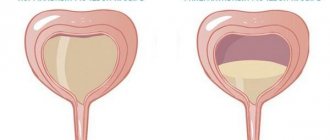
In professional language, urinary retention is called ischuria or UUR - this is a fairly common disease; recently, not only elderly people, but also young patients are turning to doctors for it. Acute urinary retention is a modern disease that must be treated without delay.
This condition causes a lot of discomfort; the person feels a constant urge to urinate, but the bladder is partially emptied or no urine is released at all. Since, in the absence of timely treatment, urinary retention has a bad effect on health and provokes various complications, it cannot be left to chance. At the first symptoms, you must immediately seek qualified help.
Symptoms
Photo: s3-ap-southeast-1.amazonaws.com
First of all, a person pays attention to the lack of urination. In rare cases, when acute urinary retention begins abruptly, there is an interruption of the stream during urination, and further outflow of urine becomes impossible.
Since the walls of the bladder are stretched, which leads to irritation of the receptors, pain in the lower abdomen is observed. Initially, the pain is nagging in nature, but as the process progresses, the pain intensifies and becomes excruciating. In addition, the clinical picture of ischuria includes frequent urge to urinate and pain in the groin areas. If there is partial ischuria, the possibility of minor urination remains. In this case, this can be achieved by pressing on the suprapubic area, as well as by strongly tensing the muscles of the abdominal wall. This produces a weak, thin stream of urine. Against the background of acute urinary retention, which is accompanied by severe pain, changes in human behavior appear. He is excited, rushes around the room, cannot find a comfortable position.
Chronic urinary retention often develops gradually. A person retains the ability to urinate independently, while paying attention to a decrease in the amount of urine excreted, which occurs due to a large amount of urine remaining in the bladder. As a rule, there is no strong urge to urinate, but there is a feeling of incomplete emptying of the bladder.
It is important to be able to distinguish between ischuria and anuria, which occurs due to impaired renal function, as a result of which urine is not produced by the kidneys and does not enter the bladder. In this case, the urge to urinate may be absent or not as pronounced as with urinary retention. Also notes the absence of pain in the lower abdomen. As a rule, anuria is a manifestation of acute or chronic renal failure, so the clinical picture will contain symptoms of the disease that caused the development of failure.
Providing medical care
The algorithm of actions for providing emergency medical care for acute urinary retention is provided by ambulance specialists at the prehospital stage. An important element of primary therapy is rapid determination of the cause of acute urinary retention.
Since laboratory and instrumental diagnostic methods are not available in the field, the main source of information is the patient himself. They examine him, palpate the problem area, and receive information from the victim or relatives.
Possible options for assistance:
- Reflex emptying. The perineum is washed by thermal currents of water, which can partially relax the spasmodic area and promote urination;
- Catheterization. It is performed with a soft catheter by inserting it through the urethra directly into the organ cavity. For men, it is performed from a supine position with legs spread apart. For women - Valentine's position.
Catheterization can be performed with the appropriate skills, fully knowing the structure of the catheter itself and organs, with the obligatory absence of severe pain during the procedure.Direct contraindications to the procedure are the presence of a prostate tumor, urethral rupture, acute prostatitis, abscess, urethritis and cystitis in a complicated stage. If the medical procedure during the provision of assistance was not successful after 2 attempts, then the activity is stopped and the patient is immediately taken to the urology department;
- Subcutaneous administration of drugs. A combination of solutions of Proserin and pilocarpine hydrochloride (one milliliter of 0.05% and 1%, respectively) promotes urination.
Causes of anuria
Since anuria is a complete absence of urine in the bladder, it is logical that the problem lies above this organ, namely, in the ureters or kidneys. As a classic example in the medical literature, the cause of anuria is a blockage of the ureter by a urinary calculus (“stone”). But if you look at it, in order for the outflow of urine into the bladder to completely stop, it is necessary that two ureters be blocked at the same time. It is necessary to agree that such a clinical situation in practical medicine is quite rare, so it must be considered with maximum criticism.
Much more often, anuria is observed in other diseases. For example, in case of cancer of neighboring organs, when the tumor, reaching a large size, can symmetrically compress the ureters, blocking the outflow of urine from the kidneys to the bladder.
In addition, anuria is quite often observed in patients with cardiovascular insufficiency. As you know, if the pressure level in the renal artery does not exceed 80 mmHg, then the kidneys simply stop filtering urine.
In addition, severe alcohol or metal poisoning can also contribute to impaired filtration and, as a result, lead to the development of anuria.
Of course, we should not forget about kidney diseases, such as chronic pyelonephritis or glomerulonephritis, which lead to a gradual thinning of the renal parenchyma and impaired urine filtration. Despite the fact that today they no longer have their former significance in the development of anuria, sometimes similar clinical examples come across.
- I don't feel the urge to urinate after giving birth
Anuria can also develop due to blood transfusion, which differs in type or Rh from the recipient’s blood. Often such cases were observed in wartime conditions, when there was not enough time to thoroughly check the blood type and biological fluid was transfused based on medical history.
Treatment of nonspecific syndrome
In the vast majority of cases, the procedure for treating the pathology that caused urinary retention is performed in a urological hospital. Treatment of acute pathology includes both conservative therapy and surgical intervention.
The primary measures, carried out regardless of the cause of the acute syndrome, are the organization of the removal of biological fluid from the bladder. Basic procedure:
- Antispasmodic preparation . Warm heating pad on the groin area, injections of myolytics – Drotaverine, Papaverine;
- Catheter selection and installation . This device can be Teflon, latex, silicone. Made from soft, semi-rigid or hard materials. Its end is rounded, and the diameter is selected depending on age and gender. The doctor correctly selects the position of the body, if necessary, performs local anesthesia, and then, following the catheterization technique, installs the device through the urethral canal;
- Additional procedures. If there are tissue decay products, small stones, or pus in the bladder, the organ is washed using a cystoscope and a soft catheter;
- Induction of urine output. A heating pad on the bladder area and injections of Proserin, Pilocarpine.
If it is impossible to carry out classical low-traumatic catheterization, a trocar cystostomy is prescribed, which is the insertion of a corresponding tube through the abdominal wall in the pubic region by puncturing the bladder to create an emergency outflow of urine.
After the acute symptom is removed, a full diagnosis is made to identify the causes of the development of the pathological process and specific therapy is prescribed, including a variety of medications (antibiotics, steroids, diuretics, chemotherapy drugs, etc.) and surgical operations strictly as prescribed.
Treatment
Photo: zdozh.ru
Elimination of the cause of urinary retention leads to the elimination of the pathological condition, resulting in the disappearance of disturbing symptoms. Acute urinary retention requires immediate help, which consists of restoring urodynamics. The simplest and most accessible method of restoring urodynamics is bladder catheterization. This manipulation promotes the outflow of urine from the bladder. During catheterization, the following rules should be observed:
- to prevent the development of an ascending bladder infection, the skin and visible mucous membranes in the urethral area should be pre-treated with an antiseptic;
- To avoid damage to the mucous membrane of the bladder, it is necessary to carry out the manipulation carefully and without sudden movements.
There are the following contraindications to bladder catheterization:
- urethral rupture;
- acute infectious and inflammatory diseases of the urinary system;
- urethral fistula;
- priapism (involuntary painful erection not associated with sexual arousal, lasting 4 hours or more).
If catheterization of the bladder is impossible, for example, with severe strictures, “impacted” stones, tumors of the urethra and prostate gland, cystostomy is used to help. This is a surgical way to solve the problem, which consists in the formation of an external fistula of the bladder. This operation allows urine to flow out of the bladder, bypassing the urethra. After the installation of cystostomy drainage in the early postoperative period, it is strongly recommended to carry out bladder training, which is necessary to maintain the functioning volume of the organ. The training consists of periodically clamping the drainage, followed by releasing the drainage from the clamp and emptying the bladder. The clamp is removed from the drainage when the urge to urinate occurs or no later than 2 hours after clamping the drainage. This workout should be done 2 times a day. Failure to comply with this recommendation leads to loss of reservoir function of the bladder.
With the development of ischuria against the background of psychoemotional stress, sedatives are prescribed. In some cases, stressful urinary retention is eliminated after exposure to the sound of flowing water and washing the genitals.
Urgent actions
An extremely dangerous feature of the development of pathology is that only medical workers can provide emergency care. If the patient’s relatives or witnesses to the attack do not have medical education or first aid skills, you must immediately call an ambulance team or independently transport the victim to the nearest health care facility.
To remove stagnant urine, catheterization is performed. This is the name of the procedure during which a rubber catheter is inserted into the urethra and the fluid, which is already dangerous to the body, is “pulled out”.
When catheterizing the bladder, a number of important rules must be followed:
- The diameter of the device must correspond to the size of the patient’s urethra;
- Before use, the catheter is treated with any lubricant (glycerin, petroleum jelly).
It should be remembered that if the first attempt at catheterization fails, reinsertion of the catheter should be the last. In this case, the victim is immediately taken to a medical facility, where other emergency methods of eliminating stagnant urine are used. A change in emergency tactics will also be necessary in case of contraindications to catheterization:
- Urethral injury;
- Acute urethritis;
- Presence of stones;
- Orchitis.
An alternative way to remove stagnant urine is cystotomy. It is carried out only in a medical institution. The essence of the technique is to dissect the bladder, after which stones and other unnecessary organic particles are removed from the organ. To resume the correct natural outflow of urine, a special tube or catheter is used, with the help of which it will freely “leave” the organ.
Before medical workers arrive and carry out special procedures, the patient’s condition can be alleviated by using warm sitz baths or applying heating pads to the lower abdomen. You can also use a reflex effect: turn on the water tap. The sounds of pouring water cause reflex acts of urination.
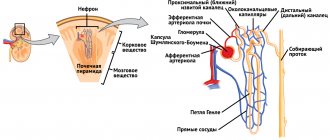
Pathogenesis
The pathology of the neurogenic bladder can manifest itself at two levels. Either it is a lesion of the bladder itself, that is, its increased or decreased tone. Or it is a lesion of the sphincter, which is also characterized by impaired muscle tone. Improper functioning of the sphincter leads to conditions such as urinary incontinence or acute or chronic retention.
In the formation of one or another type of pathology, it is not the cause of damage to the nervous system that plays a role, but the level at which problems with innervation arose. The relationship between the level and pathogenesis of urinary disorders:
- Damage to the central nervous system, that is, the brain (the centers responsible for this process) - uncontrolled urinary incontinence, lack of urge;
- Complete destruction of the nerves of the spinal cord above the centers responsible for urination - increased tone of the bladder muscles, but lack of urge;
- When 2-4 lumbar vertebrae , an atonic bladder develops.
The listed pathologies are extreme forms of destruction of the nervous chain. Most often in clinical practice, incomplete variants of the disease are encountered. In rare cases, mixed pathologies are diagnosed if innervation disturbance occurs at different levels.
- False urge to urinate: Symptoms, Causes, Diagnosis, Treatment
Tablets for ischuria
When the disruption of urine outflow is chronic, you cannot do without medication. Their action will be aimed at relaxing the sphincter. Then the bladder will empty regularly, without outside help.
Prescribing tablets is possible only after a complete examination - tests, ultrasound examination.
Expert opinion
Kovaleva Elena Anatolyevna
Doctor-Laboratory Assistant. 14 years of experience in clinical diagnostic services.
Ask a question to an expert
When using a catheter, you need to take uroseptics - drugs that accumulate in urine and destroy pathogenic microorganisms inside the affected organ.
Medicines
Photo: medicinaytusalud.com
Sedatives are prescribed when urinary retention occurs due to the impact of psycho-emotional stress on the body. As a rule, after eliminating urinary retention, sedatives are used to create a favorable psycho-emotional background. The duration of the course varies between 1 - 2 months. This group includes bromine preparations and herbal preparations. The sedative effect of drugs is to reduce the body's response to various external stimuli. Currently, the prescription of sedatives is widely practiced in various fields of medicine. The main indications for their use are:
- sleep disorders;
- nervous excitability;
- irritability;
- neuroses;
- neurosis-like conditions.
Compared to other drugs, such as tranquilizers, sedatives, especially herbal ones, have a weak sedative effect, however, they are well tolerated and almost never cause side effects.
In some cases, antispasmodics are used to reduce smooth muscle tone. The following subgroups of antispasmodics are distinguished:
- myotropic antispasmodics (drotaverine, papaverine), the effect of which is to act on smooth muscle cells;
- neurotropic antispasmodics (atropine, platyphylline). Their action is based on preventing the transmission of nerve impulses to the smooth muscles of internal organs.
If you experience urinary retention, it is not recommended to self-prescribe any medications. It is necessary to immediately consult a doctor, who, in turn, will determine the need for certain medications.
Symptoms
This disease is accompanied by a number of symptoms in patients. First of all, when the patient’s bladder is completely filled, the urge to urinate disappears. A healthy person excretes approximately one and a half liters of urine per day, with an approximate frequency of four to six times a day. When urinary retention occurs, a person is unable to completely empty the bladder on their own. Also a characteristic sign of this pathology is pain during bowel movements. During pregnancy, women suffer from the problem of incomplete emptying of the bladder. The patient's urine changes color, becomes darker, and may also contain blood. In addition to the above symptoms, general malaise, nausea and often increased blood pressure are added.
Enuresis
Enuresis
- bedwetting, observed mainly in childhood. Its most common causes are neurotic conditions, intoxication due to previous infectious diseases or existing inflammatory foci, such as tonsillitis. Under these conditions, the urination reflex is not formed in a timely manner due to the dissociation of impulses in the central nervous system, which arise as a result of the lack of stable connections between the cortex, subcortex and spinal cord. This entails a disruption in the conduction of impulses from the detrusor of the bladder in the subcortex to the cortex, and the closure of the reflex arc of the nervous system that regulates the act of urination does not occur at the level of the spinal cord, or the urge is activated so weakly that it does not awaken the child. Thus, enuresis is similar in mechanism to temporary neurogenic bladder. In recent years, it has been proposed to consider enuresis in children not only as a result of a violation of the urinary reflex, but also as a symptom of various urological diseases (cystitis, vesicoureteral reflux, bladder diverticulum, etc.).
Main symptoms
As a rule, the diagnosis is obvious and beyond doubt. The patient is in an agitated state due to severe discomfort and complains of the inability to urinate with a full bladder.
Sometimes it is necessary to carry out diagnostics when the patient is unable to formulate complaints (in severe encephalopathy, in paralyzed patients with stroke, unconsciousness due to injury, alcohol intoxication).
When collecting a medical history and examination, it is necessary to try to establish the possible cause of urinary retention.
What is a neurogenic bladder?
All urinary disorders associated with neurological lesions occur in the form of a neurogenic bladder. There are two forms of this process:
- Hypotonic. This type of pathology is characterized by the absence of the urge to urinate when the bladder is full. The absence of urge leads to the fact that a large amount of urine accumulates in the bladder, that is, it overstretches. In such patients, urination is rare, and the urine stream is sluggish. Chronic incontinence is also characteristic, when, due to the overflow of the bladder, urine begins to flow drop by drop from the urethra.
- Hypertensive. This form is characterized by increased muscle tone, which is why even a small amount of urine causes the urge to urinate. Due to chaotic and excessive muscle contractions, the urge can be very strong, sometimes leading to manifestations of incontinence. Such people urinate frequently, in small portions.
Neurogenic voiding disorders are a risk factor for various chronic kidney diseases, which can lead to the development of renal failure. In addition, pathologies significantly worsen the quality of life and therefore require immediate treatment.
Prognosis and possible complications
If you do not take any action, ischuria can have a very negative impact on the body. In particular, the channel may be damaged, as a result of which catheterization will no longer be possible.
In addition, overfilling the bladder can lead to its rupture, and this is a direct threat to the patient’s life. As for the prognosis, it is quite favorable if the patient consults doctors on time. Inserting a catheter at the first stage is the main action to resume normal urination. Of course, taking various antibacterial, anti-inflammatory and other drugs plays a very important role.
You can also watch a video where a specialist explains the causes of urinary retention, as well as how this disease is treated.
Symptoms
Symptoms of urinary retention include the inability to empty the bladder when it is full or small doses of urine are released. The first signs may appear completely unexpectedly, and in addition to urinary retention, they also manifest themselves as pain in the lower abdomen and even during movement. Another option for the development of the disease is a gradual increase in unpleasant symptoms. In addition, nausea, vomiting, weakness, increased body temperature, insomnia, and bloody discharge in the urine may occur. Urinary retention is manifested by especially frequent urges at night, while swelling and protrusion of the abdomen are visually noticeable from an overfilled bladder.
Urinary retention occurs more often in men than in women and occurs due to blockage of the urinary canals with a stone, narrowing or inflammation of the foreskin of the head, prostatitis, adenoma, urinary tract infections, various injuries to the bladder and urethra, and tumors in the pelvis.
Urinary retention in women can occur for the same reasons as in men, but there are also those that, due to their anatomical structure, are unique to women. One is weakness of the muscles between the bladder and vagina, causing part of the urethra or bladder to sag, causing either incontinence or urinary retention. Large fibroids and other tumors cause such pathological symptoms. Urinary retention occurs during pregnancy. This often occurs in late pregnancy before childbirth due to the fact that the enlarged uterus puts pressure on the organ. Retention of urination after childbirth is also possible, because... muscle tone is weakened, there may be swelling of the bladder neck or injury during the passage of the fetus through the birth canal.
Urinary retention in the elderly may depend on gender. In women, this occurs due to prolapse or removal of the uterus, as a result of which a void is formed and the bladder is deformed. In older men, the prostate and other disorders of the urinary system, including dysfunction of the nervous regulation of the process, most often develop.
It is a violation of the mechanism of nervous regulation or a neurogenic bladder that most often explains urinary retention in children. This is due to the fact that they have not yet fully developed the reflex, i.e. the actions of the nervous system with its endings on the walls and sphincter of the bladder are not coordinated. Other causes include various infections, cerebral palsy, and birth injuries. Girls are more susceptible to this pathology.
Reasons for violations
What to do if a woman or man does not pass urine? First you need to figure out why this happened. Among the main reasons are:
- The presence of an obstacle that interferes with the normal excretion of urine. These can be a variety of pathologies affecting the urinary system - prostate, stones, malignant neoplasms.
- Conscious delay - occurs during a nervous breakdown, fright, after surgery.
- Valves of the posterior urethra - folds of the mucous membrane can interfere with the outflow of fluid.
- Nervous diseases - concussion, epilepsy, stroke, etc.
- Uncontrolled use of certain medications.
In men, problems can arise with prostate adenoma, acute inflammation of the prostate gland. Women have their own specific reasons:
If urine does not flow in an elderly woman, we are talking about age-related changes that impair the patency of the urethra.
Complications of anuria
Since anuria directly impairs kidney function, it means that protein metabolic products, which are normally excreted by this organ, remain and accumulate in the blood. This leads to another serious urological symptom – uremia.
- Constant urge to urinate in women - why it occurs and what to do
If such a clinical condition is not amenable to drug or hardware correction, then the patient’s function of the nervous structures of the brain is disrupted, which, in turn, leads to a number of neurological symptoms that find their logical conclusion in coma. As you know, uremic coma is very serious not only in terms of treatment, but also in terms of prognosis. Even those patients who manage to avoid death may emerge from a comatose state with obvious neurological deficits.
Symptomatic treatment of anuria
After confirming the diagnosis of anuria, even before determining the exact cause of this pathology, patients are already undergoing certain measures aimed at eliminating anuria. First of all, they are prescribed loop diuretics such as furosemide. If the cause of anuria was cardiovascular disorders, then for some time after the administration of furosemide it is possible to obtain the first portion of urine. A completely opposite situation is observed, say, with bilateral ureteral obstruction. After the administration of a diuretic, only an increase in clinical symptoms is observed. In a way, this is a kind of test that allows you to distinguish renal anuria from subrenal anuria.
If, against the background of the administration of a diuretic, an increase in clinical symptoms is observed, then they resort to the second stage of symptomatic therapy - the application of a nephrostomy. Nephrostomy allows you to “unload” the kidney, which leads to an immediate improvement in the clinical condition due to the elimination of the urinary block.
If we are talking about uremia, which is associated with a direct violation of the renal membrane, and diuretics are ineffective in this situation, then doctors have only one option - to transfer the patient to an artificial kidney. After the patient's condition improves, further diagnostic searches can be carried out and other treatment methods can be tried.
Hemodialysis
Acute urinary retention: symptoms
If your health worsens, you should immediately see a doctor. A specialist can detect the presence of urinary retention during a general examination, since such a condition is accompanied by a number of very characteristic symptoms.
The pathology is accompanied by overfilling of the bladder and a significant increase in its volume. A painful protrusion forms above the pubic bone, quite hard to the touch - this is the bladder.
Patients complain of a frequent urge to urinate, which does not lead to emptying the bladder, but is often accompanied by severe pain in the lower abdomen. The pain can spread to the genitals, perineum, etc.
This pathology is also characterized by urethrorrhagia - the appearance of blood from the urethra. Sometimes it can be only small spotting, sometimes it can be quite massive bleeding. In any case, blood in the urethra is an extremely dangerous symptom that requires emergency care.
Other signs directly depend on the cause of this condition and the presence of certain complications. For example, when the urethra and bladder are damaged or ruptured, patients develop severe pain, which leads to traumatic shock.
If there is a rupture of the proximal urethra, then urinary infiltration of the pelvic tissue is observed, which often causes severe intoxication. During vaginal or rectal (in men) examination, such patients experience tissue pastiness and severe pain when pressed. With intraperitoneal rupture of the bladder, urine spreads freely throughout the abdominal cavity, which leads to acute pain in the lower abdomen.
Causes
In medicine, there are several reasons why a patient does not have the urge to urinate. Ishuria and anuria are the names of diseases in which the main symptom is urinary retention. The main causes of these diseases are the presence of stones or tumors in the urethra, kidney problems and damage to the spinal cord.
Diseases and special conditions of the body
When a patient does not urinate, the doctor immediately understands that the cause is a serious illness. This could be cancer of the genitourinary organs, prostatitis in an acute form, or hyperplasia in a benign form. A serious disease, one of the symptoms of which is the lack of desire to empty the bladder and pain when doing so, is urethral stricture. Stones in the genitourinary system can also be the cause. Urinary retention often occurs after surgery in the pelvic area. Most often, these problems are diagnosed in women after cesarean section. Injuries to the groin also cause problems with urethral emptying. A disease such as phimosis also refers to a special condition of the body in which the patient experiences pain during urination.
Video : Do you have problems urinating?
Direct output. Do you have problems urinating
Nervous system diseases
Diseases of the central nervous system are often accompanied by ischuria. If a patient has a tumor or various types of injuries in the spinal cord, difficulty urinating is a fairly common accompanying symptom. In this case, the patient cannot empty the urethra, which is full of urine. In this case, urinary retention can be acute (if it occurs unexpectedly) and chronic (with prolonged increasing pathology). Patients who have suffered a stroke are diagnosed with other urinary problems - urinary incontinence. This pathology is also a complication of certain brain diseases.
Psychological disorders
Many diseases in the human body are psychosomatic in nature. Difficulty emptying the bladder is no exception. In case of a somatic disorder, functional deviations of a person’s internal organs are diagnosed. The cause of urinary dysfunction is often severe stress or upheaval in the patient’s life. In medicine, namely in the field of neurology, there is a diagnosis of hysterical anuria, but not all medical professionals and scientific researchers agree with it. Although the fact that urinary retention, which lasts no more than a day and a half, is caused by stress or exhaustion of the patient, is not in doubt.
Violation of reflex activity
Reflex activity of the pelvic organs is carried out through the pelvic nerves. Problems with urine excretion from the body caused by disruption of the reflex activity of the nervous system have the most complicated form. The urge to urinate occurs in a person at the level of reflexes. When this function is impaired, a person feels the bladder full, but cannot empty it on his own.
Features of the structure of the body
The anatomical structure of the body of each person has its own characteristics, which sometimes become the causes of deviations in the functioning of the body. These deviations lead to the occurrence of various diseases in humans; as a rule, these diseases are chronic. In men, such features as narrowing of the foreskin, genital prolapse and underdeveloped condition of the genital organs are distinguished. In women, problems with urination arise due to genital endometriosis, inflammation of the labia and their subsequent deformation.
Treatment methods
The causes of pathology identified at an early stage are quite treatable. The most important task of the patient is to see a doctor in a timely manner. Urology deals with urinary problems.
Most likely, acute pain will require emergency hospitalization. If the ambulance is delayed, it is advisable to give the patient a warm bath.
Upon admission to the clinic, the patient will first begin to have urine excreted. The manipulation is carried out using a urethral catheter. Quite often this causes some trauma. Or they use trocar cystotomy (puncture of the skin and bladder, insertion of a special tube).
There may be contraindications for the urine drainage procedure:
- the patient's immunity is severely weakened;
- elderly patients;
- history of multiple chronic diseases.
During catheterization, it is possible to introduce an infection into the urinary tract. Therefore, even a minimal violation of the integrity of the mucous epithelial layer should be a sufficient reason to refuse this procedure. After urine is removed, diagnostics begins. Identifying the causes of the pathology allows the doctor to make the necessary decision on the form of treatment: conservative (medicinal) or surgical intervention.
Possible complications
If urine is difficult to pass and treatment is not carried out, other problems may occur when urinating.
Among the main negative consequences are:
- the appearance of blood impurities in urine,
- inflammation of the bladder or kidneys,
- acute renal failure.
To avoid these problems, you need to go to the doctor immediately after the appearance of alarming signs indicating a disruption in the normal process of urine excretion.
Diagnostics
Diagnostic measures for neurogenic urinary disorders in men and women include a number of examination methods. These include:
- Collecting the patient’s history and complaints (it is especially important to clarify whether there were any injuries or other damage to the nervous system);
- OAM (allows you to evaluate the chemical and physical properties of urine, as well as determine the composition under a microscope);
- Clinical blood test;
- Blood biochemistry (with its help you can estimate the quantitative content of various substances and elements in the blood);
- Urinalysis according to Nechiporenko (allows you to detect cells indicating pathology of the excretory system, such cells include: leukocyte and erythrocyte cells, and cylinders);
- 24-hour urine test (kidney concentration function is assessed);
- Bacterial inoculation on various nutrient media (infectious agents of bacterial origin are identified, this also includes a test for sensitivity to antibacterial drugs);
- Ultrasound examination of the pelvic organs (allows you to visualize the kidneys and bladder, detect changes in their structure, and also assess the level of residual urine);
- Magnetic resonance imaging or MRI for short (assessing the condition of the spinal cord and brain, excluding or confirming a tumor process);
- Cystourethroscopy (allows you to visually assess the condition of the walls of the bladder and urethra);
- Radiography using various contrast agents (especially successfully reveals anatomical anomalies in the structure of the urinary system);
- Complex urodynamics (with its help, the functioning of the bladder during its filling and emptying is assessed);
- A set of neurological examinations (to identify the etiological factor of urination disorders);
Additionally, consultations with neurological and psychotherapeutic specialists may be prescribed. A neurogenic bladder is established in the presence of pathology of the nervous system or when any other etiological factors are excluded.
Sources used:
- https://yellmed.ru/bolezni/zaderzhka-mochi
- https://medicalj.ru/symtoms/male-groin/1147-anuriya&parent-reqid=1573780983484045-640485730458241934800127-man1-3484-tch&lite=1
- https://brulant.ru/health/neyrogennye-narusheniya-mocheispuskani/
- https://kurology.ru/simptom/otsutstvie-pozyvov-k-mocheispuskaniyu/
- https://medbe.ru/materials/obshchee-v-urologii/simptomatika-urologicheskikh-zabolevaniy-narusheniya-mocheispuskaniya-dizuriya/
- https://ilive.com.ua/health/ostraya-i-hronicheskaya-zaderzhka-mocheispuskaniya-chto-delat-pervaya-pomoshch_128032i15997.html
- https://fb.ru/article/196030/ostraya-zaderjka-mochi-pervaya-neotlojnaya-pomosch-prichinyi-simptomyi-lechenie
- https://uromir.ru/vospalenie-mochevogo-puzyrya/raspoznanie/zaderzhka-mocheispuskaniya.html
Types of treatment for urinary retention in women
To determine the therapeutic plan, the doctor is guided by the results of ultrasound of the urogenital system and x-ray examination. Sophisticated radiation imaging methods (MRI, CT) make it possible to identify the tumor process. Often after they are performed, a biopsy is performed - taking part of the organ tissue for subsequent histological examination. Laboratory diagnostics help confirm the presence of inflammation, bleeding, diabetes, and hormonal disorders.