Kissing disease is the name given to cytomegalovirus infection a few decades ago, a disease that affects more than 70% of the entire world population to one degree or another. According to WHO statistics, this infection is found in almost 100% of the adult population of the world. Such high activity is due to the fact that the virus can be transmitted in almost all ways known to medicine: sexually, airborne, household, from mother to fetus, through mother's milk and through saliva during kissing (hence the original name of the infection).
Until 2006, cytomegalovirus infection (CMVI) was one of the sexually transmitted diseases, but later it was included in the list of dangerous viral infections that can be contracted not only through sexual contact.
Cytomegalovirus (CMV) - what is it?
The ICD-10 code assigned to the disease is B25. The name in Latin is cytomegalovirus hominis (abbreviated as cmv).
The causative agent is a virus that is part of the herpesvirus subfamily, which causes diseases such as herpes zoster, herpes, chickenpox, Epstein-Barr virus and others. Read about what the Epstein-Barr virus is in this material.
CMV contains two strands of DNA, multiplies in the nuclei of cells without causing any visible damage to them, but suppresses cellular immunity. A typical location for the virus is connective tissue (fibroblasts).
In the 19th century, very little was known about this disease; they called it “the kissing disease” because they believed that it was transmitted from person to person exclusively through a kiss.
It was possible to study the virus thoroughly, see what it looks like, and give a detailed description of it only in the middle of the twentieth century: first, very large cells were discovered in the tissues of a deceased patient, which were defined as “owl eyes”, and later called cytomegals (“huge cells”). .
The main discoveries were made by scientist Margaret Gladys Smith in 1956, it was she who described the virus in detail.
Today, CMV (due to its rapid spread across the planet) is called a “disease of civilization,” which is actively expanding its “black list,” and, of course, not only through kisses.
The infection manifests itself in different ways: asymptomatic or with damage to internal organs . The first scenario is usually observed if the carrier of the infection appears in the body for the first time.
Complications in adults and children arise if a person’s immunity sharply decreases for some reason, and then the virus is able to become more active.
Diagnostics
The virus is diagnosed by taking human biomaterial and conducting research. The analysis is prescribed exclusively by the doctor after examining the patient and collecting an anamnesis. For tests, they can take not only blood, but also other materials. For example, saliva, urine, urogenital smears, prostate secretions, feces, breast milk, ejaculate and even amniotic fluid. There are several diagnostic methods.
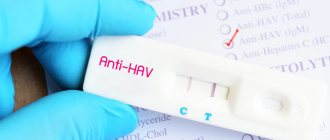
Serological diagnosis
A type of diagnostic that determines the presence of virus antibodies in the blood. There are lgg, lgm and lga antibodies. Antibodies can be present in the blood even if the patient is not sick. They only indicate that the person was in contact with the pathogen. Serological tests have a quantitative option and determine how many antibodies are contained in the body:
- G – maternal, transmitted to the baby.
- M, on the contrary, reflect the acute course of the infection.
Regardless of the quantitative indicator, the acute form cannot be fully diagnosed. At a minimum, these tests are taken over time. Antibody tests are often performed using ELISA.
Analyzes are carried out using immunofluorescence and immunofluorescence methods.
PCR
Polymerase chain reaction helps doctors establish the picture more accurately. PCR is characterized by a high degree of accuracy and in a short period of 1-2 days gives information about the qualitative and quantitative characteristics of the study. PCR of biological materials is not always a sign of infection, so studies are prescribed in a comprehensive manner. Smears from different locations can be used as biomaterial for research.
- from the throat;
- urogenital;
- from the nose;
- sputum.
The method is determined by DNA; it cannot be used to determine the duration and nature of the infection. In this case, the doctor prescribes a range of additional studies.
Culture method
A highly sensitive, precise method that requires some time. The material is sown in the medium, germinated, and then the result is read. If antigens are present, the result will be visible within a few days.
Causes of the disease
After the initial infection, the cytomegaly virus may become more active after some time, and this will be associated with a weakened immune system:
- in women - during pregnancy;
- in the fetus - due to weak barrier functions of the placenta (this happens if the expectant mother suffers from any extragenital diseases);
- in people of different ages and genders – after taking medications that suppress the immune system.
According to statistics, in the first year of life, every fifth child is infected with CMV.
Where does the virus come from in children's bodies? Among the main reasons are intrauterine infection and transmission of the virus through mother's milk.
Subsequently, infection occurs in children's groups. Among teenagers, 15 percent of children already become carriers of the virus, and by the age of fifty, only 1 percent of people remain “not covered” by the disease of civilization.
This article provides a list of corticosteroid drugs, their indications and contraindications, and classification for your information. Find out more!
Mustela for seborrheic crusts: how to use, how much does it cost, is the product effective? Find answers to your questions in our publication.
Congenital cytomegaly
Sometimes the mother of a newborn baby hears a “sentence” - CMV. What is it like in a child? Unfortunately, we are talking about a congenital pathology. Most often, a baby becomes infected from a mother who carries active CMV during pregnancy.
It is difficult to predict how pathology will affect the baby. This largely depends on the stage of pregnancy at which the woman suffered the infection. Sometimes babies, protected by maternal antibodies, easily tolerate it. But very often the symptoms characterizing congenital CMV indicate that the child has a severe pathology.
The main signs of the disease are:
- prematurity, low weight, developmental delay in the womb;
- respiratory system disorders;
- hepatitis, enlarged spleen, liver;
- symptoms of cardiovascular failure;
- hemorrhagic rash;
- prolonged, pronounced jaundice;
- microcephaly, chorioretinitis, neurological disorders;
- lymphadenopathy;
- thrombocytopenia, anemia;
- interstitial nephritis.
Such manifestations make themselves felt in the first 3-5 weeks from birth. Severe infection often leads to death. Sometimes a child may remain disabled.
How is cytomegalovirus infection transmitted?
The following routes of transmission of the virus exist:
- airborne;
- through saliva (with kisses, you really need to be careful);
- during blood transfusions in medical institutions;
- during the baby’s stay in the womb, during childbirth and subsequently during breastfeeding.
The contact-household method is very common in families and children's groups. Infection occurs through things that everyone uses and through personal hygiene items (they can be infected with saliva, blood, urine).
The airborne method is associated with the entry into the body of sputum, saliva and even tears from a sick person to a healthy one. This occurs during sneezing, coughing - through the mouth and upper respiratory tract.
People become infected through sexual contact through unprotected sexual intercourse. The partner (or partner) transmits the virus to each other through mucous membranes, sperm, and vaginal mucus.
The oral route is the method of infection through the mouth. An ordinary kiss threatens both men and women with CMV infection.
Children most often become infected through dirty hands and due to the habit of checking any thing “by tooth.”
Transplacental infection is the infection of the fetus in the womb (the virus can, for example, enter the baby’s body through the umbilical artery).
The iatrogenic way the virus enters the body is through a blood transfusion (if the donor blood is infected).
According to scientific data, a single transfusion very rarely gives such an unpleasant result. Problems usually arise in patients who have to undergo a similar procedure regularly, and their immunity is reduced due to a serious illness.
The virus uses the transplant route of infection during donor organ transplantation. The situation may be aggravated by the fact that such patients (to avoid organ rejection) are given drugs that reduce immunity.
And here is how the virus acts when it enters the body, for example, through the mucous membrane. First it moves along the bloodstream. Having detected immune defense cells, it multiplies in them (scientists detect characteristic changes in phagocytes and leukocytes - they become larger in size, and viral inclusions form in the nuclei of these cells).
At this stage, the process can be considered complete - “the Moor has done his job” and will be ready to continue if he receives the appropriate signal.
Practice shows that the incubation period can last for years without affecting a person’s quality of life.
You can find out how cytomegalovirus is diagnosed and what positive igg antibodies mean by following the link.
Decoding the analysis results
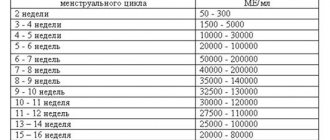
The tests taken as a whole are easy to decipher. The interpretation depends on the ratio of the levels of immunoglobulins of different classes.
- Antibodies IGG – negative, IGM – positive. The acute course of the disease may mean that the infection occurred recently.
- Antibodies LGG – positive, LGM – negative. The presence of immunity, the person is a carrier, the disease is passive.
- Antibodies G and M are negative. There was no contact with the infection, there is no immunity, the person is not sick with the virus.
- Antibodies G and M are positive. The body encountered an infection, but the disease again became acute.
- An avidity value below 50% may mean that a person is sick for the first time. Above 60% means that the person has already encountered the virus and is immune, or has been sick with it more than once.
- An avidity value of 50 to 60% requires a retake after some time to avoid errors in interpretation.
- A negative value (0% avidity) makes it clear that the immune system has not encountered the virus.
Classification of CMVI: types and forms
A unified classification of CMVI has not yet been developed. Most often, the time when the disease appeared is taken as a basis, so there are 2 types of infection - congenital and acquired.
Congenital is presented in two forms: chronic and acute. If the first does not pose a threat to life, but can affect the brain, eyes, and is often accompanied by conjunctivitis, then the acute form is extremely dangerous.
Is it possible to die? Unfortunately, yes, especially if the fetus is infected in the early stages of pregnancy.
When children are born, they are diagnosed with multiple organ failure (this is what experts call the inability of several functional systems of the body to work normally at once).
In such patients, problems often grow like a snowball - one unpleasant diagnosis follows another.
As for patients with acquired CMV infection, this type also includes various forms - latent (hidden, without external manifestations) and acute, which is characterized by:
- high fever with chills and heavy sweating;
- pain – headache and muscle pain;
- general weakness;
- loss of appetite.
Experts consider the so-called generalized form of the disease to be the most severe form of the disease . Its “background” is very often some serious disease, which complicates the general diagnosis: sialadenitis (inflammation of the salivary glands), encephalitis and meningoencephalitis, myelitis (spinal cord disease).
Here are the symptoms that distinguish the generalized form from other forms:
- intoxication of the body;
- very high temperature;
- soreness of the lymph nodes;
- increase in liver size.
If you are interested in which shampoo to choose for seborrheic dermatitis on the head, we recommend using this review article.
Read about how to treat oral dermatitis on the face in this material.
Reviews of the cream with hyaluronic acid Skin Active are presented here: https://udermatologa.com/prep/instruktsiya-po-primeneniyu-skin-activ-krema-s-gialuronovoy-kislotoy/.
Warning signs
In order to detect cytomegalovirus infection in time, you need to pay attention to the presence of its characteristic symptoms.
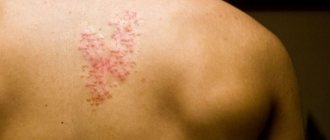
The acute form of cytomegalovirus infection is accompanied by pain and sore throat in children and adults. The lymph nodes in the neck area become enlarged. A sick person becomes lethargic and drowsy, and loses ability to work. He develops a headache and cough. Body temperature may rise and the liver and spleen may enlarge. Sometimes a rash appears on the skin in the form of small red spots.
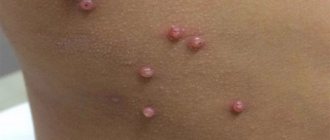
Infants with a congenital form of cytomegaly are found to have an enlarged liver and spleen. Hydrocephalus, hemolytic anemia, or pneumonia may be present. If cytomegalovirus hepatitis develops, the child develops jaundice. His urine becomes dark and his stool becomes discolored. Sometimes the only sign of cytomegalovirus infection in a newborn is petechiae. They are round dotted spots of a rich red-purple color. Their size ranges from a dot to a pea. Petechiae cannot be felt because they do not protrude above the surface of the skin.
Newborns with cytomegaly exhibit disorders of swallowing and sucking. They are born with low body weight. Strabismus and muscle hypotonia are often detected, followed by increased muscle tone.
If such signs are observed against the background of a positive test result for IgG antibodies, you should immediately consult a doctor.