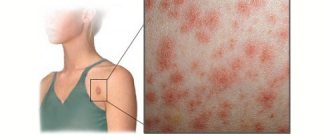
Translated from Latin, “angina” means to squeeze, squeeze. This is an acute infectious disease accompanied by damage to the tonsils. The causative agents of sore throats (tonsillitis) are most often fungi and viruses.
Microbes (usually streptococci) enter the oral cavity, usually through dishes and other objects used by a sick person.
Sometimes the pathogenic microflora present in the pharynx is in a passive state, but as soon as a favorable environment for the development of microbes arises, they begin to actively multiply and infect the entire body.
For people with weak immunity, in order to catch a sore throat, all they need to do is:
- get your feet wet;
- swim in a pond;
- stand in a draft;
- eat ice cream or drink cold water in the heat.
In addition, tonsillitis can be provoked by all kinds of irritating substances that systematically enter the throat (smoke, alcohol, dust, pollen). The cause of the development of sore throat can be nasal congestion, in which breathing is only possible through the mouth, adenoids and other pathologies of the nasopharynx.
Systematic tonsillitis can be caused by purulent inflammation of the paranasal sinuses and oral cavity (sinusitis, caries).
Different types of tonsillitis may have different symptoms, but the main symptoms of diseases in this group accompany any type of sore throat.
- Weakness, general malaise.
- Acute pain in the throat.
- Increased body temperature.
- Pain in joints and muscles.
- Enlarged lymph nodes.
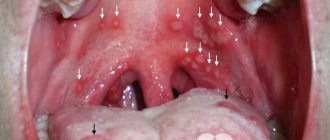
- Redness of the tonsils, uvula, and soft palate.
- Accumulations of pus or plaque on the tonsils.
These signs can be mistaken for a cold, but sore throat is much more difficult to tolerate.
Sore throat concept
In the medical reference book, as a rule, there is another name for the pathology - acute tonsillitis, but the people most often call the disease angina. The term comes from the Latin word ango, which means “to choke”.
The disease can lead to inflammatory processes on one or both sides of the throat, according to which the pathology is divided into:
- unilateral tonsillitis;
- bilateral tonsillitis.
Despite the fact that the disease is viral or bacterial in nature, sore throat often occurs due to hypothermia, especially in damp, cold weather. Pathology can also be a consequence of previous serious diseases, such as influenza, scarlet fever, diphtheria.
The infection is transmitted from a sick person to a healthy person by airborne droplets. In some cases, illness can result from eating dairy products made from raw materials taken from an unhealthy animal.
Both children and adults are susceptible to the disease. However, in children under the age of five, pathology with a viral nature of origin is more common, in older ages, as well as in the adult population, bacterial (streptococcal) tonsillitis (angina).
The types of sore throats known to medicine today are discussed below.
What causes the disease?
The name of the group of diseases comes from the Latin term angere, which means “to squeeze”, “to squeeze” (according to some sources, this word is of Greek origin). Most often, sore throat is caused by bacteria, less often by viruses and fungi.
Streptococci, the main causative agents of sore throat, enter the throat through household items shared with a sick person, for example, dishes, towels, etc. or by airborne droplets from sneezing and coughing.
Often the disease is provoked by microbes that live in the throat of every healthy person. They begin to become active under the influence of external factors: hypothermia of the body, sudden changes in air temperature, a general decrease in immunity, etc. For some people, it is enough to eat ice cream, swim in the river or simply get their feet wet - and a sore throat is guaranteed. Often, a sore throat is caused by irritating substances that enter the throat: dust, smoke, alcohol, etc.
The disease can also develop as a result of chronic inflammation of the tonsils, the presence of carious teeth, purulent diseases of the nose and paranasal sinuses (sinusitis), in which nasal breathing is impaired.
Classification of tonsillitis. Catarrhal form
As noted earlier, tonsillitis is an inflammatory disease that affects the organs of the upper respiratory tract, most often the tonsils. Signs of pathology appear very quickly and are expressed by pain in the throat when swallowing, high body temperature, and muscle tension. However, the course of the disease can be different, with some features. In this regard, pathology is classified into several forms:
- catarrhal;
- follicular;
- lacunar;
- fibrinous;
- phlegmonous;
- herpetic.
This classification fairly fully characterizes what types of sore throat there are. Let's look at each of them separately in more detail.
The catarrhal form of the disease is characterized by the sudden onset of symptoms such as dryness and constant sore throat. The patient has an enlargement of the lymph nodes in the submandibular area, and upon visual examination of the throat, reddened palatine tonsils are visible. Malaise, along with chills and muscle weakness, is quickly replaced by high body temperature. Catarrhal tonsillitis is characterized by headaches - migraines, which cause the patient to become delirious.
Catarrhal sore throat
Many doctors consider this mildest form of angina to be the initial stage of other, more complex and severe forms. Its signs are familiar to everyone, but not every patient exhibits their entire complex. Often the disease is characterized by the presence of 1-2-3 manifestations. What signals may indicate the onset of catarrhal tonsillitis?
Symptoms of catarrhal tonsillitis
- Intoxication and general malaise. Unlike other forms, with catarrhal lesions they appear earlier than the main clinical signs. The patient may feel weak and slightly nauseous.
- Abdominal pain.
- Headaches, often very severe, that progress if the disease is not diagnosed in time and treatment is not started.
- Tonsillitis. Most often they are enlarged in size, have a bright red color, but there is no purulent discharge on them. In rare cases, they are covered with a thin film, which can be easily removed or removed by rinsing. Sometimes a very fine infiltrate (accumulation of bloody or lymphatic discharge) is noticeable on the tonsils.
- Inflammation and swelling of the pharynx, tongue, larynx, etc. In this case, the patient has a feeling of “dry throat”. The patient complains of soreness, a scratching or burning sensation. When swallowing, all unpleasant manifestations intensify, a “lump in the throat” appears, making breathing difficult. The cough may not appear.
- Enlarged and painful lymph nodes.
- On the second to fourth day after the onset of the disease, the symptoms reach their maximum, and the person’s temperature rises. Most often with catarrhal angina it is subfibrile (not exceeding 37.5°), but sometimes lasts more than a week. A higher temperature may indicate the development of sepsis (the entry of pathogens into the blood) or septicemia.
Typically, the condition of a person with catarrhal tonsillitis begins to improve 6-8 days after the onset of the disease, but only with timely treatment. If treatment is prescribed incorrectly or is completely absent, catarrh can develop into more severe forms or cause complications.
Treatment of catarrhal tonsillitis
Despite the fact that the external manifestations of catarrhal tonsillitis differ markedly from other forms, the doctor is required to take a swab from the throat and tonsils of patients before starting treatment to identify the pathogen. While the smear is being examined, the patient must follow all medical instructions.
- Maintain bed rest, especially at elevated temperatures.
- Gargle with herbal infusions (chamomile, calendula, etc.), as well as medications prescribed by your doctor.
- For enlarged lymph nodes, wear a warm bandage during the day and apply a warm compress (alcohol, honey, etc.) at night.
- To soften the throat and eliminate the “lump” when swallowing, take warm inhalations.
- Take vitamins and immunoprotectors prescribed by your doctor to strengthen your immune system.
Medical statistics claim that in most cases the causative agents of the catarrhal form of acute tonsillitis are staphylo- or streptococci. The danger of these bacteria is that they produce toxins that deprive the cells of the human body of the ability to function normally, poisoning them.
To treat catarrhal tonsillitis caused by bacterial causes, the doctor may prescribe penicillin or cephalosporin antibiotics.
Follicular and lacunar types of tonsillitis
Both the symptoms of the disease and the general condition of the patient in these types of pathologies are very similar.
In comparison with the catarrhal form, follicular tonsillitis is the most serious disease associated with various complications. This form of the disease is characterized by a long course and requires only inpatient treatment - the patient must be constantly under the supervision of medical specialists. The symptoms of the disease are very similar to those of the catarrhal form, but their severity is much stronger. In addition to headache and high temperature, a characteristic sign of follicular tonsillitis is increased salivation.
The lacunar form of tonsillitis is also a rather dangerous disease, accompanied by pain when swallowing. Sometimes the pain can radiate to the ear. A constant companion of the pathology is a very high body temperature (up to 40 degrees), severely swollen and reddened mucous membrane of the tonsils. The palatine arches also change, swell and turn red. The lacunae of the tonsils are covered with a white or light yellow coating, which is a mixture of dead cells and bacteria.
Therapy of different forms
Treatment of sore throat in children:
- medicinal;
- through surgery;
- with the help of physiotherapy;
- other methods.
Medicines
a) antibiotics.
How to cure a child's sore throat? With the help of doctor-prescribed antibiotics, here are some of them:
| Name | Description | Price |
| Ibuprofen | Sore throat remedy reduces pain, swelling and fever, suitable for children | 50 rub. |
| Paracetamol | reduces pain, reduces temperature | 15 rub. |
| Aspirin | reduces temperature, has anti-inflammatory and analgesic effects | 220 rub. |
| Amoxicillin | has a bactericidal effect, prescribed for bacterial sore throat for children | 70 rub. |
| Cephalosporin | bactericidal remedy for sore throat in children, effectively fights staphylococci and enterobacteria | 460 rub. |
| Erythromycin | has an antibacterial effect, prescribed to children with sore throat to destroy streptococci | 110 rub. |
| Ampicillin | semisynthetic antibiotic prescribed for the treatment of respiratory tract pathologies. | 30 rub. |
b) for sore throat you can give aids to children:
- to strengthen the immune system - “Immunity” (helps the body resist viruses and pathogens, fights infectious processes, prevents complications);
- for gargling, you can use furatsilin, chlorophyllipt, decoctions of herbs, a solution of salt and soda (1/2 teaspoon each) with a few drops of iodine;
- absorbable tablets and lozenges (possible after five years).
Surgical intervention
The decision on surgical intervention is made by an otolaryngologist if there are a number of indications.
Tonsil removal surgery is prescribed:
with 6 cases of sore throat within one year, diagnosed by laboratory means (or if for two years in a row sore throat occurred four times in a year/three years in a row three times);
- the chronic form cannot be treated with antibiotics;
- with repeated paratonsillar abscess;
- if there were complications (glomerulonephritis, cardiomyopathy, rheumatoid arthritis, meningitis).
Physiotherapy
To treat uncomplicated forms of sore throat for children, you can do physical therapy (as prescribed by a doctor) - laser or magnetic laser.
It is carried out using matrix emitters that generate infrared waves with a length of 0.8 to 0.9 microns when exposed to contact on the skin of the neck under the lower jaw.
The exposure time on one side is 5 minutes, the duration of the course is from 7 to 10 procedures.
Other recommendations from doctors
There are often cases when a child’s body has various sources of infections, for example, in the oral cavity - caries, gum disease. They can, under certain conditions, provoke a sore throat, so experienced doctors recommend sanitation of the oral cavity after a course of antibiotics in order to cure diseases and reduce the likelihood of recurrences.
Fibrinous and phlegmonous tonsillitis
Lacunar tonsillitis at some point can turn into fibrinous. This form of pathology, as a rule, is characterized by a thick white-yellow coating not only in the area of the tonsils, but also beyond them. General signs of the disease appear very quickly and are accompanied by severe chills, turning into a feverish state, as well as intoxication of the body as a whole, often leading to damage to the membranes of the human brain.
It should, however, be noted that the lacunar form of the disease can occur independently, and not be a consequence of another type of this disease.
Phlegmonous tonsillitis is a very rare form of pathology. However, its occurrence is associated with serious violations of the integrity of the tissues of the tonsils, namely their “melting”. With this disease, the patient, in addition to high body temperature, headache and signs of intoxication of the body, experiences an increase in lymph nodes in the neck. The size of the tonsils is also changed, their surface is tense. In this case, impaired function of the masticatory muscles and asymmetry of the pharynx with a limited surface of the soft palate are characteristic. As a rule, phlegmonous tonsillitis affects any one tonsil, i.e. the disease is one-sided.
Causes of tonsillitis
The disease most often occurs in children, since their tonsils have not yet fully formed, which means that the body does not have a sufficient level of protection. After 35 years, sore throat practically does not occur, since the tissue of the tonsils begins to atrophy.
The main cause of tonsillitis is the activity of bacteria. The disease can be viral or fungal in nature. If the disease affects only the surface of the tonsils, we are talking about catarrhal, “mild” sore throat. If not cured in time, the disease spreads deeper, leading to lacunar and follicular forms.
In the most severe cases, the inflammation does not stop at the tonsils, but moves on to other internal organs. The result is long-term loss of ability to work and other, even more serious consequences.
Tonsillitis is caused by widespread bacteria. You can become infected from a person who does not have a sore throat, but is a source of microbes (even if the acute form of the disease does not manifest itself).
A common option is tonsillitis, which begins to develop not from the outside, but from the inside of the body. In the body of every person there are many bacteria that can cause inflammatory processes for months and years. In such cases we talk about chronic tonsillitis. Any hypothermia or decreased immunity will lead to an exacerbation in the form of acute tonsillitis.
The parasitic form is relatively rare. Its causative agents are amoebas living in the oral cavity.
Main symptoms
The first sign is a sore throat, which can be quite severe. The discomfort becomes more intense when swallowing. The temperature rises (sometimes with chills). If you examine the throat at this stage, you will see reddened and enlarged tonsils. The lymph nodes under the jaw also “grow.”
If the lacunae of the tonsils have expanded, and pus is visible at their mouths, lacunar tonsillitis has occurred. In this case, the temperature can rise to 40 C. With the follicular form, the tonsils are covered with yellow spherical formations.
Lacunar and follicular forms lead to intoxication of the body. Microbial waste products spread throughout the body, leading to weakness and headaches.
Viral sore throat has slightly different symptoms. It causes a runny nose and cough, the eyes become inflamed, and the voice becomes hoarse. The viral form is distinguished from other diseases by a sore throat and reddened tonsils.
Degrees of the disease
There are several degrees of severity of the disease.
- Primary. Diagnosed if the pharyngeal ring is affected.
- Secondary. Develops against the background of other infectious diseases (for example, scarlet fever or measles).
- Specific. This category includes the ulcerative-necrotic form, as well as all types of tonsillitis of fungal origin.
In a normal situation, the microflora living in the oral cavity does not cause any discomfort to a person. However, it is enough to disrupt the balance (for example, by a sharp change in air temperature or excessive hypothermia), as the body’s natural defenses weaken and bacteria begin to harm the body.
How to identify the disease
In most cases, angina is easily diagnosed. Difficulty can only arise when determining the form of the disease. So, if tonsillitis is exclusively viral in nature, the tonsils become red, but there is no plaque on them. If white dots appear, most likely we are talking about the follicular form. The bacterial nature of the disease is revealed by a strong enlargement of the tonsils. The appearance of pus and swelling indicates the lacuraine variety.
If your neck swells with a sore throat, consult a doctor immediately - this symptom indicates the appearance of an abscess.
When diagnosing, special attention is paid to the detection of hemolytic streptococcus. The specifics of treatment (the need to prescribe antibacterial therapy) depend on its presence or absence.
To understand whether a streptococcal infection is occurring, the following procedures are performed.
- Laryngeal swab. The result is examined in the laboratory. Experts find bacteria and determine how resistant they are to antibiotics. A smear is the easiest way to detect streptococcus, but it takes too much time, so faster methods are often used.
- Express test. A slightly less accurate option, but it takes about 10 minutes. It is performed by a doctor directly at the appointment.
- Blood analysis. Makes it possible to determine whether the body produces antibodies to streptococcus. If the answer is yes, then there is an infection.
General urine and blood tests may also be used. In complex cases (if there are complications), an MRI or CT scan is performed.
Purulent sore throat
Types of sore throat that are streptococcal in nature require certain therapy to prevent inflammatory processes in the early stages and prevent the development of complications. The concept of “purulent tonsillitis” is not used in medicine. Basically, this term is more popular among the people and is used to refer to a pathology in which purulent plaque forms on the tonsils. In medicine, it is understood that the appearance of purulent masses on the tonsils can be a consequence of poorly treated lacunar or phlegmonous forms of tonsillitis.
Like other types of pathology, the purulent form of the disease is accompanied by a set of symptoms, including:
- pain when swallowing;
- high body temperature;
- enlarged tonsils covered with purulent plaque;
- bad breath (purulent);
- headache;
- impaired speech.
Treatment of purulent tonsillitis involves actions aimed at eliminating the infection and inflammatory process in the body, and antibacterial therapy. In addition, painkillers can be used to relieve pain symptoms, and corticosteroids can be used to eliminate swelling.
The most severe forms of sore throat
What kind of sore throat in adults is considered the most severe? The most severe condition is necrotizing tonsillitis, which has all the symptoms listed above, but in a more pronounced form.
- Persistent severe fever.
- Confusion.
- Frequent vomiting.
- The blood reveals pronounced neutrophilia, leukocytosis, a significant increase in ESR, and a shift in the leukocyte formula to the left.
The affected tissue of the tonsils is covered with a thick coating, which goes deep into the mucous epithelium. Often, the affected areas become saturated with fibrin and become very dense, so when they are removed, a bleeding wound remains on the surface of the tonsils.
After rejection of necrotic areas, a deep defect with an uneven tuberous bottom, often of irregular shape, remains. Tissue necrosis can spread beyond the tonsils to the uvula, posterior wall of the pharynx, and arches.
Ulcerative membranous tonsillitis - its cause is considered to be a symbiosis of a spirochete and a spindle-shaped rod, which often live in the oral cavity of healthy people. The changes are characterized by necrotic damage to the surface of the pharynx with the formation of an ulcer.
Symptoms of pathology:
- Sensation of a foreign body when swallowing.
- Increased salivation.
- Putrid odor from the mouth.
- There is moderate leukocytosis in the blood.
- On the affected side, an increase in regional lymph nodes is observed.
The disease can last up to several months.
Sore throat in children. Herpetic form
Forms of childhood pathology are classified according to the same criteria as in adults. Accordingly, the types of the disease exactly repeat the types of sore throat in adults described earlier.
The symptoms of the disease in children are very similar to the symptoms of the disease in adults. However, their severity may be stronger. For example, children often have a fever, and 40 degrees is quite common. The duration of the disease in children is also longer than in adults. So, usually an adult can have a sore throat for about 10 days, a child – 5-7 days longer. And to the general signs of lacunar tonsillitis in an adult in a child, vomiting and loose stools may be added.
However, there is another form of the disease, which in most cases occurs in childhood - herpetic, and, accordingly, it complements all other types of sore throat in children described earlier.
This name is due to the appearance on the surface of the organs of the upper respiratory tract - tonsils, palate, pharynx - small characteristic bubbles reminiscent of herpes. The disease is also manifested by vomiting, high fever, and muscle pain in the abdominal area. After a few days, the blisters disappear and the mucous membrane takes on a normal appearance.
What types of sore throats affect children?
Most often, preschool children and primary schoolchildren get angina, and less often - teenagers and young people. This disease usually affects adults before the age of 35-40.
In children, especially in spring and autumn, follicular and lacunar tonsillitis is often diagnosed with a sharp increase in temperature. In addition, children suffer from catarrhal, phlegmonous, fibrinous, fungal, herpetic and monocytic tonsillitis. Let's look at the latter in more detail.
Monocytic tonsillitis
This type of sore throat is symptomatic. The disease develops as a complication after infectious mononucleosis and occurs following an enlargement of the spleen and lymph nodes. This disease is typical for preschoolers and school-age children. Infection with this virus occurs through airborne droplets. The incubation period is 1-2 weeks.
The observed pathological changes in the pharynx are similar to other typical forms of tonsillitis. A characteristic sign of monocytic tonsillitis is the presence of up to 20-30 thousand leukocytes in the blood and a large number of altered monocytes (atypical mononuclear cells) in the blood smear.
Viral sore throat
Young children are more susceptible to viral sore throat than adults. This type of disease is characterized by the appearance of shiny red bubbles along the edge of the palate. In addition, the child has a “coated” tongue and enlarged tonsils.
Sore throat is a rather dangerous disease. If you do not start treating it on time or treat it incorrectly, complications such as otitis media, pyelonephritis and even rheumatism may occur.
It is also important to understand that sore throat is a contagious disease, so the patient must be isolated from other household members and have separate utensils and household supplies. Attention! All the above information is provided for informational purposes. Based on these data, you should not make diagnoses or self-medicate. Sore throat is treated strictly under the supervision of a doctor!
Treatment of sore throat
The symptoms of a sore throat are similar to the initial manifestations of a cold or acute respiratory viral infection. However, this disease is more insidious and dangerous. It can cause complications and cause concomitant diseases of various organs and systems. Therefore, this pathology requires immediate treatment.
Moreover, therapy must be comprehensive and must include the use of external antiseptics, medication, and strict adherence to bed rest. It is also important to remember that after a course of antibiotics it will be useful to restore the disturbed microflora. In this regard, it is possible to prescribe various probiotics.
As with a cold, it is recommended to drink plenty of fluids to get rid of a sore throat as quickly as possible. It can be water, green tea, raspberry infusion, all kinds of fruit drinks.
An integral element of the treatment of sore throat are various types of gargling. For solutions you can use salt, soda, iodine, and tinctures of various herbs. It is also easy to find a variety of antiseptic rinses in pharmacies.
Disease prevention
What preventive measures are recommended to be taken when a child’s disease is defeated?
Normalization of lifestyle
To avoid relapse of the disease, it is necessary to maintain:
- proper nutrition (give your child foods rich in vitamins, introduce nuts and freshly squeezed juices into the diet, avoid drinking carbonated drinks);
- moderate loads (you need to be especially careful in the first month after illness);
- sound sleep and comfortable conditions (protect the child as much as possible from all kinds of stress factors);
- more careful adherence to personal hygiene rules (frequent hand washing, separate towels, clean clothes).
Also, in order to maintain and strengthen the immune system, it is recommended to treat the child’s teeth with care (timely treatment, care, prevention of caries) and harden his body.
Hardening should begin gradually:
- air baths,
- cold rubbing,
- dousing,
- sports training,
- cold and hot shower,
- walking barefoot,
- consumption of chilled food and drinks in moderation (they are excellent for training the child’s mucous membranes).
In addition, it is necessary to carefully ensure that the air humidity at home is 40-60%. With insufficient humidity, the mucous membrane of the nasopharynx dries out and cracks, which leads to easier entry of bacteria into the body).
Often, for some reason, parents neglect this point and are too lazy to find out what the air humidity is in their home, but this is very important for the baby’s health.
Tests and medical examination
After recovery from a sore throat, it is extremely important for a child to:
- take blood and urine tests, and a month after the illness, do an ECG and consult with a doctor (this is mandatory!);
- undergo a general medical examination (especially regarding the functioning of the endocrine system, in particular the thyroid gland), in addition, monitor whether the child has developed new foci of inflammation on the body; this may indicate incomplete disposal of bacteria that cause the disease.
If a child develops symptoms such as swelling, shortness of breath, pain in the joints and chest, you should immediately show him to a doctor. It is quite possible that he will prescribe a course of recovery after complications arise.
Sunbathing
Ultraviolet irradiation (with a lamp or when traveling south) is extremely useful for preventing the development of sore throat in children. They restore the balance of vitamin D in the body.
It has been proven that children who visit the southern seas at least once a year are much less likely to suffer from colds and sore throats, since their immune system is stronger.
Vitamins and supplements
After the symptoms of the disease disappear, children who have completed a course of antibiotics are recommended to take prebiotics to restore the intestinal microflora, as well as a course of vitamins and immunomodulators. This will help their weakened body recover faster.
Remember, prevention of relapse in the treatment of sore throat in children is in second place in importance after antibiotic therapy. It is important not only to achieve results, but also to consolidate them.
Please note that this article is educational in nature, so use it as a supplement to the information that your doctor will give you, and then the sore throat will go away quickly and without a trace, and your child will grow up healthy and strong!
Drug therapy
Since the nature of the disease is ambiguous, the approaches to treating the pathology will be different. For example, with a viral form of the disease, medications can be used only to relieve painful symptoms and alleviate the patient’s general condition. Viral sore throat goes away on its own after a certain period of time. But if the cause of the disease is streptococci, then antibiotic therapy is mandatory. This is a necessary measure to prevent the development of complications, such as heart disease. As a rule, antibiotics of the penicillin group are used to treat sore throat. In case of drug intolerance, first generation cephalosporins or macrolides.
Typically, the course of medication lasts up to 10 days. It is important to remember here that you should not self-medicate, but must strictly adhere to the doctor’s prescriptions. When the first improvements in health occur, it is not recommended to cancel the prescribed treatment on your own.
It is worth mentioning separately the situation when a person is a carrier of a streptococcal infection, but the disease does not manifest itself in any way. In most cases, antibacterial therapy is not indicated for such individuals. The number of bacteria in carriers, as a rule, is very small, and such people do not pose a potential danger to others. However, it should be remembered that the situation can radically change if the body’s immune functions decrease or any diseases appear, for example, leukemia.
Possible complications and prevention
Treatment of sore throat must be carried out until complete recovery; many parents stop taking antibiotics after visible symptoms disappear.
Such an attitude towards the child’s health will undermine him for many years and can lead to serious complications: disorders of the kidneys and cardiovascular system, rheumatism.
To prevent sore throat, it is recommended:
- promptly treat acute and chronic ENT diseases;
- during the cold season, treat the nasopharynx with Aquamaris so that the mucous membrane is periodically moistened;
- monitor the child’s diet - it must contain the vitamins necessary for full growth;
- perform high-quality cleaning of teeth and oral cavity;
- ventilate the living space and humidify the air in the nursery.
Pediatrician of the 2nd category, allergist-immunologist, graduated from the Belarusian State Medical University of the Federal Agency for Health and Social Development. Read more »
Complications
As already noted, all types of sore throat with streptococcal nature are dangerous with various complications. The consequences of unsuccessful therapy are divided into two groups:
- local complications;
- general complications.
Of the first group, inflammation of the lymph nodes is the most common. Common fairly severe complications include heart disease (myocarditis), kidney disease (for example, pyelonephritis), inflammation of the meninges (meningitis), and otitis media. In order to verify the true recovery of the body after a sore throat, as a rule, a blood test (twice, with some frequency) and an electrocardiogram are prescribed to exclude complications in the heart.
However, there are consequences of the disease that require immediate hospitalization of the patient in a hospital and often surgical intervention. These manifestations include abscesses. This process is the formation of cavities that are filled with pus. The danger is that the infection can spread further throughout the body, poisoning it with waste products from various microbes, causing inflammatory processes in other tissues and structures. In this case, the patient’s condition sharply worsens, the soft palate swells, its morphology changes and food, when chewed, from the oral cavity can enter the nose and nasopharynx.
Complications of various sore throats
If treatment for tonsillitis was started untimely or the doctor prescribed the wrong therapy, the disease can lead to serious complications, which can be divided into two groups.
General complications are considered the most dangerous, as they affect important organs and systems and threaten life:
- Rheumatism causes damage to the joints, brain and heart.
- Chest infections.
- Kidney diseases leading to severe kidney disorders.
- Inflammation of the membranes of the brain.
- Infectious-toxic shock.
- Gastrointestinal diseases. Sore throat often provokes acute appendicitis.
- Sepsis is the most serious complication because it often leads to the death of the patient.
Although local complications after a sore throat cannot be called harmless, they are still less dangerous than general ones.
- Cellulitis is an unlimited, diffuse accumulation of pus.
- Soft tissue abscesses, in which large cavities are formed filled with purulent contents.
- Inflammation of the middle ear.
- Bleeding from the tonsils.
- Swelling of the larynx.
If you see a doctor on time, all these complications can be avoided.
Tonsil removal
If a sore throat occurs again and again, and the cause of relapse is a streptococcal infection, there is a possibility that the disease will become chronic. In this case, the morphological structure of the tonsils changes, their barrier functions weaken and become insolvent. The present permanent inflammatory process can spread to other tissues and organs, causing disruption of their functioning, blood poisoning (sepsis). In order to avoid various kinds of complications, in such a situation, doctors often suggest removing tonsils with pathology. Indications for such an operation may include:
- relapses of the disease with a streptococcal nature, confirmed by laboratory, three times within three years or more often;
- chronic sore throat with streptococcal nature, not amenable to antibacterial therapy;
- recurring abscesses;
- severe complications caused by pathology.
There are also contraindications for such surgical treatment. The operation is not performed in the following cases:
- heart defects of varying degrees of severity;
- incoagulability of the patient's blood;
- concomitant serious diseases, such as diabetes.
How dangerous is the disease?
Sore throat is dangerous due to complications; carrying it on your feet and taking a careless approach to therapy is extremely undesirable. To avoid infecting other people, treatment of its bacterial forms should be carried out in a hospital.
During bacterial infections, joint tissues and the heart muscle take on a particular burden. Kidney function is impaired.
The list of possible complications is quite long:
- Asphyxia with rapid development of edema.
- Chronical bronchitis.
- Cellulitis of the neck.
- Blood poisoning.
- Arthritis.
- Various diseases of the lymphatic system.
- Rheumatism.
- Otitis.
- Bacterial pneumonia.
- Abscesses.
- Chronic tonsillitis.
Read more about the complications of sore throat in our video:
Diagnosis of the disease
Signs of tonsillitis may be similar to those of other diseases. An example of such a pathology is, for example, diphtheria of the oropharynx and pharynx, in which plaque also forms on the tonsils, but it has a dense structure and gray color, is difficult to remove and is not subject to rubbing.
Plaque on the tonsils can also be caused by scarlet fever, candidiasis, and blood diseases. That is why, when diagnosing a child, the primary suspicion will be diphtheria, and only then the assumption that it is a sore throat.
Types of sore throats with a bacterial nature of origin are diagnosed in the same way. The main method is pharyngoscopy - a visual examination of the pharynx. In this case, all the patient’s complaints about the state of health and previous diseases are taken into account. To determine the nature of the pathology, a smear of mucus from the tonsils is performed.
The resulting material is sent for research to the laboratory. Three types of tests are usually performed:
- PCR analysis, which helps to establish the totality of microorganisms in the oropharynx;
- antigen tests that identify bacterial species;
- sowing.
Unfortunately, to date, no vaccine has been invented for streptococcal strep throat, and the only preventative measures in the fight against the disease will be a healthy lifestyle, proper nutrition, and good immunity.
Description of the disease
Sore throat is an acute infectious and inflammatory disease (acute tonsillitis). Pathogens: staphylococci, pneumococci, streptococci, less often - fungal flora, other pathogenic viruses and bacteria. The formation of pathology occurs in the presence of a favorable environment for reproduction, for example:
- hypothermia;
- poor nutrition;
- avitaminosis;
- inactive lifestyle;
- constant physical and psychological stress;
- viral infections.
The damage spreads to the palatine tonsils - inflammation begins with hyperemia, increase in size, and swelling. Parents do not always understand the severity of angina.
The entire body suffers from intoxication and the rapid progression of pathology. It becomes difficult for the patient to breathe: if you do not promptly seek medical help and do not carry out treatment, then a small child (especially under one year old) risks dying from asphyxia.
Incubation period and contagiousness of sore throat
Sore throat is contagious to others of any age. With a weakened immune system, short contact with a person who is a carrier of the pathogen is sufficient. Infection is also possible during the incubation period, that is, during the period of time from the infection entering the body until the first symptoms appear. The length of the incubation period depends on:
- etiology of the pathogenic agent;
- general condition of the body;
- the patient has chronic diseases;
- types of sore throat;
- degree of functioning of the immune system.
Depending on these factors, the incubation period for sore throat in children varies in duration from 12 hours to 12 days. During this time, pathogenic bacteria and microorganisms settle in the oral cavity and begin active reproduction. Infection is possible not only in the midst of pathology; a child’s sore throat is contagious to others during therapy and taking antibiotics.
Initial stage of the disease
When the incubation period passes, the child’s well-being deteriorates sharply. At the early stage of development of sore throat, a runny nose, sore throat appears, body temperature rises, headaches and muscle spasms occur, and “aches” throughout the body.
At the initial stage of a sore throat, not only does the throat hurt, but also a runny nose appears and the temperature rises
Upon visual examination, enlarged tonsils and hyperemia of the throat are visible; the cervical and submandibular lymph nodes also become significantly larger than normal. At the initial stage of a sore throat, the first thing you should do is contact a pediatrician: he will establish a diagnosis and prescribe treatment, the direction of which depends on the causative agent of the disease and the form of the pathology.
Folk remedies in the fight against sore throat
Treatment of sore throat with folk remedies consists of increasing the body's protective functions and its resistance to bacteria and infections, as well as taking antiseptic measures on the infected areas of the oropharynx. Of course, it should be noted right away that natural methods will be more effective in the fight against sore throat of viral origin.
Among folk remedies, the most popular for angina is the use of propolis, especially in the form of an alcohol tincture. This remedy is effective in treating the throat and eliminating pain. Although today in pharmacies you can find various throat sprays that perform the same functions, for example, “Proposol”, “Ingalipt”, etc. Propolis can also be used in its natural form - chew it after eating. It should be remembered that natural propolis may cause slight discomfort and burning in the mouth.
In the fight against sore throat, rinses based on water and apple cider vinegar with iodine are used. A classic recipe known to everyone: an aqueous solution of salt, soda and iodine. Rinses based on lemon and beet juice are also popular.
Thus, in our article we examined the main provisions that are associated with tonsillitis; elaborated on the reasons why the disease occurs; We have described angina - types, treatment of the disease. In addition, we learned that the pathology is dangerous due to complications and its treatment should be approached seriously and under the strict guidance of medical specialists.
Causes
A sore throat infection can spread to the tonsils in a variety of ways, including:
- exogenous (from the outside): airborne (contact with a carrier of infection), enteral (through food or drink), as a result of surgery on the nasopharynx;
- endogenous (from the inside): in the presence of chronic diseases - tonsillitis, rhinitis, sinusitis; due to pathological processes - dental disease, purulent sinusitis, gastroenteritis;
- hematogenous (through blood).
Causes of sore throat in children:
- infection through contact with a carrier of bacteria;
sudden changes in ambient temperature (for example, if in very hot weather you enter a room with an air conditioner circulating cold air);
- hypothermia of the legs or the whole body;
- consuming excessively cold food and drinks;
- unfavorable living conditions;
- decreased immunity due to illness or taking any medications (fungal tonsillitis in children most often occurs for this reason);
- the presence of other sources of infections in the body.
Herpangina
The herpetic type of sore throat is most typical for children aged 5–9 years. It appears extremely rarely in adults. The main culprit of the inflammatory process is the Coxsackie virus. The disease is highly contagious and is easily transmitted by airborne droplets. A characteristic sign is small red bubbles that form in the area of the soft palate, uvula, palatine arches, tonsils and posterior pharyngeal surface.
Herpetic (herpetic) sore throat is included in Preobrazhensky’s classification solely because of its symptomatic similarity. Moreover, it is not caused by herpes viruses, but by Coxsackie viruses (especially group A) and echoviruses. It got its name because vesicles similar to herpes blisters appear on the mucous membrane in the throat.
Herpes sore throat has several features:
- among other forms, it least often affects adults (over 16 years of age), the main contingent of patients are children under 12 years of age;
- depending on the strain of the virus, the pathology picture also varies - for example, Coxsackie group B is able to penetrate the tissues of almost any organ, including such vital organs as the heart and brain, forming rapidly developing complications of myocarditis, meningitis or encephalopathy;
- the risk of complications is very high in infants, but every year as the child grows older, it decreases more and more;
- has no specific treatment: antibiotics are useless for viruses, and no special antiviral drug has been created for these pathogens;
- after successfully surviving the disease, the patient develops long-term immunity specifically to the virus that was the cause (but such immunity will not protect against other viruses that cause herpangina).
Knowing what a sore throat looks like, a person will be able to take the necessary measures for treatment in time. Seeing small bubbles filled with serous matter in his throat, he will immediately understand that he is dealing with herpetic sore throat. Such ulcers in this form of the disease affect not only the larynx, but also the anterior oral cavity, tonsils, palate, and small tongue.
A person has all the so-called flu symptoms, ranging from loss of appetite to very high body temperature. In a more serious form, he may develop nausea, vomiting, and diarrhea. The incubation period ranges from 7 to 14 days, after which the disease begins with a sharp fever. Indicators reach 39-40 ºС.