How does the disease occur?
In young people, it most often results from injuries during physically demanding work or sports activities. But nevertheless, acute and chronic arthrosis of the knee joint, or gonarthrosis (“goni” translated from ancient Greek means “knee”), is mainly the lot of older people, due to the general decrepitude of the musculoskeletal system. Both one and both limbs are affected, so the disease can be unilateral or bilateral, respectively.
Women are more susceptible to this disease than men. Especially those who suffer from excess weight and varicose veins of the lower extremities. As a rule, in most women with full complexions, acute inflammatory processes in the joints occur after 40–45 years.
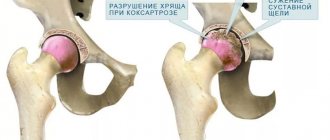
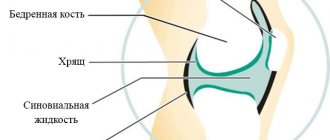
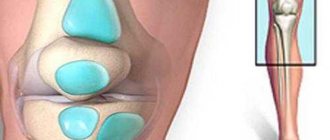
Initially, degenerative changes occur in cartilaginous tissues. They soften, become thinner, crack and delaminate. In the absence of timely and adequate treatment, cartilage is completely destroyed. In this case, the bones become exposed and, when they come into contact during movements, cause incredible pain to the person.
In addition, with arthrosis of the knee joint - in contrast to osteochondrosis of the spine - soft tissues also suffer: joint capsules, ligaments, membranes. At the same time, the production of synovial (intra-articular) fluid—a kind of “lubricant” of the bones—changes.
Finally, the muscles that hold the joints in a stable state during a wide variety of movements also suffer. And if the muscle fibers weaken, then the joints take on loads that exceed the norms calculated by nature itself. As a result, the articular ligaments harden, the membranes become inflamed, and the cartilage tissue gradually degrades.
Diagnosis
Gonarthrosis is diagnosed using an X-ray examination of the knee joint and a laboratory blood test. An increased ESR in a blood test indicates the presence of an inflammatory process in the body. Using an x-ray, you can see what changes have occurred in the joint and diagnose the stage of development of the disease.
Why does the disease occur?
The causes of this disease have not yet been fully studied. A very likely hypothesis is that arthrosis of any joints develops due to a hereditary predisposition. A number of scientists suggest the presence of a special gene, the “breakage” of which leads to a failure in the production of cartilage tissue. Established causes of gonarthrosis include:
- weakened ligamentous apparatus;
- increased physical activity;
- injuries;
- primary diseases of the knee joints;
- metabolic disorders;
- severe stress.
There are people with very flexible bodies who have no difficulty doing the splits or performing complex gymnastic exercises. In such people, unusual joint mobility is due to weakened (“loose”) ligaments. However, such flexibility is fraught with microtrauma to the knees. When there is a lot of damage, quantity turns into quality: arthrosis begins to develop. Weakness of the ligamentous apparatus is dangerous because a person does not feel pain due to microtraumas, does not notice them and does not see a doctor.
Physical activity when playing sports should be determined taking into account your age. Often, older people continue to exercise just as intensely as they did in their younger years. In such cases, sports only harm the joints. After about 40 years, increased loads are unacceptable. The most dangerous things for knee joints are squats and running on asphalt sidewalks.
In older people, gonarthrosis is often complicated by arthritis. In inflamed joints, synovial fluid accumulates, tumors form, and as a result, cartilage tissue is also destroyed. In young people, the most common cause of gonarthrosis is bone fractures. During their treatment, the damaged limb is temporarily fixed in a motionless state. However, because of this, blood flow deteriorates, and post-traumatic arthrosis of the knee joint develops. Removal of the meniscus leads to this consequence in 90% of cases.
Excess weight does not directly destroy cartilage tissue, but provokes microtraumas of the menisci, which result in gonarthrosis. Its most severe form develops when obesity is accompanied by varicose veins of the lower extremities. The condition of cartilage and bones is worsened by the leaching of calcium from them due to metabolic failures. And even severe stress and long-term depression are harmful to joints.
Ointments and creams
Treatment of a disease such as arthrosis of the knee joint should include the local use of gels and ointments. These forms of medications should not be relied upon as the only treatment option; their use should be considered as a necessary addition to the intake of NSAIDs and chondroprotectors.
Such drugs significantly reduce discomfort, pain, swelling, and improve joint mobility.
How does the disease manifest itself?
Characteristic signs that appear as gonarthrosis progresses:
- crunch in the joint;
- pain;
- accumulation of synovial fluid;
- limitation of joint mobility;
- knee deformity.
Joints often crack when bent, both in healthy people and in those whose joints are too mobile or who have weakened ligaments. A distinctive feature of crunching with arthrosis is sharp sounds and the presence of pain. The initial stages of the pathology usually occur with mild pain. They occur only with excessive physical exertion. Such phenomena can be observed for many months and years - until the disease worsens.
Then the pain becomes stronger, and not only with increased loads, but even in a calm state. Gonarthrosis can worsen many times. Instead of isolated discomfort, prolonged pain attacks occur. Especially after carrying heavy objects or walking for a long time. Standing still brings only temporary relief, as continued movement again causes pain in the knee.
Over time, exacerbation of arthrosis can lead to the production of excess synovial fluid in the cavity of the inflamed joint. As it accumulates, it puts more and more pressure on the surrounding tissues, “expanding” the knee and causing excruciating pain at the slightest movement. In such cases, doctors diagnose synovitis and suggest pumping out the fluid or surgery.
In the later stages of gonarthrosis, the mobility of the affected joint is so limited that the person is unable to fully bend and straighten the leg. Attempts to increase the range of motion cause severe pain. The period of exacerbation of the disease can last a long time.
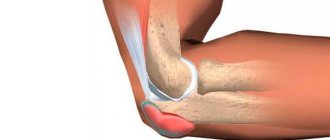
In the absence of effective treatment, the joint gradually deforms. This is noticeable upon visual inspection. At first the knee only swells, but then loses its shape.
Characteristic symptoms
Characteristic symptoms accompanying the various phases of gonarthrosis include:
- discomfort in the knee, expressed in pain;
- synovitis is an excessive accumulation of joint fluid in the joint cavity, which can lead to the appearance of cystic formations on its posterior wall;
- crunching and clicking when bending and straightening the leg at the knee;
- joint deformity;
- mobility impairment.
Discomfort in the knee
At the initial stage of development of the disease, a person either does not feel any discomfort or experiences mild pain, which is not associated with the development of arthrosis. This condition can last for years until the disease moves to the next stage, in which a person begins to experience mild but constant pain while walking, running, and other physical activity. Sharp pain that occurs during physical activity is not a sign of arthrosis, but indicates an injury: pinching, dislocation, fracture.
With arthrosis of the 2nd degree (moderate severity), the pain is felt more strongly and now appears not only during exercise, but also at rest. After long walks, the pain can be unbearable. In order for the discomfort to go away, you have to constantly increase your rest time. But as soon as you resume movement, the pain and discomfort return.
The last (stage 3) is accompanied by severe and constant pain, which can be either aching or sharp. Discomfort and pain intensify when the weather changes and is especially disturbing at night. Only nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) help you sleep.
Crunching and clicking
Crunching in the knees is a phenomenon common not only among patients, but also among healthy people. Crunching and clicking sounds when bending the legs at the knees in healthy people indicate weakness of the ligamentous apparatus or excessive mobility of the joint. The person does not experience any pain.
Crunching and clicking with arthrosis sounds sharp and is accompanied by pain. This symptom indicates that the disease has progressed to stage 2 or even stage 3.
Mobility impairment
Impaired mobility occurs at the last stage of the disease. The leg can neither be bent nor straightened. It bends only at an angle of 90°. Each movement is given with great effort and is accompanied by severe pain. At this stage, the knee may already be immobile. Patients often walk on bent legs.
Joint deformity
Simultaneously with impaired mobility, joint deformation also appears. At the last stage it is well visualized. At the initial stage, the knee appears swollen, but its shape is maintained.
Degrees of the disease
Treatment tactics for gonarthrosis largely depend on the stage of development of the pathological process. It is customary to distinguish 3 degrees of this disease. The 1st degree is determined by mild pain during active movements, which quickly disappears at rest. A small amount of synovial fluid may accumulate inside the joint. The process of cartilage damage is already underway, but this is not expressed outwardly, since the knee looks completely healthy.
With gonarthrosis of the 2nd degree, the joint space is significantly narrowed, the cartilage tissue becomes much thinner, and the bones grow. All this is clearly visible on an x-ray. Every movement of the patient causes sharp pains, which subside for a while in a calm state. But when movements are resumed, they appear again, accompanied by a characteristic crunch. The functions of the joint are significantly limited.
The 3rd degree of the disease is determined by the complete thinning of individual sections of cartilage, exposure of bones and many osteophytes - salt deposits in the form of sharp bone growths.
Aching pain becomes a constant companion of the patient even at rest. For many, it intensifies when the weather changes, as meteosensitivity increases. Pain prevents you from falling asleep, causing insomnia and dramatically reducing your quality of life.
Visual changes in the sore knee become obvious. If at first the disease affects only the internal structures of the joint, then at the last stage it also affects the external tissues. The knee may become completely immobilized. And then the person, having become disabled, with great difficulty, barely moves on unbending legs.
More often than not, a sad fate befalls overweight people, especially women.
How is the disease treated?
The treatment of gonarthrosis, as well as the treatment of arthrosis of the fingers and hip joints, is the same, since these diseases are based on the same pathological process. In all these cases, cartilage tissue is affected.
In case of acute arthrosis of the knee joint, treatment can be carried out according to the method of rheumatologist P. V. Evdokimenko. It is based on the integrated use of medication, manual therapy and physiotherapeutic procedures.
This combination makes it possible:
- quickly relieve pain;
- activate blood flow in the cavity of the affected joint;
- enhance metabolism in cartilage cells;
- restore mobility of the knee joint.
How to relieve pain with arthrosis? Dr. Evdokimenko considers effective the use of non-steroidal drugs that have analgesic and anti-inflammatory effects, intra-articular injections, creams and ointments with analgesics. Compresses with “Bishofite” and “Dimexide” are effective. Chondroprotective drugs relieve pain and help restore cartilage tissue: Dona, Teraflex, Chondrolon, Chondroxide, Structum. In addition, a therapeutic diet is important.
According to Dr. Evdokimenko, with grade 1 gonarthrosis, painful symptoms can be relieved and the patient can be completely relieved of the disease within a year. Stage 2 disease has to be treated for several years. Severely advanced grade 3 gonarthrosis does not respond to conservative methods of therapy and requires radical, that is, surgical care.
A completely different technique was proposed by Dr. S.M. Bubnovsky. The therapeutic effect is achieved without drugs and surgeries. In his opinion, it is better to relieve pain by applying ice and taking a contrast shower. The main goal of treatment is to reduce the production of synovial fluid, the excess of which prevents the joint from functioning normally. Dr. Bubnovsky’s method is based on physiotherapy and kinesitherapy - sets of special exercises, often with exercise equipment.
These exercises allow you to activate blood flow in the sore joint, improve the nutrition of cartilage cells, and restore elasticity to the ligaments. Gradually, the treatment is supplemented with massage, swimming in the pool and bath procedures.
Diagnostics
Determining knee osteoarthritis begins with a physical examination by the doctor, a medical history, and a conversation with the patient. Be sure to draw the doctor's attention to what most often causes pain, and tell us about cases of the disease in the family, if any.
Additional diagnostics are carried out using:
- X-rays, which may show the presence of bone spurs and changes in cartilage;
- magnetic resonance imaging;
- Blood tests can detect autoimmune disorders.
How to treat arthrosis of the knee joint, what medications are needed for this? Find answers to these questions below.
Medical nutrition
Since the cause of gonarthrosis often lies in metabolic disorders, it is important to eliminate overeating and balance the diet. Excess weight should be vigorously combated. But it is a mistake to resort to strict diets for weight loss or fasting - such radical measures will not spoil your stomach and intestines for long. In addition, calcium is washed out of the bones, which is strictly unacceptable in case of gonarthrosis.
Should be excluded:
- fatty meats;
- semi-finished products, sausages, smoked meats, canned food;
- fried foods;
- hot seasonings, marinades, pickles;
- fresh tomatoes, bell peppers, white cabbage;
- oranges, lemons, sour apples, plums, bananas, grapes;
- chocolate, candies, cakes, pastries, sweet sodas.
Useful for patients with gonarthrosis:
- jellied meat, aspic;
- boiled low-fat fish;
- chicken, turkey, rabbit;
- dishes made from beans, peas, lentils;
- oatmeal and buckwheat porridge;
- milk;
- cottage cheese;
- cheese;
- low-fat cream, sour cream;
- dairy products;
- fresh herbs;
- fruit jelly, marmalade;
- nuts.
Breakfast should be complete and satisfying, so that it stimulates metabolism and charges the body with energy for the whole day. Then it is recommended to eat food 3-5 times, but in small portions. Light dinner - 2-3 hours before going to bed. It is advisable to drink 1.5–2 liters of water per day if your kidneys are healthy.
Possibilities of traditional medicine
Treatment with folk remedies can be successful at the initial stage of gonarthrosis as an additional method that helps speed up regeneration processes in the diseased joint. In addition, using traditional medicine recipes you can relieve acute pain. The most popular recipes are:
- At night, a paste of grated horseradish root on a clean cloth is applied to the inflamed joint, tied with a woolen scarf and kept until the morning. Make such compresses once a month.
- Aloe leaves cut in half are applied with the inside side to the sore knee overnight.
- For acute joint pain, warm compresses of honey and table salt are also made at night: per 100 g of honey - 1 tbsp. salt.
- A popular remedy is dandelions. Every day, 5-6 fresh flowers are picked, washed and eaten. Or 1 tbsp. dried flowers are poured into a glass of boiling water, left to cool, drink 1/3 glass before breakfast, lunch and dinner.
- Cinquefoil tincture: a 0.5 liter bottle is filled to the top with dry grass and topped with vodka. After 1 month, the liquid is filtered. Make compresses with this tincture and take 20 drops morning and evening.
It is impossible to completely get rid of gonarthrosis using folk remedies, but it is possible to stop its further progression. The greatest therapeutic effect is obtained by combining compresses with decoctions and herbal tinctures. However, you must first obtain the approval of your doctor.
OrtoCure.ru
Many people believe that joint diseases are the lot of people over 50 years old. Having encountered them at a young age, they do not know what to do or how to treat them. Today, arthritis and arthrosis affect young people.
More often, the joints of the lower extremities (hip, knee, foot joints) are susceptible to arthrosis; they experience enormous stress, bearing the entire body weight.
Acute arthrosis is a disease characterized by degenerative destruction of cartilage tissue inside the joint. In medicine, the disease is called deforming osteoarthritis. Destruction occurs slowly in the initial stage of the disease. In the long term, degeneration of periarticular tissues, restructuring of the ends of bones, and an inflammatory process occur.
Diagnosis of the patient
Osteoarthritis destroys the cartilage located on the surface of the bones that form the joints. Cartilage tissue becomes less elastic and becomes rougher in texture, which leads to disruption of the normal sliding of adjacent joint surfaces and a decrease in the shock-absorbing function of cartilage during impacts. Most arthrosis occurs in the area of the knee, hip, and foot joints.
Acute arthrosis, depending on the location, is divided into types:
- Arthrosis of the hip joint - coxarthrosis;
- Arthrosis of the knee joint - gonarthrosis;
- Arthrosis of the foot;
- Arthrosis that affects several joints at the same time - polyarthrosis;
- Kellgren's disease is polyarthrosis of hereditary etiology.
Treatment of arthrosis of the knee joints
Conservative - anti-inflammatory drugs, painkillers, muscle relaxants, vascular, chondroprotectors, compresses, kinesiotaping, physical therapy, physiotherapy, orthoses.
Minimally invasive - paraarticular blockades (Novocaine + medication relieves pain and inflammation), injection of artificial lubricant into the joint itself, plasma lifting.
Surgical - arthroscopy (a low-traumatic method of treating intra-articular pathologies and removing damaged structures), endoprosthetics.
Conservative methods are most effective at the initial stage of the disease.[9][16] They help reduce pain and temporarily slow down the destruction of cartilage. In stage II, more effective methods are needed.[8][23] The introduction of hyaluronic acid preparations into the joint cavity is used to reduce friction and trauma to the cartilage. There is no clear evidence for the restoration of cartilage, but it is good for lubricating surfaces. “PRP therapy” (plasmolifting) is the injection of platelet-rich plasma into the knee joint, which is obtained from the patient’s own blood by centrifugation.[4][13][18] It nourishes cartilage and promotes its restoration, since autoplasma platelets contain numerous growth factors and cytokines that promote the regeneration of damaged tissue.
Endoprosthesis replacement is a common and effective surgical method for treating severe gonarthrosis,[16][24][25] which allows you to maintain limb mobility and the ability to lead a full life subsequently. This is a high-tech operation lasting approximately one and a half hours. In the postoperative period, long-term rehabilitation and development of the joint are necessary.[16][18] After 25-30 years, when the artificial joint wears out, it needs to be replaced again.
Etiology of acute arthrosis
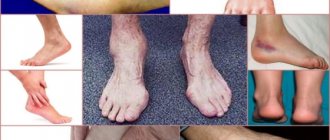
Arthrosis of the knee, hip, and foot joints is more common in women. The reason is women's addiction to tight high-heeled shoes. To be more attractive, the fairer sex makes sacrifices, paying for the admiring glances of others with their own health. Wearing uncomfortable shoes leads to foot deformation. When arthrosis affects the hip, knee, foot joint, or other area of the lower extremities, the load is redistributed to the remaining joints of the body.
Treatment at home
There are primary and secondary forms of arthrosis, which differ in the origin of the disease. Primary arthrosis appears due to biochemical changes in the human body, due to changes associated with the patient’s age. Both reasons can be combined. The secondary form of arthrosis is the result of injuries, a consequence of diseases (diabetes, thyroid disease), disruption of the functioning of certain body systems (failure of vascular functionality, etc.).
Inflammation of the joints of the lower extremities (hip, knee) can be caused by congenital flat feet. To avoid severe deformation of the foot, it is worth carrying out treatment as early as possible and wearing corrective orthopedic shoes.
There are common causes of arthrosis:
- Excess body weight;
- Genetics;
- Congenital diseases (flat feet, etc.);
- Strong, systematic load on the joints;
- Metabolic disorders;
- Hormonal disorders.
The listed factors initially cause minimal damage to cartilage tissue, which does not manifest itself. Gradually, the area of localization increases, causing inflammation and pain. In advanced cases of the disease, growths on the bones—osteophytes—appear. Their formation is laid down by nature. The growths play the role of limiting the movement of the damaged joint, slowing down the destruction of cartilage tissue.
Acute arthrosis of the knee, hip, and foot joints often causes disability with loss of ability to work. When you detect the first signs of the disease, you should seek help from professionals who will prescribe the correct treatment.
Pathogenesis of arthrosis of the knee joints
There are primary and secondary osteoarthritis.[8][15][20]
Primary arthrosis:
- Articular cartilage is constantly destroyed and renewed; normally, these processes are balanced. With age, cartilage renewal slows down and destruction begins to predominate, which is called the process of degradation or degeneration.[12] A person’s weight plays an important role, since with a mass of 70 kg in 20 steps we carry 700 kg on each leg (70 kg x 10 steps), and with a mass of 120 kg we already carry 1200 kg on each leg. Therefore, weak cartilage wears out much faster;
- it is necessary to remember: the joint receives nutrients and is restored while it moves; A sedentary lifestyle reduces metabolic processes, and the necessary elements do not reach the cartilage;[18]
- There is controversial evidence about the hereditary role in the occurrence of the disease. If the parents had arthrosis, then the likelihood of its occurrence in children increases;
- occurs due to autoimmune synovial inflammation.
Secondary arthrosis is caused by:
- injuries (fractures, meniscal and anterior cruciate ligament tears).[15][19] Unfortunately, in any person, regardless of age, these injuries lead to excessive stress on the cartilage. A fracture of any part of the bones covered with cartilage is accompanied by the formation of an unevenness - a “step”.[26] In this area, when moving, abrasion occurs and arthrosis forms;
- rheumatoid arthritis, Koenig's disease (osteochondritis dissecans), consequences of purulent inflammation in the joint (gonitis), etc.;
- regional vascular disorders;
- chronic exudative-proliferative and cicatricial adhesive processes in the joint.
With arthrosis (osteoarthrosis), in addition to the progressive destruction of cartilage, loss of its elasticity and shock-absorbing properties, bones are gradually involved in the process.[7][29] Under load, sharp edges (exostoses) appear, which are mistakenly considered “salt deposits” - with classic arthrosis, no salt deposition occurs. As arthrosis progresses, it continues to “eat” the cartilage. Then the bone is deformed, cysts form there, all structures of the joint are affected, and the leg becomes bent.[11][17]
In addition to the inner or outer part of the knee, arthrosis can also affect the surfaces between the patella and the intercondylar groove of the femur. This option is called patellofemoral arthrosis .[16]
Its cause is usually a subluxation, fracture, or lateralization of the patella.
Clinical manifestations of osteoarthritis
Osteoarthritis is an insidious disease that develops slowly and imperceptibly. An elementary crunch of the knee joint is evidence of the development of the disease. Almost no one starts treatment at the initial stage. Patients go to doctors when it is necessary to undergo surgical treatment, but before that they try to fight the disease on their own, self-medicating.
The main manifestations of arthrosis are:
- Crunching when bending the knee, hip, ankle joints;
- The presence of pain during movement and exertion, which goes away when the limbs are inactive;
- Deformation of the lower extremities, which becomes more and more noticeable;
- Swelling in the area of the knee, hip, ankle joints;
- Severe muscle tension in the affected joints;
- Swelling at the location;
- Reddened skin;
- Feeling of heaviness in the limbs after a hard day's work;
- Stiffness of movements.
Pain in osteoarthritis may worsen at night. This is caused by stagnation of blood in the vessels due to deforming processes occurring in the affected joint.
If the disease is not treated in time, then biomechanical disorders of the spine and other joints cannot be avoided. There are frequent cases of intervertebral hernias due to neglect of osteoarthritis of the lower extremities.
Arthrosis in the picture
Risk factors for the disease
People with the following factors are at risk for acute osteoarthritis:
- Women who regularly wear tight, high-soled shoes;
- Elderly people;
- Genetic predisposition to the disease;
- Excess weight;
- Previous surgery to remove the meniscus;
- Leg joint injuries;
- Strong physical stress;
- Professional sports training;
- Prolonged stay in a squatting or kneeling position;
- Systematic walking over long distances (over 5 km);
- Carrying heavy objects;
- Frequent, long walks on stairs.
If at least one of the factors is present, it is almost impossible to avoid the development of the disease. If the number is more than two, it is worth taking preventive measures and regularly visiting doctors. They will prescribe supportive treatment to slow down the destructive processes occurring in the joints of the legs.
Overload on joints
Prevention and timely treatment are considered a way to rid yourself of the complex consequences of the disease.
Stages of the disease
The acute form of osteoarthritis is detected as a result of certain tests and studies (X-rays, etc.). Based on the data obtained, the stages of the disease are distinguished:
- Stage 1, characterized by mild symptoms of the disease. The X-ray image shows a slight sharpening of the extreme parts of the joints, narrowing of the gaps between them;
- Stage 2, manifested by palpable pain with significant limitation of mobility. The image shows the resulting osteophytes.
- Stage 3 is characterized by limited mobility, constant pain of severe intensity, which does not allow basic movements. An X-ray image shows the absence of cartilage tissue, abrasion of bones, and clearly defined deformation of the joints.
Conventionally, it is customary to distinguish the 4th stage of the disease.
If an X-ray examination is not enough to establish a complete picture of the disease, an MRI may be prescribed.
Treatment of osteoarthritis
Modern medicine is powerless in terms of treating arthrosis and arthritis. It is impossible to completely cure diseases.
Treatment comes down to slowing down the destructive effects of the disease. The main goal when carrying out therapeutic manipulations is to prevent the cartilage tissue from being completely worn out.
For treatment to be effective and for periodic exacerbation of osteoarthritis of the foot and other affected joints to not occur, it is necessary to eliminate the factors contributing to the development of the disease. It is necessary to rest your legs after heavy exertion. If you are overweight, get rid of it. A good way to prevent arthrosis is swimming.
In the drug treatment of arthrosis, it is customary to use anti-inflammatory ointments and drugs containing chondroprotectors. You can do massage and special physical therapy exercises.
OtNogi.ru
Acute arthrosis of the knee joint can occur at any age, even in young people who actively lead a healthy lifestyle.
The disease is always painful, accompanied by limited mobility of the limb and causes the patient a lot of suffering. But why does the disease occur and how to treat it?
Reasons for the development of the disease
Acute arthrosis of the knee joint according to ICD-10 has code M17. It occurs because degenerative processes are started in the cartilage joint tissue, which after the exacerbation subsides can become chronic. The development of osteoarthritis can be triggered by:
- Knee meniscus injury. Due to the injury, long-term immobilization of the limb is required. Long-term immobility leads to disruption of the trophism (nutrition) of cartilage.
- Great physical activity. Due to the nature of a person’s upright posture, the knees have to withstand heavy loads, and intense physical training can lead to microtraumas of cartilage tissue.
- Obesity. Heavy weight puts excess pressure on the cartilage tissue of the knee, reducing its elasticity and worsening metabolic processes. Lack of nutrients leads to the development of destructive processes.
- Poor nutrition. For the prevention of acute arthrosis of the knee joint, diet plays an important role. If a person abuses alcohol (especially beer drinks) and drinks a lot of coffee, then there is a risk of “washing out” collagen fibers and calcium from the cartilage tissue, reducing the strength and elasticity of the cartilage.
- Joint diseases. Often acute arthrosis of the knee joint occurs after arthritis or other joint inflammatory diseases.
These are the most common causes of the development of pathology, but it can also be provoked by stress, metabolic disorders in the body and other factors.
How does the disease manifest itself?
When acute arthrosis of the knee joint develops, the symptoms increase gradually:
- The pain syndrome is mild at first, and for several weeks (sometimes months) a slight, barely painful discomfort is felt. But under the influence of unfavorable factors (hypothermia, bruise, etc.), acute pain occurs with arthrosis of the knee joint, often accompanied by hyperemia and swelling of the knee. Mobility may not be impaired.
- Gradually, the destruction of the cartilage leads to its deformation, and acute arthrosis of the knee joint of the 2nd degree will be accompanied not only by swelling and pain, but also by a pronounced limitation of mobility. A crunching sound may appear even with gentle movements. With stage 3 damage, the knee sometimes does not bend at all.
If timely examination and treatment of the pathology is not carried out, then the person will soon lose the ability to move normally.
How is the disease treated?
When acute arthrosis of the knee joint occurs, treatment is carried out in several stages:
- Medication aimed at relieving acute pain in the knee due to arthrosis and reducing inflammation (non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs, analgesics). Medicines are introduced into the patient’s body both in the form of injections (intramuscular or intra-articular), and with the help of ointments and.
- As the inflammatory reactions subside, the patient is prescribed physiotherapy (laser, electrophoresis), massage and therapeutic exercises. Early inclusion of physiotherapy and exercise therapy in the treatment process allows you to maintain knee mobility.
- During the period of remission, such patients are advised to eat well, avoid hypothermia and overload of the knee, and regularly do therapeutic exercises. Additionally, depending on the degree of cartilage damage, a physiotherapist may prescribe kinesitherapy - special strength training to strengthen muscles and ligaments.
Folk recipes
In addition to medical recommendations, treatment with folk remedies can be carried out. But before you start treatment at home, it is recommended to consult with your doctor. To reduce pain you can use:
- Pork fat. Rub in before bed for a month, repeat if necessary after a 2-3 week break.
- Massage with honey. Rub liquid honey into the skin with soft massage movements, and rinse with warm water after the procedure. To achieve a lasting analgesic effect, 2 weeks are enough.
- Sunflower oil. A massage with warm oil is almost as effective as honey massage.
- Cabbage compress with honey. Spread a cabbage leaf with honey and tie it to the sore joint. Change the compress twice a day. It is recommended to wear it until the pain disappears.
- Burdock leaves. Rinse the burdock well and treat it in the same way as with a cabbage-honey compress.
In addition to external treatment methods, it is advisable to use orally:
- Lemon. Eat one small lemon a day, preferably with the peel.
- Apple vinegar. 2 tablespoons of vinegar per glass of warm water, and the healing drink is ready. Drink in small portions throughout the day.
- Mokrets. This weed is mercilessly exterminated in gardens, but it has healing properties and a pleasant taste. It must be eaten raw, adding to various salads. Regular consumption of midge helps improve metabolic processes and stimulates partial regeneration of damaged cartilage. For the winter, you can prepare the herb in the form of an alcohol tincture: fill a large container with it to the brim and fill it with vodka. Take a tablespoon 3 times a day not only for therapeutic purposes, but also as a prevention of exacerbations.
But even if traditional methods help reduce pain, there is no need to self-medicate. Alternative medicine should complement primary treatment, and not be used instead of it.
Acute arthrosis in the knee can develop at any age, and only timely treatment under the supervision of a specialist will help maintain limb mobility.
Denial of responsibility
The information in the articles is for general information purposes only and should not be used for self-diagnosis of health problems or for therapeutic purposes. This article is not a substitute for medical advice from a doctor (neurologist, therapist). Please consult your doctor first to know the exact cause of your health problem.
I will be very grateful if you click on one of the buttons and share this material with your friends
osteohondrosy.net
Arthrosis of the knee joint, or, otherwise, gonarthrosis, is a disease that deforms the tissues of the knee joint and causes acute pain and problems with movement. Gonarthrosis appears in old age and is more likely to develop in people who are overweight, especially women.
The disease is dangerous not only because of motor dysfunction, but also because of its consequences. It requires timely, correct treatment.
Stages of arthrosis
The disease is divided into three stages, each of which is worse than the previous one:
- The deformation is insignificant. Pain occurs when moving the knee joint, after exercise. Most people at the first stage do not pay attention to the symptoms and allow arthrosis to develop further
- The pain in the knee area intensifies , and it is difficult not to notice the disease. The deformation is significant, and it is almost impossible to move due to the discomfort. There is increased accumulation of joint fluid. The leg hardly bends.
- Movement is impossible. The pain is constant and does not disappear even with rest. The changes in tissues have become completely corrosive.
Important! With proper treatment, the second and third stages can be avoided. The main thing is the course of therapy.
Prevention of knee arthrosis
It all starts with basic prevention and pain prevention measures. Only after viewing them should you move on to the drugs.
Follow a few tips:
- Lose weight . If there is excess, this will help you relieve stress on your knee joints.
- Get plenty of rest and don't stand on your feet for long periods of time . Deformation occurs faster with excess load
- Avoid physical fatigue. Excess stress will worsen a bad condition, as will activity
- Be sure to consult a specialist. Only competent consultation will lead to the right course of treatment and an adequate choice of funds.
Complications of arthrosis of the knee joints
The most common complication of stages II and III is tenosynovitis of the adductor group of the thigh muscles.[22][24] This is manifested by pain along the inner surface of the joint, which intensifies with movement. The cause is muscle imbalance and deformation. With a long-term decrease in range of motion, contracture develops.[11][14] In addition, synovitis often occurs. Advanced gonarthrosis affects the entire musculoskeletal system, disrupting the biomechanics of the spinal column and other large joints of the lower extremities. This can lead to herniated discs and arthritis in other joints.[16] The second knee joint is overloaded (if the disease is one-sided), since the patient spares the sore leg, transferring the weight to the other, healthy one.
Problems that treatment aims to combat
When it comes to arthrosis, the patient is faced with several manifestations of the disease at once. The question arises: what are the specific symptoms of problems with the knee joint? These include both joint formations and pain.
The full list of symptoms is much broader:
- Acute paroxysmal or regular pain. They can lead to both minor discomfort and serious problems in life and activities.
- Weakening of the muscles associated with the affected joint. Therapy is aimed at strengthening, restoring and further maintaining the condition.
- Problems with blood circulation in affected areas. The broken connection of pinched vessels deprives the tissue of the necessary nutrition, which must be present, especially during recovery
- Decreased joint mobility. The leg does not bend precisely for this reason; the symptom must be eliminated to continue active life
- Increased pressure on the joints during deformation and the deformation itself, the main symptom of gonarthrosis
These symptoms vary in strength depending on the above stages, but any of them already requires elimination. Many drugs have been developed that need to be taken to combat them.
Classification and stages of development of arthrosis of the knee joints
Regardless of the cause, there are three stages of the disease:
- Stage I - initial manifestations. It is characterized by primary changes in hyaline cartilage.[12][18] Bone structures are not affected. The blood supply in intraosseous vessels and capillaries is disrupted. The surface of the cartilage becomes dry and it loses its smoothness. If the disease is accompanied by constant tense synovitis, then a Baker cyst develops (hernial protrusion of the joint capsule of the popliteal region).[15] After significant stress on the joint, dull pain occurs. There may be slight swelling that goes away after rest. There is no deformation.
- Stage II - the cartilaginous layer sharply becomes thinner, and in some places is completely absent.[22] Osteophytes appear along the edges of the articular surfaces. The qualitative and quantitative characteristics of the synovial fluid of the joint change - it becomes thicker, more viscous, which leads to a deterioration in its nutritional and lubricating properties.[14][16] The pain is more prolonged and intense, and a crunching sound often appears when moving. There is a slight or moderate restriction of movement and slight deformation of the joint. Taking analgesics helps relieve pain.
- Stage III - absence of cartilage in most affected areas, severe sclerosis (hardening) of the bone, many osteophytes and a sharp narrowing or absence of the joint space.[8][15] The pain is almost constant, gait is impaired. Mobility is sharply limited, and joint deformation is noticeable. NSAIDs, physical therapy, and other standard treatment methods are ineffective.[11]
Depending on the number of affected joints, unilateral and bilateral gonarthrosis is distinguished.
Fighting the disease
After finding a specialist, the patient must take care of purchasing the prescribed medications. They are selected according to the individual characteristics of the person and the stage of his disease.
Treatment options are as follows:
- injections into joints
- pain relieving ointments
- compresses
- manual therapy
- taking medications and tablets: chondoprotectors, which help restore the cartilage tissue of the knee joint, and non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs)
Let's take a closer look at the latest drugs:
1) NSAIDs. The basis of treatment, without which it is impossible to begin the necessary manual therapy. Allows you to simultaneously avoid pain and stop inflammatory processes, which is a priority for arthrosis. Options for NSAID tablets: indomethacin, piroxicam, Celebrex.
2) Chondoprotectors . If the first option does not eliminate the disease itself, but only smoothes out acute symptoms, then these drugs are aimed at eliminating arthrosis. Chondoprotectors nourish cartilage tissue and restore damaged tissue. Please note that this type does not act immediately and requires several courses of treatment. At the last stage it is completely ineffective.
Due to a misconception that has recently spread, this treatment is considered unnecessary. This is not true: protectors are an indispensable component of treatment. They must not be neglected.
The drugs consist of two substances: chondroitin sulfate and glucasamine. Manufacturers are arguing whether to use them together or not, and this debate has been going on in the medical world for quite some time. The patient does not have to think about this issue, because he is not the one who prescribes the course. But be prepared that different doctors may prescribe different medications.
Examples of drugs: Teraflex, Dona, Atra (foreign), Chondrolone and Elbona (domestic).
Important! Do not self-medicate. Treatment should be carried out only under the supervision of a specialist who can correctly calculate and adjust the amount of funds required. The medications should be taken strictly according to his prescription.
Manual therapy for arthrosis
In addition to taking pills, you should also use manual therapy. It is indispensable for motor dysfunctions and will help quickly get rid of symptoms.
Before carrying out therapy, it is necessary to use warming procedures. They can consist of light exercises, or the best solution for arthrosis of the knee joint is visiting the pool and physical therapy. Such exercises do not put stress on the joints and are absolutely painless for the patient.
After the warm-up stage, they move on to the therapy itself. It can be carried out in water if the disease has become serious.
So, the order of its implementation:
- Movements are carried out along the lymph flow to enhance the effect
- Pain and discomfort should not be allowed. If this happens, change your doctor - he is not qualified.
- The patient can practice massage for arthrosis independently, but only after consultation with the attending physician
- For additional heating, special ointments and compresses are used.
Warming agents both relieve discomfort and make tissues more susceptible to treatment.
Diagnosis of arthrosis of the knee joints
The diagnosis is made by an orthopedic traumatologist, and in the vast majority of cases, an examination and x-ray of the knee joint in two projections (direct and lateral) is sufficient.[2][19] Clinical data and images help determine the stage of the disease.
In the early stages of the disease, with minor changes in bone tissue, X-ray examination is not so valuable.[5][8] At this stage, gonarthrosis can be diagnosed through arthroscopy.[5][8] The accuracy of the method is very high; only its invasive nature and price can stop it.
Ultrasound does not allow clear visualization of changes in articular cartilage and intra-articular structures.[15] MRI can detect changes in the bone, cartilage and soft tissue structures of the joint, as well as subchondral bone, with 85% accuracy.[15] Scintigraphy can be used to assess the metabolic activity of periarticular bone tissue.
An increased content of phosphorus and calcium in dehydrated synovial fluid is evidence of the destruction of osteochondral tissue of the joint and the accumulation of degradation products. Blood is also examined - general analysis and erythrocyte sedimentation rate (ESR); determine the level of fibrinogen, urea and other biochemical parameters of blood and urine.[16]
Preventing further manifestations
Osteoarthritis of the knee requires constant monitoring. The prevention tips presented above should not be neglected.
A few more points are added to them if you want to consolidate the result:
- Do physical therapy. It will help strengthen the muscles around the joints and reduce the risk of relapse.
- Exercise therapy is also useful for general development
- Avoid overload even after completing a course of treatment. They are always harmful to joints
- Visit your doctor regularly and get examined at the slightest suspicion.
Arthrosis is a disease that requires timely treatment. Its consequences are colossal if the disease is neglected. Contact a specialist if you find symptoms of gonarthrosis without delay.
www.medware.ru