Nature of pain under the right shoulder blade
The shoulder blade is an integral part of the shoulder girdle. In addition to it, this includes the humerus, collarbone, tendons and muscles. Between the rubbing structures there are synovial sacs and bursae that support motor function. Pain that is local or reflects the condition of the internal organs may appear in different parts of the shoulder girdle.
There are a number of reasons that influence the occurrence of subscapular pain:
- Muscle inflammation.
- Bone disorders.
- Pain caused by monotonous movements, uncomfortable body position.
- Bursitis.
- Internal illnesses.
Pain under the right shoulder blade from the back
The shoulder is an unstable joint, so the pain that occurs in it has a variety of causes, reflecting both internal diseases and local ones.
Pain varies by type:
- Local. They occur both at the site of damage to the body and close to it. This type is typical for disorders of the musculoskeletal system and soft tissues.
- Reflected. Diseases of some internal organs create pain discomfort that is distant from the original source.
- Irradiating. Pain spreading beyond the affected area is characteristic of diseases of the lungs, liver, and spleen.
- Mixed pain. Occurs in response to irritation of pain receptors, as a protective reaction of the body. Its development is influenced by social factors and emotional stress.
It's a dull pain
The classic symptom is a dull pain that is aggravated by raising and lowering the arms, but relieved by rest. Sometimes the pain extends throughout the arm. It is caused by excessive stretching of the muscles, most often due to physical exercise, uncomfortable posture during sleep, or carrying heavy objects. Develops with osteochondrosis, sprained ligaments.
Acute pain
The pain under the right shoulder blade from the back becomes sharp with intercostal neuralgia and pneumonia.
Often develops as a result of:
- hepatic colic;
- acute inflammation of the gallbladder;
- dyskinesia of the gallbladder.
The developing acute pain affects not only the subscapular region, but also the epigastric region, shifting to the upper part of the body. Increased muscle tone and diseases of the spine give rise to acute pain in the morning, which weakens or disappears completely during the day.
Sharp pain
Inflammatory diseases of the peritoneum, which have passed into the acute stage, make themselves felt with intense subscapular pain.
Purulent infiltration, hepatic colic, contribute to the appearance of the syndrome in the right scapula, its lower sector, while other signals appear:
- itching in the anal area;
- fever;
- painful urination.
Disorders such as scapular osteomyelitis, glomerulonephritis, perforation of an ulcer are factors against which sharp subscapular pain occurs.
Stitching pain
Cutting pain is typical for:
- lesions in various parts of the spine;
- intervertebral hernia.
After a night's sleep in an uncomfortable position, in addition to numbness, shooting pains along the shoulder blade are felt. Bruises that affect cartilage, bone, and soft tissue also provoke this type of pain.
Diseases that cause stabbing pain:
- tracheobronchitis;
- tuberculosis in latent form;
- pneumonia.
Nagging pain
Sharp contractile movements of the muscles in the shoulder and structural changes in the spine lead to the appearance of nagging pain under the shoulder blade. They intensify in the morning after waking up and weaken during the day. Changes in the position of bone structures and abrasion of cartilage tissue create additional stress, which also causes pain.
Diseases against which this type of pain develops:
- lung abscess;
- acute bronchitis;
- Sprengel's disease;
- vegetative-vascular dystonia.
Constant pain
Persistent pain is caused by impaired motility in the biliary tract, when the tone of the sphincter that controls the bile flow is reduced. The pain appears not only in the scapula area, but also affects the shoulder. It does not create any particular discomfort, is easily tolerated, but almost always indicates impaired gallbladder function.
Other reasons:
- stones in the kidneys;
- gastroduodenitis;
- acute cholecystitis.
Burning pain
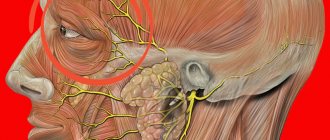
The pain under the right shoulder blade from the back becomes burning at the moment of compression of the dorsal scapular nerve.
The pain becomes burning in nature:
- with osteochondrosis;
- pneumonia affecting the right lung;
- angina pectoris;
- with damage to the peripheral nervous system.
Pain when coughing
Pain under the shoulder blade during coughing attacks occurs from tension in the chest. This pain is reflective and indicates diseases of the bronchi and lungs.
Pain when inhaling
Difficulty in inhalation indicates intercostal neuralgia. When inhaling, the expanded diaphragm pinches the nerve endings, which provokes the development of pain. With pneumonia, the pain is reflected under the shoulder blade and worsens with a deep breath. Additionally, there is a burning sensation in the chest and muscle tension. The developing subphrenic process is characterized by pain under the scapula.
There are a number of other diseases in which every breath is accompanied by pain:
- tuberculosis;
- asthma;
- acute bronchitis;
- osteochondrosis;
- intercostal neuralgia.
When driving
Discomfort that occurs when turning the body, neck, or raising arms indicates the appearance of neuralgia, a disorder in the musculoskeletal system. Lesions affecting the nerve roots in the cervicothoracic and lumbar regions cause an attack of acute pain.
Presumably it occurs for other reasons:
- poor posture;
- disc protrusion;
- chronic pancreatitis in the relapse stage;
- osteochondrosis.
What can cause pain under the left shoulder blade?
One of the most common causes of pain under the left shoulder blade is damage to the scapula itself. This, fortunately, happens quite rarely. According to medical statistics, fractures of the scapula make up less than one percent of all fractures, that is, this bone is the least likely to break (which is not surprising, given its location; it is strange that anyone manages to break it at all). Fractures of the scapula can occur due to direct force, such as a fall from a motorcycle or a car accident. In this case, severe pain will be felt in the back of the shoulder, under or above the left shoulder blade. Without treatment, an injury to the scapula can lead to chronic pain.
Very often, pain under the left shoulder blade is accompanied by chest pain. Any time chest pain is referred to the left shoulder, left arm, or jaw, there is concern that the person is having a heart attack. A heart attack may not be accompanied by any painful sensations at all, but if the pain under the left shoulder blade or between them is combined with tightness in the chest or difficulty breathing, you should urgently call a doctor.
Possible causes of right-sided back pain, additional symptoms
Pain from the back, under the right or left shoulder blade, often frightens a person, since the causes of its occurrence are not always obvious.
Gallbladder diseases
The development of cholecystitis causes a feeling of heaviness in the right side, giving off pain in the scapula. With cholelithiasis, the pain becomes acute. The attack provokes pain that runs from the upper abdomen to the shoulder. With biliary colic, sharp pain always appears unexpectedly, starting in the right hypochondrium, and then moving to the scapula.
Associated symptoms:
- Intensity of pain.
- Nausea, vomiting, dryness and bitterness in the mouth.
- Fever.
- Pain in the right side, extending to the shoulder.
- The pain develops more often in the morning.
Subphrenic abscess
During inflammation of the pancreas, development of a tumor, cyst or infection in the liver, referred pain is present. Indigestion from fatty and rich foods causes pain in the epigastric region, which radiates to the back area.
Associated symptoms:
- the pain is sharp;
- worsens when breathing;
- possible increase in body temperature.
Bronchopulmonary diseases
Problems with the lungs create pain not only in the chest, but also in the shoulder blades. It could be:
- Pancoast tumor. A type of tumor that grows in the upper part of the lungs. Usually affects long-time smokers.
- Pleurisy. Inflammation of the mucous membrane of the lungs develops pain under the shoulder blade when inhaling.
- Pneumothorax. Air retention between the lung and chest wall. The pain is accompanied by sudden shortness of breath, which can be acute.
Kidney diseases
The right kidney lies not far from the shoulder blade, so when it becomes inflamed, it reflects pain to this area. Kidney stones, infections, tumors, all of these can cause pain. When the right-sided kidney becomes inflamed and purulent infiltrates occur, the pain radiates to the right shoulder blade and becomes acute and paroxysmal.
Constant pain coming from the lower back, rising to the shoulder blade, often accompanied by nausea and vomiting, develops against the background of pyelonephritis. The pain can be of varying intensity, but most often it is aching and dull.
Diseases of the musculoskeletal system
Inflammation of the ligamentous apparatus of the shoulder, scapula, and periarticular tissues develops pain near the working arm.
Nagging pain is caused by:
- herniated disc;
- arthrosis of the facet joints.
- scoliosis;
- disorders in the spinal disc.
Bursitis and scapular tuberculosis are characterized by pain in the subscapularis. The pain inherent in these diseases intensifies when coughing, and numbness of the limbs develops.
Causes of pain under the shoulder blade
Like a flashing check engine light in any vehicle, pain in any part of the body is a sign that something is wrong and needs to be checked.
Moreover, the intensity of pain does not always indicate the severity of the problem. Causes of pain under the shoulder blade can include muscle injuries or more serious problems, such as a heart attack or internal bleeding. One of the causes of pain under the scapula may be a subscapularis injury. The rotator cuff is made up of four muscles. The subscapularis muscle, as its name suggests, is located just under the shoulder blade. Injury or chronic overuse can cause this muscle to spasm or tear. The location of this muscle makes it very difficult to massage it independently. And professional massage therapists and chiropractors have to use all their skills to get to it.
Other causes of pain under the shoulder blade may be in the field of neurology. Many internal organs do not have their own nerves that serve as pain receptors. Sometimes organs share part of the nervous system with a neighboring area of the body, so a reaction to injury or external irritation in one organ can be reflected in another. For example, something that happened to the stomach can be signaled by pain in the left shoulder blade. In general, pain in any of the abdominal organs can provoke pain in the right or left shoulder, or in the center between the shoulder blades. By the way, the combination of abdominal pain and pain between the shoulder blades is considered an emergency when you need to call a doctor.
Differential diagnosis
Based on a physical examination alone, it is difficult to determine the cause of pain in the shoulder blade.
In addition to visual inspection, tests and studies are carried out:
- Radiological: chest x-ray;
- CT scan of organs that raise suspicion of various diseases;
- MRI of the chest, soft parts of the body.
- ECG;
- blood analysis;
Initially, you should visit your doctor at the clinic, who will prescribe analgesic therapy. In many cases this is enough.
If necessary, the doctor will refer you to other specialists:
- traumatologist;
- surgeon;
- cardiologist;
- neurologist.
What to expect?
With a benign course, the prognosis is quite favorable, with the exception of the giant cell form, because with this type, survival depends on the characteristics of the course.
When a malignant disease is diagnosed, the main symptom of which is pain under the scapula , the prognosis is unfavorable. Five-year survival rate with early diagnosis and combined treatment varies from 50% to 75%, depending on the degree of progression, histological findings and the presence of metastases.
Medicines
Treatment for pain depends on the underlying cause. If it is associated with muscle strain, bruises, disorders in the bony area of the scapula, then painkillers, non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs, and muscle relaxants are used. At the next stage, heat and physical therapy help.
| Name of drugs | Mode of application |
| Nimesulide | Prescribed for acute pain, take the drug after meals, 1 tablet. 2 times a day |
| Indomethacin | Used in the form of tablets for various diseases of the articular syndrome, prescribed from 25 to 50 mg 3 times a day. It is used externally for exacerbation of joint diseases: ointment and gel are applied no more than 2 times a day. |
| Ibuprofen | The daily dose of tablets depends on the cause of the pain; you can use a gel or cream, applying and rubbing until completely absorbed 3-4 times a day. |
| Mydocalm | Relaxes muscles, increases their tone, take 1 tablet in tablet form. per day, maximum dose – 3 pcs. The solution is used intravenously, no more than 100 mg per day, intramuscularly no more than 200 mg. |
For treatment, ointments are used that provide a long-term warming effect:
- Finalgon.
- Diclofenac.
- Viprosal.
- Capsicam.
If you experience pain under your right shoulder blade with increasing intensity, you should consult a medical professional rather than self-medicate.
In what cases can pain under the shoulder blade indicate the development of cancer?
When pain in the scapula area appears for the first time, rarely does anyone think about the oncological process. Most likely, pain on the left side is a consequence of osteochondrosis, myocardial ischemia, hypertensive crisis, pathology of the lung tissue or spine, gastric ulcer or intercostal neuralgia.
Localization of pain on the right may indicate inflammation of the urinary tract (nephritis, pyelonephritis), hepatic colic, cholelithiasis or subphrenic abscess.
If pain is located between the shoulder blades, it is worth thinking about pathology of the heart, digestive tract or spine.
As for scapula cancer, it can be suspected if a person had a bone injury the day before or was exposed to strong radiation. Especially often, the scapula can be affected by metastasis when the primary focus is localized in another organ.
When a patient is diagnosed, for example, with lung or breast cancer, and subsequently develops pain in the area of the scapula or other bone, the progression of the underlying disease and the formation of metastases should be suspected.
Physiotherapy
Gymnastics, massage, and developing correct posture can help relieve pain under the right shoulder blade from the back. Before starting exercise, you need to warm and relax your muscles using a bath, hot compress or hair dryer.
Shoulder massage. It is carried out in a lying position on a hard surface:
- Stroking the scapular area.
- Pinching using the pads of the fingers, thumb and forefinger.
- Comb-like rubbing. It is carried out with the phalanges of the fingers of a hand clenched into a fist.
- Circular kneading. It is done with the pads of the thumbs of both hands.
- Spiral rubbing. It is performed using the pads of 4 fingers in a circular motion.
- Stroking the shoulder blade and surrounding area of the body.
The lesson lasts 20 minutes, the course includes 10–15 sessions, which can be carried out daily or every other day.
Scapula stabilization exercise, repeated 10–15 times:
- Lie face down on the edge of the sofa.
- Place one hand under your forehead and extend the other above the floor.
- Keeping your arm straight, slowly raise it, pressing your shoulder blade back toward your spine. The pose resembles a half-T.
- Stay in this position for 3-4 seconds, then slowly return to the starting position.
Exercise to stretch the scapular muscles:
- In a standing position, take a large soft ball and hug it with your hands.
- Continue squeezing the ball as much as possible.
- When squeezing, strain your back as much as possible, pushing your hands away from you.
- Lower your face down.
- Try to feel the stretch in the area where there is pain.
- Stay in this position for 30 seconds.
- Relax.
- Repeat the exercise 2-3 times.
Treatment
If pain appears under the left shoulder blade from the back, patients should urgently seek medical help, because such a pain syndrome may indicate an emergency condition (myocardial infarction, splenic rupture, ulcer perforation, etc.). It is not recommended to take painkillers, because... analgesics can hide symptoms and complicate subsequent diagnosis!
- Osteochondrosis. Basic therapy includes non-steroidal and steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (Diclofenac, Nimesil Diprospan). Mydocalm is used to get rid of muscle spasms. As long-term treatment aimed at slowing down the destruction of the intervertebral disc, Teraflex, Rumalon, etc. are prescribed.
- Angina pectoris. An acute attack is relieved with the help of nitrates. However, general therapy is based on lifestyle changes, the use of acetylsalicylic acid (to “thin” the blood), as well as statins to lower cholesterol levels (Atorvastatin).
- Pneumonia. The main drug in the treatment of pneumonia is an antibiotic (Amoxicillin, Cefotaxime), the choice of which depends on the causative agent of the infection.
- Stomach ulcer. Treatment of ulcers consists of destroying the provoking bacteria (Helicobacter). For this purpose, several antibacterial agents are prescribed (Clarithromycin + Amoxicillin), as well as drugs that reduce the level of acidity of gastric contents (Omeprazole).
- Vegetative crisis. In most cases, treatment for panic attacks can be limited to psychotherapy sessions. At the same time, the prescription of psychotropic substances (antidepressants, tranquilizers) is most often unjustified.
Folk remedies
To relieve tension in muscle trigger points, methods available at home are used.
Baths
Hot baths relieve pain and can be combined with massage.
Bath solution prepared in advance:
- 250 g Epsom salt.
- 1 tbsp. baking soda.
- 10 drops of peppermint essential oil.
- 5 drops of eucalyptus, rosemary, lavender oil.
- 2 tbsp. l. dried lavender.
- 1 tbsp. l. sprigs of rosemary.
Mix everything in a bowl, add dry ingredients on top. Transfer to a jar and use as intended.
A bath with ginger improves blood circulation. To do this, grate a piece of root, soak in hot water for 15 minutes, add the solution to warm bath water. Take a bath with additives for no more than 20 minutes; you should not rinse with water after the procedure. To keep warm, you should wrap yourself in a warm robe.
Decoctions and infusions
Eucalyptus tincture:
- Take 10 g of crushed leaves, 200 ml of alcohol, mix everything.
- Place in a warm place for 14 days. Shake the jar of solution periodically.
- Strain the prepared solution into a glass bottle and close with a lid.
Ginger tincture:
- Fresh root, 50 g, vodka or alcohol 200 ml, honey 1 tbsp. l. (not necessary).
- Pour chopped ginger with alcohol, add honey, leave for 2 weeks.
- Strain the prepared solution, pour into a glass bottle, and close with a lid. Can be stored for up to 2 years.
Rub the solutions onto the inflamed area before going to bed, then apply an insulating bandage.
Cat's claw decoction:
- Take 2 g of herb, add 0.5 liters of water, boil for no more than 10 minutes.
- Strain, cool and use as intended.
- The decoction can be used as a compress.
Compresses
Warming compresses increase blood flow and relieve spasms:
- Roll the bandage in several layers.
- Soak in hot water (at least +70˚С).
- Apply to the sore spot.
- Place a film and warming material on top.
- As the dressing cools, warm it in hot water.
Wound Dressing
Pain-relieving compresses:
- St. John's wort oil. Rub the area of inflammation with oil.
- Place gauze, film, warm material or a woolen scarf on top.
- Wrap the compress with a bandage around the chest.
- You can leave it overnight.
Herbal compress:
- Mix dried chamomile flowers, tricolor violet, burdock and plantain roots in equal parts. 1 tbsp. l. Pour the mixture into a glass container, pour boiling water over it, and leave until the herb softens.
- Apply the steamed broth to the sore spot, cover with cotton cloth, cellophane, and a warm scarf.
- After 15 min. remove the compress. The optimal treatment option for pain under the right shoulder blade from the back is a combination of medications and non-drug approaches. Complex therapy will help you quickly cope with the disease and get rid of pain.
Lump on back hurts when pressed
- 01 August
- 0 rating
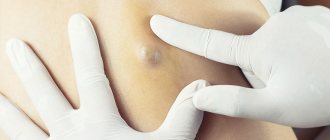
A lump on the back in the spinal area is considered the most common pathology of modern medicine.
Self-treatment in this situation will not give positive results, so you shouldn’t even take the risk. As for the size of the formation, they can be different and may not even cause discomfort to the patient. Doctors distinguish several types of formations, which differ in their localization and nature of formation. For treatment to be effective, it is necessary to correctly establish the cause that provoked this condition and establish the features of its occurrence.
Types of tumors on the back
Back lesions can be of various types, which will determine the treatment method. Each type is characterized by its own characteristics and symptoms, as well as the causes of its occurrence.
Lipoma
Lipoma is a benign formation that consists of adipose tissue. It is soft and even mobile, localized under the skin. It can occur on any part of the back and does not have a negative effect on internal organs. As the lipoma grows, it gradually pushes the tissue apart. The tumor is in its own capsule.
The reasons that provoke this benign formation:
- Disturbed metabolism in the body.
- Blockage of sebaceous ducts.
- Wrong lifestyle and unhealthy diet.
- Gradual mechanical irritation.
- Poor environmental condition.
In most cases, it occurs in professions such as loader or porter. This pathology also occurs in the female half of the population, whose age group is over 30 years.
As for the size of the lipoma, it can be the size of a small pea or reach the size of a child’s head.
Symptoms of this formation include:
- Rare pain that can be triggered by the pressure of a growing lipoma on the nerve endings. A small lipoma does not cause pain.
Diagnosis of this benign formation is difficult. To make an accurate diagnosis, the patient undergoes radiographs, histology, ultrasound and CT. As for treatment, if the lipoma does not cause any discomfort, then no therapy is performed.
Treatment is prescribed in situations where the pathology increases in size or causes certain inconvenience. Acceptable procedures are surgery or laser therapy. Laser therapy is an effective and affordable method, after which there are no relapses and does not leave scars. They may also recommend liposuction.
Atheroma
Atheroma is a pathology that occurs due to poor outflow of sebaceous gland secretions.
The secretion gradually begins to accumulate and form a formation that may resemble a cyst in shape. Atheroma has its own capsule, which is filled with a gray thick mass.
There is an advantage in the place of accumulation of glands , as well as near the hairline. Distributed throughout the body.
The reasons that provoke the occurrence of this pathology:
- External causes: injury to the sebaceous glands, injury to the sebaceous duct, unfavorable environmental conditions.
- Internal causes: hyperhidrosis, the basis of which is intense sweating, hormonal imbalance, metabolic disorders, skin diseases.
Symptoms of atheroma:
- The appearance of a defect on the skin. It looks like a swelling that can reach 6 cm in size.
- The color of the skin is not changed, since there is no inflammatory process.
- Clear outline, dense, elastic and mobile formation.
- There is no pain.
Atheroma can also cause certain complications.
There is a purulent form, which has its own pronounced symptoms:
- Swelling and formation gradually increases.
- The contents move and are palpated.
- There is redness of the skin.
- Painful sensations may occur when palpated.
- Purulent formation can cause increased body temperature, deterioration of health, problems with appetite and, as a result, intoxication.
Requires careful diagnosis and effective treatment. To recognize this pathology, it is worth carefully studying the symptoms and self-education. The patient is required to undergo histology and morphological analysis.
Treatment of atheroma can be carried out in several ways:
- Surgical intervention.
- Radio wave method.
- Ethnoscience.
- Laser therapy.
In most cases, the atheroma is removed. Folk remedies are ineffective in this situation. During the operation, both the contents of the formation and its capsule are removed. If the operation is performed poorly, there is a risk of relapse. Anesthesia is required.
The radio wave method ensures complete absence of relapse. Also, after the procedure, no defects remain on the skin, and the wound heals very quickly. No hair shaving required. Laser therapy is also considered an effective method, with positive aspects.
Hemangioma
Hemangioma is a benign neoplasm that develops from blood vessels. Does not grow and does not provoke metastasis. Considered to be common. Surgical intervention is required, preliminary diagnostics are carried out. Does not differ in severe symptoms.
Causes of lumps
Formations under the skin can be caused by a number of factors:
- Improper functioning of the sebaceous glands, which are located on the back.
- Accumulation of sebaceous secretions and impaired secretion.
- Disturbed process of formation and functioning of glands.
- Injury to pores and hair.
- Heredity.
- Hormonal imbalance in the body.
Hemangioma occurs due to intense enlargement of blood vessels ; eliminating this anomaly is difficult. Therefore, it is easier to diagnose, since it differs in its color.
Any formation on the back is considered benign, which is not capable of causing pain upon palpation. But, if the patient begins to feel pain , this indicates the development of an inflammatory process under the skin. Therefore, in such a situation, you should not postpone a visit to a specialist.
Stories from our readers!
“I cured my bad back on my own. It's been 2 months since I forgot about my back pain. Oh, how I used to suffer, my back and knees hurt, lately I couldn’t really walk properly. How many times have I gone to clinics, but they only prescribed expensive pills and ointments, which were of no use at all.
And now it’s been 7 weeks, and my back joints don’t bother me at all, every other day I go to the dacha to work, and it’s a 3 km walk from the bus, so I can walk easily! All thanks to this article. A must read for anyone with back pain!”
Seeing a doctor
If the patient has a formation on the back, then it is necessary to seek additional consultation and examination, first of all, with a surgeon , who, if necessary, can refer either to an oncologist or a dermatologist.
Diagnostics: methods
In modern medicine, the following types of examinations of lumps on the surface of the back are distinguished:
- General blood analysis. Biochemistry.
- Ultrasound examination of benign formation.
- CT scan.
Source: https://papillomnet.ru/papillomy/shishka-na-spine-bolit-pri-nadavlivanii.html