability to think sensibly, lack of emotions, and pain in the limbs.
- Mercury poisoning has several signs that distinguish this condition from other types of encephalopathy. In addition to weakness, insomnia, tachycardia, the patient experiences pain in the abdomen and chest, the presence of a blue border on the lips, trembling of the arms and legs.
- Lead encephalopathy most often develops from inhalation of lead dust. It is characterized by copious salivation, a metallic taste in the mouth, and severe cramping pain in the epigastric area. There is also a change in the shade of the mucous membranes of the oral cavity to purple or lilac. When a large amount of a toxic substance enters the body, paralysis and polyneuritis of varying degrees of severity are observed.
- Gasoline poisoning is characterized by the following symptoms: muscle cramps, pathological changes in the liver and kidneys, sleep disturbance, severe weakness in the muscles of the limbs.
- Intoxication caused by arsenic poisoning affects the brain and spinal cord. It is characterized by the appearance of pain throughout the body, hair loss, white stripes appearing on the nails, dryness and peeling of the skin.
- Some drugs cause the development of drug-induced encephaloneuropathy. Hormonal, non-steroidal anti-inflammatory, hypnotic drugs in large doses provoke the appearance of the following symptoms: nervous and mental disorders, dyspepsia, slow response to external stimuli.
Read also: Nausea on an empty stomach in the morning and afternoon: possible causes
Depending on the type of toxic lesion, a treatment regimen for the patient is developed.
Forms of poisoning of the body
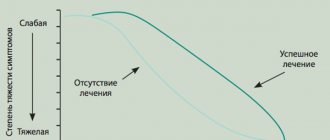
The clinical picture of the disease has two forms: chronic and acute.
Chronic encephalopathy is a consequence of regular intake of small doses of toxic substances into the body over a long period of time. Neurons are destroyed under the influence of toxins, which leads to the appearance of characteristic symptoms of poisoning.
The acute form of the pathological condition occurs less frequently. The mechanism of its development is identical to the chronic one, differing only in the speed of the body’s reaction.
Methods for diagnosing encephalopathy
Based on the patient’s complaints and external manifestations, the specialist makes a preliminary diagnosis. To confirm it, it is necessary to conduct a biochemical blood test.
Additional methods will be the appointment of a clinical urine test, consultation with an ophthalmologist and neurologist, computed tomography and electroencephalogram. The results obtained will help to determine the cause of poisoning and the consequences of the poison on the patient’s organs.
In some cases, diagnosis is difficult. Patients who systematically consume large doses of alcoholic beverages and narcotic substances often want to hide this fact from the doctor. Quite often the patient is unaware of the toxins entering the body. For example, an industrial worker may not be aware of the risks of his or her profession.
Brain tumor
Pathological formations of cells not characteristic of the brain, causing an increase in intracranial pressure, are called tumors. They are divided into benign and malignant.
The first symptom of this disease is headache. It becomes more frequent and intense as the tumor grows and intracranial pressure increases. Most often it occurs in the morning. Gradually, vomiting joins it, mental disorders and impaired thinking appear. The tumor can cause paralysis of the limbs, increased sensitivity to pressure, cold or heat. These changes are caused by impaired cerebral circulation. The reaction to light is impaired, the pupils are different in size. A growing tumor that is not diagnosed in time can cause displacement of the brain, further disrupting its function. In the early stages, the tumor is surgically removed, giving hope for recovery. In advanced cases, the patient receives palliative treatment - temporary maintenance therapy.
Treatment of toxic damage
Therapeutic measures are aimed at removing toxins from the body and restoring lost functions. In case of acute poisoning, the primary goal is to normalize the person’s condition. The treatment regimen for toxic encephalopathy includes several points:
- Intravenous drip infusions of glucose with vitamin C, saline, Neohemodez, Rheosorbilact, Ringer to speed up the process of cleansing the body. Cleansing enemas and gastric lavage are also performed. In rare cases, hemodialysis is prescribed.
- Prescribing sedatives and tranquilizers to reduce the patient’s excitability and eliminate seizures.
- To normalize metabolic processes in the brain, Cinnarizine, Piracetam, Cerebrolysin and other drugs are used.
- If the patient’s condition is severe, drugs that normalize the functioning of the liver and all internal organs are added to the treatment: Glutargin, Heptral.
- During the recovery period, physiotherapeutic procedures are required, for example, massage, mud baths, acupuncture, physical therapy to strengthen muscles.
Read also Fluid retention in the body: causes and methods of treatment
If a patient suffers from chronic alcoholism or drug addiction, a visit to a narcologist and psychiatrist will be a necessary part of treatment.
Possible consequences of intoxication
Complications after toxic brain damage largely depend on the severity of the patient's condition. At advanced stages of chronic intoxication, it is impossible to completely restore the functionality of organs and systems.
The most common complications are considered to be the following: significant memory impairment, signs of partial paresis of the muscles of the limbs, disorders of the nervous system, manifested by an unstable emotional state, sleep disturbance, pathologies of the liver and urinary system, frequent depression, multiple sclerosis.
To minimize the consequences of toxic brain damage, it is necessary to regularly undergo preventive therapy to maintain the body.
Causes of encephalitis
Of the most common causes of brain encephalitis, viruses are identified that occupy a leading position (mosquito virus, tick-borne encephalitis virus).
There are two known ways of transmitting encephalitis:
- When bitten by a blood-sucking insect (tick, comora).
- When consuming milk from an infected animal.
This group is characterized by natural focality and spring-summer seasonality.
Enteroviruses (Coxsackie, ECHO) can also be causative agents. Enteroviral encephalitis is characterized by vomiting, paralysis of the limbs, and epileptic seizures. Herpes viruses (herpes simplex virus, herpes zoster, cytomegalovirus infection), retroviruses, myxoviruses (influenza virus, parainfluenza).
More than eighty percent of the population is infected with the herpes simplex virus, but it is in a state of sleep; as soon as the immune system reduces its activity, it begins to activate. Today there is a tendency towards the appearance of encephalitis, which is caused by the rabies virus. With the development of meningoencephalitis, the causes of brain encephalitis can be mycobacteria, spirochetes, streptococci, meningococci, and rickettsia.
Pathology prevention measures
Following simple preventive measures will help avoid poisoning and possible complications after treatment:
- Do not exceed the recommended dosage of medications.
- It is recommended to stop smoking and taking drugs, and drink alcoholic beverages in minimal quantities.
- If your professional activity involves hazardous production, all safety measures must be observed.
A healthy lifestyle and a balanced daily menu will significantly improve your quality of life.
Toxic encephalopathy is a dangerous pathology that affects all human organs and systems. If left untreated or not promptly seeking medical help, it can be fatal.