Classification
In clinical work there are:
- right-sided, left-sided or bilateral cysts;
- single-chamber or multi-chamber;
- uncomplicated (the most common option), complicated.
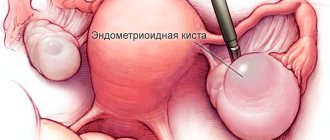
A special type of serous pseudotumor formations are papillary serous cysts. These structures are formed when epithelial tissue grows into the cyst cavity and require more attention due to their tendency to degenerate into a malignant tumor.
Causes of ovarian cystodenoma formation
This disease may be preceded by:
- hormonal imbalance or diseases of the endocrine system;
- unprotected sexual contact with a person with a transmittable disease;
- infectious inflammation affecting the outer and inner surface of the genital organs;
- inflammatory processes occurring in the fallopian tubes and ovaries (adnexitis, salpingo-oophoritis);
- pathological processes after surgery on the pelvic organs, as well as after abortion or cesarean section;
- frequent and prolonged stressful conditions, long-term abstinence from sexual intercourse or, conversely, excessive sexual activity with different partners;
- intense physical activity, diet.
When diagnosing a serous ovarian cyst, the following methods are used:
- Making a diagnosis after examination by a gynecologist. Based on the results of examinations, tests and personal visual examination, the doctor determines the size of the cyst, activity, consistency and traces the possible risks of damage to nearby organs.
- Ultrasonography. This procedure is carried out a week after the start of menstruation using a transvaginal sensor. Thanks to this examination, it is possible to determine the size of the cyst, its thickness and the intensity of blood circulation in the tumor. Also, special attention is paid to the area of proliferation of cystic formations.
- Magnetic resonance and computed tomography (MRI or CT). They are carried out in cases where an in-depth study of cystodenoma is necessary.
- A detailed blood test for tumor markers of cystodenoma indicates the presence of an inflammatory process or a purulent abscess in the ovaries, which is typical for the development of an oncological process.
- Fibercolonoscopy of the colon and fibrogastroscopy of the stomach (FCS and FGDS).
Doctors do not have a consensus about what reasons lead to the formation of serous cysts.
A number of other reasons are suggested that provoke the appearance of a serous cystoma.
- Hormone imbalance. Problems with the thyroid gland;
- Inflammation of the ovaries;
- External and internal infectious inflammation of organs;
- Obesity;
- Venereal diseases;
- Inflammations caused by abortion, unprofessional surgical intervention, gross careless gynecological examination, birth injuries.
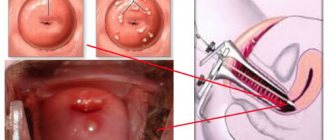
Diagnostics
Cystic formations of the ovaries are usually detected already at the stage of a routine gynecological examination during a bimanual examination. At the same time, the size of the cyst, its location, mobility and consistency are determined.
If a formation is detected in the projection of the ovaries, it is necessary to conduct additional diagnostics. Its goals are:
- Clarification of bimanual examination data.
- Determining whether a tumor is benign or malignant.
- Analysis of the capsule structure and contents of the formation.
If serous ovarian cystadenoma is suspected, the following additional research methods are performed:
- Ultrasonography. It is performed both transvaginally and through the abdominal wall. Allows you to clarify the size and location of the tumor, as well as identify ascites. In addition, ultrasound allows you to clarify the structure of the capsule of the formation and the nature of the contents.
- Tumor markers – CA 125, HE 4, calculation of the ROMA index. Deviation of these parameters from normal allows us to suspect malignancy of the tumor.
- Computed and magnetic resonance imaging. They are carried out as a complement to ultrasound examination and allow us to clarify the diagnosis, especially in complex cases.
It should be noted that simple serous cystadenoma in the early stages of its development has a similar ultrasound picture to functional ovarian cysts. In such cases, dynamic monitoring of the size of the cyst is performed and conservative treatment is attempted.
If treatment is ineffective and the size of the ovarian mass remains unchanged in different phases of the menstrual cycle, a diagnosis of a true ovarian tumor is made.
Complications
Possible associated conditions:
- Torsion of the legs of the cyst, necrosis, hemorrhage (can be provoked by: increased physical activity, prolonged sun exposure) - manifested by sudden intractable pain, impaired intestinal function and other signs of an acute abdomen.
- Rupture of the cyst, bleeding into the abdominal cavity with the possible development of a state of shock.
- Compression of surrounding organs (ovary, fallopian tubes, bladder, urinary tract, intestines). In severe cases, it can lead to infertility, acute intestinal obstruction, and acute urinary retention.
- Rarely - infection of the tumor formation. Possible routes of infection are lymphogenous, hematogenous. Accompanied by a deterioration in general condition, sudden increases in temperature to febrile values (38-390C), and signs of intoxication.
- Rarely - degeneration into a malignant tumor.
Symptoms of the disease
With a small size, the serous cyst is benign and does not cause much trouble. This is why many women do not notice the symptoms of the disease for a very long time and do not feel the clinical manifestations of the disease. Often, cystodenoma is detected by a gynecologist during a routine examination or when a woman addresses other issues that concern her.
When the formation increases in size, it causes discomfort and manifests itself in the following symptoms:
- aching painful sensations in the abdominal cavity, in the lower or lateral part, in the groin or lower back;
- unpleasant pain during sexual intercourse or physical activity;
- frequent urge to urinate as a result of the enlarged cyst putting pressure on the bladder;
- disruption of the menstrual cycle, changes in the volume of discharge;
- low temperature, indicating the presence of an inflammatory process in the body;
- nausea and weakness during the day, disruption of hormonal status, which causes causeless irritability;
- impaired intestinal motility, resulting in constipation and other gastrointestinal disorders;
- unexplained abdominal enlargement due to cyst growth;
- asymmetry of the abdomen as a result of bulging of the abdominal wall on the side where the cyst affected the ovary.
The main reason for seeking medical help for a woman should be ascites - an enlargement of the abdominal cavity as a result of the growth of a cyst and a large volume of internal fluid. Acute pain that appears can lead to complications - the collapse of the cyst stalk or even its rupture. The bending of the pedicle can affect the blood supply to the ovary, which will lead to an inflammatory process. And its rupture will entail the pouring of internal fluid into the abdominal cavity.
Folk remedies for prevention and treatment
Such methods are available and relatively safe, but do not have as pronounced an effect as drug therapy. Treatment of serous cysts with folk remedies involves the use of bee products and herbal preparations. So, one of the leaders in effectiveness in herbal medicine against cysts is rightfully considered to be the hogweed, the red brush and the umbrella winterweed.
Traditional healers advise taking peony tincture (you can buy it at a pharmacy) 40 drops per day, excluding menstrual days.
It is also recommended to apply a waffle towel to the lower abdomen, which should be moistened in a solution of table salt (a tablespoon per glass of water). The solution is also called hypertonic. Its action is based on the property of salt to draw out liquid. It is believed that along with it pathogens, viruses, and microbes leave the body and the inflammatory process gradually stops. The course of treatment is 7-14 days.
Burdock juice has a good effect.
- You need to wash and dry the leaves of the young plant, grind them using a meat grinder, and squeeze the juice out of the resulting mixture through gauze or a sieve.
- In total, you will need about 2 liters per course of treatment, but it is better to prepare it in small portions, otherwise the juice may turn sour.
- The prepared product can be stored for no more than 2 days. Drink 1 tablespoon before meals in the morning and evening.
Includes general principles for all cystic lesions:
- Regular preventive examinations by a gynecologist with ultrasound examination (including subsequent dynamic monitoring).
- Prevention of infectious and inflammatory diseases of the genital organs. Their timely identification and elimination.
- Undergoing blood tests for tumor markers (especially if tumors have been identified in relatives in the family.
Treatment
The method of eliminating a cyst is selected depending on its type, location, history of development, and age characteristics of the patient. At the initial stage, drug therapy is applicable, including drugs aimed at resolving the tumor and having an anti-inflammatory effect. Vitamin therapy and hormone therapy are used. Physiotherapy, mud therapy, acupuncture, proven methods of traditional medicine are used as an auxiliary element, only after the recommendation of a specialist.
Hormonal therapy is used for pregnant women to avoid ovarian torsion, as well as the threat of miscarriage. According to experts, a cyst, the size of which does not reach three centimeters, is not an obstacle to bearing a fetus. The risk for pregnancy during the 12-week period is a large tumor. Nature has a mechanism for lifting the uterus into the abdominal cavity at this time, while the leg of the cyst can twist and provoke a miscarriage. To avoid such troubles, surgical intervention is performed. During pregnancy, the use of laparoscopy is considered relatively safe.
Cystodenoma grows to an abnormally large size in the later stages. If the disease has been advanced, surgery is performed, during which it is possible to perform histological tests to determine the presence or absence of oncology.
Serous cyst of the left ovary
The reasons for the appearance of a serous cyst on the left ovary in medical practice have not been fully studied. The main ones are: disorders of embryonic development, hormonal imbalance during puberty, menopause and abdominal trauma.
Also, the reasons for the appearance of a serous cyst on the left ovary can be:
- early puberty (first menstruation before age 11);
- anomaly of follicular maturation;
- hypothyroidism, endocrine system disease, hormonal imbalance;
- carrying out operations to terminate pregnancy at a young age;
- disruptions of the menstrual cycle;
- availability of information about previously identified cystic formations of other forms;
- treatment of breast cancer with tamoxifen;
- diseases of the genital organs caused by various infections;
- inflammatory processes of the ovaries or fallopian tubes;
- traces of surgical intervention in the treatment of diseases of the pelvic organs.
As the left ovarian cyst grows, the following symptoms may appear:
- ring-shaped pain in the lumbar region;
- frequent urination as the cyst grows;
- difficulties with bowel movements;
- irregular menstrual cycle;
- general malaise not associated with vigorous activity during the day;
- asymmetry of the abdominal line as a result of cyst growth, nausea, low temperature.
Clinical picture
At the beginning of its appearance, the serous cyst is still very small and may not make itself felt. It can be detected completely by accident during an ultrasound or a routine gynecological examination.
As the tumor grows, it begins to put pressure on nearby organs and cause the characteristic symptoms of an ovarian cyst:
- aching and cramping pain in the suprapubic region, groin;
- disruptions of the menstrual cycle (pain during menstruation, heavy or very scanty discharge);
- emotional overexcitation;
- apathy;
- poor sleep;
- chronic fatigue;
- regular urge to urinate.
READ ALSO: The first signs and symptoms of ovarian cancer in women: predisposing factors for the development of the disease and methods of its treatment
Possible complications
The main danger of a serous cyst is compression of surrounding organs, as a result of which their functionality is impaired and acute conditions occur. If the patient has a very high temperature, sharp, unbearable pain, nausea, vomiting, or headache, this may indicate torsion of the cyst stalk. In this condition, necrosis of the tissues of the formation develops, there is a high risk of rupture of the capsule and leakage of serous fluid into the peritoneum. Bleeding, severe headaches, pale skin, and loss of consciousness occur.
Serous cyst of the right ovary
The main reason for the formation of a serous cyst on the right ovary is hormonal disorders.
Women with the following symptoms are at risk:
- irregular periods;
- the onset of menstruation at a very early or very late age;
- the onset of menopause in women after 50 years;
- diseases of the genital organs – chronic venereal diseases, entometritis);
- infertility;
- repeated miscarriage.
Symptoms of the appearance of right-sided serous ovarian formation:
- pain and discomfort in the right lower abdomen;
- disorders of a woman’s reproductive function (difficulty conceiving);
- disruption of the menstrual cycle (delays, bleeding);
- frequent urination and constipation;
- compaction of the mammary glands.
Reasons for the development of pathology
It is often difficult to trace the cause-and-effect relationship of cyst development.
A number of factors can lead to this disease, including:
- hormonal imbalance;
- problems in the endocrine system;
- diseases transmitted through sexual contact;
- infectious inflammation of the genital organs;
- inflammation of the ovaries or uterus;
- frequent stress;
- long-term sexual abstinence
- inflammation of surgery, for example, after abortion;
- frequent change of partners;
- excessive physical activity;
- abuse of diets.