Drops for conjunctivitis in adults
Treatment is based on the causes of inflammation, and they can be very different: from viral infection to allergic reactions. Therefore, you cannot do without professional diagnostics.
In this article
To understand how to treat conjunctivitis in an adult or child, you need to determine its shape and type. Only an ophthalmologist can make a diagnosis. To identify the cause of its development, a specialist conducts a survey about diseases, working conditions and probable contacts with a carrier of a viral disease.
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=https:accounts.google.comServiceLogin
A study of discharge from the eye is also carried out: this method allows you to determine the causative agent of the disease. Sometimes additional consultations are carried out with other doctors, for example, an allergist.
If conjunctivitis is mild, it can be cured fairly quickly, and the danger is not the disease itself, but the possibility of its spread. Following the rules of hygiene will help reduce the risk of the disease spreading to the healthy eye and other people. Among them:
- using your own towels and pillowcases;
- regular hand hygiene;
- avoiding contact with other people and visiting public places;
- avoiding contact of chlorinated water with eyes.
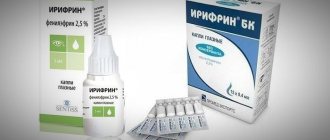
Most often, an ophthalmologist prescribes a 20% solution to an adult patient. Before you start using it, you must carefully read the instructions that come with the bottle.
The medication should be used at least every 5 hours. In some cases, the doctor prescribes a special treatment regimen.
Instillation procedure:
- First, wash your hands with detergent. Then, using a disinfectant solution, remove purulent discharge from the eyelid.
- The medicine is slightly warmed in the palms, rubbing the bottle between the fingers.
- The head is pulled down, the gaze should rest on the ceiling. The lower eyelid is slightly retracted and fixed in this position. Carefully, trying not to touch the mucous membrane, release a certain number of drops into the eye.
- Close and carefully distribute the preparation with your fingertips throughout the apple.
Only the attending physician is able to determine the duration of the course of use of the ophthalmic agent. Its duration depends on the diagnosis, the identified causative agent of the pathology and the degree of its neglect.
If the symptoms of conjunctivitis have not disappeared within 10 days, then you need to undergo additional examination by a doctor.
Before treating conjunctivitis, it is necessary to find out the reason that triggered its development. Drops for instillation differ greatly in their composition. So, to eliminate conjunctivitis caused by bacteria, antibiotics are used; for the infectious form, drugs with antiviral effects are used. The allergic form is treated with antihistamines.
To eliminate viral conjunctivitis in adults, the following medications help:
- Oftalmoferon. Good drops with antiviral, antihistamine, immunomodulatory effects. They are characterized by rapid action, eliminating the symptoms of the disease in the shortest possible time. In the first days, Oftalmoferon is instilled up to 8 times a day. As soon as the symptoms begin to subside, the number of instillations is gradually reduced.
- Ciprofloxacin. Broad-spectrum antibiotic. It is dripped drop by drop every 2 hours for 2-3 days. For the next 5 days, instillations are done every 4 hours. Do not use in children under one year of age.
The most effective drops don't have to be expensive. There are many inexpensive but effective drugs:
- Levomycetin. The drug is very popular due to its low cost and high effectiveness. These eye drops are recommended to be used for 3 days, even without a doctor’s prescription, for different types of conjunctivitis. Levomycetin should not be taken during pregnancy or newborn children.
- Tobrex. Eye drops that successfully relieve inflammation of the conjunctiva caused by Escherichia coli, Pseudomonas aeruginosa, and staphylococci.
- Albucid. Inexpensive drops, the use of which is approved for adults and children. Available in different concentrations of the active substance (20% and 30%). The disadvantage of Albucid is its rather aggressive effect on the eye. Many people experience itching, burning, and swelling of the eyelids when using it. In this case, you can replace Albucid with Tsipromed.
- Tsiprolet. An antibacterial drug that contains the antibiotic ciprofloxacin. Tsiprolet is effective against spirochetes, gonococci, and Klebsiella. Not recommended for use in pregnant, lactating women, children under 2 years of age, patients with viral keratitis, patients with hypersensitivity to fluoroquinolones and specifically to ciprofloxacin. An analogue of Tsiprolet is Tsipromed.
- Phloxal. Antibacterial drops with antiviral effect. The active substance is Ofloxacin, which effectively fights conjunctivitis caused by coccal infection, Pseudomonas aeruginosa, and fungi. Floxal also causes side effects, such as tearing, itching, burning, temporary decreased vision, which is completely restored after 30 minutes. It is prohibited to instill Floxal in pregnant and lactating women.
- Taufon. An effective drug whose main active ingredient is taurine. Taufon quickly eliminates numerous pathogenic bacteria from the surface of the eye. Taufon is prescribed for the spread of conjunctivitis to the cornea of the eye. The number of instillations and dosage of the drug is calculated strictly individually.
- Nevanak. The active substance is nepafenac, which has an anti-inflammatory effect, eliminates itching and swelling. Long-term use of Nevanac leads to decreased vision. The use of an ophthalmic agent in children is prohibited; it is prescribed after 18 years of age.
- Tobradex. Powerful combined drops with anti-inflammatory and antibacterial properties.
- Okomistin. A modern drug with an antiseptic in its composition.
- Sofradex. The drops contain framycetin sulfate (destroys harmful bacteria).
- Signicef. Antibacterial drops of the fluoroquinolone group. They are highly efficient. After instillation, they remain in the tear film for a long time, providing a therapeutic effect. May cause severe burning.
Elimination of allergic conjunctivitis begins with limiting contact with the allergen. Then drops are prescribed, which should eliminate redness, watery eyes, and swelling of the eyelids.
Such drugs are:
- Allergophthal. An ophthalmic agent containing naphazoline hydrochloride and antazoline phosphate. It has a vasoconstrictor effect (constricts blood vessels, thereby eliminating redness, pain, and swelling of the eyelids) and has an antihistamine effect. The drug is not prescribed to children under 6 years of age who have high blood pressure or heart disease.
- Cromozil. An antihistamine based on tetrazoline hydrochloride (a vasoconstrictor). Prescribed for adults and children.
- Nafcon. The composition contains naphazoline hydrochloride (vasoconstrictor) and pheniramine maleate (antihistamine). These eye drops are recommended for use from the age of twelve.
- Dexamethasone. A potent drug with the same active substance.
- Sofradex. In addition to the antibacterial effect, these drops perfectly relieve inflammation and allergic swelling, thanks to the dexamethasone component.
Children are often diagnosed with viral and bacterial conjunctivitis. Moreover, even if the inflammation of the conjunctiva began against the background of a respiratory disease, then after a couple of days a bacterial infection occurs.
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=ytcopyrightru
Frequent morbidity in young children is associated with failure to comply with basic hygiene rules. In addition, children often rub their eyes with dirty hands, which leads to infection.
The disease is contagious and spreads especially quickly in children's groups. As soon as one child comes to kindergarten with conjunctivitis, almost the entire group will become infected.
The best eye drops for children in this case are:
- Levomycetin drops;
- Phloxal;
- Tobrex.
Few doctors prescribe Albucid for the treatment of conjunctivitis in children. This is due to the fact that such a drug has a number of side effects.
The cause of inflammation of the conjunctiva in infants is often obstruction of the lacrimal ducts. In this case, the eye is constantly moist and this environment is ideal for the growth of bacteria. For dacryocystitis, massage, antibacterial eye drops, and in severe cases, probing are indicated.
General recommendations for the use of drops for conjunctivitis
The main principle of using such drugs is strict adherence to the doctor’s advice. Children's eye drops for conjunctivitis should be used according to age recommendations. However, it is also important:
- notify your doctor in time if uncharacteristic reactions to the drops occur;
- store the drug correctly;
- Wash your hands well before use;
- you need to bury it in the corner of the eye near the nose, slightly pulling down the skin of the lower eyelid;
- do not apply the dropper to the skin, mucous membranes and eyelashes;
- when you need to instill several drops at one time, you should take a break after each couple of drops;
- After the procedure, the eyes should be blotted with separate wipes.
Treatment of allergic conjunctivitis
Conjunctivitis can be acute or chronic. Treatment of the acute form of the disease takes on average about a week. The chronic stage is treated for more than a month.
In addition, the disease is divided into groups, depending on what caused it:
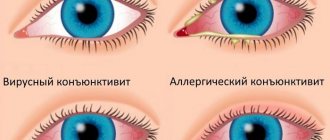
- Viral. This form of the disease is caused by viruses. Inflammation of the eye mucosa often develops as a complication of ARVI or influenza. In acute viral conjunctivitis, the discharge from the eyes is purulent and mucous, often accompanied by a bacterial infection and the discharge from the eyes becomes simply purulent. This form of the disease often leads to complications.
- Bacterial. In this case, the disease is caused by pathogenic bacteria. Usually, at the beginning of the disease, only one eye is affected, and then the infection spreads to the second. The discharge is copious and purulent. The patient cannot open his eyes normally in the morning because the eyelashes stick together. This form of the disease often occurs with high fever and general symptoms of intoxication.
- Allergic. This form of the disease is often observed in the spring, during mass flowering of vegetation. But often the cause of allergies in adults and children is household dust, animal hair and some food products. The disease occurs with characteristic symptoms - severe redness of the conjunctiva and eyelids, as well as profuse lacrimation and itching of the eyes. Problems with the visual organs most often occur against the background of other allergy symptoms - skin rashes, rhinitis and constant sneezing.
Conjunctivitis can be herpetic and chlamydial. In hot climates, children may experience an epidemic form of the disease. Newborn babies may have blenorrhea. This is an inflammation of the eye mucosa caused by gonococci. This disease develops in infants if they become infected while passing through the mother's birth canal.
If the inflammation is caused by an allergy, the doctor will select eye drops with an antiallergic effect. Quite often people encounter this problem in spring and early summer, during the flowering of bushes and trees. But the cause of illness can be household dust or allergenic foods.
Eye drops for allergic conjunctivitis should be prescribed by a doctor. Such drugs not only eliminate allergy symptoms, but also reduce the inflammatory process. The most commonly prescribed medications are:
- Opatanol;
- Lecrolin;
- Dexamethasone drops.
Allergy treatment is supplemented with systemic antihistamines. The most commonly prescribed drugs are the latest generations, which have few contraindications and side effects - Cetrin and Tavegil. In some cases, it is advisable for the patient to receive injections of Suprastin.
Allergic conjunctivitis can affect both children and adults. This disease is treated much faster and easier than other forms of this disease. To do this, it is necessary to eliminate the allergen and take medications that relieve the symptoms of conjunctivitis. Unpleasant sensations from allergic conjunctivitis are relieved with Lacrisify drops, etc. The drugs will help relieve itching, reduce redness, and relieve rhinitis.
Features of treatment of different types of viral conjunctivitis
A viral infection is a serious test for the body, especially if the main sense organs - the eyes - are affected. We will talk about viral conjunctivitis, treatment in adults and children, as well as all the features of this pathology below.
Causes and types of viral conjunctivitis
Conjunctivitis is an eye disease that affects the conjunctiva - the mucous membrane of the eyelids and sclera. In addition to the viral origin of the pathology, its bacterial and allergic forms are known. More rare cases of the disease are fungal and atypical chlamydial varieties.
Viral conjunctivitis is divided into several subtypes depending on the causative agent of the disease.
- The primary disease (isolated conjunctivitis) is caused by enterovirus, herpes (types 1, 2 or 3), Coxsackie virus, adenovirus.
- As an associated pathology, inflammation of the conjunctiva can develop against the background of other viral infections: rubella, measles, mumps, influenza or chickenpox. This happens much more often than isolated viral conjunctivitis.
2/3 of cases of the disease occur due to human infection with a so-called hospital infection. Conjunctivitis is highly contagious and can be transmitted by airborne droplets (in rare cases), through direct contact with a sick person, or through unwashed hands.
As a rule, with pathology, the inflammatory process begins on both conjunctivae at once, however, there are cases when a viral infection first affects only one eye, spreading over time to the second.
The treatment of viral conjunctivitis in adults and children directly depends on the nature of the virus. Let's consider different types of pathology depending on its causative agents, as well as how to treat each of them.
Conjunctivitis due to herpes virus
The inflammatory process on the mucous membrane of the eyelids can begin due to infection with the simplex virus (types 1 and 2) or the herpes zoster virus (type 3). This pathogen is the most common cause of pathology.
Typically, this type of disease takes on a chronic form. Viral conjunctivitis in children is most often caused by herpes. This type of disease is very contagious and is almost always characterized by the appearance of blisters with infection typical of herpes on the eyelids.
Herpetic conjunctivitis is in turn divided into follicular (vesicular-ulcerative) and catarrhal forms.
- The first is characterized by the appearance of vesicles on the eyelid, which over time transform into ulcers covered by a transparent layer of epidermal cells. The infection process is difficult. The patient develops photophobia.
- The catarrhal form passes more easily, since its clinical picture is weakly expressed. This is mainly redness of the mucous membrane.
Often, with herpes, immediately after the inflammatory process of the conjunctiva, the cornea is affected. Then the doctor diagnoses the patient with dendritic keratitis.
If a patient develops herpetic conjunctivitis, the attending physician prescribes therapy, including the use of antihistamines, antivirals, and interferon drugs.
In order for medications to act faster, it is necessary to prescribe eye drops and ointments. An example of such a drug is Acyclovir. Another drug that cures the disease is Zovirax.
If the disease is diagnosed in a child, then before applying the ointment to the affected eyelids, they must be wiped with a cotton pad soaked in an infusion of sage or chamomile (if the child is not allergic to these plant components).
Ordinary tea is also suitable for rinsing. The specifics of using ointments can be obtained from your doctor. If bubbles appear on the eyelid, they can be smeared with ordinary brilliant green.
Treatment drops must contain interferon. Moreover, you are supposed to use them first, and only after half an hour apply the ointment.
If the pathology has spread to a large area around the eyes, the doctor may prescribe the patient to take oral medications against herpes and immunomodulators. The latter are necessary to strengthen the body’s immune response, since it was its decrease that led to the development of the disease.
Adenoviral conjunctivitis
Damage to the conjunctiva caused by an adenovirus is also called pharyngoconjunctival fever. The viral origin of this disease was discovered relatively recently. A sign of adenoviral conjunctivitis is inflammation of the pharyngeal mucosa along with damage to the conjunctiva, high body temperature.
In adults and children, the symptoms listed above usually develop at the very beginning of the infectious process. They are immediately followed by manifestations of eye disease: redness appears first in one eye, then develops in the second.
Just like herpetic conjunctivitis, adenoviral conjunctivitis is divided into 3 types according to its manifestations:
- Catarrhal. With this type of viral conjunctivitis, the symptoms are mild and the inflammation of the mucous membrane is minor. With proper treatment, the disease lasts no longer than 6-7 days.
- Membranous - accounts for 1/4 of all cases of adenoviral conjunctivitis. A characteristic feature of this form is the formation of a thin translucent film on the conjunctiva, which is easily removed with a cotton swab. If acute viral conjunctivitis occurs, the formed film may adhere tightly to the membrane and its removal exposes the bleeding surface. Such a symptom may signal the development of diphtheria in the patient.
- Follicular - by analogy with this type, with herpetic conjunctivitis, bubbles of different sizes filled with liquid appear on the patient’s eyelids.
Treatment of this disease in adults should be systemic. The process largely depends not only on the patient’s age, but also on the likely ophthalmological complications that may develop in the future.
The incubation period of the disease can last several days. In this case, the patient complains of burning and stinging of the eyelids, sometimes there is a feeling of a speck in the eye.
The infectious process in the patient occurs against the background of headaches and inflammation of the parotid lymph nodes. If the pathology is treated incorrectly or not treated at all, due to heavy discharge from the eye, the eyelids may stick together with thick pus overnight.
If the patient has developed a mild catarrhal form of the disease, the doctor can determine how to treat viral conjunctivitis. It is necessary to take interferon drugs and immunomodulators. If at the same time the patient adheres to the rules of personal hygiene, the duration of therapy will be no more than 10 days.
In the case of an aggravated pathological process, the patient needs to take broad-spectrum antiviral medications (for example, Laferon).
For greater effect, eye drops are prescribed, which should be instilled frequently into the eyes during the first week of treatment (up to 8 times a day), and then the frequency of the procedure should be reduced to 2-3 times a day.
A qualified specialist, after examination and additional research, can tell what form of conjunctivitis the patient has and how long the treatment period lasts.
If a bacterial infection occurs with adenoviral conjunctivitis, the patient is prescribed antibiotic drops. To enhance the effect of the drugs, antihistamines are added to therapy to relieve inflammation of the mucous membrane.
Inflammation of the conjunctiva due to picornavirus
The group of picornaviruses includes enterovirus and Coxsackie virus, which also provoke the development of conjunctivitis, namely its acute hemorrhagic form. Occurs more often in young children, during the late summer - early autumn.
A working method to restore vision! You will throw your glasses in the trash in just 3 days...
Restoring vision. Real life story.
The latent period of the disease can take up to 2 days. The process is acute. The patient complains of sharp pain in the eyes; over time, lacrimation and photophobia, and a feeling of speck in the eye appear.
The rest is the same as in the normal course of the disease: red conjunctiva, copious discharge from the eye, swelling of the eyelids. With timely consultation with a doctor and proper therapy, an acute state of pathology can resolve in 1.5-2 weeks.
As treatment, the doctor prescribes tetracycline or erythromycin ointment and kanamycin drops to the patient. Washing the eyes with various solutions can only be done on the recommendation of a specialist.
Rules of therapy and prevention
For each type of pathology, specific therapeutic approaches are being developed. However, there are a number of general rules that must be followed to prevent viral conjunctivitis from spreading to other family members:
- The patient should have separate towels, soap and dishes from which he eats. The same applies to napkins, handkerchiefs and other hygiene items.
- People caring for the patient need to be patient, as it is not always possible to cure the infection quickly. Those around you should wash their hands thoroughly immediately after contact with the sick person.
- Pipettes or glass rods used to apply the medicinal substance to the affected eye must be sterilized every day in boiling water. Alcohol cannot destroy viral particles, while high temperature does this.
- The room in which the patient stays must be ventilated every day, but make sure that there are no drafts. Since the patient may develop photophobia, treatment in children and adults should take place in a room darkened by curtains.
For viral conjunctivitis, prevention includes mandatory adherence to personal hygiene rules. Very often, the virus gets onto the mucous membrane of the eyes due to friction with dirty hands. Bedding should be washed regularly.
If a person develops an acute infectious process, he should be isolated from society as soon as possible until complete recovery.
Any attempts at self-medication can negatively affect the patient’s health. You should not experiment, but it is better to contact a specialized medical institution at the first signs of illness. An experienced ophthalmologist will tell you how to treat a particular case of the disease.
Video
What to do for conjunctivitis: first aid for the patient
Please note these requirements:
- Use a 20% solution of albucid or 0.3% solution of chloramphenicol. The products must be instilled behind the lower eyelid, 1-2 drops. It is recommended to repeat the procedure every 3 hours. For preventive purposes, you can also instill drops into a healthy eye, but to avoid infection, it is better to do this with a healthy pipette.
- Avoid exposure to bright light; if present, it is recommended to wear sunglasses.
- There is no need to put a blindfold on your eyes.
Conjunctivitis is an inflammation of the mucous membrane of the eye. Irritation causes blood vessels to dilate, causing the eye to turn red. The causes of the development of the disease depend on its form: it can be an allergic reaction, or a consequence of a viral or bacterial infection. In any case, it is accompanied by unpleasant symptoms, and therefore it should be cured as soon as possible.
In the most advanced cases, it is not possible to quickly cure conjunctivitis, and the specialist prescribes complex treatment, including physiotherapeutic techniques. The purpose of these measures is to stop the suppurative process and eliminate unpleasant symptoms in the form of itching and reactions to external stimuli.
One of the most effective methods for curing advanced conjunctivitis is electrophoresis with antibacterial drugs. To carry it out, Penicillin and Ceftriaxone are most often used. They help extinguish the active inflammatory process. If severe itching occurs, then lidocaine with dimexide is added to the medications.
What is conjunctivitis
Conjunctivitis is an inflammatory process affecting the mucous membrane of the eyeball and the inner surface of the eyelids (conjunctiva).
In this case, the sclera (the white of the eye) takes on a pink tint, and blood vessels are clearly visible on the surface of the conjunctiva. The disease is accompanied by the following symptoms :
- Itching and burning in the eye area;
- Photophobia;
- Swelling of the eyes;
- Copious discharge;
- Deterioration of health.
Some forms of the disease are contagious and quickly spread from patient to patient through airborne droplets or contact.
Quick treatment of conjunctivitis using traditional medicine
Conjunctivitis will not be so difficult to cure with the right approach. Most often, bacterial conjunctivitis occurs in children, since they usually neglect hygiene and touch their eyes with dirty hands. If a woman has a bacterial infection, the disease can also affect her newborn baby.
How to get rid of conjunctivitis? The first measure in the rapid treatment of bacterial conjunctivitis is the use of antibacterial drops that eliminate pathogenic microorganisms. Among the most commonly prescribed antibacterial agents:
- "Floxal";
- "Tobrex";
- "Oftadek";
- "Albucid";
- "Tsipromed", etc.
For conjunctivitis during pregnancy, antibiotics are selected individually, taking into account the characteristics of the course of pregnancy. Before carrying out the procedures, you need to wash the eyes, since the lacrimal glands do not always cope with this task on their own. Sometimes there is so much purulent discharge that it sticks together the eyes. This usually occurs during the acute stage of development of conjunctivitis. An infusion of chamomile and a solution of furatsilin are suitable for rinsing.
If drops for conjunctivitis do not help and the acute course of the disease drags on, you need to treat it with ointments. They are placed behind the eyelid, after which the patient should close his eyes and make rotational movements. Most often, tetracycline ointment is used for these purposes, which effectively affects pathogenic microorganisms.
The course of treatment is quite long - up to 14 days. This is due to the complexity of treating purulent conjunctivitis and frequent relapses. You cannot make a decision on stopping treatment on your own, since untreated conjunctivitis can arise with renewed vigor.
To get rid of conjunctivitis, you can use not only pharmaceutical drugs, but also folk remedies. They have an equally strong effect, but they should only be used in conjunction with medications. The most effective:
- Chamomile infusion has a gentle effect on the eyes, but at the same time perfectly relieves the inflammatory process. To prepare it, you need to take a spoonful of the dry plant and pour a glass of boiling water. The product must be infused for several hours. Chamomile infusion is used for rinsing and as a lotion on the eyes, which is done for 15-20 minutes up to 5 times a day.
- You can also use regular tea. This remedy is even used to treat a newborn child. It is necessary to brew tea, moisten a cotton pad in it and apply it to the inflamed eyes, removing mucous and purulent discharge from them.
- Dill juice therapy - this remedy has a specific smell. To prepare it, you need to take a bunch of dill, chop it and squeeze out the juice. Soak a cotton pad in the liquid and apply it to the eyes for 15 minutes.
- Dill seeds, horsetail, chicory and marshmallow root are taken in equal quantities and mixed. A tablespoon of the mixture is poured into a glass of boiling water. After the infusion has cooled, a disc is moistened in it and applied to the eyes. Before this, instill a few drops of the product.
- Pour two teaspoons of ground rose hips into a glass of water, bring to a boil and remove from heat. When the broth has cooled, rub your eyes with it. Repeat the procedure up to 4 times a day.
It is worth noting that the use of each remedy should be coordinated with your doctor. Conjunctivitis is a complex ophthalmological disease that, without proper and timely treatment, can lead to serious complications. These include complete loss of vision and soft tissue necrosis. After getting rid of the disease, you should remember about preventive measures and do not forget to apply them.
For the bacterial form of the disease, eye drops with broad-spectrum antibiotics are prescribed. The most commonly prescribed medications are:
- Levomycetin drops. This is a cheap but quite effective drug that will help cope with eye infections in a matter of days. The price of these drops in pharmacies starts from 9 rubles. This medicine can be prescribed to both adults and children. During the acute period of the disease, it is recommended to drip the medicine every 2 hours, then the frequency of procedures is gradually reduced.
- Albucid. Inexpensive but a good drug for treating bacterial eye infections. This medicine has an analogue Sulfacyl sodium. It is considered one drug, just under different trade names. One disadvantage of Albucid is that it causes a strong burning sensation after contact with the conjunctiva. This side effect goes away after a few minutes.
- Phloxal. These eye drops are used to treat the eyes of newborn babies immediately after birth. Due to this, it is possible to prevent the development of blenorrhea, even if the child became infected during childbirth. Floxal is also used to treat conjunctivitis and dacryocystitis. The medicine is also available in the form of an eye ointment.
- Tobrex. Eye drops with a powerful antibacterial effect. Can be prescribed for the treatment of adults and children. They help eliminate the symptoms of the disease in just 2-3 days, but they need to be used for at least 5 days.
- Tsiprolet. This medicine is prescribed for severe cases. This is a powerful antibiotic that has a detrimental effect on many types of bacteria.
Other medications may be prescribed at the discretion of the doctor. In especially severe cases, it is advisable to prescribe systemic antibiotics in tablets, suspensions or injections.
All antibacterial drugs should be used for at least 5 days, otherwise a superinfection may develop, the treatment of which is very difficult.
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=ytadvertiseru
Babies are not protected from inflammation of the mucous membrane of the eye. The ophthalmologist should decide which drops to treat conjunctivitis in a baby, since the treatment regimen is drawn up for each specific case.
Allergic conjunctivitis appears due to the action of a certain irritant on the human body. In each specific case, an individual selection of medications is necessary. The age of the little patient also makes adjustments.
The most effective antihistamine drops:
- Allergodil. Designed for children over 4 years old. It has virtually no contraindications and has a long-lasting effect.
- Nedocromil (Tailed Mint). Prescribed to children from 2 years of age mainly to relieve itching. The drug is easily tolerated by children, as side effects are extremely rare.
- Spersallerg. Drops based on tetrazoline chloride (vasoconstrictor) and antazoline hydrochloride (antihistamine). The drug is prescribed for the treatment of allergic conjunctivitis in children over 2 years of age. Sometimes it is possible to use Spersaller earlier in consultation with a pediatric ophthalmologist.
- Garazon. Drops based on the antibiotic gentamicin and the corticosteroid beclamethasone. Approved for use in children over 2 years of age.
- Okumetil. The drug contains naphazoline (vasoconstrictor) and diphenhydramine (antihistamine), zinc sulfate (antiseptic). Approved for use from the age of two.
Typically, viral conjunctivitis develops on only one side at first. But children often begin to touch the sore eye, rub it, and then the other eye, so they can spread the infection to the second organ of vision. Instillation into both eyes at once will help to avoid this.
How much, when and what eye drops to take for children is determined by a pediatric ophthalmologist. The best means are:
- Aktipol. The medicine is suitable for adults and children. Drop 1-2 drops 4-8 times a day. After signs of inflammation disappear, treatment continues for at least another week.
- OftanIdu. Popular drops that can be used from the age of two. Instillations begin every hour during the day and every two hours at night. After eliminating the symptoms, to consolidate the result, it is necessary to drip OftanIda three times a day for another week.
Today, pharmacies sell high-quality and inexpensive drops for conjunctivitis caused by bacteria.
These include:
- Levomycytin drops. The active substance of the drug quickly blocks the production of proteins by bacteria, which stops the spread of infection. Used as instillations 2 times a day to get rid of purulent conjunctivitis in the initial stage in children over 2 years old.
- Sulfacyl sodium. The active substance of this antimicrobial drug is sulfacetamide, which suppresses the proliferation of pathogenic microflora. In acute conjunctiva, sodium sulfacyl is one of the first to be used.
- Tobrex. Antibacterial drops, the active ingredient of which is tobramycin, which actively destroys a large number of bacteria. It has side effects such as swelling and redness of the conjunctiva.
- Dancil. The basis of the medicine is Ofloxacin. This is an antibiotic that kills most bacteria. The drug is maximally concentrated in the tear fluid after 4 hours.
- Ciprofloxacin. Broad-spectrum antibacterial drug based on fluoroquinolones. Copes well with pathogenic microflora, preventing it from multiplying. Effectively eliminates some gram-positive microorganisms (staphylococci, staphylococci, enterococci) and destroys absolutely all gram-negative pathogens.
- Lomefloxacin (Lofox). Drops for conjunctivitis based on the antibiotic fluoroquinolone. They cope with most gram-positive and gram-negative pathogens that cause inflammation of the conjunctival membrane.
- Phloxal. Perhaps the best antibacterial drops that work well against streptococci, Klebsiella, and spirochetes. They begin to have an effect 10 minutes after instillation, and the therapeutic effect lasts for 6 hours. Floxal has virtually no side effects.
- Framycetin. When deciding which drops are better, you should pay attention to this powerful antibacterial and bactericidal agent. Due to the penetration of the active substance through the bacterial membrane, Framycetin prevents them from multiplying.
- Tsiprolet (analogue – Tsipromed). You can carry out instillations in very young children (up to a year), instilling them every 2 hours for a week. After this, the number of instillations is halved.
- Vitabact. The drug is well tolerated and has strong antiseptic properties. It is prescribed, as a rule, when other drops have not given the desired results.
Cost of medicines
| A drug | Image | Cost in the Russian Federation (rubles) | Cost in Belarus (rubles) | Cost in Ukraine (hryvnia) |
| Oftalmoferon | 300 | 10 | 123 | |
| Poludan | 500 | 16 | 205 | |
| Aktipol | 300 | 10 | 123 | |
| Zovirax ointment | 200 | 7 | 82 | |
| Acyclovir ointment | 30 | 1 | 12,3 | |
| Virolex ointment | 300 | 10 | 123 | |
| Cycloferon | 200-800 | 7-27 | 82-328 | |
| Valtrex | 1000-4000 | 33-132 | 410-1640 |
Attention! You can find out about other analogues of the described medications and their costs from pharmacists. But you should not replace the prescribed remedy with another without first consulting with your doctor.
Determining the cause of conjunctivitis
To know how to quickly cure conjunctivitis, it is important to correctly determine its nature. Symptoms of the disease differ depending on the causes of its occurrence:
- Viral conjunctivitis can occur in one or both eyes at once. The patient suffers from photosensitivity. This form of the disease is extremely dangerous because it quickly spreads to healthy people and is difficult to treat. The main efforts should be aimed at preventing its complications.
- Bacterial conjunctivitis: It is accompanied by purulent or mucous discharge that accumulates in the corner of the eye. Like the previous type of conjunctivitis, bacterial can affect one or both eyes and is contagious.
- Allergic conjunctivitis: accompanied by other symptoms of an allergic reaction, such as nasal congestion. The disease develops in both eyes, is not transmitted to other people and responds well to treatment.
What to do with conjunctivitis occurring in each of these forms will be discussed later in this article.
Bacterial inflammatory process
Various bacteria provoke the development of bacterial conjunctivitis. Symptoms of the disease may vary depending on the origin of the bacteria. Certain types can cause purulent discharge, while others can make the skin around the eyes and mucous membranes very dry. The child may experience pain in the inflamed eyes.
To treat a bacterial eye disease, the doctor prescribes a drug with an antibiotic that can effectively defeat the microorganism that caused the inflammatory process:
- 20% solution of Albucid, which has another name - “Sodium Sulfacyl”. The cost of the composition is quite reasonable, its medicinal properties are widely known. You need to instill 2-3 drops in both eyes, 5-6 times a day, until complete recovery;
- A composition based on chloramphenicol is no less effective against harmful microorganisms, but it should not be instilled in children under 2 years of age. The course of treatment is 7-8 days, the medicine is used only once a day, one drop in both eyes;
- Vitabact. You can hear a lot of positive reviews from both doctors and patients about this drug. It is used to eliminate the inflammatory process of the eyes, instilling one drop at least 7 times for 7-10 days;
- Floxal medicinal drops can be prescribed for the treatment of conjunctivitis, both bacterial and viral. Often this composition in combination with other drugs is prescribed for chronic inflammatory process of the eye mucosa.
Drops for viral conjunctivitis
A disease such as conjunctivitis can occur in adults and children. It is most often infected in autumn and winter, when human immunity decreases. The main means of combating the disease in this form are interferon drops and antiviral drugs in tablet form. If eye damage in an adult patient is caused by the herpes virus, Ophthalmoferon, Tebrofen, Laferon and other drugs are prescribed.
The greatest danger with viral conjunctivitis is dry eye syndrome. The lacrimal glands stop producing secretions that moisten the mucous membrane. As a result, any movement of the eyelid leads to severe irritation. To relieve unpleasant symptoms, it is recommended to use artificial tears.
When the acute course of the disease has stopped, it is worth intensifying treatment with immunostimulating drugs. They will help get rid of sluggish conjunctivitis and will be an excellent preventive measure.
Individual intolerance to drops is extremely rare. In addition, bacterial microflora may be insensitive to them. In this case, the specialist prescribes products that can replace them.
Most often, it is recommended to choose the following external medications for the treatment of conjunctivitis:
- Vitabact;
- Levomycetin;
- Tobrex;
- Phloxal;
- Tsipromed, etc.
They do not differ too significantly in their price characteristics. However, self-medication with drops for conjunctivitis is completely excluded. All drugs can be used only after examination by a doctor and prescribing one or another type of pharmacological agent.
If the cause of inflammation of the conjunctiva is a virus, then the doctor prescribes antiviral agents that contain interferon. Most often prescribed:
- Poludan;
- Oftalmoferon.
In most cases, an infection of a mixed nature is observed, in which case complex treatment is advisable. Antiviral and antibacterial agents are prescribed simultaneously.
In case of a viral form of the disease, systemic medications can also be prescribed - Groprinosine, Isoprinosine, Anaferon or Viferon. They should be taken according to the schedule determined by the attending physician.
Eye drops for allergic conjunctivitis
The allergic nature of conjunctivitis manifests itself:
- constant itching;
- profuse flow of tears;
- swelling of the upper eyelid;
- runny nose (in some cases).
Medicines must contain an antihistamine component. Such drugs include:
- Allergodil (relieves symptoms of the disease after the first use; contraindicated in children under 12 years of age);
- Lecrolin (the course of treatment must be repeated periodically to avoid relapses; not prescribed for children under 12 years of age);
- Hi-Krom (based on cromoglycic acid, which blocks histamine; given to children from 4 years old);
- Lodoxamide (stabilizes mast cells; used to treat children from 2 years of age).
Features during pregnancy
Eye drops should be used in a course that averages 5–7 days. Even after all the symptoms disappear, you need to use medications for a couple more days.
The shelf life of the medicinal solution is no more than 3–4 weeks after opening the bottle. The medicine should be stored in the refrigerator; before use, the bottle is slightly warmed by holding it in your hand.
Before instilling eye drops, wash your hands thoroughly with soap, after which the lower eyelid is slightly pulled down with the fingers of one hand. And the second one lightly presses on the bottle, squeezes 1-2 drops of solution into the conjunctival sac. After treating the mucous membrane with a medicinal solution, it is recommended to close the eyes and actively rotate the eyeball for several seconds so that the medicine disperses evenly.
If the doctor has prescribed several medications at the same time to treat the eyes, then the interval between their use should be at least 15 minutes. Eye ointment is always used last.
The difficulty of treating inflammation of the eye mucosa in pregnant women is that it is impossible to drip into the eyes for conjunctivitis the same drugs that are used to treat other adults. At the beginning of pregnancy, they are limited to the use of local agents that do not penetrate the blood, but their choice is very limited.
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=ytaboutru
In subsequent trimesters, your doctor will prescribe most of the medications prescribed to adults. The exception is medications with glucocorticoids, hormones, and heavy metal salts. The doctor decides which drops to use for conjunctivitis during pregnancy. All medications must be strictly coordinated with him and not exceed the indicated dosage.
How to instill drops correctly
In order to avoid complications, the following rules must be followed:
- Before starting the procedure, you need to wash your hands thoroughly with soap;
- If the bottle is not equipped with a dropper, then you need to draw the liquid into a sterile pipette;
- Tilt your head back and gently pull back the lower eyelid so that the conjunctival sac is visible;
- Release drops there without touching the tip of the dropper to the surface;
- Try not to close your eyes for a few seconds or blink a little so that the drops get inside;
- Carefully close the bottle without touching the tip of the dropper with your hands, and store it in the refrigerator. Almost all eye drops after opening the bottle are stored for no more than 28 days;
- Before opening the package, you need to pay attention to its integrity and the shelf life of the drops;
- After the procedure, wash your hands thoroughly again.
What do patients say about the treatment of viral conjunctivitis?
Surely you are interested in what people say who once had to deal with a disease such as viral conjunctivitis. So, in order to satisfy your interest, I have collected reviews from patients who shared ways to get rid of this ailment:
“More than once, with the help of Floxal drops, I have been able to achieve a positive result in the treatment of conjunctivitis. From my own experience, I am convinced that thanks to strict adherence to medical recommendations and a full therapeutic course, the likelihood of a complete cure for viral conjunctivitis will be maximum.
In addition, regular eye drops with Floxal reduce the likelihood of recurrence of this sore,” Pavel, 40 years old.
“Once my friends and I went to the pool. I usually swim with goggles, but that time I decided to leave them at home, which I later regretted very much... When I woke up the next day, my eyes were very swollen, itched terribly and were stuck together from pus. The attending physician recommended Diclofenac drops, which have an anti-inflammatory effect.
I put drops in my eyes 3-4 times daily for 6 days and soon the symptoms of viral conjunctivitis completely disappeared. In parallel with this, I carried out treatment with folk remedies - I washed the inflamed organs of vision with chamomile infusion twice a day. This comprehensive approach helped me forget about this eye disease,” Karina, 29 years old.
“And I prefer traditional medicine recipes when it comes to viral conjunctivitis. For these purposes, I use thin slices of fresh cucumber, which I apply to my eyelids for 15-20 minutes, and then I wash my eyes with a decoction of birch leaves.
But the most effective remedy turned out to be a honey solution, for the preparation of which I mix 1 tbsp. l. honey with 2 tbsp. l. boiled water. I put the resulting solution in my eyes every morning (3 drops in each eye). I don’t know how others treat viral conjunctivitis, but this remedy helped me a lot,” Nadezhda, 37 years old.