Weight problems, persistent anxiety or depression, chronic acne, irregular periods or even infertility are all problems that many women face and may be symptoms of one of the most common female hormonal disorders.
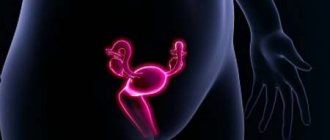
Polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS) is a common disorder, the exact cause of which is still unknown, and the name itself indicates a whole range of symptoms.
The name “syndrome” is used because this disorder manifests itself in different ways: a different set of symptoms occurs from woman to woman, which can arise for various reasons.
Many girls ignore polycystic ovary syndrome for a long time due to the absence of classic symptoms, but this cannot be done, since the far-reaching consequences can be serious:
- infertility,
- type II diabetes,
- high cholesterol,
- hypertension (high blood pressure),
- endometrial cancer.
But a diagnosis of PCOS does not mean that a girl is doomed to suffer from chronic health problems for the rest of her life. Although there is no specific known cure for this disorder, there are still ways to successfully manage it.
“Polycystic ovary syndrome is highly treatable with diet, lifestyle changes and therapeutic agents,” say gynecologists. “About 20% of patients are women with polycystic ovary syndrome. A diagnosis of PCOS should not be an obstacle to having a child. If a woman is willing to change her diet and lifestyle, and take a number of medications, fertility will be restored and pregnancy will occur.”
The first step in the fight against PCOS is to fully understand this endocrine disorder.
Classification and symptoms
According to physiology, the disease is usually divided into three forms:
- The typical course of the syndrome is accompanied by increased production of androgens of ovarian origin. This means that hormonal imbalance occurs precisely due to dysfunction of the gonads.
- The central form of the disease suggests a major role in the pathogenesis of neurogenic mechanisms, namely the hypothalamic-pituitary system. A similar genesis of the syndrome is ensured by a change in the controlling action of the central nervous system. Often the problem is combined with a number of other diseases that affect the endocrine glands.
- The mixed form of pathology involves hyperandrogenism of both ovarian and adrenal origin. In such cases, there is a high probability of failure of the function of central control mechanisms.
There are several other classifications of the problem, for example, according to etiology and based on individual clinical manifestations, but they are conditional and are not considered generally accepted.
As a rule, the first symptoms of polycystic ovary syndrome appear in adolescence. In girls whose sexual cycle is still at the formative stage, long delays between menstruation are possible. In some cases, such manifestations are normal and do not require correction. However, if such symptoms occur, it is recommended to consult a gynecologist, since they signal a malfunction in the female body. The classic clinical signs of polycystic ovary syndrome are:
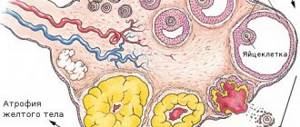
- Lack of regularity of the menstrual cycle is ensured by the cessation of ovulation. The process of follicle maturation is accompanied by the subsequent release of an egg. This cascade of reactions is ensured by many metabolic transformations that are controlled by hormones of the pituitary gland and gonads. When endocrine disruption occurs, the sex cells do not mature and menstruation does not occur. Initially, long delays in menstruation are possible, which are later replaced by their complete absence - amenorrhea. In parallel, there is a thickening of the inner layer of the uterus, which can lead to significant bleeding.
- Increased secretion of androgens is accompanied by symptoms that are not related to disorders of the reproductive system. Girls with PCOS often exhibit increased secretion of the sebaceous glands, the formation of acne and pimples, the symptomatic treatment of which does not lead to the desired result. The condition of the scalp also worsens, which is accompanied by the development of seborrhea.
- Rapid weight gain is a common symptom of polycystic ovary syndrome. Obesity is caused by significant changes in hormonal levels. In this case, there is often a deposition of lipids of the androgenic type, that is, in the abdominal area. In severe cases, the process is complicated by the development of diabetes mellitus, which worsens the prognosis of the disease.
- Hirsutism is also observed in polycystic ovary syndrome. This term refers to increased male pattern hair growth, that is, in the abdomen, inner thighs and above the upper lip.
- Pelvic pain is caused by the growth of tumors in the gonads. As the cysts develop, they stretch the capsule of the gonads and lead to compression of the tissue, which is accompanied by very unpleasant sensations.
- The most dangerous symptom and at the same time a consequence of PCOS is infertility. When the disease occurs, it is primary in nature and is difficult to treat in the later stages of the disease. Pregnancy does not occur due to the lack of ovulation and, as a consequence, a mature egg ready for conception.
Symptoms of polycystic ovary syndrome may be mild. The problem can be corrected with medication, but only in the early stages of formation. Therefore, if such signs appear, you should seek medical help.
Clinical manifestations of PCOS
- Typically, the reason for contacting a gynecologist is menstrual irregularities, usually manifested by periodic delays, irregular, rare menstruation or absence of menstruation at all.
- The second most common complaint is unsuccessful attempts to get pregnant.
- Our patients also turn to cosmetologists or dermatologists in connection with acne (acne, pimples), seborrhea (excessive production of sebaceous glands), alopecia (hair loss), as well as hirsutism (excessive hair growth on the upper lip, chin, back, lower back, chest, abdomen, shoulders and inner thighs).
- Our patients are often overweight. Endocrinologists call PCOS a disease that steals femininity: a pear-shaped figure gradually becomes an apple.
- Another symptom of the disease, which manifests itself when changes in the body are already far advanced, more often in the presence of obesity, is acanthosis nigricans - skin hyperpigmentation, localized mainly in the folds (on the neck, in the axillary and groin areas).
Causes of the disease
The clinical manifestations of the disease are directly determined by the characteristics of its origin. The physiology of the development of polycystic ovary syndrome primarily includes disorders of the hypothalamic-pituitary system, changes in the secretory function of the adrenal glands and an increase in the secretion of hormones by the pancreas. Although the exact cause of PCOS is currently unknown, it is definitely associated with cellular resistance to insulin and, as a result, obesity. The suspected connection with this compound is that it helps regulate ovarian function. The gonads, in response to increased secretion of this hormone by the pancreas, respond by producing androgens, which in high concentrations lead to the absence of ovulation. It is the cessation of follicle maturation that signals the presence of an abnormality in the functioning of the ovaries.
An increase in gonadotropin-releasing hormone, produced by the hypothalamus to control gonadal function, further worsens the problem. In this case, the follicle-stimulating compound remains in normal or low concentrations for a long time. In the later stages of PCOS development, even exogenous administration of high doses of this substance is not accompanied by ovulation.
There are several etiological factors that can lead to the development of dysfunction of the gonads. In most cases, polyendocrine disorders are detected, that is, malfunctions of several organs at once. The most common causes of polycystic ovary syndrome are:
- Disorder of the function of the central nervous system, in particular the pituitary gland and hypothalamus. It is these structures that have a stimulating and controlling effect on the gonads. It is realized through the release of gonadotropic hormones into the blood, which either enhance or suppress the activity of the ovaries. If their work is disrupted, the endocrine function of the adrenal cortex fails, affecting reproductive health.
- Pathological changes directly in the ovaries also take place in the development of pathogenesis. They can be triggered by inflammatory and infectious lesions, the development of tumor formations, prolonged exposure to stress and physical strain.
- Malfunctions of the adrenal cortex are classified as a separate etiological group, since they can cause the formation of cysts in the gonads even in the absence of disruption of the nervous system. Increased secretion of androgens provokes hormonal changes and suppresses ovulation.
- Diseases of the pancreas, manifested by increased production of insulin with tissue insensitivity to its effects. Such problems lead to the development of not only diabetes, but also ovarian failure, as well as obesity, which only worsens the course of the disease.
Genetic predisposition to PCOS
There are several reasons leading to the disease. First of all, PCOS has a genetic basis (very often patients say that their mother also had rare menstruation and problems with conception), affecting many genes. But whether this basis is implemented or not depends both on the degree of changes in the genome and on the impact of other unfavorable factors: stress, poor nutrition, low physical activity, unfavorable working and living conditions.
The disease in its classic form is, to put it mildly, unpleasant, but its cosmetic manifestations are just the tip of the iceberg. The fact is that the suffering of patients is far from being limited to the reproductive period (in which the body compensates for a lot and easily tolerates), but runs like a red line throughout their entire lives, threatening serious complications in the future.
Possible complications
The consequences of the development of cysts in the gonads are mainly reduced to disturbances in the reproductive function of women. One of the most common problems resulting from the disease is infertility. It develops in patients of childbearing age and poses a serious problem. Along with this, the risk of developing cancer of the uterus and mammary glands increases, since some tumors are hormonal-dependent. Since PCOS is often combined with obesity, patients with the disease are more likely to suffer from diabetes. Such metabolic disturbances lead to an increased risk of developing atherosclerotic vascular lesions, which, in turn, lead to myocardial infarction and cerebral stroke.
Pregnancy with illness
Infertility with the development of cysts in the ovaries is most often associated with a lack of ovulation. Moreover, even if the egg matures, the hormonal background does not allow the embryo to develop in the uterus, since its inner layer is not properly prepared. That is why, when planning pregnancy, much attention is paid to excluding PCOS. Since the disease often cannot be cured, conceiving and further bearing a healthy baby is possible only with the use of surgical techniques and the use of medicinal support for the woman using hormones.
Is PCOS curable?
I assure you, PCOS is treatable, and infertility caused by this disease is a solvable problem, and, as a rule, without the participation of assisted reproductive technologies (ART).
Another question is that treating a disease requires enormous work on oneself, a revision of one’s lifestyle, volitional efforts, and constant self-control, and this is not at all easy.
If you are suddenly diagnosed with this, remember firmly that PCOS is terrible in its consequences and poses a threat to health only if you ignore the disease, do not take care of yourself, eat everything and let life take its course.
I cannot but agree with the popular expression of one of the founders of preventive medicine, Nikolai Mikhailovich Amosov: “Doctors treat diseases, but you need to achieve health yourself!” Well, we are not us if we don’t get it!
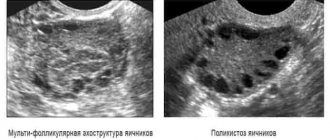
Diagnostics
Confirmation of polycystic ovary syndrome requires the patient to have characteristic signs of the disease. Combinations of symptoms of the disease are often detected. Many problems can cause infertility, so a comprehensive examination is carried out to make a diagnosis. Examination in a gynecological chair allows palpation to detect an increase in the volume of the ovaries, as well as significant pain. Changes in the size of the gonads are confirmed using ultrasound of the pelvic organs. The gonads in the photo taken during this examination have a characteristic appearance. Fluid-filled cavities called cysts are visualized inside. The ovarian capsule thickens, local blood flow increases. The ultrasound method is highly informative if the development of polycystic disease is suspected, and therefore is used by doctors very often. Along with characteristic changes detected through visual methods, increased secretion of androgens and gonadotropic hormones is recorded during laboratory diagnostics. In some cases, cortisol produced by the adrenal cortex also increases, which depends on the etiology of the disease. To exclude the development of a tumor in the gonads, MRI is required, as well as laparoscopy for an accurate visual assessment of the condition of the glands and sampling of material for histological analysis.
Treatment of polycystic ovary syndrome - what to do
Treatment of polycystic ovaries is a very complex process, sometimes lasting several years. A gynecologist-endocrinologist selects therapy individually, based on medical history and diagnostic data.
The goal of therapy is to regulate the menstrual cycle, lose weight, eliminate skin defects and normalize the ovulation process for subsequent pregnancy.
Is it possible to get pregnant with polycystic ovary syndrome? No, because the follicles that mature in large numbers in the ovary are underdeveloped and cannot be fertilized. And the production of sex hormones in a sick woman is seriously impaired.
Conservative treatment of PCOS
- Veroshpiron. With proper use of the drug, symptoms such as acne, increased oiliness of the skin and hair, and the presence of hair in unusual places begin to disappear. The drug deactivates male hormones and reduces their production. The disadvantage of this remedy is that an early pregnancy is impossible during treatment with it.
- Siofor. The active ingredient of the drug metmorphine normalizes blood sugar levels and prevents the production of androgens. Thanks to the drug, metabolic processes in the body are normalized, excess weight is reduced, the menstrual cycle is regulated, and the chance of getting pregnant and bearing a healthy baby increases.
- Belara. This drug belongs to the group of oral contraceptives and has androgen suppressing properties. Treatment is quite long, sometimes reaching 12 months. Before use, blood clotting tests should be performed and metabolic disorders identified.
- Jess. The drug is similar to that described above, but contains a low concentration of the hormone. The external manifestations of polycystic disease decrease, the woman’s body weight does not increase. When taking pills, it is important to remember that the effect is noticeable no earlier than after 6 months.
- Yarina and Yarina-plus. These are also birth control pills. But their important difference is the presence of drospirenone in the composition and the prevention of anemia.
- Glucophage. It is a hypoglycemic agent that increases insulin sensitivity and reduces blood sugar and cholesterol levels. In case of renal failure, the drug is used with caution.
- Cyclodinone. This is a drug that has only a symptomatic effect and reduces pain and swelling of the mammary glands.
- Utrozhestan. The drug does not cure the disease, but only regulates the menstrual cycle.
- Cyclovita. This is a whole complex of vitamins and minerals - ascorbic acid, zinc, selenium, vitamins B1, B6, B12, D3, lipoic acid, nicotinamide, etc. The drug normalizes the functioning of the female reproductive system.
- Diana is 35. This is a combined contraceptive drug in the form of pills. The visible effect occurs after 3-4 months of use. Menstruation becomes regular, manifestations of excess androgens decrease, and the chance of conceiving a child increases.
Diet for polycystic ovary syndrome
The goal of the diet is to normalize metabolism, reduce sugar and weight. Quickly digestible carbohydrates should be replaced with slower digestion sugars. It is also important to increase the amount of fiber-rich foods. It is recommended to eat at least 5 times a day in small portions. This type of therapy is used in combination with other methods.
Allowed:
- Chicken, turkey, young beef.
- Fish pike perch, pollock.
- Chicken and quail eggs.
- Tomatoes, beans, zucchini, broccoli, peppers, garlic, cucumber, asparagus, dill, lettuce, pumpkin, basil, apples, figs (figs), cherries, plums, cherries, pears, prunes, kiwi, grapefruit.
- Durum pasta.
- Whole grain bread, bran.
- Fermented milk products with low fat content.
- Brown or brown rice, oats, buckwheat porridge.
Prohibited:
- Fatty meat and fish, sausages.
- Smoked, spicy, canned.
- Margarine.
- Starchy foods.
- Sauces, spices.
- Semi-finished products.
- Confectionery.
- Semolina.
Modern methods of treatment
After a diagnosis of PCOS is made, it is necessary to begin correcting the patient’s condition as soon as possible. Conservative therapy involves the use of hormonal agents. Combined oral contraceptives, antiestrogens and gonadotropins are used. To stimulate ovulation, Duphaston is actively used, which is approved for use even during pregnancy planning. Clinical recommendations for polycystic ovary syndrome include a diet that involves eliminating animal fats from the diet and limiting calories.
In the early stages of the disease, surgical techniques are also used. The operation is carried out using special endoscopic equipment and consists of partial removal or cauterization of the affected parts of the gonads. This procedure leads to normalization of ovarian function and restoration of physiological hormonal levels. In the future, women require medication support in order to become pregnant.
Is weight important when treating PCOS?
Life is easier for patients with PCOS and normal body weight! They do not have severe metabolic disorders, and therefore the essence of treatment comes down to the formation of a normal menstrual cycle, assistance in pregnancy, elimination of cosmetic problems, prevention of depressive conditions and possible long-term consequences that are unlikely to occur in a person who keeps himself in shape.
Overweight and obese patients have it much worse. Yes, merciless genetics decreed this, but in the end, our weight still depends on our will! Yes, it’s unfair that someone doesn’t have to make any effort to be slim, but here there are constant restrictions and efforts. I understand everything, but you can complain as much as you like, this will not change our genome for the better, PCOS will not disappear, and we will not get any better!
There are patients to whom you explain the consequences a hundred times, tell them how to change their lifestyle, describe therapy. And the result is zero! Do you know why? No, not because the drugs don’t work, or because I prescribed a “bad” regimen. Because women are ready to take pills, but not to change their lifestyle!
Often patients want to lose weight with the help of “magic” pills, but drug therapy has its own indications (of course, the doctor will prescribe you drug therapy if necessary, and what’s more, there are situations when you have to resort to surgical methods), and everyone has to take drugs for Weight loss is not necessary and treatment is limited in time. And then there is only one thing left: change your lifestyle! And this is hard everyday work!
Lifestyle modification is an integral, main and sometimes even final part of the treatment of PCOS.
The vast majority of patients with PCOS are overweight and obese. Moreover, the mechanisms of development of PCOS and obesity are largely similar: obesity is often either a trigger for PCOS, or an independent disease with very similar clinical manifestations, primarily delayed menstruation and fruitless attempts to get pregnant. In this case, doctors have to differentiate what the patient actually has: PCOS or obesity.
Normalizing body weight always has a beneficial effect: obese patients recover, and with PCOS, the parameters of fat and carbohydrate metabolism improve.
And for weight to go away, energy expenditure must exceed its intake into the body. Therefore, we eat less and move more!
Unconventional methods
You can treat the problem at home only after consulting a doctor.
- In folk medicine, red brush tincture is widely used, which has adaptogenic properties and helps restore hormonal levels. To prepare the product, you will need to pour 80 g of plant roots into 0.5 liters of vodka and leave in a dark place for a week. Drink half a teaspoon of the medicine 3 times a day before meals.
- Borovaya uterus is also used in the fight against gynecological problems. A tablespoon of the plant is poured into a glass of boiling water. After infusing for at least an hour, the medicine is gradually drunk throughout the day.
Unconventional methods can be combined with conservative therapy if there is a doctor’s recommendation.
Diet
It is impossible to get rid of polycystic ovary syndrome forever. But if it is not treated periodically, health-threatening conditions will begin to develop over time. The patient’s diet is of great importance in pathology. In most cases, it is the diet for PCOS that can enhance the positive effects of medications, especially if the disease is accompanied by a significant increase in body weight.
Basic principles of nutrition for polycystic disease:
- The caloric content of the diet should be reduced to 2000 kcal per day. It should not be less than 1200 kcal, as this is dangerous to health. The doctor can calculate the ideal calorie content of the daily diet for the patient using special formulas. She can do this on her own.
- You need to eat food that contains an acceptable amount of calories. The basis of the diet should be: fruits, vegetables, lean meats, herbs, fish, dairy products, seafood.
- It is necessary to reduce the amount of carbohydrates entering the body. At the same time, you need to increase your intake of foods rich in proteins.
- It is necessary to reduce the amount of animal fats, replacing them with vegetable ones.
- It is necessary to exclude from the diet sweet, salty, smoked, pickled, spicy foods, as well as any alcohol-containing drinks.
- To cleanse the body, it is important to arrange fasting days 1-2 times a week.
Compliance with these recommendations, coupled with physical activity and taking medications prescribed by a doctor, is the key to getting rid of the disease as quickly as possible.