Analysis for the coxsackie virus is one of the most accurate types of research. It helps determine the presence of a pathogen in the patient’s body. Every person needs to know what the coxsackie virus is and what consequences it has. In this article we will tell you why diagnosing this strain is so important.
This pathogen is a group of pathogenic microorganisms that are active in the gastrointestinal tract. To date, 30 subspecies are known, which are divided into two families. The virus is moderately dangerous, since its complications can lead to aseptic meningitis. This strain is transmitted by contact through human body fluids: blood, saliva and urine. Children under 10 years of age are most vulnerable. Adults are rarely infected.
What is the Coxsackie virus?
The main feature of this bacillus is its ability to instantly spread with maximum breadth . In particular, thanks to her, the Coxsackie virus, soon after it was diagnosed by doctors for the first time, soon appeared in different places almost all over the planet.
The danger of catching the Coxsackie virus exists through direct contact with the patient himself (the bacilli can spread, in particular, by coughing through airborne droplets), his personal belongings and biomaterial (saliva, blood, urine, feces, etc.). Due to the enormous survivability of Coxsackie viruses, the risk of infection remains for up to two months from the moment a child or adult becomes a carrier of the disease. Moreover, the probability of contracting Coxsackie viruses in such cases is 98%.
The vitality of Coxsackie viruses is manifested in the fact that they remain viable for seven days, being on various objects; they are not afraid of treatment with 70% alcohol, nor a solution of chloride acid, nor the acidic environment inside the stomach. But disinfection measures such as treatment with a 0.3% formaldehyde solution , exposure to very high temperatures, ultraviolet light and irradiation are deadly for them.
The main source of infection with Coxsackie viruses, as medical statistics show, are kindergartens and other places of mass concentration of children, where they are in direct contact with each other.
According to some data, Turkish resorts are also considered unfavorable in terms of the danger of infection with Coxsackie viruses, especially for a child. It is not uncommon for symptoms of infection to appear almost immediately upon arrival. However, the Turkish side, as a rule, by hook or by crook, seeks to prove that a child who fell ill on vacation was infected in his homeland, and in Turkey the symptoms of infection have only just begun to appear. And parents, as a rule, do not have the opportunity to argue with them in a reasoned manner.
The likelihood of catching Coxsackie viruses exists both indoors and outdoors, and they spread most actively in conditions of high air humidity . Therefore, the most favorable conditions for infection by them occur in the summer and autumn, when this indicator is especially high.
Most often, children under 10 years of age are affected by Coxsackie viruses, while children under 5 years of age belong to the main risk group. However, in some cases, adults can also catch the infection.
Routes of infection
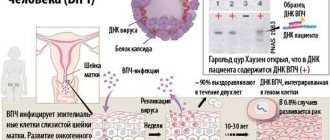
Coxsackie viruses are pathogenic microorganisms that are part of a large group of enteroviruses. Their development and reproduction after entering the human body occurs in the gastrointestinal tract.
There are three main routes of transmission:
- Fecal-oral;
- Airborne;
- Contact and household.
In children's groups, the microorganism spreads very quickly, which leads to outbreaks of the disease in one age group. The virus can remain for a long time on unwashed plant fruits, household items, and personal belongings. The incubation period from the moment of infection to the appearance of obvious clinical symptoms ranges from 3 to 10-14 days.
The clinical picture of the disease depends on what type of Coxsackie virus has entered the body:
- Coxsackievirus type A infects mucous membranes, skin, and eye membranes. The disease in this case manifests itself as stomatitis with the formation of vesicles in the oral cavity, hemorrhagic conjunctivitis, herpangina, and damage to the upper respiratory tract;
- Coxsackievirus type B infects the tissues of the heart, liver, pleura, and pancreas, causing inflammation of these organs.
A person is most contagious with the acute form during the first 5-7 days after the onset of symptoms, but the virus, along with feces, can leave the body for another 7-8 weeks.
Coxsackievirus in children: symptoms and diagnostic difficulties
Among the most common manifestations of the disease in a child are:
- High temperature during the first three to five days after infection.
- Blisters on the body and/or mouth.
- Severe itching where blisters form.
Further it is worth dwelling on these and other symptoms in more detail.
The main noticeable symptom in children is red blisters with a diameter of about three millimeters that appear on the patient’s body. They often help to recognize the Coxsackie virus. Photos showing these manifestations of the disease are not very rare today.
Often these blisters itch constantly, and this itching is so strong that the child cannot eat or sleep, and refuses to swallow due to a sore throat. In such cases, it often becomes possible for him to eat and drink only after taking medications that reduce itching. If the child who has contracted the Coxsackie virus is under three years old, the situation is complicated by the fact that such drugs are contraindicated for him due to his age and it is permissible to relieve his suffering only with cool water. If we are talking about an infant who, due to intense manifestations of the disease, begins to refuse the mother’s breast, it is recommended to moisturize it more than usual.
Itching in the mouth often causes increased salivation. Because of this, a child who has contracted the Coxsackie virus is recommended to be placed strictly with his head to one side - so that excess saliva does not clog into the respiratory tract during sleep.
In the first three days after infection with the Coxsackie virus, the temperature of the person affected by it rises sharply - up to 39–40.5 degrees. In some cases, the most painful stage of the disease can last up to five days, and only after this period does the infected child begin to feel better.
Due to this combination of symptoms, the Coxsackie virus can easily be confused with chickenpox. This set of symptoms is also typical for allergies. laboratory tests of the patient’s biomaterial become critically important for accurate diagnosis .
However, among the characteristics of Coxsackie viruses, the main places where blisters appear are the arms, legs, area around the mouth and the oral cavity. Due to this circumstance, damage by Coxsackie viruses has the common name “leg - hand - mouth”. However, such blisters, which look like ulcers, can also form on the buttocks, over the entire area of the legs, on the genitals, and in the navel area.
High temperature, due to which the Coxsackie virus can easily be confused with the flu and colds, because they are also characterized by this symptom, usually lasts for the first three days after infection.
with food poisoning is quite high if the course of the disease is accompanied by symptoms such as nausea and vomiting. However, this usually happens when the Coxsackie virus affects a child who already has intestinal problems.
Infection with group B Coxsackievirus in a child may also be accompanied by severe muscle pain, progressing in direct proportion to the increase in temperature.
There are also cases where, along with other symptoms, inflammation of the mucous membrane of the eyes, convulsions, paralysis, fainting, continuous redness on the skin, heart complications due to damage to the heart muscle, frequent urge to stool , mucus and bloody discharge in the stool, enlarged liver... If in boys the Korsaki virus penetrates the testicles and the necessary measures are not taken in a timely manner, male infertility may subsequently develop. However, such precedents are rare in medical practice.
If the expectant mother turns out to be the carrier of the virus in the last trimester of pregnancy, in most cases the child will be born already infected with it. However, for infants the situation is different in that mother's milk contains immunoglobulins that suppress the development of Coxsackie viruses. Therefore, one of the effective ways to combat the disease in this case will be to offer him the breast all the time.
Difficulties with an infant may arise later due to the fact that, as one of the consequences of a previous infection with the Coxsackie virus, aversion to breast milk . This often becomes the reason for switching to artificial nutrition. But it is possible that simply giving the child medical lactase for a while will be sufficient. However, this must be done strictly in agreement with the doctor and under his supervision.
How does the Coxsackie virus manifest in adults?
Due to the high probability of infection, there is no guarantee that adults will not catch the Coxsackie virus. The symptoms in this case are different from the manifestations of the disease when a child is infected with it. Even if an adult does not have immunity to the Coxsackie virus, usually everything proceeds without any special complications, and often it does not manifest itself at all.
And if any symptoms appear, they usually do not last more than three days. Although in some cases the disease can also manifest itself in the form of a rash and peeling of the skin, muscle pain, and fever is not excluded.
In the most severe case, symptoms in adults can last up to ten days. For comparison: for a child the process is delayed on average by one to two weeks.
In rare cases, the Coxsackie virus can provoke dangerous diseases in an adult, such as meningitis, encephalitis, diabetes, myocarditis, hepatitis , etc.
Coxsackie virus: treatment first carried out in 1948
The disease got its name from the American town where polio researcher Gilbert Dalldorf first isolated strains of the virus in feces. And although more than 60 years have passed, not even all doctors know about this disease. This is partly due to the fact that Coxsackie affects mainly children aged 3-10 years. Partly because viruses like to disguise themselves as each other, and full diagnostics are not always carried out in medical institutions.
An important point is that the name “Coxsackie” actually hides a whole bunch of viruses – 29 serotypes have been identified today. They are not very different in symptoms from each other. And, in fact, all manifestations come down to three subtypes of enterovirus, which, as you know, likes to multiply in the gastrointestinal tract (stomach and intestines).
The Coxsackie virus sometimes claims lives, although it is considered a harmless childhood infection. Many types of viruses with the same symptoms appear outwardly as three types of enteroviruses.
Treatment of Coxsackie virus in adults and children
The course of treatment is prescribed depending on the age of the patient and the symptoms through which the disease manifests itself. In particular, the following measures are practiced:
- To relieve the suffering caused by itching on the skin and/or mouth, various gels and other drugs with corresponding effects are prescribed. For adults, your doctor may also prescribe chamomile tea.
- At elevated temperatures, antipyretics are taken, with the exception of analgin (the latter is strictly not recommended in this case).
- Drugs and vitamins can be prescribed to normalize processes associated with metabolism, various means to increase immunity (usually those based on interferon), especially if the patient is weakened, and in this case the disease is more difficult to tolerate.
However, self-medication, as in most other cases, is better not to practice, but to act in accordance with the recommendations and prescriptions of the doctor.
How does treatment occur with Coxsackie?
The Coxsackie virus itself, in fact, cannot be treated, like any other similar cellular “conqueror”. Therapy is carried out to alleviate general well-being and treatment is aimed at eliminating symptoms - due to their pain.
As a result, with a diagnosis of Coxsackie, treatment is as follows:
- bed rest;
- intoxication can be relieved by drinking - avoid dehydration, in difficult cases it is possible to take antiviral drugs;
- to protect yourself from the effects of diarrhea, take Regidron or a similar remedy;
- a stomach-friendly anti-inflammatory diet that takes into account the presence of vomiting and diarrhea;
- to dull pain in the muscles, in the head, to lower the temperature, take anti-inflammatory drugs, Ibuprofen is indicated for children;
- treat skin rashes with brilliant green or furatsilin;
- The same furatsilin or another antiseptic is used to rinse the mouth when there is a rash on the mucous membrane; a gel used on the gums during teething also helps;
- for a sore throat, use sprays;
- taking antihistamines is indicated;
- After eating you need to rinse your mouth.
Important! Antibiotics do not help against viruses, therefore they are excluded for Coxsackie. Unfortunately, there is no vaccine.
Within 3 days there should be relief, and in 8-10 days there should be a cure. If this does not happen, see a doctor immediately! In mild cases, Coxsackie does not require special treatment, like any virus. The patient should drink a lot. He is prescribed a diet. Therapy is aimed at relieving and eliminating symptoms.
Prevention of Coxsackie virus in children and adults
Doctors’ recommendations in this regard do not deviate from the standard set of measures for the prevention of most infectious diseases:
- wash your hands thoroughly after being outside the home;
- Be sure to wash fruits and vegetables before eating;
- Immediately dispose of personal hygiene products such as diapers and pads.
If it becomes known that one of the family members has already caught the bacillus, it would not be superfluous to provide him with separate dishes and cutlery for the period until complete recovery, and again thoroughly wash his hands after each contact with his things.
But if you still failed to protect yourself from the Coxsackie virus, this is not yet a reason to despair. As is the case with many other infections, having been ill once, a person acquires a stable immunity to it, eliminating the possibility of the disease developing again.
Symptoms of the coxsackie virus
Diagnosis of Coxsackie virus. What tests can the doctor prescribe?
enterovirus infections
symptoms tonsillitis
Coxsackie virus
laboratory diagnostics
1. virus 2. additional examination:
- general blood analysis;
- general urine analysis;
- cerebrospinal fluid analysis (if symptoms of meningitis are present);
- other types of studies prescribed depending on the damage to a particular organ ( radiography ()
,
MRI of the brain ()
,
ECG (),
etc.).
Analysis of cerebrospinal fluid in serous enteroviral meningitis
- The liquor is clear;
- moderate increase in the level of leukocytes (up to 500 cells in 1 ml) due to lymphocytes;
- total protein is normal or slightly reduced;
- normal glucose and chloride levels.
PCR diagnostics for enteroviral infections
Material for PCR diagnostics:
- swabs from the nasopharynx – up to 3 days of illness;
- feces - on the 1st-14th day of the disease;
- cerebrospinal fluid – for meningitis, encephalitis;
- a smear of discharge from the conjunctiva - for conjunctivitis;
- biopsy material obtained during surgical interventions (for encephalitis, lymphadenitis, mesadenitis, pericarditis and other pathologies).
Read more about PCR diagnostics
Blood test for antibodies to Coxsackie viruses
antibodies Markers of Coxsackie viruses:
- Class M immunoglobulins (IgM) to Coxsackie viruses – antibodies of the acute period of the disease;
- Immunoglobulins G (IgG) to Coxsackie viruses are antibodies of the disease.
diagnosticsMore about blood tests