Introduction
Folic acid (vitamin B9) is a yellowish powder and is a water-soluble vitamin that primarily promotes the growth and proper development of the circulatory and immune systems.
This is especially important at the stage of intrauterine development of the fetus and in early childhood. It also regulates fat and carbohydrate metabolism. It was obtained in 1930 from the leaves of spinach.
The human body cannot synthesize this vitamin on its own, so it can only be obtained from food or vitamin complexes.
Functions in the body
Folic acid promotes the production of new cells and the growth of all body tissues. It also strengthens the cardiovascular and nervous system, which helps get out of depression.
With its help, the activity of the brain, liver and gastrointestinal tract is normalized, and appetite improves.
This vitamin improves appearance by helping to restore hair structure, accelerate hair growth and strengthen roots.
With its help, the condition of the nail plates improves.
It renews the skin and protects it from the harmful effects of direct rays of the sun. This slows down the appearance of wrinkles and prevents premature aging.
With age, many people develop such a dangerous disease as osteoporosis. Folic acid is an important element in its complex treatment.
What are the dangers of folic acid deficiency?
Disorders caused by insufficient levels of folic acid are dangerous for the body and can cause the following conditions:
- Iron deficiency in the body;
- Disturbances in the functioning of the musculoskeletal system, in particular the spine in newborns;
- Disturbances in the functioning of the brain and other organs of the nervous system, mental retardation;
- Mental disorders, phobias, apathy, suicide;
- Sexual disorders: women of mature age experience menopause very early, and development is delayed in adolescents;
- Male infertility.
This problem occurs three times more often in women than in men. It is especially worth paying attention to acid levels during pregnancy and taking the necessary medications for prevention.
Symptoms of deficiency in the body
The daily intake of folic acid may vary depending on the group of people:
- For adults – 400 mcg;
- For pregnant women – 600 mcg;
- For nursing women – 500 mcg;
- For children - from 150 to 300 mcg.
Most often, folic acid deficiency is observed in pregnant women, children, people experiencing heavy physical activity, and athletes.
In adults
Apathy and loss of interest in life;
- A sharp decrease in activity and performance;
- Irritation and aggressiveness;
- The appearance of various manias and phobias;
- Insomnia and fatigue;
- Weakening of attention and memory;
- Headache;
- Indigestion;
- Sudden weight loss;
- Anemia;
- Psoriasis;
- Acne.
Among women
In addition to these main symptoms of folic acid deficiency, women’s bodies experience deterioration in the condition of skin, hair and nails, and the appearance of early gray hair.
Also, hormonal changes during menopause occur with greater complexity.
In children
Since folic acid is responsible for the development of many body systems, fat and carbohydrate metabolism, its deficiency can cause developmental defects in children.
Therefore, during the period of active growth of the child, parents should carefully monitor the diet and health of the child.
If he experiences apathy, weakness, or lack of appetite, he should consult a specialist for examination.
In athletes
Athletes may exhibit all of the above signs of folic acid deficiency that are present in the average adult.
But they can be observed much more often. This is due to the fact that during physical activity there is a large consumption of this vitamin.
Why shouldn't there be a shortage?
The most important danger is iron deficiency anemia, as well as a negative effect on cell growth. Due to a lack of folic acid, pathological processes in the central nervous system are triggered. The risk of strokes, heart attacks, and coronary syndromes increases. Also, with a lack of vitamin B9, disruptions in the immune system can occur, causing megaloblastic anemia.
If folic acid deficiency is observed in a pregnant woman, there is a high risk of giving birth to a child with developmental pathologies and diseases of the central nervous system. This can often cause spina bifida and growth retardation.
Blood analysis
A blood test is performed to determine folic acid levels.
In order for the results to be reliable when taking it, you must follow a number of rules:
- The optimal time for donating blood is from 8.00 to 11.00;
- You should not eat large amounts of food the day before. The last dose should be taken at least 8 hours before the test;
- The consumption of water is not prohibited, but it must be without gas;
- Blood donation should take place in a calm physical and psychological state;
- You should not smoke for an hour before the test.
Important! The normal level of folic acid in the blood is 3-17 ng/ml.
Reasons for shortage
There can be many reasons for folic acid deficiency in the human body. This could be an unbalanced diet, pregnancy, heavy physical activity and a number of other factors.
Nutrition
Since folic acid is not produced by the human body and does not accumulate in it, its amount must be replenished daily through nutrition.
If the menu does not contain foods high in this vitamin, then naturally a deficiency will occur. Therefore, you need to reconsider your diet and balance it.
Pregnancy
Almost all pregnant women are deficient in folic acid, especially in the first trimester. The development of the fetus increases the consumption of this vitamin by the body several times; it is not possible to completely replenish it through nutrition.
Therefore, at the beginning of pregnancy, every woman is prescribed medications with this vitamin.
Physical exercise
During physical activity, more folic acid is consumed than during a normal lifestyle.
Therefore, people involved in sports or hard work need to carefully monitor their diet, and possibly take medications to compensate for the deficiency of this vitamin.
Smoking
Smokers are also deficient in this vitamin. Consuming large amounts of nicotine interferes with the normal absorption of folic acid.
Alcohol
People who abuse alcoholic beverages tend to suffer from folic acid deficiency more often than others.
They do not monitor the quality of their diet, and they mainly get calories from alcohol, which contains them in large quantities.
Diseases and medications
A deficiency of this vitamin in the body can be caused by prolonged stress or depression.
It can also be various forms of anemia, Crohn's and Alzheimer's disease, diseases of the gastrointestinal tract (colitis, gastritis, dysbiosis and others), liver pathologies, various infections, as well as taking anticonvulsants, antibiotics, contraceptives, acetylsalicylic acid.
All this reduces the body's ability to absorb folic acid.
Symptoms
The clinical signs of folate deficiency anemia are in many ways similar to the manifestations of other types of anemia.
Typical complaints of the child are:
- headaches or dizziness;
- rapid fatigue under normal loads;
- feeling tired even after a night's rest;
- weakness in legs and arms;
- noise in ears.
It is difficult for a child to concentrate, memory deteriorates in schoolchildren, and they lag behind in their studies.
All these symptoms of anemia are associated with insufficient oxygen supply to the brain.
Manifestations of anemic syndrome are also:
- increased heart rate;
- decreased blood pressure;
- increased breathing.
This is how the body tries to cope with oxygen starvation in the tissues (caused by insufficient hemoglobin and a decrease in the number of normal red blood cells in the blood) using compensatory mechanisms - increased work of the cardiovascular and respiratory systems.
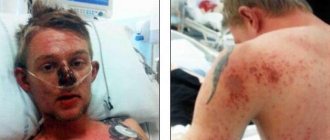
Outwardly noticeable are the manifestations of skin syndrome inherent in any type of anemia:
- pallor of the skin and mucous membranes, its severity depends on the severity of anemia;
- dry skin;
- splitting, brittleness and striation of nails;
- increased sensitivity to cold (constantly freezing, fingers and toes cold to the touch);
- fragility, dryness, loss of shine of hair;
- increased risk of fungal infection of the skin and mucous membranes.
Manifestations of gastrointestinal syndrome are often caused by:
- the presence of an underlying disease of the digestive organs (aggravating anemia by reducing folate absorption);
- associated with deterioration of blood supply to the gastrointestinal mucosa during anemia.
In any case: diseases of the digestive system lead to anemia, and anemia disrupts the normal function of the gastrointestinal tract - a vicious circle is formed.
Possible manifestations of intestinal syndrome:
- poor appetite in a child;
- pain or feeling of heaviness in the abdomen;
- bowel dysfunction in the form of diarrhea or constipation (or alternating them);
- weight loss (emaciation);
- damage to the oral mucosa (ulcers, glossitis, stomatitis).
Exhaustion is due to the fact that gastromucoprotein is produced in insufficient quantities in the stomach. This is a protein that protects the mucous membrane from the effects of food and enzymes. As a result, the gastric mucosa is damaged, which interferes with the breakdown of foods and their absorption, so the child not only does not gain weight, but, on the contrary, loses it. Attempts to forcefully feed the child end in vomiting.
Impaired folate metabolism causes decreased liver function. Frequent diarrhea leads to an imbalance of intestinal microflora, which further aggravates the poor absorption of folic acid.
Pain in the tongue, swelling and redness can be a constant concern. Glossitis (inflammation of the tongue) is associated with degenerative changes in the muscles as a result of a lack of oxygen in them with severe and long-term untreated anemia. Because of this, the child may refuse to eat to avoid increased pain.
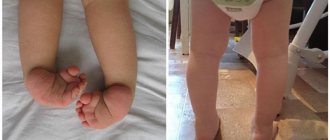
If a double deficiency occurs (folic acid and vitamin B12), severe cases of neuropathy with impaired skin sensitivity and coordination of movements can develop.
With insufficient supply of folic acid to the fetus, defects in the development of the central nervous system develop, which accounts for about 70% of birth defects. These children have an increased risk of developing autism and diabetes.
The most typical birth defects due to a lack of folic acid in a pregnant woman (and, therefore, in the fetus) are:
- hydrocephalus;
- impaired brain development (sometimes even to the point of its complete absence - anencephaly);
- non-closure of the bone marrow canal.
But other defects can also develop.
Content in food
Folic acid is found in many foods, both plant and animal. Its greatest amount is contained in:
Beef and beef liver;
- Chicken;
- Fish, its caviar, cod liver, and seafood;
- Legumes and cereals, cereals (rice, buckwheat, oatmeal, pearl barley);
- Carrots, beets, cauliflower and Brussels sprouts, broccoli, corn, tomatoes, pumpkin, onions;
- Mushrooms, asparagus;
- Parsley, dill, green salad, spinach;
- Cherries, gooseberries, currants, strawberries, raspberries, rowan;
- Bananas, oranges, avocados, kiwis, pomegranates, watermelons, melons, apricots, grapes, mineola, grapefruits, apples, pears, lemons, avocados, figs;
- Sprouted grains, nuts (almonds, hazelnuts, cashews and others);
- Milk and fermented milk products;
- Cheese;
- Brewer's yeast;
- Sunflower seeds;
- Eggs.
Important! In the summer, it is recommended to add beet, radish, dandelion and nettle leaves, which are quite rich in this vitamin, to various salads and snacks.
If you create a balanced menu, you can get the daily requirement of folic acid during meals.
At the same time, vegetables and fruits included in recipes for various dishes must be fresh, since during heat treatment this vitamin is almost completely lost in plant foods.
It also quickly deteriorates when exposed to direct sunlight and during long-term storage. The most resistant to destruction is folic acid, contained in meat products.
Important! It is believed that folic acid is absorbed better from medications than from natural sources. It is also recommended to take it together with vitamin B12 and bifidobacteria.