Lumboischialgia degree of prolonged exacerbation
It is the sacral lumbar region that is affected during the disease with vertebrogenic lumboischialgia; gradually the pain moves to the area of the buttocks and the back of the legs to the knees. Based on the research and complaints of patients, it was found that pain in this disease occurs very sharply, even if nothing had previously been predicted. The pain begins on the right side of the lower back and then covers the left side.
Gradually, after a few days, the pain moves to the lower part of the body, making it difficult for the patient to bend and straighten his legs. Thus, the patient, in order to reduce his pain, reduces the load as much as possible, carefully not standing on the entire foot. Thus, the patient tries not to load his legs with all his weight, which is why this disease is so characterized by lameness, which can periodically manifest itself at an early stage of the disease.
Vertebrogenic lumboischialgia: what is it?
Most people on the planet experience lower back pain.
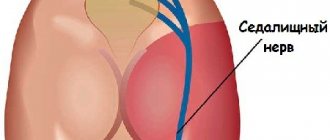
Due to pinching of the sciatic nerve, the symptoms spread to the gluteal muscle and reach the feet. Few people know that this condition is called lumboischialgia. The pain syndrome usually appears suddenly, it is provoked by sudden movement or lifting of weight. There are several forms of pathology; consider the vertebrogenic type, which is characterized by two main signs: pain in the lumbar region, radiating to both legs. Vertebrogenic lumbar sciatica code according to ICD-10 – M 54.4. This code indicates pain on the right, left, or both sides. In the diagnosis, the physician indicates not only the disease code, but also information about the stage of development of the pathological process, the clinical manifestations of the disease.
Symptoms
- shooting, burning, aching pain in the lumbar and back area, radiating to the leg;
- pain that intensifies when trying to straighten your back and when changing positions;
- rotation of the body in the lower back is limited;
- tension in the muscles of the back, lumbar region, leg muscles;
- blood flow in the lower extremities is impaired;
- changed color of the skin of the legs;
- decreased sensitivity in the legs;
- "Crawling of goosebumps";
- convulsions;
- numbness;
- bent back, leaning forward;
- skew of the body to the supporting leg side;
- the beginning of the development of lordosis, scoliosis;
- difficulty getting up from a lying position;
- Particularly severe cases lead to spontaneous urination.
Mechanism and reasons for development
Vertebrogenic lumboischialgia is formed against the background of unsuccessful rotation of the torso, bending, or prolonged stay in one position.
Other negative factors may influence the pathological process:
- protrusion and herniation of intervertebral discs;
- natural age-related changes in the spine (begin to appear after thirty years);
- chronic stress;
- incorrect posture;
- excess weight, bad habits;
- lack of physical activity;
- pregnancy;
- hypothermia, traumatic injuries to the lumbar region;
- infectious diseases;
- other diseases associated with pathological processes in the spine.
The causes of vertebrogenic lumboischialgia are negative effects on the nerve roots. This situation leads to unpleasant sensations; the muscles around the affected area tense, which provokes the appearance of nodules in them.
How to treat grade 2 scoliosis in both children and adults? View a selection of effective treatment options.
The causes of cervical kyphosis of the spine and methods of treating the pathological process are written on this page.
How does lumboischialgia manifest?
A person suffering from the initial stages of the disease begins to experience discomfort suddenly. BS has a burning, shooting or aching nature. It can manifest itself as a result of pressure and/or irritation of the nerves of the spinal structure in specific areas (the source can be prolonged stress on the body or high overvoltage). Such a pathological process provokes a reflex muscle contraction, as a result of which the level of BS increases significantly. The main complaints of patients with the presented illness:
- A painful attack begins from the dorsal area and the back of the thigh.
- Restrictions appear in the motor ability of the spine.
- Pronounced pain begins when you want to change your position, lift a heavy object, or simply straighten up.
- The characteristic position of the patient is bending forward and in a half-bent position.
- Changes in gait, as a person shifts the load from the affected limb to the healthy one.
- Feeling of constant tension in muscle tissue.
- Manifestations of scoliosis, flattening of lumbar lordosis, etc. are likely.
- Patients are unable to sit normally on a hard surface and constantly rest their hands on the edge of a chair/chair.
- The change in position occurs due to auxiliary actions, when first a person turns over the healthy side, and then, with the help of his upper limbs, he pulls the affected side towards him.
Types and forms of the disease
Vertebrogenic lumbar sciatica is not an independent disease; the pathological condition is always preceded by certain circumstances.
Depending on the root cause of discomfort, lumboischialgia is divided into several types:
- musculoskeletal. Formed against the background of various diseases of the patient’s musculoskeletal system in the lumbar region and lower extremities;
- angiopathic. Pain syndrome appears after damage to the veins or arteries that supply the lower limbs and lumbar region. Trouble causes deterioration in tissue nutrition and ischemia;
- neuropathic. Discomfort appears when the nerve roots in the lumbar region are pinched, which spreads along the entire length of the sciatic nerve;
- mixed. This form is common and includes several negative factors simultaneously (pinched nerves, spinal diseases and other troubles).
Only after finding out the cause of the pain can you begin treatment. By stopping the symptoms without affecting the real problem, it is impossible to achieve a positive result.
Forecast and prevention of lumbago with sciatica
If the underlying disease does not lead to disability of a person, and also after successful surgical treatment, the prognosis for the disease is favorable.
The diagnosis of lumboischialgia is not a death sentence.
Usually the pain is well controlled by a complex of medications and physiotherapeutic measures.
Timely treatment will minimize the risk of exacerbations.
Prevention measures include:
- Do not occupy an uncomfortable position for a long time.
- Do not wear shoes with high heels.
- Sit only on comfortable chairs.
- At work, do muscle-relaxing exercises.
- Don't carry heavy things.
- Don't get too cold.
- Stop smoking.
- Lose weight.
- Treat diseases of the joints, spine, and blood vessels in a timely manner.
Lumboischialgia is an unpleasant but not life-threatening disease that can be treated. If you follow all the doctor’s recommendations and pay close attention to your own health, stable remission or complete cessation of lower back pain is possible.
TV show “Live Healthy!” Lumboischialgia - what causes back pain:
In order to define the concept of “lumbago with sciatica,” it is important to understand what both of these words mean. The term “lumbago” is commonly used to describe a sudden attack of severe pain in the lumbar region. Such pain is a consequence of degeneration of the cartilage tissue of the intervertebral disc , displacement of the vertebrae, trauma or excessive muscle tension of the back and lower back. Sudden shooting is a characteristic feature of such pathologies as hernia and protrusion of discs.
If a patient does not seek help with lumbago, this can lead to the development of sciatica - damage, pinching, and inflammation of the sciatic nerve . The development of sciatica is associated with the unnatural position of the nerve fibers in the canal changed due to protrusion or displacement.
When both syndromes are combined, lumbar sciatica develops , a condition in which it is important for the patient to consult a specialist. Ignoring symptoms can lead to dysfunction of the circulatory system in the legs, large intestine, and bladder.
Clinical picture
Any type of lumboischialgia has two forms: acute and chronic, vertebrogenic is no exception. For several days, the victim feels sharp and severe discomfort. Then follows the stage of remission; the lack of adequate treatment leads to the transition of the pathology to a chronic form, which is quite difficult to cope with.
The acute form of the disease occurs periodically (approximately every two weeks) and is accompanied by the following symptoms of lumbar sciatica:
- throbbing acute attacks of pain that are observed on one or both sides of the lumbar region;
- discomfort spreads to the gluteal muscle, knees, feet, calves. Initially, pain appears on one side, gradually spreading to the other;
- the body loses its former mobility, all movements are given to the patient through pain;
- acute shooting pain is observed during body rotation, after bending in different directions;
- advanced stages of the pathology are accompanied by problems with the gastrointestinal tract and sexual dysfunctions.
Some cases are easily confused with kidney or liver failure, so self-treatment is prohibited. Only a doctor will determine the cause of discomfort and prescribe the necessary therapeutic course.
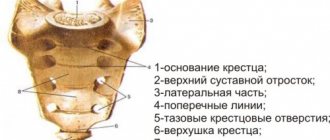
X-ray of the lumbar spine – lumboischialgia
According to the private medical practice of Sarklinik (Saratov), scoliosis of the lumbar spine and smoothness of the lumbar lordosis are observed on x-rays with lumboischialgia. Schmorl's hernias are less common than with lumbodynia. There is a decrease in the height of the intervertebral spaces, lateral displacement of the vertebral body, and fish-like vertebrae. Congenital anomalies of the lumbosacral spine are common. They help reduce the static stability of the spine and accelerate the development of degenerative changes in the disc adjacent to the anomaly with increased physical activity.
Diagnostics
If vertebrogenic lumboischialgia is suspected, the patient is first examined by a neurologist, then the doctor refers the victim to other specialists.
To confirm the diagnosis, several proven diagnostic methods are often used:
- x-ray of the lumbar region;
- blood and urine tests (to determine the presence of causes of pathology and other associated ailments);
- MRI, CT. Research allows us to examine the condition of nearby tissues, blood vessels, and nerve endings;
- ultrasound, myelography, densitometry.
After all diagnostic measures have been carried out, the doctor makes a diagnosis and selects an individual therapeutic course.
Therapeutic measures
Usually an attack of vertebrogenic lumboischialgia overtakes a person suddenly. What to do if acute pain occurs?
Follow special rules that will help alleviate the condition and prevent complications:
- lie down on a hard surface, try not to move;
- take any pain reliever (for example, Baralgin or its analogues);
- You can use a heating pad and rub in indomemethacin ointment to alleviate the condition.
It is important to know! In case of disturbances in the functioning of the intestines, stomach, or genitourinary system, call an ambulance. Self-treatment leads to negative consequences.
Medications
Depending on the root cause of vertebrogenic lumboischialgia, different drugs are selected.
There is a list of specific products that are suitable for all patients:
- NSAIDs (Ibuprofen, Movalis). The drugs relieve pain and cope with the inflammatory process in tissues. The positive effect on the body helps to increase the mobility of the damaged area of the spine, degenerative processes slow down;
- muscle relaxants. Designed to eliminate muscle spasms, which increase the likelihood of pinching the sciatic nerve and lead to acute discomfort;
- B vitamins, chondroprotectors and other agents aimed at restoring cartilage and nervous tissue, increasing the victim’s immunity.
Physiotherapeutic procedures
Effective treatment procedures:
- massage. Starts metabolic processes, blood circulation, improves mobility of the lumbar region and lower extremities;
- physiotherapy. Exercises are prescribed and shown by a specialist, taking into account the characteristics of the patient and the severity of symptoms;
- acupuncture, magnetic therapy, electrophoresis. All physiotherapy procedures are aimed at reducing pain, relaxing muscles, and slowing down degenerative and inflammatory processes.
Coordinate all therapeutic measures with your doctor, get plenty of rest, go to the pool, try not to strain your back (not just the lumbar region). The combination of treatment measures will show excellent results.
Folk remedies and recipes
Natural remedies do an excellent job of relieving discomfort and rarely cause side effects.
There are many healing recipes:
- turpentine. Pre-roll out 100 grams of dough with rye flour, pour a teaspoon of turpentine on top. Rub turpentine oil into the sore spot until the skin turns red, apply the cake to the lumbar spine, and wrap it in cellophane. Leave the compress for an hour; in case of severe burning, immediately wash the product off the skin. Duration of therapy – three days;
- valerian. Buy valerian alcohol tincture. In case of exacerbation of pain, thoroughly soak gauze in valerian tincture and apply to the sore spot. Place a low cushion under your lower back and knees, and wrap your lower back in cellophane. Keep the compress for several hours; leaving the product on overnight is not recommended (there is a high probability of skin irritation);
- red clay. Mix red clay and hot water, take so many ingredients that you end up with a mass similar in consistency to thick sour cream. Distribute the resulting product over the lumbar area, wrap it in a warm towel, and leave for half an hour. This treatment is recommended to be carried out over several weeks.
Consult your physician before attempting home therapy. It is recommended to combine folk remedies with traditional treatment methods to enhance the effectiveness of both methods.
Treatment options for lumbar sciatica
The main goal of relieving the patient of a pain attack is to treat the original source, which has a direct effect on increasing the intensity of PD. If the patient is on bed rest, it is recommended to use a high-quality bed with an optimal level of rigidity and elasticity. To reduce the level of discomfort, the doctor prescribes medicinal injections, which are aimed at pain relief and elimination of the inflammatory process. The doctor prescribes physiotherapy to help reduce the pain threshold (use of pepper patch, special rubbing of the affected area, distraction techniques, etc.).
Possible complications and prognosis for recovery
If vertebrogenic lumboischialgia is detected at the beginning of its development, the prognosis for the patient is positive. The presence of a chronic form of the disease, drug therapy does not help much, the victim is shown therapeutic exercises to restore spinal mobility.
The danger of the pathology lies in the fact that there is a high probability of malfunctions in the functioning of the urinary system and intestines. In some situations, complete paralysis of these systems is observed, which leads to sharply negative consequences and disability of the patient. Keep this possibility in mind when postponing going to the doctor.
How to get rid of dizziness with cervical osteochondrosis and prevent its reappearance? We have the answer!
Read about the benefits of therapeutic exercises and the rules for performing gymnastics for cervical osteochondrosis in this article.
Go to https://vse-o-spine.com/lechenie/medicamenty/plastyr-voltaren.html and find out the instructions for using the Voltaren transdermal treatment patch to relieve back and lower back pain.
Useful tips
Simple useful recommendations from specialists will help reduce the chances of vertebrogenic lumboischialgia and increase the duration of remission:
- try to reduce the load on your legs as much as possible (do not stand for a long period of time, periodically sit down on a comfortable surface);
- when working sedentarily, place a cushion under your back, maintaining the natural arch in the lower back, place a small stand under your feet, reducing the load on the spine;
- exercise regularly (swimming, yoga, Pilates are suitable);
- in case of obesity, reduce your weight, maintain it at the same level;
- give up bad habits;
- In case of forced long trips behind the wheel, stop regularly and warm up.
Simple rules will help support the spine, strengthen the spinal muscles, and prevent the occurrence of vertebrogenic lumboischialgia. If a pathology is diagnosed, begin the necessary course of therapy, follow the doctor’s recommendations. Refuse to self-medicate; most of these endeavors end in suffocation of the situation and the emergence of serious complications.
Video. A specialist from the Moscow Doctor clinic about the causes and features of the treatment of vertebrogenic lumboischialgia: