Causes of the disease
There are various reasons why this pathology appears in children and adults. Most often, the disease develops due to viral infections, which include influenza and other colds. The disease also occurs as a result of the human body’s reaction to injury or allergens.
Many people are interested in what age people suffer from false croup most often. This type of disease is diagnosed only in children and adolescents under 15-16 years of age. In adults, not false, but true croup often appears. The disease develops under the influence of diphtheria and other infectious diseases.
What is croup and why is it dangerous for children?
Croup is a respiratory disease that occurs in children in infancy and early childhood. Accompanied by inflammation of the larynx and difficulty breathing. There are true and false croup. Their main difference is that the true one occurs when a foreign body enters the larynx or with diphtheria. False one occurs against the background of acute respiratory infections.
The nature of the disease is such that with inflammation and narrowing of the larynx, it is difficult for the baby to breathe. And if first aid is not provided on time, suffocation will develop and the patient may die.
Did you know? Until the 1960s,
the nature of false croup was not known.
Therefore, when children had similar symptoms, but of a different etiology, the disease began to be called false, in contrast to the well-known diphtheria (true) croup. Often true croup is complicated by the following diseases:
- pneumonia;
- otitis;
- bronchitis;
- meningitis.
Classification and types of disease
Having understood what false croup is, it is recommended to familiarize yourself with the varieties of this pathology. The disease differs in its etiology, depending on which the bacterial and viral forms are distinguished. There are other signs by which pathology can be classified. For example, based on the absence or presence of complications, a disease can be uncomplicated or complicated.
The most common classification is based on the stage of laryngeal stenosis. The first stage is not contagious to other people and is accompanied by mild shortness of breath when overworked. At the next stage, the symptoms intensify and appear even without physical activity. The third and fourth stages are considered the most dangerous, as they sometimes lead to the death of the patient.
Symptoms of croup in children
At first it all starts with a common cold, the symptoms of which can also be observed in family members, but after a while a new symptom appears, characterized by hoarseness or loss of voice. At night, the child has the hardest time, as a severe, rough cough begins (which is also popularly called a barking cough, as it looks like a dog barking). The child cannot clear his throat, breathes heavily, and it is very difficult to fall asleep. Also, during a cough, you may hear a kind of whistling sound when the child tries to draw air into the lungs, but it has difficulty passing through the narrowed, inflamed channels. These sounds are called inspiratory stridor. The process of coughing, as well as the process of trying to ease breathing, is accompanied by strong tension in the abdominal muscles (many note that after this, the abdominal muscles hurt for several days, as after an intense workout).
If no measures are taken, despite the fact that croup may go away on its own as the infectious disease gets rid of, the airways may be completely blocked and the child will not be able to breathe or cough.
Symptoms of false croup
It is recommended to familiarize yourself with the characteristic symptoms of the disease in advance in order to know how false croup manifests itself.
The clinical picture of the disease directly depends on the degree of laryngeal stenosis:
- First degree. With this form of pathology, patients suffer from severe shortness of breath that occurs during physical exertion. In a calm state there are no problems with breathing. Some patients complain of rapid heartbeat and mild cough.
- Second degree. In this case, the patient’s well-being worsens, and symptoms appear that are often found with parainfluenza. The patients' skin turns pale, and slight swelling appears around the mouth. Over time, breathing worsens, causing shortness of breath to become bothersome even in a state of calm. The cough also intensifies, and hoarseness appears in the voice.
- Third degree. This form of the disease is called decompensated stenosis, in which most patients experience lethargy and clouded consciousness. Blood pressure gradually decreases and the heartbeat increases.
- Fourth degree. This is the most dangerous stage of laryngeal stenosis, in which many patients lose consciousness. The patient's breathing almost completely stops, and blood pressure drops to critical levels. Patients with fourth degree stenosis must be hospitalized immediately, since without timely assistance they may die.
Symptoms
Usually this disease can be easily distinguished from the manifestations of other ailments. The greatest likelihood of developing false croup occurs when a child suffers from colds, so the symptoms are similar in some cases. Often, young children have a fever; it is the result of an infection entering the child’s body.
There is such a sign of the disease as stridor - this is a kind of breathing, it is labored and bubbling. The manifestation of this symptom will directly depend on how severe the swelling of the larynx is. Sometimes it is painful for a child to inhale due to this swelling. If the breathing noise increases, this means that the disease is progressing, in which case calling an ambulance is extremely necessary. Despite the seriousness of the disease, stridor does not occur out of the blue and is usually preceded by a kind of dry cough, which should alert parents.
The voice changes, usually it becomes hoarse and hoarse, reminiscent of the one that occurs after a long scream. But, this symptom may indicate the development of false croup if it appears in combination with other symptoms, since it often happens that a child has hoarseness due to the development of another disease.
For example, this appearance of hoarseness may be a sign of laryngitis, which occurs without serious swelling of the larynx.
It is the presence of difficulty breathing that becomes the main opportunity to distinguish croup from laryngitis, since when the latter occurs, there are no breathing problems. But this does not mean at all that you can turn a blind eye to the disease; there are cases when laryngitis is a stage in the process of the appearance of false croup. Therefore, if such symptoms occur, it is better to see a doctor so that there is no serious danger.
Some people may wonder why breathing problems occur with this disease? This is primarily possible due to the fact that swelling of the larynx occurs and the lumen decreases. The problem also occurs because there is too much mucus in the airways, although this is natural during an inflammatory process. When the lumen narrows, there may be muscle spasms of the larynx, which cause pain in the child during inhalation and exhalation.
If you are encountering such symptoms for the first time, you may not know all the features of the disease, so the best option would be to call an ambulance.
Possible complications
Like many other diseases, false croup is often accompanied by serious complications. Most often they appear only at the third and fourth stages of stenosis. In this case, a purulent film gradually forms in the patients’ larynx, which makes breathing difficult.
Some people develop attacks of pneumonia due to false croup and develop tracheobronchitis.
If the progression of the infection is not stopped in a timely manner, the person will develop symptoms of purulent meningitis, sore throat, otitis media and conjunctivitis.
Stages of disease manifestation
Usually this disease affects young children aged 2-3 years, but there are also cases when the disease occurs at other ages. Fixed data indicate that the disease does not appear in children under 4 months and after 5 years. If the cause of the disease is a virus, then usually the course of the pathology first occurs as a minor manifestation of a viral infection, and then the main signs of false croup suddenly appear. Because of this, breathing problems and coughing in a child may begin at night, during sleep.
The course of the disease has so-called stages, which can be used to determine how serious the problem is.
At the first stage, all the usual symptoms of the disease appear, but they appear during exercise. Stenosis lasts several hours or a couple of days, and shortness of breath occurs only when inhaling. In the second stage, signs of the disease begin to appear even at rest. It gets to the point where the child’s breathing can be heard even from a distance. The child is overexcited and his anxiety is noticeable; some children develop a bluish tint to the skin around the mouth, and the face becomes pale. Attacks during this period can last up to 5 days.
It is in the first two stages that it is recommended to begin treatment, because with a timely approach, eliminating the disease will not be a big problem.
The third and fourth stages are very serious and can cause further complications. At the third stage, the first signs of suffocation appear, problems with the gas composition of the blood arise, which naturally affects the general condition of the child. Breathing, like the child’s condition, varies from active to very slow. It is very important not to bring the child to the fourth stage, when asphyxia begins. The child's condition is so serious that during certain periods there is no air supply at all, and the child stops breathing and a coma develops.
Diagnostics
Before treatment, it is necessary to carry out a differential diagnosis in order to accurately verify the presence of false croup. To establish a diagnosis, they contact an otolaryngologist or pediatrician so that they can use the anamnesis and clinical picture to draw a conclusion about the patient’s health status. During the differential diagnostics, a visual examination of the patient is performed and auscultation of the lungs is performed.
Some patients have to be additionally examined, and therefore a smear culture is performed for them, with the help of which the causative agent of the pathology is determined. Also during diagnosis, enzyme immunoassay and polymerase chain reaction may be prescribed. This will help identify pathogens that belong to the chlamydial flora.
Features of the disease
Croup in children is a stenosing laryngotracheitis in acute form, which most often begins at night. This disease manifests itself as hoarseness, barking cough and specific wheezing.
Croup in a child can only occur before the age of 4 years. In older children and adults, the airways are already more developed, so the cartilage in the walls is less elastic. Due to this, swelling of the mucosa during inflammatory processes does not cause such pronounced symptoms. When such a disease occurs, the parents of a sick child become very frightened and often panic. But it is worth noting that croup rarely poses a great danger and almost always goes away without any treatment or consequences .
If your child coughs at night, you need to lift him up and calm him down. Warm tea can be given to soothe a sore throat.
Treatment of the disease
When the first signs of false croup appear, it is necessary to immediately begin treatment of the pathology.
There are cases when symptoms develop too quickly, and the patient immediately becomes ill
. In this case, you will have to do first aid to improve the person’s well-being.
To do this you need:
- Call emergency ambulance. It is recommended to immediately invite specialists to examine the patient.
- Calm the patient. A person with such a disease must be reassured, since in this state people consume less oxygen.
- Provide access to fresh air. It is no secret that people with false croup have difficulty breathing, and therefore it is imperative to improve the supply of fresh air. To do this, it is recommended to take the person out onto the balcony for 5-10 minutes.
When treating pathology, antihistamines are used, which help quickly eliminate swelling and get rid of cough. In the final stages of the disease, it is recommended to use glucocorticoid medications that help restore the condition of the larynx. Before using any medications, visit a doctor and get tested.
Folk remedies
Many people are interested in how to relieve the symptoms of false croup using traditional methods.
It is highly not recommended to use alternative medicine to treat the disease at home, as it is life-threatening.
Many people do not know this and use some traditional methods of treatment.
Warming up
It is contraindicated to warm the larynx with hot steam or take a bath with hot water, as such procedures intensify the inflammatory process. This leads to a worsening of the condition and the development of swelling of the larynx.
Vomiting reflex
Some believe that the vomiting centers are located close to the respiratory centers and therefore, by provoking vomiting, people improve their breathing. However, this is not the case, and artificially inducing a gag reflex will only worsen breathing for a while.
Inhalations
Often people try to be treated with inhalations using hot steam. However, in this case, this method of therapy is contraindicated, since hot steam will worsen the cough and pain in the larynx.
Fluid intake
The only safe traditional medicine method that can be used to cure false croup is regular fluid intake. Constantly drinking water or warm tea will improve your breathing and prevent the fluid accumulated in the larynx from thickening.
First aid during an attack
Every mother should know how first aid is provided for croup in children. Call a doctor immediately, and before he arrives, perform the following procedures:
- take care of the flow of fresh air (open the windows; in winter you need to go out into the fresh air, after dressing warmly);
- Your baby needs to breathe cold, damp air, so if possible, turn on a humidifier. Otherwise, turn on a faucet in the bathroom with warm, but not hot, water and be there;
- Give your child milk and soda to drink (dilute a teaspoon of soda in a glass of milk and drink in small sips);
- calm the patient by picking him up and sitting him in an upright position so that he can breathe easier;
- You can inject an antiallergic drug to relieve laryngeal spasm.
Important! Do not self-medicate under any circumstances. Urgent hospitalization is required.
Prevention measures
To prevent the emergence and development of pathology, it is necessary to engage in prevention. Many people are interested in what needs to be done to prevent false croup.
Some people take antibiotics for this, but this will not help. The disease is viral in nature, and therefore antibiotics will not protect against it.
To prevent the disease, the following measures are taken:
- do not contact people who are sick with a viral infection;
- regularly ventilate the room so that there is fresh air in it;
- drink plenty of fluids every day;
- limit your time spent near sources of strong and unpleasant odors.
By following the above preventive measures, people will be able to protect themselves from pathology, and therefore they will never have to treat false croup.
Treatment of croup in children
Most often, direct treatment with medication is not required. You can relieve your child's condition at home and allow him to sleep at night. The most important treatment for croup is getting rid of the disease itself, against which the croup developed.
The first thing you can do if your child starts coughing a lot and cannot breathe fully is to take him to the bathroom, close the door and turn on the hot water. Moist warm air quickly relieves symptoms.
The second good remedy for relieving symptoms is warm milk with honey. In a warm glass of milk (approximately 40 degrees), add a spoonful of honey (if your baby is not allergic), a piece of butter (about a teaspoon), and a little soda (on the tip of a teaspoon). The baby should drink the milk before it cools down.
You can also create more comfortable conditions in the room - install a humidifier if you feel that the air in the room is quite dry (dry air greatly aggravates croup). If you don't have a humidifier, hang wet towels around the room. Smoking is strictly prohibited in the apartment.
The child tolerates the symptoms of the disease much easier in a sitting position, so put a headrest on him while he sleeps. If your baby is crying, this is a good sign, it means he is breathing freely.
Manifestations of the disease
The disease at the first stage is difficult to distinguish from a simple acute respiratory infection. The same symptoms are present: cough, runny nose, nasal congestion, elevated body temperature. After a couple of days, other symptoms appear that distinguish false croup:
- hoarse, rough, dull voice;
- paroxysmal dry, barking cough;
- breathing becomes difficult, whistling sounds are heard when inhaling.
Viral croup in children develops due to severe swelling of the larynx. First, the body temperature rises to 39 degrees, and then a dry cough develops. The attack most often occurs in the evening or at night. The child becomes restless, tosses and turns in bed, and cries. Breathing becomes difficult and noisy.
With a severe lack of oxygen, the child turns pale, becomes lethargic, the nasolabial triangle turns blue, and sometimes loss of consciousness may even occur.
If treatment is not started on time or treated incorrectly, complications may arise in the form of sore throat, otitis media, conjunctivitis, tracheitis, bronchitis, pneumonia or purulent meningitis.
To make an accurate diagnosis, the doctor needs to examine the patient and prescribe additional examination methods: microlaryngoscopy, throat culture, blood tests, including a blood test to determine the degree of hypoxia, and x-ray of the lungs.
What is true croup, what signs does it have and how does it differ from false croup? True croup in diphtheria is characterized by a slow increase in symptoms and can lead to complete loss of voice. False croup begins abruptly, there is no complete loss of voice, only its timbre is disturbed. True croup is most often characteristic of adults.
True croup has the following symptoms: a sudden rise in temperature, drowsiness, fatigue, an emerging attack of barking cough, a hoarse voice or its complete loss. It differs from false croup in that during examination the doctor notes the formation of fibrinous films on the larynx.
False croup in a child and first aid – blog of the ON Clinic medical center
False croup or acute obstructive laryngitis is an emergency pathology that affects the upper respiratory tract. False croup is based on a sharp narrowing of the lumen of the larynx: breathing is impaired, a “barking” cough and hoarseness appear.
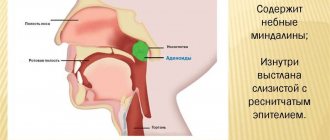
False croup affects children from 6 months to 6 years. This is due to the anatomy and physiology of the respiratory tract: in children, the diameter of the vestibule and the funnel-shaped shape of the larynx are small, the folds are short and located high.
These structural features contribute to the development of the croup.
In children of different ages, the prevalence of croup varies: more than 50% of patients are children from 2 to 3 years old, children aged from 6 to 12 months are less common. Children over 5 years of age almost never get false croup.
What causes false croup?
Acute obstructive laryngitis develops due to a viral infection. 80% of croup cases are the result of the parainfluenza virus. The remaining 20% is influenza A and B virus, respiratory syncytial virus, enterovirus, adenovirus, rhinovirus or coronavirus.
The following factors increase your risk of developing croup:
- immaturity of reflexogenic zones;
- predominance of the parasympathetic nervous system;
- soft and pliable cartilaginous skeleton;
- congenital anomalies of the respiratory tract.
Predisposing factors also include: allergies to medications, damage to the central nervous system during childbirth, prematurity, overweight of the child and allergies in parents.
The source of infection is a sick person who transmits viruses or bacteria through coughing and sneezing. The incubation period is from 7 to 10 days. The incidence of false croup depends on the season: the risk of infection increases in autumn and winter.
Symptoms of false croup
False croup begins with nonspecific symptoms. In the first three days after the onset of the illness, the child develops a cough and runny nose, and the body temperature rises to 37–39 0C. The child is agitated, sleeps poorly, cries, refuses toys and does not want to eat.
Signs of the disease begin 3 days after the incubation period. Symptoms usually worsen in the evening or at night. The child suddenly wakes up with a “barking” and rough cough. Noisy and labored breathing appears, as if the child is not getting enough air. The child gets scared, begins to worry and cry. This condition lasts another 1–2 days.
Symptoms are caused by gradual inflammatory swelling in the subglottic region of the larynx. The vocal cords leak out with a cellular infiltrate, and thick mucus accumulates on the walls of the airways.
At this stage, the main symptoms of false croup appear:
- hoarseness (dysphonia);
- difficulty breathing;
- “barking”, jerky and short dry cough.
Inspiratory stridor joins the clinical picture. This is wheezing, which occurs due to the fact that air quickly passes through the narrowed lumen of the larynx.
When it becomes difficult for a child to breathe, the auxiliary respiratory muscles of the chest are activated, and the supraclavicular and jugular fossae are retracted. Outwardly, it becomes noticeable how the child’s nose wings expand to inhale more air.
Due to lack of oxygen in the blood, other symptoms appear. The child becomes lethargic or agitated. The skin becomes pale and the area around the mouth turns blue.
How does false croup occur?
The disease progresses differently in children. The severity of false croup is determined by four degrees:
- First degree of severity. The child periodically gets excited or becomes lethargic, but clarity of consciousness remains. Swollen wings of the nose are visible, breathing is not rapid. There is slight hoarseness and a “barking” cough. With little physical activity, breathing becomes noisy. The first degree lasts from 2–3 hours to 1–2 days.
- Second degree. Consciousness is clear, but the child is in constant agitation: he cries, screams, cannot sit still, does not sleep. When breathing, the intercostal spaces are retracted. Breathing and pulse are slightly increased. In a state of calm, the child breathes loudly. The face is pale. The second degree lasts up to 3–5 days.
- Third degree. Consciousness is confused: the child is disoriented, lethargic and drowsy, may not recognize his relatives and may not understand where he is. All auxiliary muscles of the chest are included in the respiratory act. Breathing is shallow. The voice has shrunk. The cough is rough and loud.
- Fourth degree of severity. This is a state of asphyxia when almost no oxygen reaches the lungs. The child is unconscious, the auxiliary muscles are almost not involved in the respiratory act. The breathing itself is intermittent and inconsistent. The pulse is hard to palpate. Seizures may occur due to a serious disturbance in the blood gas composition.
Acute obstructive laryngitis can be complicated by bacterial tracheitis, purulent laryngotracheobronchitis and pneumonia. In the most severe cases, death occurs.
If you notice a specific triad of symptoms (hoarseness, barking cough and difficulty breathing) and signs of an acute respiratory viral infection (fever, runny nose, drowsiness or restlessness in a child), call an ambulance.
For diagnosis, doctors collect medical history, complaints and information about vaccination. The doctor examines the child, measures body temperature, records the number of respiratory acts and heart rate.
Afterwards, laboratory and instrumental methods are prescribed: general blood test, biochemical blood test, radiography, virological diagnostics, bacteriological examination.
To clarify the diagnosis, the doctor invites an ENT specialist for a consultation and prescribes fibroendoscopy of the larynx.
The parent can call a doctor at home. In this case, the doctor conducts a rapid diagnosis: assesses the voice, the presence of a “barking cough”, looks at the child’s breathing, and clarifies how long ago the signs of an acute respiratory viral infection appeared.
To objectively assess the child’s condition, the doctor assesses the patient’s severity using the Westley scale.
This scale includes the following indicators: wheezing noisy breathing, blue skin tone, degree of consciousness, breathing and retraction of auxiliary muscles in the respiratory act.
If the child is objectively at grade 2, 3 or 4, urgent hospitalization is indicated. The latter is also indicated in the following cases:
- child is less than 1 year old;
- the medications had no effect;
- the child was born premature;
- the patient has a concomitant disease or congenital malformations.
If you see that the child has a second or more severe degree, there are indications for hospitalization, call an ambulance or get to the hospital on your own.
Treatment of false croup in children
The doctor’s task is to restore breathing as quickly as possible, improve the child’s general condition and prevent the progression of laryngeal stenosis. To do this, the doctor prescribes glucocorticosteroids, which block inflammation, relieve local swelling and reduce the permeability of the vascular walls.
When providing emergency care, a string or membrane nebulizer is used, which contains a glucocorticosteroid - budesonide.
This substance quickly enters the respiratory tract and has a strong local anti-inflammatory and vasoconstrictor effect. The effect occurs 15–30 minutes after administration of the medicine.
The sustained effect of budesonide occurs within 3–6 hours. If budesonide is not available, the emergency medical team uses epinephrine, an adrenal hormone.
In hospital conditions, systemic glucocorticosteroids - dexamethasone or prednisolone - are used to treat acute obstructive laryngitis. To stabilize the condition, medications are administered for another 2–3 days. When the child gets better, the doctor reduces the dose.
Other means are used to treat false croup:
- antiviral: they are prescribed if the doctor knows that false croup is of viral origin. Neuraminidase inhibitors have proven clinical effectiveness in stopping the influenza virus. The greatest effect of antiviral drugs is observed in the first 48 hours after the onset of the disease;
- antibacterial agents: prescribed if there are laboratory signs of bacterial origin. In addition, they are given to the child if complications of a bacterial nature are observed;
- if there is obstruction of the lower respiratory tract, the doctor prescribes bronchodilators, for example, Berodual or salbutamol;
- when the acute period of the disease has passed, the doctor prescribes mucolytics - medications that thin the sputum. Medicines are administered by inhalation or orally.
The doctor observes the little patient for several days. Treatment is considered effective in the following cases: the larynx allows air to pass through and the child breathes freely, body temperature is normal, and there are no bacterial complications. If the criteria are met, the child is discharged from the hospital.
What to do after leaving the hospital:
- the next day after discharge, you need to call your local doctor to examine the child;
- continue symptomatic treatment of acute respiratory viral infection;
- Vaccinate your child against influenza within two weeks after complete recovery (if vaccinations have not been done before).
Parents should forget about traditional medicine when their child has acute obstructive stenosis. While ineffective and untested “grandmother’s” treatment methods are used, swelling of the larynx increases and it becomes increasingly difficult for the child to breathe.
While parents are waiting for the ambulance, you need to calm the child down and use a distraction therapy method - put a warm compress on the neck with Vaseline oil.
The essence of the method is that heat has a local effect on soft tissues: the neck muscles relax and it becomes easier for the child to breathe. It should be remembered that this will only give a temporary effect and cannot replace full treatment with a warm compress.
The use of steam inhalation is not recommended. They are excluded from international protocols for the treatment of croup.
Which doctor treats false croup?
False croup and its complications are treated by a pediatrician, a pediatric infectious disease specialist and an ambulance doctor.
How to prevent false croup in a child?
To prevent false croup in a child, you need to adhere to the following measures:
- vaccinate against influenza every year;
- increase the child’s overall resistance to infections with proper nutrition and good sleep;
- prevent infections by constantly and thoroughly washing your hands, ventilating the room with cool and moist air, and drinking plenty of fluids.
Some prevention methods need to remain in history. For example, prevention with vitamin C, herbal remedies and homeopathic medicines has no proven effectiveness.
Source: https://onclinic.ua/blog/lozhnyj-krup-kak-pomoch-rebenku
What not to do if you have croup
To ensure that your child’s croup is as easy as possible, you need to adhere to the following medical recommendations:
- You should not give your baby honey or any oily ingredients..
- During a cough attack, it is not advisable to give medications that contain mint, as well as mint tea. This can trigger an allergic attack and worsen the cough.
- Trying to soften the cough with a spray, in this case the condition may worsen significantly.
In addition, it is forbidden to start giving your child antibacterial drugs without a doctor’s prescription . It is not a fact that croup is caused by bacteria and in this case a superinfection may occur.
When a child has croup, it is important to follow all the recommendations of the attending physician. A small patient should be regularly examined by a pediatrician and an ENT doctor.
Treatment methods
It is advisable to carry out treatment in a hospital; attacks of false croup are very dangerous. Be prepared to provide first aid to your child.
On our website you can learn about other diseases of the ENT organs in children. Read about sinusitis here; about catarrhal sore throat is written here; Find out what to do if your child has ear pain from this article. Tracheitis is written about on this page; We have a separate article on treating a runny nose with folk remedies.
First aid during an attack
Before providing qualified medical assistance, parents should take measures to alleviate the baby’s condition:
- Calm the child and put him on the bed. The upper part of the body should be on a hill. A regular pillow will do.
- Open the window, humidify the air in the room (with a humidifier or using wet towels);
- Free the child from constrictive clothing that constricts the chest.
- Give the child a warm alkaline liquid (2% soda solution or Borjomi) to drink. This will help moisturize the mucous membranes and make phlegm thinner.
- Inhale with mineral water. It's good to use a nebulizer. (Read more about nebulizer inhalation in this article).
- Place vasoconstrictor drops into the nose.
- To relieve swelling, you can give an antihistamine (Erespal, Fenistil).
- In case of temperature and fever, give an antipyretic (Nurofen, Paracetamol).
- If breathing stops, induce vomiting. This will stimulate the respiratory center.
Drug therapy
After the ambulance arrives, the doctor will assess the severity of the child’s condition and determine his treatment regimen. In case of severe attacks, you cannot risk the child’s health and hospitalize him in a hospital.
Therapeutic measures for stage 1 false croup:
- good air supply;
- drinking plenty of warm water frequently;
- mustard plasters on the calf muscles;
- inhalations with sodium bicarbonate solution, vitamin A, hydrocortisone, aminophylline;
- taking antispastic drugs (Papaverine, Atropine);
- taking hyposensitizing and sedative drugs (Pipolfen, Diphenhydramine);
- vitamin therapy.
READ ALSO: How and what to treat a runny nose in a 1-year-old child: medications and effective traditional medicine
If there is no effect from such treatment, a novocaine blockade is performed in the nose. It reduces swelling of the mucous membranes and relieves reflex spasm. For fever at stage 1 of laryngotracheitis, antibiotics are prescribed.
False croup grade 2 is treated in the same way as grade 1. Additionally, the following is used:
- humidified oxygen;
- hypertonic solutions of glucose and calcium gluconate are administered intravenously to relieve edema;
- hormonal therapy (Hydrocortisone, Prednisolone);
- cardiac solutions are prescribed intravenously (Korglikon, Strophanthin);
- neuroleptic drugs (Promazine, Aminazine).
For grade 3 stenosis, Prednisolone is administered intravenously. The first dose should be ½ daily. They expand the intake of cardiac medications and give sodium oxybutyrate.
Broad-spectrum antibiotics are administered:
- Tetraolean;
- Tseporin.
If there is no result from treatment, laryngoscopy is performed. During the procedure, mucus and blood crusts are sucked out using a polyethylene catheter. Then the mucous membrane is lubricated with ephedrine, hydrocortisone, vaseline or peach oil. Sometimes bronchoscopy is indicated. During this procedure, the bronchi are washed, pus and mucus are removed, and antibiotics are administered intratracheobronially.
If all measures are ineffective or the child has severe progressive 4th degree stenosis, intubation or tracheostomy is indicated.
Learn how to treat and what allergic rashes on the body of babies look like.
How to properly dress a child in the spring is written at this address.
At https://razvitie-malysha.com/novorozhdennye/aksessuary/podguzniki.html, read about how to make a gauze diaper for a newborn with your own hands.
Prohibited actions
Laryngotracheitis is especially dangerous for children who are prone to allergies, overly excitable, and with lymphoid growths in the nasopharynx. Therefore, therapy for them must be selected with caution. Adviсe:
- In order not to increase swelling in allergy sufferers, you should not give citrus juice, honey, or raspberry jam.
- To avoid causing spasms of the laryngeal muscles, do not use essential oils or mustard plasters.
- There is no need to rush to give antitussives. A wet cough is a protective function of the body. When you cough, phlegm containing harmful toxins is expelled.
Treatment algorithm
To cope with pathology, it is very important to choose complex therapy. This should be done by the attending physician, depending on the clinical picture of the disease.
Medication
In case of stenosis of 1-2 degrees, the baby is hospitalized in the infectious diseases department. Pathology of 3-4 degrees requires placement of the child in the intensive care unit.
For severe stenosis, the following drugs are prescribed:
- Glucocorticoids—drugs such as prednisolone and hydrocortisone can be given parenterally, orally, or rectally.
- Antispasmodic drugs - the doctor may prescribe no-shpa.
- Antihistamines - suprastin, diphenhydramine, fenistil.
- Sedatives - bromides, valerian extract.
- Oxygen inhalations.
- Antibiotics - such drugs are indicated for bacterial diseases.
- Antiviral agents - used for viral croup.
- Bronchodilators - this category includes solutan, bromhexine.
- Antitussives - prescribed for non-productive cough.
- Calcium gluconate - this drug is administered intravenously when there is a large accumulation of sputum.
If conservative therapy does not produce the desired results, intubation and tracheostomy are indicated.
Inhalations
The simplest method of treating pathology is inhalation:
- An effective method of treatment is the use of alkaline mineral waters. To do this, pour 2-4 ml of liquid into the device and do the procedure for 10 minutes. Carry out such inhalations 3-5 times a day.
- A good method of therapy is inhalation using salbutamol, aminophylline, berodual. In this case, the drug in the required dosage must be mixed with 2 ml of saline solution. The procedure is carried out 2-3 times a day.
- An effective method of treatment is inhalation administration of pulmicort, cromohexal, and dexamethasone.
Homeopathy and folk remedies
Unconventional remedies must be used with great caution. Using honey or citrus fruits can only worsen the child's condition. For false croup, it is useful to drink warm milk mixed in equal parts with mineral water. You can also put mustard plasters on your feet.
Dr. Komarovsky tells how to treat false croup:
Characteristics of the disease
What is stenosis, and how does false croup differ from other diseases? Laryngotracheitis is an inflammation of the mucous surface of the larynx and upper trachea. The disease, depending on how the symptoms occur, is called: false croup, stenosing laryngitis, acute laryngotracheitis.
Allergic false croup is accompanied by swelling and irritation of the larynx, which leads to stenosis. In this condition, complete or partial blockage of the lumen of the larynx occurs. Air does not circulate well through the respiratory tract.
A feature of false croup from laryngitis is stenosis of the larynx. Stenotic croup leads to the fact that air does not flow to the internal organs. A state of hypoxia sets in, and an attack of suffocation and coughing develops. The functioning of internal organs, including the heart, blood vessels and central nervous system, is disrupted.
False croup can be caused by viruses and bacteria and can occur with or without complications. Allergic laryngotracheitis has 4 degrees of severity:
- Breathing becomes heavy with various movements or anxiety. The duration of stenosis ranges from several hours to two days.
- Difficulty breathing at rest. Children become restless and sleep is disturbed. The skin becomes pale, a bluish nasolabial triangle is observed. During coughing, tachycardia develops. The attack may be permanent or temporary. Duration – up to five days.
- Symptoms characteristic of the 3rd degree of the disease are as follows: shortness of breath appears, the flow of air into the lungs is disrupted, the patient looks restless and drowsy. Normally, the volume of the chest should increase when inhaling, and decrease when exhaling. This degree of croup causes the chest to function backwards. The attack is accompanied by severe cardiac arrhythmia, shortness of breath, wheezing, and blood pressure may decrease.
- Lack of air leads to a stop in the functioning of internal organs. Often this degree of the disease leads to death.
Children under one year of age must continue treatment in a hospital, regardless of the degree of illness. Treatment of children older than one year can be carried out at home, provided that the severity is low.
Treatment
If the child’s condition is serious and he is admitted to a hospital, then the first thing health workers do is restore the patency of the respiratory organs. To do this, you should use all possible ways to reduce spasm and swelling of the larynx, and in addition, clear the airways of accumulated mucus. Treatment of croup in a hospital setting is carried out according to the following algorithm:
- The little patient is given hormonal drugs that can quickly relieve swelling of the larynx. In the last couple of years, leading pediatric doctors have recommended administering such medications through a nebulizer. In this case, the medicine is delivered directly to the lesion.
- Medicines are prescribed to relieve laryngeal spasm. If the spasm is too pronounced, it is recommended to use sedatives.
- The patient is prescribed medications with ambroxol to facilitate sputum discharge. These medications are best administered through a nebulizer.
- If your child is prone to allergies. Then the introduction of long-acting antihistamines is indicated.
If conservative treatment turns out to be ineffective, then tracheal intubation or tracheotomy is performed . In this case, the patient is connected to a ventilator.
If croup is caused by bacteria, antibacterial drugs must be prescribed.
Disease Prevention
Croup can be prevented if you follow certain recommendations:
- If possible, young children should be protected from respiratory diseases.
- When treating acute respiratory infections, you must follow all doctor's recommendations.
- Your home medicine cabinet should contain medications that can relieve laryngeal stenosis..
- The air temperature in the home should not exceed 20 degrees, humidity should be 60%.
- The room in which the baby is most often located must be regularly ventilated.
- If your baby has a tendency to allergies, you need to protect him from allergens.
- The baby's nutrition should be healthy and balanced.
If a child has any problems with the respiratory system, it is necessary to immediately consult a doctor. Many dangerous pathologies can be successfully treated if you go to the hospital in a timely manner . Although croup rarely causes complications, medical supervision is necessary.
Just don't panic! If your child has croup
Croup is difficulty breathing due to a narrowing of the larynx, which most often develops in children between 6 months and 6 years of age1,2. In young children, the larynx is quite narrow, and if the mucous membrane swells, it can completely block the lumen of the larynx, and air will not enter the lungs2.
What types of croup are there?
Croup is divided into true and false. In both cases, this is an inflammatory process of the larynx, due to the narrowing of the lumen of which the child’s breathing becomes difficult.
True croup develops with diphtheria. This is a dangerous infectious disease in which the lumen of the larynx is blocked by dense films2. Thanks to vaccinations, this disease has fortunately become rare2.
The cause of false croup is acute viral infections. Most often, it is caused by influenza, parainfluenza, and adenovirus infection1,3. The mucous membrane becomes inflamed, swollen, and it becomes difficult for the child to breathe. False croup is designated by medical terms such as acute obstructive laryngitis or acute stenosing laryngitis.
How can I tell if my child has croup?
Usually, the usual symptoms of acute respiratory infections appear first, that is, runny nose, cough, fever. The onset of croup is often sudden, predominantly at night or in the evening1-3. The child develops hoarseness, a rough “barking” cough, and noisy difficulty breathing when inhaling.
At first, inhalation becomes “noisy” only during crying or anxiety. Over time, these symptoms persist even in a calm state2. With croup, it is difficult for the baby to inhale, that is, the inhalation is noisy, with effort, but the exhalation remains normal.
During inhalation, you can notice how the jugular fossa (the depression in the lower part of the neck between the collarbones) is drawn inward2.
What should I do and what should I not do?
Croup is a dangerous condition because... symptoms can develop very quickly3. However, under no circumstances should you panic, because the child will feel his mother’s fright, and this will worsen his condition.
You need to calm the baby down, because... When excited, the muscles of the larynx contract, and breathing becomes even harder. Offer your baby his favorite toy to distract him from unpleasant sensations, hug him and cheer him up.
If for the first time you encounter the appearance of such symptoms as a rough “barking” cough, difficulty breathing in a child due to ARVI, immediately call an ambulance, and the doctor will prescribe the necessary therapy to quickly restore breathing.
While the ambulance is driving, turn on the hot water in the bathroom and let the child breathe in the moist air2. It is not recommended to use steam inhalation (“breathe over potatoes”), because
The effectiveness of such methods is low1. Cough syrups will also not help in this situation. These drugs have an expectorant effect, i.e.
remove phlegm, but they have no effect on swelling and inflammation of the airways in croup3.
How is croup treated?
According to clinical guidelines, the preferred therapy for croup is inhaled glucocorticosteroids (ICS) through a nebulizer3. ICS are local hormonal drugs, i.e. they act only in the respiratory tract, eliminating inflammation2.
ICS begin to act within a few minutes and allow rapid restoration of respiratory function3,4. Currently, this is the most effective and safe way to cure croup. Corticosteroid hormones do not have any side effects in a child with croup, because
used in moderate doses and for short periods of time1.
For severe croup, the emergency physician may inject a systemic corticosteroid intramuscularly1-3 and suggest that the child be hospitalized because, after temporary relief, breathing problems may recur2.
How long does it take to treat croup?
The duration of treatment for croup is determined by the doctor depending on the severity of the disease - with a mild degree of croup, 1-2 days are enough to completely cope with the symptoms; with a more severe condition, croup is treated for 5 days, until the symptoms of laryngeal stenosis completely disappear6.
With timely detection of croup and proper therapy, the prognosis for the course of the disease is always favorable1.