Types of disease
The disease is divided into several types depending on the nature of its course, the severity of symptoms and other distinctive features. When determining the type of disease, the ability of blood to circulate through the vascular system is taken into account.
Kinds:
- Stagnant type. Pathology, in turn, is divided into right ventricular and left ventricular. In the first type, the development of stagnant processes throughout the body is noted. This causes swelling to form. The left ventricular type of disease is characterized by congestion in the area of the pulmonary circulation. The condition is dangerous due to the development of complications.
- Hypokinetic appearance. It is also divided into several subtypes depending on the severity and symptoms - arrhythmic and pain shock.
In severe cases, a chronic form of the disease develops, requiring immediate hospitalization and treatment.
Stages and degrees
According to the classification introduced in 2003, the pathology has 4 stages or degrees of severity. The degree is determined based on the severity of symptoms and stagnant processes in the small circle.
Classification:
- 1st degree. There are no stagnation phenomena. Blood circulation in the peripheral part is not impaired. In this case, no pathological changes in the skin are noted.
- 2nd degree. There are stagnant processes in the area of the pulmonary circle. There are no signs of venous blood outflow. The skin is moist but warm.
- 3rd degree. The condition is characterized by dry and cold skin. In this case, failure develops in the peripheral region.
- 4th degree. Signs of peripheral circulatory failure are accompanied by the formation of stagnant processes in the pulmonary circulation.
Grades 3 and 4 require immediate contact with a specialist due to the high risks of complications.
Symptoms
Acute heart failure is a pathological process that has different symptoms depending on the form and type of disease.
Signs of the right ventricular type of disease:
- shortness of breath - develops independently against the background of spasms in the bronchi without any physical activity;
- pain in the chest area;
- yellowness or cyanosis of the skin;
- sweat that has a cold and sticky consistency;
- an increase in the size of the jugular veins;
- pain in the area of the right hypochondrium;
- increased liver size;
- development of hypotension;
- formation of swelling in the lower extremities;
- ascites is an excessive accumulation of fluid in the abdominal cavity.
Symptoms of the left ventricular form of the disease:
- rapidly developing shortness of breath, turning into suffocation;
- signs of arrhythmia, irregular heartbeat;
- presence of cough with blood impurities;
- formation of wheezing in the lungs.
The left ventricular type of the disease is in most cases accompanied by pulmonary disorders. In this case, the patient takes a sitting position.
First aid algorithm
An acute attack can lead to the death of the patient within an hour. Sometimes the onset of symptoms lasts up to several hours, but even in this case, emergency care for heart failure is required.
- When a patient with high blood pressure shows the first signs, you should immediately call a doctor.
- The next action is to transfer the victim to a sitting position, allowing him to rest his hands on the armrests or knees. In this position, the intercostal muscles will be better involved in the respiratory act.
It is necessary to transfer the victim to a sitting position.
- Rest is required. It is necessary to give access to fresh air, but so that the patient does not move.
- To drain the blood, hot water is used, into which the lower limbs of a person are placed.
The feet are placed in a warm bath.
If possible, place a nitroglycerin tablet under the root of the tongue. The drug is not used if the patient’s blood pressure is below 110. The use of any drugs in case of impaired consciousness, loss of vision or other acute manifestations is also excluded.
Reasons for appearance
Pathology occurs for several main reasons. The disease can be provoked by both congenital cardiovascular disorders and other internal disorders not related to the cardiovascular system. In the overwhelming majority of cases (60-70%), the disease develops against the background of a previous myocardial infarction.
The process is associated with the death of cells in the muscle layer, resulting in disruption of circulatory functions. In this case, the symptoms depend on the degree of damage. Heart attack is considered the most common cause of death.
Other reasons:
- Myocarditis.
- Surgical interventions associated with the use of auxiliary devices that provide artificial blood circulation.
- Exacerbations (relapses) in the presence of a chronic form of the disease.
- Pathological processes in the valve area.
- Arrhythmia.
- Lesions of the respiratory system leading to circulatory disorders in the pulmonary circulation.
- Hypertensive crisis.
- Infectious diseases - influenza, ARVI, pneumonia, endocarditis.
- Rapid weight gain.
- Excessive alcohol consumption.
- Abuse of drugs that affect the removal of fluid from the body - steroids, estrogens.
- Previous brain surgery, brain injuries.
- Stroke.
In old age, the most common risk factor for developing the disease is diabetes. Also, in people over 60 years of age, the cause of the disease can be hypertension - it occurs in 4% of all patients.
Diagnostics
Acute heart failure is a process that is often asymptomatic, which is why it is necessary to undergo regular preventive examinations even in the absence of any signs of disease development. When making a diagnosis, it is necessary to pay attention to the general well-being of the patient - dyspnea, chronic fatigue, fatigue.
A visual examination by a specialist helps to identify signs such as swelling in the lower extremities and skin color. Measuring procedures are also carried out - pulse rate, blood pressure, listening to the lungs.
Diagnostic methods:
| Procedure name | Description | approximate cost |
| ECG (electrocardiogram) | research is a necessary and most basic means of identifying the disease. In this case, disturbances are recorded in various parts of the heart. The diagnostic method involves installing special sensory suction cups to the chest area. Monitoring and determination of the disease is carried out using a computer that records cardiac activity. | 450-560 rub. |
| General blood analysis | A mandatory procedure to determine the level of leukocytes in the blood. ESR is also recorded, and the electrolyte and gas composition of the lymph is studied. | from 120 rub. |
| General urine analysis | The composition of urine is studied for the presence of impurities or elevated levels of some components. | 150 rub. |
| Biochemical analysis | The method allows you to determine the level of glucose and cholesterol. | 210 rub. |
| X-ray | Diagnostics helps to assess the size of the heart. | from 150 rub. |
| Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) | A research method that allows one to evaluate the layer-by-layer structure of the heart in a section. | from 9000 rub. |
| Marker test | Allows you to determine the presence in the blood of highly specific biological markers that provoke the development of inflammatory processes in the heart muscle. | from 130 rub. |
The most effective methods for studying the clinical picture are blood and urine tests, as well as an electrocardiogram. Additional diagnostic tools allow you to determine the degree and form of the pathological process.
You can undergo the procedures at any public or private medical institution. Prices for services may vary depending on the region and area where the medical center is located.
What is first aid for acute heart failure?
Acute heart failure is one of the most dangerous complications of cardiac diseases, in which the pumping function of the heart is impaired.
The myocardium does not relax enough, the chambers of the heart are not completely filled with blood. The amount of blood entering the aorta is not enough to maintain the normal functioning of the body.
Acute heart failure is an emergency with a high probability of death and requires emergency hospitalization of the patient. We bring to your attention an article about first pre-medical and medical aid for acute heart failure.
Coronary heart failure (otherwise known as coronary heart failure) develops at lightning speed and, as a rule, unexpectedly.
Almost always a person feels well, and unpleasant symptoms appear suddenly:
- Various types of arrhythmia.
- Ventricular fibrillation or complete cardiac arrest.
- Feeling of pressure and burning in the chest, pain. In some cases, pain moves to areas atypical for this pathology, for example, to the epigastrium.
- Pulmonary edema, which is identified by wheezing, shortness of breath, and pinkish foam at the mouth.
- Paleness of the skin. In particularly severe situations - blueness of the hands, feet and lips.
- Loss of consciousness.
When diagnosed with coronary insufficiency, its symptoms are far from the only opportunity to determine the development of this disease.
Some diagnostic methods will help confirm the diagnosis:
- Ultrasound examination (ultrasound). Helps to see the presence of fluid in the pericardial area, heart defects, various changes in the size of its parts and an aneurysm.
- Electrocardiogram (ECG). This is an excellent opportunity to detect heart rhythm disturbances in time.
- Coronary angiography. A way to find out about the condition of the arteries.
If necessary, the doctor will prescribe a CT scan.
Acute deficiency syndrome, as mentioned above, develops unexpectedly.
The following symptoms are typical for an attack:
- loss of consciousness;
- lack of pulse in large vessels;
- lack of heartbeat;
- cessation of respiratory activity;
- lack of pupillary reaction to light;
How to help a person in this situation:
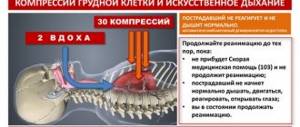
- First you need to lay it on a hard surface (preferably the floor). Call an ambulance.
- Check the pulse in one of the arteries. If it is not there, it is necessary to perform chest compressions and artificial ventilation. The massage begins with a strong fist blow to the middle part of the sternum. Then you need to do about 90 presses per minute. Ventilation of the lungs is carried out in any possible way. It must be done without stopping. The maximum duration of a break is 30 seconds.
These steps can be completed before the doctor arrives.
All other measures to rescue the victim fall on their shoulders:
- Defibrillation. This is the effect of electric current on the chest. Helps “start” the heart.
- Through a catheter installed in a vein, a certain drug is administered to the patient every 3 minutes. Usually this is Adrenaline and Lidocaine.
- If there is no effect, then the administration of other drugs is indicated - Ornid, Novocainamide, Magnesium sulfate, Atropine.
If it is not possible to administer drugs intravenously, the doctor will do it through the trachea or directly into the heart.
All activities are stopped if the heart does not start working within 30 minutes after they begin. If they have an effect, the patient is immediately taken to the hospital. Further actions of doctors depend on the general condition of the person.
Treatment of the disease
The sooner treatment for acute coronary insufficiency begins, the more favorable the outcome will be. Otherwise, complications may develop, including heart attack, cardiomyopathy, and even death. Self-medication is strictly prohibited. This will not lead to anything good.
Treatment of the disease with medications should take place in a hospital under the supervision of a doctor.
It has its own characteristics:
- Taking medications should be combined with proper nutrition, quitting smoking and alcoholic beverages, moderate physical activity, proper rest and, if necessary, weight control.
- Typically, doctors use drugs that help dilate blood vessels, restore heart rhythm, and normalize heart function.
In addition to drug treatment, in some cases surgery and intravascular measures are indicated:
- Shunting. This is a procedure for restoring blood circulation by installing special shunts in narrowed areas of blood vessels.
- Stenting. A frame is placed inside the coronary vessels.
- Angioplasty. Narrowed vessels are dilated using catheters.
- Atherectomy. Cholesterol plaques blocking the vessel are surgically reduced.
- Rotational ablation. The vessels are cleaned and dilated with a special medical drill.
Surgical intervention is indicated only when medication does not bring results.
Acute coronary insufficiency can cause death. Why? Very often a person simply does not notice the alarming symptoms. He ignores mild attacks and is in no hurry to see a doctor. Because of this, the disease develops, becomes more complex and provokes the development of complications. And they, in turn, lead to death.
There are several conditions that increase the risk of unexpected death from acute failure:
- cardiac ischemia;
- excess body weight;
- disturbances in the activity of the heart and blood vessels;
- too high cholesterol level;
- excessive consumption of alcoholic beverages;
- diabetes;
- fluctuations in the amount of potassium and magnesium;
- cardiomyopathy;
- frequent causeless fainting;
- heart failure;
- heart attack, which severely damages the myocardium;
- ventricular tachycardia;
- severe thickening of the heart muscles.
Knowing what coronary insufficiency is, its causes and complications, it is easy to create a prevention program.
- Completely stop drinking alcohol and smoking.
- Protect yourself from stressful situations. If possible, reduce the amount of emotional stress.
- Change your diet. First of all, you should avoid foods that are too fatty and spicy. Instead, you need to add as many fresh fruits and vegetables to the menu as possible.
- Add moderate physical activity. They can be anything. Pool activities, tennis, and roller skating are suitable. The main thing is not to overwork.
- Monitor your blood pressure and regularly take blood tests to check your cholesterol levels.
- If you have extra pounds, you should lose weight.
- If necessary, you can take maintenance medications. This should be done only after consulting a doctor.
If you take all the necessary measures in time, you can reduce the risk of complications to a minimum. This is possible even with congenital anomalies. In the case of them, it will be necessary to eliminate the causes that caused the deficiency. The acquired disease requires accurate diagnosis and effective treatment.
Coronary insufficiency - what is it? This is a pathology affecting the heart. Due to certain factors, they narrow, thereby disrupting the supply of oxygen and other substances the heart needs. Timely treatment of coronary insufficiency is an opportunity to avoid complications, the worst of which is death.
Acute heart failure is a pathological condition that can develop over a relatively short period of time of a few hours or days. It is characterized by a decrease in myocardial contractility with deterioration of blood flow, which does not ensure adequate supply of nutrients and oxygen to the tissues.
Causes
Acute cardiac failure is not an independent pathological process; it develops as a result of other diseases, which most often include:
- Congenital heart defects.
- Acute exogenous poisoning, characterized by the entry of toxins into the child’s body from the outside.
- Myocarditis.
- Acquired heart defects.
- Pathology of the lungs.
- Severe systemic allergic reactions.
- Arrhythmia is a disturbance in the rhythm of heart contractions.
- Thyrotoxicosis is an increase in the functional activity of the thyroid gland with a significant increase in the secretion of its hormones.
- Acute circulatory disorder in the brain with a change in the functional activity of centers that regulate the functioning of the heart and blood vessels.
Also, a pathological decrease in the contractility of the heart can develop as a result of incorrect choice of infusion volume (intravenous infusion) of saline and hyperosmolar (glucose) solutions, or excessive dosage of radiopaque compounds.
Depending on which part of the heart the decrease in contractile activity is more pronounced, several clinical variants of this pathological condition are distinguished:
- Acute left ventricular failure.
- Acute right ventricular failure.
- Total heart failure.
These clinical forms of the pathological process in a child have distinctive symptoms and also require different therapeutic approaches at the hospital stage of care.
Clinical picture
Manifestations of the development of a decrease in myocardial contractility depend on which part of the heart was affected to a greater extent:
- Damage to the left side of the heart - the main manifestation is the symptoms of cardiac asthma, which includes pulmonary edema with a severe attack of suffocation, persistent cough with the release of foamy pink sputum, which intensifies at night. The child is very frightened and tries to take an elevated, semi-sitting position. Breathing is noisy, bubbling, and distant wheezing may be heard. At the beginning of the attack, the skin becomes pale, then it acquires a bluish color, more pronounced on the fingers, lips, and in the area of the nasolabial triangle.
- Damage to the right side of the heart - clinical symptoms develop suddenly, a feeling of suffocation, pain and a feeling of tightness in the heart area appears, the skin acquires a pronounced bluish coloration, becomes cold to the touch, and becomes covered in sticky sweat. Against this background, signs of increased central venous pressure appear and intensify with pulsation of large veins (jugular veins in the neck) and the development of edema of peripheral tissues.
- Total damage to all parts of the heart is a very serious condition, which often develops in young children and is characterized by deterioration of blood circulation in the pulmonary and systemic circulation.
Prevention
Taking preventive measures helps reduce the risk of developing the disease and avoid complications caused by disorders in the cardiovascular system. However, there is no specific prevention. However, many experts recommend adhering to certain rules.
Recommendations:
- Quitting bad habits - smoking, alcoholic beverages.
- Constant control of body weight. Weight loss in case of obesity development.
- Moderate physical activity and exercise. In this case, the intensity of the load is calculated based on the patient’s condition.
- Avoiding stress and psycho-emotional overload.
- Maintaining sleep-wake and rest patterns.
- Monitoring blood pressure levels. It is carried out independently using a tonometer.
- Compliance with nutritional principles. It is recommended to avoid foods containing fast carbohydrates and animal fats.
It is also recommended to undergo annual preventive examinations with a cardiologist.
Treatment
Unfortunately, patients with this pathology have a high mortality rate even if they go to the hospital in a timely manner. About 15% of patients do not live even a year if the pathology is stage 1 or 2. Timely first aid for heart failure plays an important role in treatment.
The patient undergoes treatment in a cardiology department or center.
Conservative treatment for deficiency consists of prescribing medications, a course of which the patient undergoes in a cardiology department or center. The dynamics improve with the use of diuretics. Beta blockers help lower blood pressure and improve the quality of heart rhythm. After their administration, the amount of blood pumped is significantly reduced, which reduces the load on the myocardium.
Glycosides help improve heart function.
Glycosides have a herbal composition that helps improve the functionality of the myocardium in case of its insufficiency. The work of the heart becomes economical and productive. In large quantities, glycosides are dangerous.
The patient is placed on bed rest; even minor loads and stress are contraindicated. A mandatory item is following a special protein diet and limiting salt.
Additional treatment includes withdrawal from alcohol dependence. A patient with psychosis or other nervous disorders is prescribed a course of sedatives. Anemia is prevented with iron supplements.
Treatment methods
Treatment is aimed at eliminating the primary causes that caused the development of the disease. This requires an integrated approach, including the use of medications and physiological procedures. Before treatment, the patient must be helped into a sitting position. Legs should be down. For pulmonary edema, oxygen inhalations are performed.
Medications
Acute heart failure is a pathological process that requires immediate use of medications. To restore the contractility of the heart muscle, glycosides are prescribed, as well as drugs related to cardiotonics. However, in some cases, the use of cardiac glycosides does not lead to a pronounced therapeutic effect.
Approximate treatment plan:
- Nitroglycerin - taken before hospitalization. Use under the tongue.
- A group of analgesics and neuroleptics - helps reduce pain.
- Diuretics.
- Ganglion blockers for severe hypertension, as well as vasodilators.
- Vasodilators.
- Symptomatic amines - prescribed for low blood pressure.
Medications:
- Morphine. Opioid analgesic. Used in the treatment of cardiogenic shock, reduces pain. Prescribed for shortness of breath caused by the development of heart failure, as well as for myocardial infarction. The treatment regimen is individual. A single dosage ranges from 10 to 100 mg. The duration of the course is determined by the cardiologist. The drug has contraindications. Cost – from 90 rubles.
- Lasix. The main component is furosemide. A diuretic drug used in the treatment of edema of various origins, including edema in the development of acute heart failure. Contraindicated in renal failure and other kidney disorders. The dosage is calculated based on the patient’s body weight. The duration of treatment depends on the nature of the pathology. Cost – from 50 rub.
- Pentamin. It is prepared in the form of a solution based on azamethonium bromide. The drug has an antispasmodic and hypotensive effect. It is used in complex therapy of hypertensive crisis and spasms in the peripheral arteries. Contraindications: thrombophlebitis, renal failure and hypotension. The solution is administered intramuscularly in a dose of 0.5-3 ml. 2-3 times a day. In this case, the daily norm should not exceed 9 ml. The duration of treatment is determined by the treating specialist. Cost – from 1400 rubles.
- Isoket. The drug belongs to the group of vasodilating drugs. It is a nitrate - isosorbide dinitrate. It has a hypotensive and antianginal effect, acting directly on the venous vessels, reducing pressure in the small circle. When using, instructions must be strictly followed. The solution is injected into the oral cavity 1-3 times a day. In this case, you need to breathe through your nose. Use the product with constant monitoring of blood pressure and heart rate. There are contraindications. Cost – from 700 rub.
- Dopamine. The drug belongs to the class of cardiac glycosides. Produced in the form of a concentrate for the preparation of injections. Used for cardiogenic shock, acute heart failure, and severe forms of hypotension. It has multiple contraindications and restrictions. The solution for violations of myocardial contractile function is administered at a rate of 100-250 mcg/min. The duration of treatment is determined by the attending physician. Cost – from 65 rubles.
Other medications may be prescribed. The specific drug and dosage are determined only by a cardiologist, taking into account the characteristics of the patient’s body and the tolerability of the components.
Traditional methods
Acute heart failure is a disease that requires complex therapeutic effects, which is why traditional medicine is often used as additional therapy. Various herbs and plants that have a diuretic and sedative effect are used to prepare infusions. The most effective remedies are strawberries, mint, birch, lily of the valley, motherwort, hawthorn, and garlic.
Recipes:
- Medicinal juice. To prepare, squeeze out 1 tbsp of fresh beet and carrot juice. To the resulting mixture add the juice of 1 lemon and pre-prepared horseradish juice - 1 glass. You must add another 1 glass of natural bee honey to the juice prepared in this way. It is recommended to store the product in a cool place. Use 1 tbsp. mixture 3 times a day. Take 1 hour before meals. The course of treatment is 60 days.
- Motherwort. The plant helps restore heart function. It has a calming effect, exhibiting a diuretic effect. For cooking, take 1 tbsp. plants (dry grass) and pour boiling water in a ratio of 2:1. The container is wrapped in thick cloth and left overnight. After which the product is filtered and taken 2-4 times a day. A single dose is no more than ½ glass. It is also recommended to use a pharmacy tincture of motherwort.
- Beet juice. To prepare the product, you need to take 1 kg of beets, rinse, peel and cut into small pieces. Then add 3 slices of crumbled bread to the mixture. At the end add the juice of 1 lemon. The mass is transferred to a 3-liter jar and filled with warm water. After which the container is wrapped in cloth and placed in a dark place for 7 days. Before use, the composition must be strained. Take 2 times a day. The course of treatment is no more than 12 days. For greater effectiveness, it is recommended to add 1 small clove of garlic to each serving.
- Birch leaves. A handful of dry leaves is poured with water and boiled for 15 minutes. Then the product is cooled and filtered. Consume before meals. The course of treatment is no more than 3 months. In addition, it is recommended to consume fresh birch sap. The product has a diuretic effect. Helps eliminate swelling.
- Ginseng. Before using ginseng infusion, you should consult a specialist. To prepare the product, take the roots of the plant and grind them using a grater or blender. Then fill everything with alcohol and screw the container tightly with a lid. Infuse for 2 weeks in a dark place. Take 30-40 drops daily before meals, no more than 3 times a day. The product copes with swelling. Helps restore heart function.
- Green beans. Take 30 g of the plant and add 0.3 liters of water. Then everything is put on fire and cooked for 15-20 minutes. After which the product is removed from the heat. Cool and strain. Take 2 tbsp. 3 times a day.
- Kalina. To prepare the product, you can use berries in any form - fresh or frozen. Take 30 g of viburnum and mash until juice forms. Then add 25 g of natural honey to the mixture. Then everything is poured with 1 glass of boiling water and infused for 1 hour. Take 100 g daily 3 times a day.
Traditional medicine methods are allowed to be used only after consultation with a doctor and as an auxiliary therapy. The main treatment of pathology is carried out with the help of medications.
Other methods
In severe cases, emergency surgery is resorted to. In this case, the type of operation depends on the form and nature of the pathological process. When ascites forms, a pleural puncture is performed to remove excess fluid accumulation in the peritoneal area.
A patient with severe hypoxic syndrome is given oxygen therapy. This treatment is carried out using a breathing mask, through which the patient inhales a special mixture that increases the level of Pa02 in the blood. The oxygen concentration ranges from 40 to 70%.
Treatment of chronic heart failure
Treatment of chronic forms of cardiovascular failure is carried out at home. First of all, they get rid of the underlying disease that led to the development of the syndrome. At this stage, the patient needs to be provided with emotional peace and relieved of excessive stress. Physical activity should be limited only to physical therapy, the methodology of which will be selected by a specialist based on the history of the disease.
Changing your diet should consist of reducing the amount of animal fats and harmful, quickly digestible carbohydrates. If you are overweight, you should create a calorie deficit of 200-300 kcal per day. The amount of salt and water consumed must be significantly reduced. So, you can drink no more than 1.5 liters of liquid per day. No more than 3 g of table salt per day will be safe.
Drug therapy for the disease
To treat pathology, it is effective to use medications.
Appointed:
- Diuretics. Medicines in this group normalize blood pressure, reduce pressure in the heart chamber without lowering the pulse. In people with heart failure, these drugs reduce mortality and hospitalization due to heart disease. Diuretics such as Furosemide, Disothiazide, Aldactone are used.
- Angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitors. The principle of action of drugs of this class is based on the inhibition by the active substance of the drug of enzymes that provoke contraction of blood vessels. Medicines used are Captopril, Ketiopril, Lisinopril, Enam, Ramipril, Fozinopril, Ceronapril.
- B1 agonists. Medicines in this group increase the strength of contractions of the heart muscle. Dobutamine and dopamine are the most common β1-agonists, but their use is limited to intravenous administration for emergency indications.
- Beta receptor inhibitors. They are used for cardiovascular failure, when it is necessary to strengthen the contractions of the heart without increasing the pulse. They use drugs such as Bisoprolol, Metoprolol, Nebivolol, Betaxolol, Carvedilol.
In situations where the use of medications is ineffective, surgery may be prescribed:
- 1. implantation of a pacemaker to normalize blood flow to the ventricles;
- 2. implantation of a device to improve blood supply to the myocardium.
Possible complications
In the absence of timely treatment, the disease leads to various complications and consequences, which, in turn, can cause death.
Possible complications:
- Cardiogenic shock. When the syndrome develops, treatment with medications is not effective. The fatality rate ranges from 90 to 100%.
- Edema in the lungs. The condition leads to general intoxication of the body. In this case, there is a high probability of developing asphyxia with a complete cessation of pulmonary activity.
- Myocardial infarction. Pathology develops in most cases. In this case, the fatal outcome increases by 30-40%.
- Stroke. The condition is characterized by the rapid death of neurons.
In severe cases of acute heart failure, the patient's condition rapidly deteriorates and leads to death. This is the most common consequence of the lack of prompt medical care.
Acute vascular insufficiency.
Acute vascular insufficiency develops as a result of a sharp decrease in vascular tone. In this case, the capacity of the vascular bed becomes greater than the blood contained in it. The most important organs, including the brain, lack oxygen carried by the blood, which leads to disruption and even shutdown of their function.
Fainting.
One of the manifestations of acute vascular insufficiency is syncope - a short-term sudden loss of consciousness as a result of a sharp decrease in blood flow to the brain. Most often, fainting is accompanied by mental trauma or nervous shock. Its occurrence is promoted by exhaustion, anemia, physical fatigue, conditions such as pregnancy, hypertension. Sometimes before fainting, the patient feels nausea, lack of air, dizziness, darkening of the eyes, weakness, etc. Fainting is manifested by paleness of the skin and mucous membranes, sometimes by a decrease in blood pressure to 70-60 mm Hg. Art. Breathing becomes rare during fainting. As a rule, the duration of fainting is short-lived - a few seconds, but sometimes it can last minutes or more.
First aid.
First aid for fainting is as follows:
- It is necessary to give the patient a horizontal position; the head is lowered below the level of the body - this leads to an increase in blood flow to the brain and rapid restoration of breathing.
- Clothes that are restrictive to the patient should be unbuttoned.
- To stimulate the respiratory and vascular-motor centers, you can give the patient a sniff of ammonia, wipe or spray the face with cold water.
- It is very important to ensure a flow of fresh air into the room. In most cases, with the help of these measures it is possible to bring the patient out of a state of fainting.
- In more severe cases, cordiamine, caffeine or strychnine should be administered. Until consciousness and breathing are restored, the patient is not transportable.