A pathological process in the genitourinary system, which manifests itself as urinary incontinence, is diagnosed not only in children, but also in adult patients. Women are susceptible to the disease, which is explained by the characteristic characteristics of the body.
Sometimes girls ignore the pathology or begin self-treatment, which does not provide the desired effect. One way to treat uncontrolled urination is drug therapy prescribed by a medical specialist.
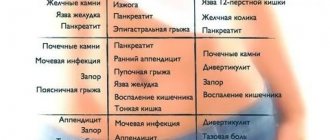
Causes of urinary incontinence in women
The main causes of urinary incontinence include:
- genetic predisposition;
- development of acute infections in the genitourinary organs;
- presence of excess weight;
- diseases that disrupt the functioning of the nervous system;
- damage to the pelvic organs.
In most cases, uncontrolled urination is caused by stress incontinence, which is characterized by weakening of the pelvic muscles.
The following factors can provoke pathology:
- carrying a child - during pregnancy, the uterus increases in size and begins to put pressure on the bladder;
- trauma received during childbirth;
- surgery of the uterus or other organs;
- age.
The patient’s treatment depends on determining the exact cause of urinary incontinence, so medical specialists approach the examination with responsibility.
Types and causes of urinary incontinence in old age
Incontinence is the inability to control urination.
It can be temporary or permanent, and it can also be the result of multiple problems in the urinary tract.
Incontinence is generally divided into four types:
- Stressful type of pathology - occurs due to weakening or improper functioning of the sphincter of the urethra and in the event of a stressful situation it will manifest itself with negative symptoms and the release of urine. In addition to a stressful situation, the development of this type of pathology can also be triggered by pregnancy, childbirth, surgery and age-related changes.
- Imperative type - with excessive reactivity of the bladder, even a minimal portion of urine can provoke the urge to go to the toilet and. The reason for the development of this type of incontinence is stress.
- Iatrogenic type of pathology - certain medications, diuretics, antidepressants and certain hormonal drugs can provoke this type of urinary incontinence.
- Other types of pathology - they can be provoked by organic root causes, such as oncology, trauma and stroke, certain diseases, for example, multiple sclerosis or stroke. In each individual case, the cause is determined by the urologist after a complete examination and examination of the woman. You should never practice self-diagnosis.
Provoking factors
Urinary incontinence in women over 50 years of age can be caused by the following factors and reasons:
- stretching of the pelvic muscles due to frequent pregnancy and childbirth; women with gestational diabetes are at higher risk;
- weakened muscles that control urination (urethral sphincter and pelvic floor muscles);
- the period of menopause, during which hormonal changes occur in the body and estrogen levels decrease;
- certain diseases that damage the nerve pathways from the bladder to the brain, such as:
- Minor's disease
- stroke
- senile dementia
- Parkinson's disease
- Alzheimer's disease
- multiple sclerosis
Symptoms of urinary incontinence in women
The main sign of pathology is frequent visits to the toilet, while the urge to urinate is sudden and can also occur under the influence of external factors. The woman notes the presence of other symptoms:
- Development of inflammation and infectious disease.
- A nervous condition that has a negative impact on relationships in the family and at work.
- Decreased sexual desire.
- Unpleasant sensations in the lower abdomen.
- Prolapse of the uterus.
Women may experience discomfort in the lower abdomen.
Each of the symptoms removes the woman from her usual lifestyle and causes inconvenience.
What are the main causes of this condition and how does it manifest itself?
Stress-related urinary incontinence
The ligamentous apparatus of the pelvic and perineal organs is weakened, the walls of the vagina and the bottom of the bladder descend. In addition, the normal closing function of the bladder neck is disrupted due to pathological changes in its shape and increased mobility. An important condition is to reduce the pressure gradient between the urethra and bladder.
The hereditary nature of the disease has been proven, that is, there is a high risk of transmitting it from generation to generation.
This condition is more often observed in older women with a history of several births, including a large fetus, when damage to the muscles and ligaments occurs.
Surgery in the pelvis may be accompanied by adhesions and disrupt the functioning of the uterus, rectum and urinary system.
In menopausal women (usually after 50 years), an estrogen deficiency occurs, the natural elasticity of the ligamentous apparatus decreases, atrophic changes in the urethra and periurethral tissues, and muscle tone decreases.
Women with excess body weight (grade 3-4 obesity) and concomitant pathologies (for example, diabetes mellitus, parkinsonism, spinal column injuries and others) are at high risk.
Long-term untreated constipation can affect the mechanisms of urine excretion.
Constant cough in “chronic” smokers with many years of experience.
Severe neurological disorders such as dementia and multiple sclerosis, in which self-control over urination is lost.
Typical complaints:
- “leakage” of urine occurs during physical activity of varying intensity, during sports, with strong laughter and coughing, even during sexual intercourse;
- the main sign of the disease is the absence of an uncontrollable urge to urinate; leakage occurs even with a half-empty bladder;
- such patients also often experience gas and fecal incontinence.
With “stress” urinary incontinence, urine output can be seen with the naked eye
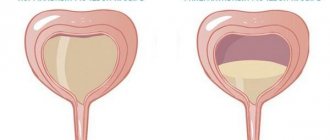
Overactive bladder
This is a condition in which there is an uncontrollable desire to urinate against the background of a small accumulation of urine in the bladder. All mechanisms of the occurrence of this disease have not been fully studied, but scientists have reliably proven the role of age-related ischemic changes in tissues and disruption of the normal process of nervous regulation in myocyte cells. There is close contact between cells that are overly excited. With a separate contraction of myocytes, a “chain reaction” occurs, leading to excitation of the entire bladder.
Typical complaints:
- the urge to urinate is constant and unbearable, appears unexpectedly and exhausts the woman;
- patients begin to be afraid to leave the house, since there may not be a toilet nearby;
- the desire to urinate is often caused by external factors (sharp sounds, bright light, the sound of flowing water, etc.);
- urine can leak even at night in a state of complete rest.
With an overactive bladder, it is constantly pathologically agitated
Urinary incontinence as a complication of taking medications
The cause of this condition is medications, the side effect of which may be a violation of the act of urination (exceeding the dose of diuretics, long-term use of antidepressants or sedatives, alpha-blockers, etc.).
Unreasonable use of large doses of diuretics often causes urinary incontinence
Other reasons
Quite rarely, incontinence can be associated with the organic nature of the disease. For example, in case of damage to the regulatory centers in the spinal cord or brain by a tumor or traumatic impact, strokes with different localizations, etc.
Types of drugs to treat urinary incontinence
Medical therapy for urinary incontinence involves the use of four groups of medications:
- Sympathomimetics - have a positive effect on bladder tissue and stop the process of uncontrolled urination.
- Estrogens should be taken if the pathology is caused by a disruption in the functioning of endocrine organs or an imbalance of hormones in the body. Urine incontinence occurs during menopause.
- Antispasmodics are used for minor symptoms. Drugs in this group have a positive effect on the bladder and stop the progression of the pathology.
- Antidepressants are prescribed by the attending physician in the presence of improper functioning of the nervous system, depression, or emotional stress.
Each group contains medications that differ in their mechanism of action, composition, and contraindications.
Driptan
The active component of the drug is oxybutin hydrochloride, the action of which is aimed at reducing the tone of the bladder. The drug is taken daily at 15 mg, divided into three doses.
The drug should not be taken for the following diagnoses:
- heavy bleeding;
- development of colitis;
- formation of intestinal atony.
Carrying a child and the period of breastfeeding are considered contraindications. The formation of side symptoms is possible - the presence of severe headaches, constant fatigue, attacks of nausea, an allergic reaction.
Spazmex
Provides an antispasmodic effect due to trospium chloride, which relaxes muscle tissue. The duration of treatment and dosage volume are determined by the doctor, based on the individual characteristics of the body. The medicine is taken 5 mg three times a day. The duration between each interval is 8 hours. In special cases, the dosage may be increased. If a woman is diagnosed with renal failure, the daily dosage is set at 15 mg. The drug is prohibited for patients who have individual intolerance to the components of the drug, as well as those suffering from myasthenia gravis.
Side effects are defined as:
- formation of chest pain;
- hypertensive crisis;
- dry mouth;
- severe nausea;
- dyspnea.
Glycine
The medication is a sedative, therefore it helps improve the quality of sleep, as well as the psycho-emotional state. The girl notes an improvement in her mood and the elimination of nervous tension.
The drug is taken as follows: one tablet is placed under the tongue. The medication must be taken twice a day, and the total duration of the course is one month.
Gutron
The medication belongs to the group of adrenergic agonists and is available in the form of tablets and drops. The main effect of the drug is aimed at increasing the tone of the nervous system and strengthening the urethral sphincter. The medicine has contraindications, which include arrhythmia, glaucoma, and arterial hypertension.
Betmiga
Urinary incontinence is eliminated with the help of mirabegton, a component that is part of the medicine. The product provides a prolonged and antispasmodic effect. Taking pills is allowed for patients who have reached the age of majority. The standard dose is 50 mg per day.
Allergies to medicinal components, renal failure, pregnancy are contraindications for use. Otherwise, unpleasant symptoms may occur: increased blood pressure, development of cystitis, swelling of the eyelids, allergies.
Pantogam
The main component of the drug: calcium salt - provides anticonvulsant effect. The advantage of the product is that it is approved for use by children who have reached three years of age.
To treat young patients, a syrup form is used. The standard dose for a patient is 1 g at least three times a day. The duration of the treatment course is 6 months.
Taking the drug is prohibited if the kidneys are not functioning properly, if you are pregnant, or if you are allergic to the composition of the drug. The side effect manifests itself in the form of skin rash, insomnia, and general weakness.
Imipramine
This remedy eliminates uncontrolled urination, which occurs at night and has an antidiuretic effect. The standard dose is set at 50 mg, which must be taken at least three times a day. In order to eliminate bedwetting, a woman takes 75 mg of medication an hour before bedtime.
The presence of heart failure, circulatory disorders, pathological processes in the kidneys and liver are contraindications to the use of the drug. Long-term use of the drug provokes the development of psychological fear and anxiety, nausea, and disrupts sleep.
Depressive and urge urinary incontinence
Often required for women who experience urinary incontinence due to a negative emotional state (depression or stress). For them, the main medications are the following antidepressants:
- Imipramine or Tofranil. They are used in cases of urgent urinary incontinence, when the urination process in women occurs spontaneously without the possibility of independent control. Such antidepressants increase sensitivity in the bladder cells responsible for storing and excreting urine. Prescribed in conjunction with taking anticholinergic drugs.
- Duloxetine. It is prescribed to prevent spontaneous contraction of the walls of the urinary storage organ and helps reduce the amount of urine leakage per day. It is prescribed as an adjuvant in conjunction with physical exercises during the treatment of the disease.
If, with urgent urinary incontinence, processes of an infectious or inflammatory nature are detected in a sick woman, then in addition to taking antidepressants, medications such as Ditrol, Ditropan and Oskitrol from the anticholinergic group are also prescribed. They help quickly eliminate urinary incontinence syndrome and retain their therapeutic effects for a long time. It is not recommended to use them more than the prescribed norm, since they can cause stagnation in the gastrointestinal tract and genitourinary system. They also affect the decrease in the functions of the visual apparatus and dryness of the oral mucosa appears.
Treatment is not complete without the use of antispasmodics, such as Oxybutynin, Tolterodine, Spazmex and Driptan. Such drugs have the most effective medicinal properties for improving bladder function, since they affect the smooth muscles of the organ, thereby preventing involuntary urination in women.
How to choose a remedy for urinary incontinence in women
Elimination of pathology such as urinary incontinence is carried out with the help of drug therapy, which is aimed at restoring the muscles and walls of the bladder. A favorable result helps strengthen muscle tissue, which makes spontaneous leakage of urine impossible.
The effectiveness of treatment depends on how correctly the diagnosis is made. After studying the examination results, the doctor prescribes medications. It is prohibited to choose a remedy on your own; each medication has contraindications and side effects. An incorrectly selected medicine can aggravate the pathology.
The cause of urinary incontinence is the activity of the bladder. In order to eliminate the pathology, the girl takes hormonal and anticholinergic medications.
Complex treatment helps relieve spasms in the bladder and also has a relaxing effect on the muscles.
How to choose the right one
Urinary incontinence (incontinence) is a pathological condition of uncontrolled urine output. The disease more often affects women than men due to the anatomical structure of the urinary system. Urinary incontinence can be pathological (with various diseases) or physiological (during pregnancy).
Despite the fact that the disease does not pose a threat to life, it significantly worsens the quality of life, putting the patient in an awkward position and forcing her to isolate herself from society. Incontinence is easily treated when the cause of the disorder is determined. However, tablets for urinary incontinence must be selected by a doctor. Self-medication can lead to worsening of the unpleasant syndrome.
Pathological urine output manifests itself differently depending on the nature of the disease.
Types of involuntary urine discharge:
- Stress incontinence (50%) is the most common pathology. It occurs against a background of weakening of the pelvic floor muscles and is activated by physical stress (when sneezing, coughing, laughing or lifting something heavy).
- Urge incontinence (18-22%) manifests itself against the background of a strong urge to urinate. The release of urine occurs immediately after the urge or against the background of a strong desire to empty the bladder.
- Mixed (30-32%) included the clinical manifestations of stress and urgency. Urine production occurs during physical stress and is accompanied by the urge to urinate.
- Iatrogenic is caused by taking medications (antispasmodics, diuretics or antidepressants). To solve the problem, it is enough to stop taking the pills that caused the pathology.
- Urinary incontinence in response to substances that irritate the bladder (tea, coffee, alcohol, citrus fruits).
The causes of the stress type of pathology are:
- pregnancy (mechanical pressure of the growing uterus on the bladder in the 2-3rd trimester or changes in hormonal levels in the 1st period;
- childbirth (perineal rupture affects the functioning of the sphincter and intra-abdominal pressure);
- surgeries on the pelvic organs (uterus, intestines, bladder);
- age-related changes (weakening of the pelvic muscles).
Pathological urination can be provoked by:
- heredity;
- overweight;
- hormone-dependent pathologies;
- diabetes;
- habitual depression and chronic stress;
- pelvic organ injuries;
- diseases of the nervous system (stroke, spinal cord injury, heart attack);
- acute infections of the urinary system.
Important! Determining the cause is paramount before starting therapy. For this purpose, you should contact a gynecologist or urologist.
Medicines for urinary incontinence are prescribed to women in order to relieve the syndrome and return the patient to a normal rhythm of life. Which tablets to use and in what dosages can only be determined by a specialist (urologist or gynecologist), taking into account the cause, type and severity of the pathology. In severe forms of the disorder that do not respond to conservative treatment, surgery may be required.
Incontinence in women is treated with drugs from four pharmacological groups:
- sympathomimetics;
- hormonal;
- antispasmodic action;
- antidepressants.
The choice of incontinence tablets depends on the patient’s age, the provoking factor, the type of pathology and general health. It is impossible to take into account all the indicators on your own without a medical education, which necessitates the need to visit a specialist (sometimes a joint consultation of several doctors may be required).
Medicines for urinary incontinence in the stress type of pathology are aimed at reducing the tone of the bladder. The following drugs have the necessary therapeutic effect:
- Antidepressants (Duloxetine or Cymbalta). Such drugs increase the tone of the sphincter and at the same time relax the tone of the smooth muscle fibers of the bladder. The therapeutic effect is achieved two hours after administration. The use of tablets must be strictly justified; there are contraindications and side effects. Abrupt withdrawal of the drug is not permissible due to severe withdrawal syndrome.
- Adrenomimetics help strengthen the tone of the urethral sphincter by increasing the tone of the sympathetic system.
- Hormone therapy is prescribed to women over 50 years of age. Normalizing the content of progesterone and estrogen in the blood helps to normalize the lost function of the genitourinary muscles.
The main group of drugs that reduce hypercontraction of the bladder muscles are anticholinergics (Driptan, Novitrapone, Detrusitol, Roliten, Uroflex, Urotol). These drugs reduce the excitability of the detrusor (bladder muscle). Side effects of this group include dizziness, constipation and drowsiness.
New generation drugs that affect the detrusor (providing a relaxing effect):
- Spazmex (trospium chloride);
- Vesicare (solefenacin);
- Enablex (Darifenacin);
- Toviaz (Fesoterodine);
- Merobegron (Begminga) is a drug with the fewest side effects and helps to increase the reserve accumulation of urine.
Important! Medicines for urinary incontinence in women have many negative consequences for the body; self-medication is unacceptable. Also, you should not use alcohol during the course of treatment with such drugs.
Treatment of urinary incontinence in women with rectal or vaginal suppositories is prescribed as additional therapy. The combination of several techniques can reduce the negative effects of incontinence pills by reducing the dosage of medications.
Ovestin is a hormonal drug, used 1-3 times a week, as prescribed by a doctor, depending on the woman’s health condition.
Important! Suppositories for the treatment of problems with urination are hormonal drugs; self-medication is unacceptable. Any means are selected individually, taking into account the level of hormones in the blood and underlying diseases.
Herbal treatment methods show high effectiveness in the initial stage of pathology; in the case of an advanced process, they improve the effect of prescribed medications and speed up recovery. To treat urinary incontinence in women, medicinal plant materials are used in the form of decoctions (teas).
General principles for preparing a remedy for the treatment of incontinence: for a tablespoon of dry crushed raw materials you will need a glass of boiled water, pour in, infuse, strain and drink.
Herbs that help overcome urinary incontinence are listed below.
- Dill seeds. Consume a glass of dill daily in 1 dose, a course until the problem is completely eliminated.
- A decoction of corn silks is used instead of tea; adding a spoonful of honey improves the healing properties.
- Use yarrow in a course of up to 30 days, a glass a day, divided into 2-3 doses (according to convenience).
- Drink freshly squeezed carrot juice (a glass a day) until complete recovery.
- Use sage as tea, drink no more than 3 glasses a day, in courses of 20 days every other week or constantly.
- Rosehip decoction, 2 cups a day, optionally with the addition of honey.
Advice! When treating with the gifts of nature, follow the simple rules of herbal treatment: take daily, preferably at the same time, prepare the decoction fresh (can be stored for up to a day in the refrigerator). If you have the slightest allergic reaction, stop taking the drug; it is better to choose a medicinal plant together with your doctor; contraindications are possible.
Urinary incontinence in women is a serious disease that affects the quality of life. Lack of treatment leads to worsening of the pathology. At the first symptoms of incontinence, you should contact a urologist or gynecologist. The doctor will select treatment. Taking tablets for urinary incontinence in women is prescribed in a course of three months.
Medicine for urinary incontinence is prescribed based on the cause of the problem. Thus, the disease can be caused by a person’s stressful state or physical reasons (urgent leakage due to increased excitability of the bladder muscles). In accordance with this, drugs for urinary incontinence are prescribed strictly on the recommendation of the attending physician.
The stress type is observed in half of the cases (more than 50% of cases). It is characterized by sudden urination with some exertion. Some doctors believe that this is only the initial stage of the disease. For treatment, medications are used that reduce the tone of the bladder and rectal sphincter. These include:
- Duloxetine Canon reduces the frequency of urine leakage; It is recommended to carry out health-improving exercises along with taking pills;
- Simbatla is a Swiss-made drug (capsules);
- Midodrine or Gutron is a hormonal drug;
- Imipramine – for the treatment of nocturnal leakage by acting on the nerve endings of the bladder.
There is a much wider range of treatments available to treat urination associated with increased bladder muscle tone, infections and inflammation.
With the urgent type of the disease (about 20% of those who apply), urination can occur at any time, even during sleep. Doctors prescribe medications to suppress muscle excitability.
As a result of complex treatment, patients' bladder volume increases and their ability to retain fluid increases. The most common medications in this area are:
- Novitropan;
- Driptan - reduces the tone of the bladder muscles;
- Rolitene;
- Detrusitol – has an antispasmodic effect;
- Uroflex;
- Urotol - reduces the tone of the smooth muscles of the bladder.
It is also worth remembering the possible side effects caused by medications.
Sometimes a third type is distinguished - a mixed type of the disease; it is observed in 30% of cases. It is related to human physiology and nervous system. In this case, urgent complex treatment is required. At the same time, urine leakage can sometimes occur due to the side effects of various medications, as well as human metabolic disorders.
Hormonal drugs
Medicines containing hormones are prescribed to patients who have urinary incontinence as a result of disorders in the endocrine system. Treatment is aimed at increasing the amount of estrogen in the body. The main drugs in this group include: Gutron, Cymbalta, Ubredit.
In addition to replenishing the deficiency of female hormones, hormonal medications have a negative effect on the body. In many cases, after a course of treatment, a girl is diagnosed with the presence of a benign or malignant tumor.
As a rule, the duration of therapy is 2 months. With pronounced symptoms, the course may increase. If a positive effect was not achieved with hormonal therapy, the woman is offered surgery.
Tablets for enuresis in adult men and women: a list of effective drugs
Urinary incontinence occurs regardless of age and gender.
Most often, enuresis develops in young children and the elderly. About 40% of women suffer from bedwetting and daytime urinary incontinence. Psychotropic and hormonal drugs, adrenomimetics and antispasmodics help to cope with the problem.
Enuresis tablets are prescribed by a urologist or gynecologist after determining the causes of the disease.
Why is urinary incontinence dangerous?
Enuresis is a pathology that greatly worsens the quality of life of people. The disease is interconnected with problems of a socio-psychological nature. Incontinence negatively affects many aspects of life. People experience:
- difficulties at work;
- difficulties in establishing and maintaining contacts;
- disharmony in marital relationships.
In most cases, patients with a delicate problem delay seeing a doctor and, as a result, the disease takes an advanced form . Enuresis causes serious complications:
- chronic inflammation of the skin and mucous layers of the genitals;
- genitourinary system infections;
- septic shock.
Severe development of sepsis ends in death.
In what case are tablets prescribed?
Drug therapy is used for inflammatory processes, infections, and disorders of bladder muscle tone. Medicines are prescribed if the problem is caused by hormonal imbalances or problems with the central nervous system.
The doctor selects medications intended for the treatment of enuresis in men, women and children individually. When prescribing a medicine, the doctor takes into account the causes of uncontrolled urination, the patient’s condition, the severity of the disease and the complications that have arisen.
Self-medication for enuresis is unacceptable. The patient is unable to independently determine the factors causing urinary incontinence.
The most effective drugs
To combat pathology, various categories of drugs are used:
- psychotropic drugs;
- medications that relieve muscle spasms;
- adrenomimetics;
- corticosteroids.
Detrusitol
The drug suppresses m-cholinergic receptors, has an antispasmodic effect, and relaxes the muscles of the bladder. After using the medication, the muscle tone of the urinary canals decreases. For a healthy liver, drink 1-2 capsules daily.
Detrusitol is prescribed if the patient has increased muscle tone of the urinary apparatus . The medicine is not used for the following problems:
- acute urinary retention;
- allergy to the ingredients of the medication;
- angle-closure glaucoma;
- aggravated ulcerative colitis;
- myasthenia gravis;
- constipation;
- abnormalities in the large intestine.
The product is not used to treat children and women bearing a child.
Urotol
Detrusitol and Urotol are drugs with a similar chemical formula and therapeutic effect on the body.
Medications weaken the muscle tone of the urinary apparatus, reduce detrusor contraction and the activity of the salivary glands.
Urotol is taken 2 times a day, 1 tablet (2 mg). The result of the treatment will be noticeable after 30 days. Dosage exceeding the therapeutic norm leads to unwanted problems:
- prevents complete emptying of the bladder;
- increases the volume of residual urine.
Tablets are prescribed to patients with the following problems:
- urinary tract hyperactivity;
- frequent urination;
- urinary incontinence.
The reasons for contraindications are the same as for Detrusitol.
Spazmex
The medication blocks ganglia and relieves muscle spasms in the urinary tract . The medicine is prescribed in the following cases:
- mixed enuresis;
- spasms of the bladder after injuries and in disorders of the nervous system;
- unstable urination;
- day and night incontinence;
- increased urination.
The drug is not used if the patient:
- suffers from heart disease, slow digestion of food or an allergy to the components of the tablets;
- needs dialysis;
- a child under 12 years of age.
Pantogam
A medicine with nootropic effects. The tablets activate anabiotic reactions in neurons, relieve agitation, convulsions, spasms and pain.
Pantogam is used for urinary disorders in children over 12 years of age and adults. The medicine is prescribed for the treatment of:
- daytime enuresis;
- pollakiuria;
- sudden urge to urinate.
Tablets should not be used in case of severe kidney disease or early pregnancy.
Vesicare
The drug relieves muscle spasms and is used to treat uncontrolled urination of varying severity.
Tablets are not prescribed for the following problems:
- renal failure;
- serious pathologies of the digestive system;
- angle-closure glaucoma.
Vesicare is not used in the treatment of children and pregnant women.
Driptan
The medication eliminates spasms and dilates blood vessels. After taking the pills, the bladder becomes larger and can hold more fluid.
The drug treats nocturnal incontinence in children and adults, spontaneous frequent urination.
Driptan is not used:
- with decreased peristalsis and intestinal obstruction;
- for the treatment of patients with glaucoma and neuromuscular pathologies of an autoimmune nature.
The medicine is prohibited from being prescribed to children under 5 years of age and to women during pregnancy and lactation.
Imipramine
An antidepressant eliminates signs of various neuropsychiatric disorders . The tablets relieve incontinence and restore the functioning of the urinary tract. The drug relieves nocturnal enuresis.
Imipramine is not used in therapy:
- pregnant and lactating women;
- children under 6 years old;
- if you are allergic to pills;
- patients with stroke, infections, epilepsy, heart, liver and kidney diseases.
The daily dose of the drug for children and elderly patients is 10 mg.
Betmiga
A drug with an effective relaxing effect. After taking the pills, the muscle tone of the bladder decreases. In patients, urination is restored.
Betmiga is dangerous for patients suffering from allergies, with liver and kidney failure, in childhood (less than 18 years).
The tablets are not recommended to be taken during pregnancy and breastfeeding.
Desmopressin
The action of the drug is similar to vasopressin, an antidiuretic hormone. Use tablets for increased urine production and frequent urge to urinate at night.
The medication should not be taken if:
- irresistible thirst;
- anuria;
- sodium deficiency;
- stagnation of fluid in tissues;
- heart failure;
- allergic reaction to pills.
Enablex
The medicine is used for increased tone of the urinary apparatus. Tablets are not prescribed:
- during pregnancy and lactation;
- if angle-closure glaucoma has developed, the motor function of the gastrointestinal tract is slowed down;
- if you are allergic to a medication.
Toviaz
The drug is prescribed for acute enuresis. Toviaz is contraindicated in patients with allergies to tablets, decreased gastrointestinal motility, ischuria and closed-angle glaucoma.
Minirin
The medicine has a pronounced antidiuretic effect. Minirin reduces the frequency of urination and the need to drink water.
The medication should not be used for pathologies requiring the use of diuretics or allergies to the components of the drug.
Melipramine
Melipramine is a good antidepressant. The tablets have an anticholinergic and mild sedative effect and increase bladder capacity.
Contraindications for use:
- allergy to medication;
- heart attack;
- heart dysfunction;
- serious pathologies of the kidneys and liver;
- urinary retention;
- angle-closure glaucoma;
- childhood;
- childbearing and lactation;
- lactase deficiency.
Picamilon
Tablets with nootropic effects.
The tranquilizer eliminates dysfunction of the nervous system, restores metabolic processes, relieves stress, and calms.
Picamilon is used to restore normal urination in adults and children. The medicine reduces detrusor hypoxia.
Do not use the medicine:
- during pregnancy and breastfeeding;
- if you are allergic to pills;
- with renal failure.
Other
The doctor prescribes medications for urinary disorders, taking into account the cause of the disease. For hormonal imbalances, women are prescribed corticosteroids. Patients are usually recommended to be treated:
- Estradiol;
- Microfollin;
- Presomen.
The doctor determines the dosage and course of treatment for each patient individually.
Hormonal drugs should not be used for self-medication. Uncontrolled use of corticosteroids leads to the development of cancer.
For men with enuresis, anticholinergic medications are prescribed:
For temporary urinary incontinence, Desmopressin is used. Tablets are included in the complex therapy regimen.
Homeopathy for enuresis gives good results . However, the course of treatment with alternative medicine methods is quite long. Urinary disorder can be eliminated with:
- Causticum (Causticum);
- Sepia (Sepia);
- Rhus tox (Rus tox);
- Bryonia.
Homeopathic remedies are used as prescribed by a doctor.
It doesn’t matter what caused daytime or nighttime enuresis. At the first symptoms of the disease, you should immediately visit a doctor. Only adequate therapy can help get rid of problems with urinary incontinence.
Source: //faza-sna.com/patologii/effektivnye-tabletki-ot-enureza
Medicines for older patients
Urinary incontinence in older women can be treated with the following medications:
- Omnic has a smoothing effect on the bladder and reduces spontaneous leakage of urine.
- Detrusitol improves urodynamics, reduces the frequency of nerve impulses that provoke frequent visits to the toilet.
- Vesicare relaxes the muscle tissue of the bladder and tones it. The advantage of the drug is its rapid positive effect.
Each of the drugs has side symptoms, so they can not only improve, but also worsen your health. To avoid complications, you are prohibited from choosing your medication and setting the dosage yourself.
Temporary incontinence
Incontinence secondary to transient causes is present in 33% of older women. Reversible or temporary causes of incontinence can be controlled with the use of diapers.
Before determining how to treat urinary incontinence in elderly women, it is necessary to determine the cause of this condition:
- Symptomatic urinary tract infection (UTI) causes frequency, dysuria, and incontinence, primarily in older adults. Asymptomatic bacteriuria does not cause incontinence. Treatment for problems associated with UTIs includes sedative-hypnotics, diuretics, and anticholinergic and adrenergic agents.
- With atrophic vaginitis and urethritis, incontinence is usually associated with frequent urge, and sometimes with a feeling of burning pain when urinating. Low dose estrogen (eg, 0.3 to 0.6 mg conjugated estrogen per day orally or vaginally) relieves vaginal dryness and atrophy, but patients require concomitant behavioral therapy or anticholinergic medications for urinary incontinence.
- Psychological causes of incontinence appear to have less impact on older women compared to younger ones. If psychological disorders (depression, lifelong neurosis, etc.) have been treated, persistent incontinence requires further evaluation.
- Excess urine output secondary to excessive fluid intake, diuretics, or metabolic disturbances (hyperglycemia and hypercalcemia) may lead to frequent urination. Diseases associated with fluid overload (eg, congestive heart failure, hypoalbuminemia) and calcium channel blockers can also lead to incontinence.
- Limited mobility is also considered a common cause of incontinence in older people. Limited mobility can result from many treatable conditions such as arthritis, hip deformity, postural or postprandial hypotension, claudication, spinal stenosis, heart failure, poor vision, fear of falling, stroke, leg problems and confusion.
Incontinence can be caused by infectious diseases
Identification of certain correctable causes may reduce urinary symptom scores.