Epididymitis in men is widespread. This disease is most often diagnosed as a concomitant complication that occurs against the background of a sexually transmitted infection. Symptoms develop quickly and are increasing in nature.
The disease can also be diagnosed in a child, but most often it affects men of reproductive age (from 20 to 40 years).
Causes of the disease
According to the observations of urologists, this disease is mainly caused by bacteria that are transmitted through sexual contact.
Also, the culprits may be coloform bacteria that live in the human intestine: Escherichia coli, staphylococci and streptococci, Proteus, Pseudomonas aeruginosa. During sexual transmission, bacteria enter the scrotum through the urethra. In this case, the disease is provoked by mycoplasma, chlamydia, ureplasma, trichomonas, and gonococci. This infection variant accounts for approximately eighty percent of cases. Moreover, sixty percent of acute epididymitis is caused by gonorrheal bacteria and chlamydia. In older men, the cause of the disease is usually E. coli.
Sometimes the disease is provoked by excessive development of fungus in the body, for example, when taking certain heart medications. Boys can get epididymitis as a result of complications from mumps (mumps).
The development of the disease occurs against the background of reduced immunity and in the presence of certain factors:
- injuries to the testicles or scrotum;
- hypothermia;
- violations of hygiene rules;
- sedentary lifestyle;
- the presence of prostatitis or urethritis;
- presence of prostate adenoma;
- significant narrowing of the urethra;
- surgical intervention for the purpose of sterilization;
- use of catheters to remove urine.
Most often, this disease is caused by infection from the urethra. Penetration of infection into the epididymis occurs when using urinary catheters or inflammation of neighboring organs (urethra, prostate, etc.).
At CELT you can get a consultation with a urologist.
- Initial consultation – 2,700
- Repeated consultation – 1,800
Make an appointment
- complications after infectious mumps (so-called mumps);
- hypothermia;
- constant difficulty urinating;
- complications of tuberculosis.
Indications
Surgical treatment is indicated in the following cases:
- Abscess of the epididymis or testicle.
- Accumulation of pus.
- Lack of results from antibiotic treatment.
- Acute form of the disease.
- Infertility due to obstruction of the appendage.
Contraindications
It is not recommended to perform surgery in case of exacerbation of chronic diseases and allergic reactions to medications and painkillers.
The development of epididymitis of the epididymis in a man’s body can be caused by a number of reasons. Therefore, every representative of the stronger sex should know them and avoid them in every possible way, so as not to ask themselves the question later - “How to treat epididymitis?”
- In more than 80% of cases, the main cause of the development of this disease in men is a bacterial infection. In medicine, there are two large groups of causative agents of epididymitis of the epididymis - STIs and intestinal bacteria. In men aged 20 to 40 years, the main cause of the development of pathology is STIs (gonorrhea, syphilis, trichomoniasis), since they are more sexually active. Intestinal bacteria provoke the development of the disease in men after 40 years of age;
- in some cases (very rarely), the cause of the disease may be bacteria or fungi;
- In childhood, viral infections become the cause of epididymitis. The epididymis can become inflamed after suffering from influenza, chicken pox, mumps, etc.;
- Taking some synthetic medications can also trigger the development of pathology. For example, drug-induced epididymitis often develops after long-term use of the cardiac drug Amiodarone;
- injuries to the testicles and scrotum. They can be different - mechanical, after manipulations and surgical interventions;
- promiscuity;
- severe hypothermia;
- sexual excesses.
The causative agent of the disease is most often pathogenic bacteria that cause infectious epididymitis. They penetrate retrogradely from the tissues of the urethra, prostate, and vas deferens. This mechanism of development of pathology is observed in 80% of patients.
In patients over 40 years of age, E. coli is more common. This microorganism often causes a bladder infection, and from there rises into the appendages. The risk of such an infection increases in people of any age who practice anal sex. In some cases, the disease is caused by staphylococci, streptococci and other microbes.
The presence of any general infectious disease can threaten the development of a complication such as epididymitis, the treatment of which is urgent. Often the pathological process involves the tissue of the epididymis with: urethritis; vesiculitis; prostatitis; flu; sore throat; pneumonia.
Epididymitis (including acute) is characterized by the following symptoms:
- pain and burning during urination;
- presence of blood in urine and seminal fluid;
- swelling of the scrotum;
- painful sensations during ejaculation;
- the appearance of pathological discharge from the urethra;
- pain in the scrotum, which intensifies during defecation;
With chronic epididymitis, the symptoms are less pronounced and may only manifest as a feeling of discomfort in the lower abdomen.
If you notice similar symptoms, consult a doctor immediately. It is easier to prevent a disease than to deal with the consequences.
Diagnostics
When examining patients suspected of having this disease, the following studies are carried out:
- general blood analysis;
- general urine analysis;
- ultrasound examination of the scrotum;
- identification of pathogens of diseases such as gonorrhea and chlamydia;
- urine culture to determine microflora.
The diagnosis of “chronic epididymitis” can only be made through a comprehensive examination and differential diagnosis.
Treatment of epididymitis
You can ask a urologist or andrologist about how to cure epididymitis. To speed up recovery, use the following:
- strict bed rest;
- fixation of the scrotum in a stationary, elevated position;
- application of cold compresses;
- antibacterial therapy;
- absorbable medicinal substances;
- enzyme preparations;
- physiotherapeutic influence.
When treating this disease, fried and salty foods should be excluded from the diet.
Danger
As the pathological process progresses, the following may develop:
- suppuration of the appendage - entails the need to open the abscess or remove the appendage;
- orchitis - can lead to obstructive infertility in men.
Risk group
The risk group for the development of this pathological condition includes men who:
- often suffer from colds;
- suffer from prostatitis;
- have many sexual partners.
Prevention
For preventive purposes you should:
- prevent infection with sexually transmitted infections;
- Treat any genitourinary tract infections promptly.
The development of the disease in men is caused by many reasons, and the main one is an infection that enters the body in the following ways:
- Bacterial and viral infection - medicine distinguishes two groups that are the causative agents of epididymitis: intestinal bacteria, which provoke the development of lesions in the male population after forty years, as well as STIs (trichomoniasis, gonorrhea and syphilis) in men from twenty to forty years old during an active sexual life.
- Bacteria and fungi.
- Viral infection is the cause of damage in childhood and adolescence, in which the appendage becomes inflamed due to mumps, influenza, smallpox,
etc. - Synthetic drugs – long-term use of some drugs develops drug-induced epididymitis, for example, the heart drug Amiodarone.
- Mechanical damage – trauma to the scrotum and testicles after surgery.
- Hematogenous route - through the blood, which can be caused by diseases such as sore throat, flu and others.
- From the bladder and intestines - infection is typical for men of the older age category.
- Lymphogenic pathway - through lymph.
- The ascending path is infections of the genitourinary system and vas deferens, trichomonas epididymitis, infection with gonorrhea, syphilis, chlamydia and others. Damage by this route is observed in young men during the period of active intimate life.
- Spread of infection from the testicle to the epididymis.
- Tuberculosis.
- The stagnant path is the development of inflammation against the background of a stagnant process in the appendage.
- Promiscuous sexual intercourse.
- Hypothermia.
Types of pathogen:
- Bacterial,
- Chlamydial,
- Viral,
- Mycoplasmic,
- Fungal.
Groups of traumatic epididymitis:
- Postoperative,
- Traumatic,
- Post-instrumental.
Classification of the course of the disease:
- Spicy,
- Subacute,
- Chronic,
- Recurrent.
The nature of inflammation is also divided into specific and nonspecific.
Acute epididymitis
The acute form of the disease affects patients aged from fifteen to thirty years and rarely men who have reached adulthood. The first sign that forces you to seek help is severe pain in the testicle area, radiating to the groin, sacrum and perineum. The disease progresses very rapidly and the peak may occur a day after the first symptoms appear.
Symptoms:
- The lymph nodes in the groin are enlarged,
- Body temperature rises to forty degrees,
- Small discharge from the urethra,
- Frequent urination
- Chills,
- Nausea and vomiting due to intoxication,
- Increased pain in the scrotum with active movement,
- Blood in urine.
All of the above symptoms become less pronounced after three to four days, and therefore many men, due to short-term discomfort, are in no hurry to see a doctor. If the disease is not treated in a timely manner, scars will gradually begin to form at the site of inflammation, obstruction of the vas deferens will occur, which will subsequently lead to male infertility - the most terrible complication of acute epididymitis.
Treatment of epididymitis in men
If initial signs of the disease are detected, treatment should be started as quickly as possible. To do this, you need to contact a urologist or andrologist, who will prescribe appropriate therapy and monitor its effectiveness. Treatment involves eliminating inflammation in the epididymis and restoring their normal functioning.
As a rule, epididymitis is treated at home, and only in extreme cases is treatment indicated in a hospital setting.
In the case of acute epididymitis, the man is advised to rest in bed and ensure absolute immobility of the scrotum. The following are treatment methods used for epididymitis:
Drug therapy
Drug therapy involves the use of:
- Antibiotics, which are prescribed according to the results of the sensitivity of infectious pathogens to them. If it is determined that the disease is caused by a sexually transmitted infection, the patient is prescribed Ceftriaxone or Rocephin in combination with Azithromycin. Typically, the course of treatment lasts approximately one week. The dose is set individually and depends on the severity of the disease. If the tests do not confirm the presence of infection, then the patient is prescribed Sulfamethoxazole, Ciprofloxacin, Trimethoprim and other similar antibiotics. The duration of antibiotic treatment in this case is 14 days.
- Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (Ibuprofen, Diclofenac), which are also indicated in case of infectious nature of the pathology. In the case of a viral type of disease, it is necessary to use Papaverine, Analgin, etc.
- Complex multivitamins that help increase men's immunity and improve their general condition. This significantly reduces recovery time.
Severity of acute epididymitis
The transition of the pathology to the acute stage is accompanied by pronounced symptoms. There are 3 stages in total: mild, moderate, severe:
- Mild – lasts up to 3 days. An ultrasound reveals an enhanced vascular pattern, and a blood test shows an increase in leukocytes to 12,000.
- Moderate – lasts up to 6 days and has severe symptoms, including an increase in body temperature to 39 degrees Celsius and pain. Ultrasound examination reveals inflammation and hypoechoic neoplasms up to 10 mm.
- Severe – lasts more than 7 days and is accompanied by severe symptoms. A blood test shows a leukocyte count of up to 25,000, which indicates a strong inflammatory process (body temperature rises to 40 degrees Celsius). The accumulation of pus is maximum, the epididymis is significantly enlarged.
At the CELT medical center you can undergo a comprehensive examination to identify epididymitis.
Typically it includes:
- general urine and blood tests;
- Ultrasound of the scrotum using Doppler ultrasound;
- PCR tests to detect infections (including chlamydia and gonorrhea);
- urine culture for the presence of pathogenic microflora;
- Magnetic resonance imaging of the scrotum.
Diagnosis of the disease
Although the disease has many symptoms, it is very difficult to make an accurate diagnosis due to the similarity between epididymitis and orchitis. Since diseases require different treatments, you need to know exactly what ailment is in the patient’s body. Sometimes both diseases occur together. In this case, the man is diagnosed with orchiepididymitis. In any case, an analysis for infectious diseases is necessary.
Since epididymitis itself develops as a result of foreign microorganisms entering the body, a similar process can be monitored through a blood test, in which (if the disease is present) the level of leukocytes, which fight harmful infections in the human body, will increase. After detecting changes in the number of leukocytes, the doctor prescribes an ultrasound using the Doppler method.
Thanks to this, it is possible to approximately determine where the tumor is developing. If the doctor finds echo signs of chronic epididymitis on the right or left, then he will be able to prescribe any medications. If you prescribe drugs without such confirmation, you can only harm the patient’s body.
Our doctors
Urologist, Head of the Department of Urology, Candidate of Medical Sciences
32 years of experience
Make an appointment
Urologist, Candidate of Medical Sciences, doctor of the highest category
33 years of experience
Make an appointment
Urologist, Candidate of Medical Sciences, doctor of the highest category
32 years of experience
Make an appointment
Urologist, Candidate of Medical Sciences, doctor of the highest category
Experience 38 years
Make an appointment
A urologist deals with the elimination of pathology. In the acute stage and rising temperature, hospitalization is carried out with strict maintenance of bed rest. Locally apply cold compresses to the scrotum and fix it in its normal position. The diet is normalized, spicy and sour foods are excluded. Next, physiotherapy, antibiotics and vitamins are taken. If pus has formed, then an opening and cleaning is performed. In extreme cases, the appendage is removed to prevent the spread of infection.
Therapy for this disease should be carried out under the close supervision of a urologist. The doctors at the CELT clinic have extensive practical experience and an impressive amount of knowledge, which means they will help you get rid of this pathology in the shortest possible time.
Modern medicine uses conservative and surgical methods to treat inflammation of the epididymis. Conservative methods are relevant in the absence of suppuration and high intoxication, when the symptoms are not so pronounced. Blockage of the seminiferous tubules, accumulation of pus, increased body temperature and acute pain during ejaculation are the main indications for surgery.
Disease prevention
The following measures are taken as prophylaxis against the development of this pathology:
- Optimal preoperative and postoperative management of patients suffering from urological diseases, prescribing a competent course of antibiotic therapy;
- Use of contraceptives, presence of a regular sexual partner;
- The inflammatory process can develop as a result of frequent sexual intercourse and masturbation.
- Sexual arousal without ejaculation can also cause inflammation of the appendages;
- Avoid hypothermia, which reduces the body’s protective properties and contributes to
- development of pathogenic microflora;
- Prevention of epididymitis, orchitis in the course before/after epididymic parotitis;
- Timely treatment of disorders in the area of the genitourinary structure - urethritis, prostatitis, pyelonephritis, and we must also not forget about the treatment of pathologies of the pelvic organs - hemorrhoids, proctitis;
- We must not forget about the treatment of sluggish infectious elements - chronic sinusitis, tonsillitis, bronchitis;
- Avoid injury to the testicles;
- Maintain personal hygiene;
- If you detect the first signs of the disease, immediately consult a doctor - timely treatment will eliminate the complications of the pathology, for example, will prevent a man from developing infertility.
Conservative treatment of acute and chronic epididymitis
Therapeutic treatment is prescribed if:
- There are no accumulations of pus.
- There is no exacerbation of pathology.
- No hematomas formed.
- Tests reveal mild or moderate stage of epididymitis.
The duration of treatment is from 1 to 4 weeks, depending on the infection or virus that triggered the development of the disease. The specialist performs tests for reaction to antibiotics, after which he selects a drug based on the client’s individual characteristics. 2 antibiotics or antimicrobial drugs may be prescribed at once for synergy and better results.
Treatment of the disease
Traditional methods cannot eliminate this disease. It is impossible to treat the disease at home, since herbs are not able to destroy harmful infections.
The only thing you can use is diuretic herbs during the chronic stage of the disease so that the urine does not stagnate for a long time. This will help prevent infected fluid from entering the testicles and, accordingly, prevent the appearance or exacerbation of the disease.
Since this disease is infectious, therefore, to cure the disease, it is necessary to destroy most harmful bacteria, viruses or fungi. Therefore, antibiotics are best suited, because they are more active than all other drugs in destroying harmful infections.
For use, it is recommended to use fluoroquinolone antibiotics. They are the most extensive and widespread. After their use, the temperature in the body decreases, pain decreases, and immunity increases.
Remember! You can start the course only after confirming the presence of the disease in the body.
In order to quickly reduce the painful consequences of acute epididymitis on the right, treatment can begin with the usual anti-inflammatory non-steroidal drugs, for example, ibuprofen or paracetamol.
In the presence of a chronic stage, it is recommended to additionally carry out physiotherapeutic procedures aimed at the site of inflammation. Such treatment will shorten the recovery period of the organ.
Surgical treatment of acute and chronic epididymitis
Lack of results with conservative treatment and severe stage of epididymitis are the main indications for surgical intervention. There are 5 types of operations:
- Orchiectomy is the complete removal of the testicle and epididymis in the most severe cases.
- Epididymectomy - removal of the inflamed appendage.
- Puncture from the scrotum - allows you to normalize the pressure in the scrotum and eliminate pain.
- Partial resection of the appendage – resection of an area with a large accumulation of pus.
- Incision - opening microabscesses and cleaning the appendage.
The choice of surgical treatment is made by the attending physician based on the medical history and data obtained during diagnosis.
Therapeutic treatment is prescribed if:
- There are no accumulations of pus.
- There is no exacerbation of pathology.
- No hematomas formed.
- Tests reveal mild or moderate stage of epididymitis.
The duration of treatment is from 1 to 4 weeks, depending on the infection or virus that triggered the development of the disease. The specialist performs tests for reaction to antibiotics, after which he selects a drug based on the client’s individual characteristics. 2 antibiotics or antimicrobial drugs may be prescribed at once for synergy and better results.
Lack of results with conservative treatment and severe stage of epididymitis are the main indications for surgical intervention. There are 5 types of operations:
- Orchiectomy is the complete removal of the testicle and epididymis in the most severe cases.
- Epididymectomy - removal of the inflamed appendage.
- Puncture from the scrotum - allows you to normalize the pressure in the scrotum and eliminate pain.
- Partial resection of the appendage – resection of an area with a large accumulation of pus.
- Incision - opening microabscesses and cleaning the appendage.
The choice of surgical treatment is made by the attending physician based on the medical history and data obtained during diagnosis.
The form manifests itself at an early age and occurs with a clear clinical picture. O. epididymitis requires quick emergency measures, treatment and relief of symptoms. In another case, it can become chronic and have serious consequences and lead to infertility. Many modern doctors believe that the main reason that can cause this disease is bacteria of different groups.
Urogenital, especially sexually transmitted. Bacteria enter the urethra, the prostate, the vas deferens of the prostate gland and enter the epididymis. Disease in the appendages on the left or right is caused by specific or nonspecific microflora. Specific epididymitis is caused by tuberculosis, syphilis, gonorrhea, or brucellosis.
Subacute epididymitis can occur with minimal symptoms and manifest only by laboratory signs. Since cellular immunity will decrease, Jg G will be produced in large quantities with great force. If you start the process, it will turn into a chronic disease.
What is acute epididymitis? It is an acute inflammation of the appendage, which has a similar picture to orchitis. It manifests itself with a vivid clinical picture with extensive symptoms. A man may complain of discomfort and nagging pain in the lower abdomen, in the scrotum area. A sharp, intermittent pain appears in the perineum and groin.
The pain intensifies with physical exertion or physical activity. An interesting fact is that the pain in most cases will begin in the lower abdomen or on the side of the vas deferens. There will be an increase in body temperature to significant levels, and chills. Palpation increases the sensitivity of the appendage, hyperemia, swelling.
Acute left-sided epididymitis occurs as a result of cold complications after a previous illness. If the function of the bladder is impaired, the disease may manifest itself as a result of urine reflux through the urethra and infection may occur. For example, microbes that penetrate the appendage from the external environment enter the appendage ascendingly through the urethra; it can also be assumed that infection occurs through the bloodstream and is carried by the bloodstream from distant or nearby foci.
Any coccal microflora - such as we know of staphylococci, streptococci, pneumococci, enterococci. Microorganisms that are transmitted through sex also pose a great danger - chlamydia, gonococci, mycoplasma, ureaplasma and a number of other no less important ones. Also, do not forget about the general intestinal group, the bacteria that populate our microflora - coliforms, Proteus, Klebsiella, Citrobacter, Enterobacter.
A. Epididymitis on the left develops more often due to the specific structure of the epididymis of the left testicle. With inflammation, testicular asymmetry is immediately visible. The left testicle is located below the right one and in its normal position the upper end faces upward. The epididymis of the left testicle is somewhat longer than the right one and due to this it becomes inflamed much more often than general pathology.
Acute epididymitis on the left, what is it - this is a left-sided inflammation of the epididymis, there is an acute process, and there is a chronic one. Characteristic symptoms include sharp pain on the side of the affected testicle, although some men feel pain in the perineum or groin, in the sacrum area. The disease develops rapidly and by the end of the day, clear clinical symptoms may appear, both local swelling and redness of the scrotum and general swelling with an increase in body temperature to 28-40 degrees, chills and nausea. The pain intensifies when moving.
Acute epididymitis on the right is a unilateral inflammation of the scrotum on the right - a characteristically asymmetric lesion. Since the left appendage is more elongated, the left testicle is more often affected. The appendage will swell and increase in size, which indicates pain in the scrotum, sensitivity becomes more pronounced, the appendage is painful on palpation, hyperemia of the entire scrotum appears, the folds straighten out and the scrotum becomes smooth.
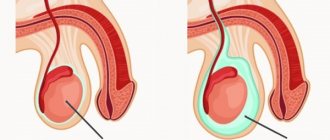
And the testicle itself becomes denser, becomes larger, it is impossible to touch it due to severe pain. The scrotum will swell due to disruption of the outflow of fluid from the cavity, the folding of the skin will increase in size, it will stretch and the skin itself will become smooth and shiny. Due to the fact that the accumulation of fluid occurs inside the scrotal cavity itself, exudate or transudate will accumulate between the membranes of the testicle, which can subsequently lead to hydrocele (swelling of the testicle) as a separate disease.
The pain will occur against the background of general exhaustion of the body with intoxication manifestations: lethargy, adynamia, depression of work activity, malnutrition, physical inactivity, and even aching joints; dyspeptic disorders are also not uncommon due to decreased immunity, diarrhea. In this case, urination will be frequent and quite painful.
Patients experience severe burning of the external genitalia. Impurities and blood can be found in the urine, pus and mucus are released from the urinary canal, and semen contains impurities of blood clots, pus, and mucus in large quantities. Epididymitis can last from 2-3 days to several months depending on the form of the process and the severity. The epididymis is well innervated and supplied with blood, so any damage to it is manifested by certain symptoms.
Acute epididymitis - diagnosis is not difficult. If you consult a doctor in time when the first symptoms appear, you can make an accurate diagnosis without delay and get help from a specialist.
Classification
According to the characteristics of the course, this disease is classified into the following types:
- Acute epididymitis (left-sided or right-sided). Characteristic signs are severe swelling and redness of the scrotum. Externally, the asymmetry of the testicles is noticeable, since the epididymis is affected in only one of them. In the case of an inflammatory process in both testicles, we are talking about bilateral testicular damage (bilateral epididymitis).
- Subacute epididymitis (bilateral or unilateral). This is an intermediate type of epididymitis that occurs during the transition from acute to chronic disease. The manifestations of this type of pathology are no longer as pronounced as in the acute form.
- Chronic epididymitis . As a rule, it proceeds without any symptoms and recurs every 6 months, and sometimes less often. Symptoms appear only during an exacerbation of the disease. The scrotum in chronic epididymitis is of normal size; during the period of remission, it is almost impossible to visually determine the disease.
Based on the type of pathogen, epididymitis is divided into the following types:
- chlamydial;
- fungal;
- mycoplasma;
- bacterial;
- viral.
If the disease occurs as a result of mechanical trauma to the testicles, epididymitis is classified into the following types:
- post-instrumental;
- traumatic;
- postoperative.
How does epididymitis manifest?
The most common symptoms of this disease are swelling, pain and swelling of the scrotum, as well as redness on the affected side.
Epididymitis also manifests itself:
- the appearance of bloody impurities in the semen;
- temperature rise to 38-39 degrees Celsius;
- discomfort and pain in the groin and lower abdomen;
- pain and burning during ejaculation or during urination;
- discharge from the opening of the urethra;
- increased pain in the scrotum during movement or defecation;
Diagnostics
Upon examination of the patient, including taking an anamnesis, the specialist makes a diagnosis. The examination plan contains:
- Ultrasound of the scrotum;
- Analysis of urine;
- Urethral swab;
- PCR analysis.
The nature of the pathogen is determined by urine culture and a smear is taken from the urethra. Ultrasound visualizes the appendage with swelling. In parallel with the patient, his sexual partner is examined. This pathology must be distinguished from orchitis and testicular torsion. Often the symptoms shift the assumption to the presence of an inguinal-scrotal hernia, appendicitis, or renal colic.
Testicular anatomy
The testicle is a paired oval-shaped glandular organ that is responsible for the production of testosterone and sperm. The weight of the testicles rarely exceeds 30 grams. They are located inside the scrotum and are covered with white tissue, which visually divides the organ into 300 small parts. All parts have approximately 2-3 seminal canals.
Male genital organs are divided into internal and external. Internal:
- Testicles
- Epididymis
- Vas deferens
- Bulbourethral glands
- Prostate
- Seminal vesicles
Testicle (testis, orchis) The testicle is a paired glandular organ responsible for the production of sperm and male sex hormones (testosterone). The testicle has the shape of an oval, flattened laterally. Its average weight is 25-30 grams. The testicles are located in the scrotum, the left testicle is slightly lower than the right.
The testicular tissue is covered by a dense tunica albuginea. From which jumpers stretch like rays, dividing the testicle into 200-300 segments. Each lobule contains at least 2 or 3 seminiferous tubules. In their shell there are special cells (Sertoli cells), in which sperm are formed. Here, between the tubules, there are Leydig cells responsible for the production of male sex hormone.
Before sperm leave the testicle, they need to travel a significant distance through many tubules of various shapes and lengths:
- 1) convoluted tubules,
- 2) straight tubules,
- 3) tubules of the testicular network,
- 4) efferent tubules,
- 5) epididymal canal.
The epididymis is located vertically along the posterior surface of the testicle. It is about 5-8 cm long and 1-2 cm wide. It serves as a place for the maturation and accumulation of sperm. Over the course of several weeks, sperm move passively along the tubules of the epididymis, due to the movements of the cilia inside the tubules. The appendage can be divided into 3 parts: head, body, tail.
Rarely, torsion of the appendage occurs, which leads to the development of acute epididymitis.
Blood supply to the testicleArteries:
- Testicular artery (a.testicularis), from the abdominal aorta
- Artery of the vas deferens (a.ductus deferentis), branch of the internal iliac artery
- Artery of the levator testis muscle (a. cremasterica), from the inferior hypogastric artery.
Vienna:
- Venous blood from the right testicle flows into the pampiniform venous plexus, and then through the internal spermatic vein into the inferior vena cava. From the left testicle, venous blood flows through the internal spermatic vein into the left renal vein. The outflow of venous blood into the left renal vein from the left testicle is more difficult. This fact explains the frequent congestion in this area and the predominance of inflammatory and infectious processes in the left testicle.
Causes of pathology
Infectious epididymitis is usually observed in sexually mature males; a disorder develops as a result of infection; the pathogenic elements are considered to be:
- Ureaplasma;
- Chlamydia;
- Mycoplasma;
- Gonococci;
- Candida mushrooms;
- Pseudomonas aeruginosa;
- Bactericidal elements of E. coli;
- Streptococci;
- Pneumococci;
- Staphylococcus;
- Enterococci;
- Bactericidal elements of tuberculosis.
Males are usually infected through sexual contact. Pathology can also manifest itself due to such moments as:
- Injury;
- Sterilization;
- Complication of brucellosis;
- After using Amiodarone.
The presence of urethritis and cystitis is considered a risk factor for the development of the disease. Organ damage occurs during tuberculosis and brucellosis. Sometimes the etiological factor is the retrograde release of urine during sexual intercourse, in the presence of a full bladder. Then experts talk about chemical epididymitis.
The following points provoke the occurrence of the disease:
- Hypothermia;
- Physical inactivity;
- Failure to comply with personal hygiene rules;
- Impaired urine outflow due to prostate adenoma;
- Introduction of an infectious element during medical treatment, during catheterization.
Of great importance in this situation is given to addiction to alcoholic substances, the development of respiratory diseases, varicose veins, the presence of proctitis, hemorrhoids is important.
Epididymitis can be of a specific/nonspecific type, acute/chronic type.
Complications of epididymitis
If epididymitis of the epididymis is treated in time, the person will fully recover. For this purpose, he is prescribed drug therapy (various groups of drugs), as well as physiotherapy, etc. In this case, reproductive capacity is preserved. But if the disease is not treated, it will develop into a chronic form and various complications may arise.
Possible complications:
- the inflammatory process will spread to the testicles and other organs;
- scrotal abscess;
- testicular necrosis;
- fistulas on the scrotum;
- sepsis;
- Fournier's gangrene;
- male infertility.
- development of a severe infectious process;
- scrotal abscess;
- formation of fistulas in the skin of the scrotum;
- transition of the disease to a chronic form;
- formation of adhesions between the testicle and scrotum;
- development of bilateral epididymitis;
- disruption of the blood supply to the testicle with subsequent hardening of its tissues.
Important! In 40-60% of cases, the epididymo-orchitis inflammatory process leads to functional death of the epididymis and testicle, which leads to infertility.
Often found in bilateral epididymitis.
Mechanisms of infertility development:
- the effect of infection on spermatozoa;
- the secretion of the sex glands is disrupted;
- the tubules through which sperm move are affected, which prevents the normal maturation and removal of sperm;
- immune mechanisms are disrupted, as a result of which antibodies are formed against their own structures.
Untimely initiation of treatment will lead to a large accumulation of pus in the appendage, which causes an increase in body temperature to 40 degrees and severe headache. The scrotum becomes more sensitive and smooth. Next, the inflammation spreads to the testicles, which provokes the appearance of orchitis. In the future, a person may become infertile, as the canals are blocked by scar tissue.
Causes
Epididymitis in men can be caused by more than one reason. There are four possible ways of occurrence of orchitis and epididymitis:
- infectious - this method includes fungi, bacteria, in some cases viruses, and in addition to some other microorganisms - nonspecific infection. Also syphilis, perhaps even tuberculosis or tuberculosis are specific infections;
- necrotic - as a result of twisting of the epididymis, as well as due to the penetration of sperm into the inner part of the epididymis;
- stagnant - in the case of prolonged presence of blood in the tissues of the testis or excessive accumulation of blood in some organs of the scrotum. This condition can be caused by the use of bicycles as transport for transportation, hemorrhoids, constipation and due to some other reasons that contribute to epididymitis;
- traumatic - a chronic and acute condition of the testicles can develop as a result of injury, after surgery, or with insufficiently careful examination by the attending physician. In this case, treatment can be effective with drugs prescribed by him.
However, it is worth noting that bacteria are the cause of the disease in more than 80 percent of cases, therefore, in case of acute condition of the appendages, antibiotic treatment is often prescribed; treatment at home is also possible, but only strictly under the supervision of specialists.
Epididymitis, the causes of which can be quite varied, usually occurs first on the right and then on the left, but both sides cannot become inflamed almost simultaneously.
First of all, the disease begins in the appendage, then it can affect many organs, so orchitis is treated carefully.
With inflammation, severe pain can also come, and not all remedies can defeat the infection. The first to become inflamed is the appendage, then the disease spreads to the testicle.
The general provoking factors of the disease are as follows:
- promiscuous sexual intercourse;
- taking certain medications that have side effects;
- weakening of the human immune system;
- difficulty urinating.
Symptoms
Disease of the male genital organs in most men develops in the tissues of the appendage, a bacterial infection. In a certain case, with acute epididymitis in men, the symptoms of manifestation are characteristic of a massive complex of diseases and it is necessary to clearly grasp each symptom, understand its occurrence and etiology.
The most common diagnostic sign is discomfort in the perineal area, a general sign of exhaustion of the body. Discomfort in the reproductive system during urination, erection, defecation, and even physical activity. Acute and sharp pain, swelling of the testicle and groin on the affected side or the entire organ, although some experience pain not only in the organ itself, but also along it, extending into the anus or pelvis.
The disease develops quickly, reaching its apogee within a day, or maybe hours. A man can feel severe swelling and redness of the scrotum, hyperthermia, feel a lump, and often you cannot touch the inflamed organ. The size of the testicle increases several times and it is difficult to find an explanation for this. When the process spreads along the canal and to the entire seminal duct, then in those cases you can palpate a painful, dense cord-like cord.
nausea, vomiting. A man can become irritable and aggressive, as his mental state worsens, panic and anxiety appear. Stress, as we know, is difficult for men to bear, and therefore they close themselves off and do not listen to advice. But the symptoms do not disappear and a number of other signs appear.
The lymph nodes in the groin area also enlarge, the patient goes to the toilet more often, but urination is painful, and there may be blood clots and streaks of pus in the urine. During erection, unpleasant-smelling discharge also appears from the urethra of the penis. If you have these symptoms, you should immediately consult a doctor so that he can help explain what is causing this condition and how to help you with it.
Epididymitis in men, symptoms, treatment are closely related to other testicular diseases, such as orchitis, epididymyorchitis, hydrocele, prostatitis and many other diseases of similar etiology. Urinary tract disease occurs at any age and can present with many signs and symptoms.
An outbreak of the disease is recorded every year, especially in young people in puberty. One in a thousand is susceptible to an acute phase disease; older people suffer from a chronic process, the cause of which is a long-term inflammatory process in the scrotum or an infection of the urinary system.
Problems with urination, for example, with prostate adenoma, can also lead to the development of inflammation of the epididymis. In this case, when urine is retained and accumulates for a long time in the bladder, it can flow back into the appendages.
Predisposing factors include:
- Sexually transmitted diseases
- Use of urethral catheters
- Tuberculosis
- Other inflammatory diseases of the genitourinary system (urethritis, vesiculitis, prostatitis)
Symptoms of epididymitis are not always pronounced, but it is important to remember that it is at an early stage that the disease is best treated. The following symptoms should not be ignored:
- Pain and discomfort in the testicles, aggravated by defecation
- Hardening and enlargement of the epididymis
- Painful sensations during urination, ejaculation, and also during sexual intercourse
- Swelling and redness of the scrotum
- Slight increase in body temperature, chills
- Presence of blood in semen
Dangerous consequences
The lack of timely and effective treatment of the acute form of the disease provokes its transition to a chronic form.
This, in turn, causes dystrophic and sclerotic changes in the epididymis, contributes to disruption of the patency of the vas deferens and, as a consequence, leads to male infertility.
In addition, delaying a visit to the doctor with obvious symptoms of the disease can lead to a scrotal abscess, when surgical intervention can no longer be avoided. The most serious complication of the disease is the penetration of infection into the blood with the development of sepsis.
What is epididymitis
Epididymitis refers to inflammation of the epididymis, which is provoked by other infectious diseases, including sexually transmitted diseases in men.
Often acute epididymitis develops after transurethral surgery, diagnosis and therapy of the urethra. Despite the fact that every day prevention methods and methods for sterilizing urological instruments are being improved and developed, this does not reduce the incidence of iatrogenic (that is, formed after medical intervention) cases of inflammation of the epididymis. In 8% of men who have undergone transurethral resection of the prostate (removal of adenoma), complications are diagnosed and epididymitis is observed. Experts classify the disease as urgent, that is, requiring urgent medical attention and appropriate treatment. Epididymitis code according to ICD 10 is N45; an additional code (B95-B97) can be used for identification.
The main complication of acute epididymitis is its transition to the chronic stage, and this is fraught with other pathological processes, such as dystrophic and sclerotic changes in the testes, deterioration of the patency of the vas deferens. All this ultimately leads to reproductive dysfunction. Inflammation of the testicle and its epididymis (epididymo-orchitis) causes atrophy of the first in 40-70% of cases. The danger is that atrophy and infertility can occur both with bilateral and unilateral epididymo-orchitis due to the relationship with the immune system. At the moment, the inability to have children after suffering from epididymitis has already become a recognized social problem.
Our doctors
Urologist, Head of the Department of Urology, Candidate of Medical Sciences
32 years of experience
Make an appointment
Urologist, Candidate of Medical Sciences, doctor of the highest category
33 years of experience
Make an appointment
Urologist, Candidate of Medical Sciences, doctor of the highest category
32 years of experience
Make an appointment
Urologist, Candidate of Medical Sciences, doctor of the highest category
Experience 38 years
Make an appointment
What is observed in advanced stages of the disease
In addition to the appearance of pain and bleeding, you may notice swelling of the surrounding tissues. Periodic discharge from the urethra is also formed, which is observed at the time of early infection. If a man has already developed chronic epididymitis, symptoms appear periodically. If these signs of inflammation are present, fever may develop.
An increase in temperature is inherent in the acute phase of epididymitis, and the symptom is observed at the time of exacerbation of the chronic form of the disease. Escherichia coli is a common source of testicular inflammation. It causes diseases in the genitourinary system: urethritis, pyelonephritis, cystitis. With such diagnoses, the risk of acquiring epididymitis increases.
Diagnosis of pathology
To clarify the diagnosis, the attending physician evaluates the man’s complaints and examines him. During palpation, the doctor identifies the affected appendage, which is felt like a dense, painful cord. Additionally, he notes an increase in inguinal lymph nodes and discharge from the penis.
To confirm epididymitis, the urologist prescribes:
- general blood test - leukocytosis is detected with a shift of the leukoformula to the left, increased ROE;
- clinical urine test - bacteria and an increased number of leukocytes are detected;
- bacteriological examination of urethral discharge - carried out to identify the causative agent of the disease;
- PCR – performed if a patient is suspected of having an STI;
- Ultrasound of the scrotum and groin area - thanks to the method, the doctor assesses the condition of the appendage and nearby structures.
3 months after the end of treatment for epididymitis, the treating urologist may recommend a spermogram. The study will show the man’s fertility and identify possible disorders of the reproductive system.
Epididymitis treatment at home with folk remedies
Traditional medicine also offers its own methods of treating this disease:
Recipe 1 Wintergreen infusion is used as a painkiller. To prepare the infusion, pour 10 teaspoons of the herb into 1 liter of boiling water and let it stand in a thermos. It is recommended to take the infusion 50 ml up to 3 times a day
Recipe 2 To relieve inflammation, prepare a decoction. To do this, you need to mix parsley, dandelion, shepherd's purse, bearberry and anise in equal proportions. Then take 6 tbsp. this mixture and pour 2 liters of boiling water. Take the decoction throughout the day, replacing regular drinks (tea, coffee).
Treatment of the disease
General principles of therapy include:
- compliance with bed rest;
- use of a suspensor, which will give an elevated position to the scrotum. This measure helps prevent hydrocele and reduce pain;
- sexual rest.
Therapy for the inflammatory process is determined by the pathogen that caused the pathology. The drug is selected taking into account the expected microbe. The doctor prefers broad-spectrum antibiotics. If the cause of epididymitis is a sexually transmitted disease, then not only the man, but also his partner receives specific treatment.
To enhance the clinical effect, suppress pain and reduce body temperature during hyperthermia, non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs are recommended. If epididymitis is caused by a viral pathogen, then immunomodulators are indicated.
Locally, on the first day of the disease, cold is applied to the groin area. In the future, the patient can use compresses that have anti-inflammatory properties. It is recommended to perform physical therapy when acute inflammation subsides: swelling decreases and body temperature normalizes. For this purpose, the attending physician performs magnetic and laser therapy, photodynamic exposure of the scrotum and groin area, and electrophoresis.
Surgery for epididymitis is needed for the following conditions:
- the pathology occurs with purulent melting of the epididymis;
- the disease is characterized by frequent exacerbations;
- The patient is concerned about chronic pain, which leads to a deterioration in the quality of life.
Surgical treatment involves puncture of the scrotum, the incision method, removal of the appendage or part thereof. Epididymectomy is rarely performed on young men because it reduces their fertility.
Signs of the disease
The manifestations of epididymitis are determined by the severity of the inflammatory process. A man is experiencing severe pain in the groin area. He notices that the skin in this area is red and swollen. With 2-sided lesions, pain is localized on both sides.
Over the course of 2–3 days, the pain increases. A person’s body temperature may rise, which occurs with chills, headache, weakness and weakness.
If the cause of epididymitis is viral parotitis, then within a few days before clinical manifestations the salivary glands become enlarged, swallowing function becomes difficult, and discomfort and pain appear in the parotid area. With the development of venereal urethritis, the disease manifests itself with urinary disturbances - frequent urge, pain during bladder emptying and after intercourse, as well as urinary incontinence. Purulent discharge appears from the penis.
When prostatitis becomes the cause of epididymitis, the patient complains of pain in the perineum, discomfort during sexual intercourse. Some patients experience enlargement of regional lymph nodes.