Benefits of probiotics
Probiotics contain beneficial bacteria that populate the intestinal microflora and prevent infectious and inflammatory diseases of the gastrointestinal tract. They create a protective layer on the mucous membrane, thanks to which pathogenic bacteria do not penetrate the blood and tissues of the body.
Probiotics contain only non-pathogenic strains of bacteria. These are lacto-, bifido-, colibacteria, entero- and aerococci, yeast fungi. They support the functioning of the gastrointestinal tract, as well as:
- normalize microflora, prevent infections and inflammation in the intestines;
- strengthen the immune system;
- improve gastrointestinal motility, as well as the absorption of nutrients;
- regulate water-salt balance.
Probiotics prevent gastrointestinal diseases, diseases caused by Candida fungi, E. coli, and rotavirus. They also reduce the risk of dysbiosis, which often develops after taking antibacterial drugs.
The beneficial properties of probiotics are described in the video:
Taking probiotics during antibacterial treatment
Translated from Greek, probiotic means “for life,” antibiotic means “against life.” These two groups of drugs produce opposite effects. The action of probiotics is aimed at the growth and reproduction of beneficial microorganisms, and antibiotics are aimed at destroying all bacteria, regardless of whether they are good or pathogenic.
Note! Probiotics restore intestinal microflora. They are useful to use after taking antibiotics.
When treating bacterial diseases, the intestinal microflora is disrupted. Therefore, drinking probiotics while taking antibiotics is not only necessary, but necessary. They populate the intestines with living bacteria, prevent the occurrence of dysbacteriosis, diarrhea, and also:
- abdominal pain, bloating, increased gas formation;
- allergies in the form of itching, urticaria, angioedema and anaphylactic shock;
- reducing the body's defenses;
- candidiasis.
The most common consequence of treatment for bacterial diseases is antibiotic-associated diarrhea - stool disorder that recurs for two or more days. It is dangerous for humans, since in this condition the gastrointestinal tract does not absorb vitamins and minerals.
Probiotics should be taken simultaneously with antibiotics from the first days of treatment. And after completing the course, you need to continue taking it and not stop until the body’s defenses are completely restored.
Probiotic preparations are of the following types:
- Monocomponent. Contains one strain of beneficial bacteria (bifidobacteria, lactobacilli, E. coli, enterococci, etc.
- Multicomponent (symbiotics). They contain several types of living microorganisms.
- Synbiotics. Preparations containing pre- and probiotics.
- Multiprobiotics. They contain more than 7 strains of bacteria.
It is difficult to answer which medications are better. After all, it is necessary to take into account not only the number of strains, but also their concentration, survival in the acidic environment of the stomach, release form, and shelf life of the drug.
But most doctors recommend taking multicomponent probiotics with prebiotics together with antibiotics. They increase each other's efficiency.
Note! Prebiotics are compounds that feed living microorganisms. They are necessary for the growth and reproduction of beneficial flora.
After the end of treatment, you can not change the product containing beneficial bacteria, but continue to use it.
List of probiotics
Modern pharmaceutical companies produce a huge number of probiotics in different dosage forms. These can be dry powders that are diluted with water, liquid forms or capsule preparations. They also differ in price: domestic drugs are cheaper, imported analogues are much more expensive.
The first generation of probiotics consists of monocomponent products that contain one strain of beneficial bacteria. The list of “live medicines” of this group consists of several popular names:
- Bifidumbacterin;
- Lactobacterin;
- Colibacterin;
- Biobakton.
Second generation drugs contain yeast-like fungi and spore bacilli. These microorganisms are not part of the typical intestinal microbiocenosis, but displace pathogenic bacteria. Drugs in this group include:
- Bactisporin;
- Baktisubtil;
- Biosporin;
- Sporobacterin;
- Flonivin;
- Enterol;
- Esterogermina.
The third group consists of multicomponent and combined products. They simultaneously contain several strains of bacteria, as well as prebiotic additives that create optimal conditions for the growth of colonies of beneficial microorganisms. The list of these medications is quite large:
- Linux;
- Acipol;
- Acylact;
- Bifilong;
- Bifiform;
- Biphilis;
- Polybacterin;
- Simbiter;
- Hilak-forte.
Medicines in this group are often prescribed to be taken with antibiotics to prevent pathologies of the digestive tract in adults and children.
Drugs of the fourth group effectively inhibit pathogenic microflora, preventing its reproduction. This occurs due to the effect of sorbed bacteria on the microbiocenosis. As a result of therapy, the symptoms of diarrhea and pain disappear. The most famous drugs in this group:
- Florin;
- Probifor;
- Bifidumbacterin forte.
Important! The list of drugs is presented for informational purposes. Any medicine must be prescribed by a doctor, taking into account the specific disease and health status of the patient. Some “live medicines” do not combine well with certain types of antibiotics. Even a relatively safe remedy for normalizing intestinal microflora can harm the body and provoke flatulence, bloating, constipation, urinary or cholelithiasis, obesity, and allergic reactions.
Review of drugs
When taking antibiotics, it is worth using probiotics that have antibiotic resistance, that is, those that have an increased ability to survive antibiotic therapy. These include drugs:
- RioFlora. Contains 8 strains of lacto- and bifidobacteria.
- Primadophilus. The drug is available in several variations - for adults, adolescents, and children under 5 years of age. It contains lacto- and bifidobacteria.
- Linux. A mixture of lacto-, bifidobacteria and enerococci.
- Baktisubtil. This drug is made from fungi, as well as spore bacilli.
- Enterol. This is an antidiarrheal agent based on Saccharomyces boulardii (yeast).
After completing a course of antibiotics, it is better to choose another probiotic, since the treatment period usually does not exceed 14 days. It can be replaced with one of the following mono- or polycomponent drugs:
- Maxilac;
- Enterozermina;
- Bifidumbacterin;
- Lactobacterin;
- Bifiform;
- Simbiter;
- Hilak Forte;
- Florin;
- Probifor;
- Acipol.
Maxilak contains 9 strains of probiotic cultures and a prebiotic. It is effective for irritable bowel syndrome. In case of allergic reactions, you should choose Probifor, as it contains a sorbent. Acipol will cope with bloating, as well as increased gas formation, and Hilak Forte will cope with diarrhea.
Is Hilak Forte a probiotic or a prebiotic?
Many have heard about the drug Hilak Forte, which is often prescribed by doctors for various digestive problems. This is a development of the German pharmaceutical company Ratiopharm. At first glance, it seems that this drug is just one of a huge group of drugs that eliminate dysbacteriosis. Let's try to figure out whether Hilak Forte is unique. There are so many analogues of this product that it can be difficult to make a choice. Some people mistakenly believe that Hilak is a bacterial drug, but this is not the case.
This product is not a probiotic; it is based on an embryoless (that is, not containing living or lyophilized cells) aqueous substrate of the metabolism of certain intestinal bacteria. In particular, these are E. coli Lactobacillus helveticus and acidophilus, Streptococcus faecalis. As excipients, Hilak contains lactic and phosphoric acid, sodium and potassium phosphate, and preservatives. The drug is available in liquid form, which makes dosing Hilak Forte convenient.
The drops must be diluted in some liquid, for which it is better to use sour juice or fruit drink, where the taste of the drug will not be noticeable. This method is well suited for children, especially infants who have already been introduced to complementary foods; in this case, they may not even notice that they are taking medicine.
Take Hilak three times a day before or during meals.
The drug is not diluted with milk - it curdles due to acid. The dosage of the drug is prescribed by the doctor. Usually this is 50 drops for adults, 30 for children and 15 for babies under one year old. The drug is taken for at least a week, then, as the condition improves, the dosage can be changed to maintenance - this is half of the therapeutic dose. An opened bottle should be consumed within a month and a half, and if sealed it can be stored for up to 4 years.
What is dysbiosis
In a healthy body, there is a balance between beneficial, opportunistic and pathogenic microbes . Together they create the microflora, or microbiome. Beneficial species and strains of bacteria are involved in metabolism, creating vitamins and antibodies for the immune system.
Dysbacteriosis is inhibition of the growth of bifidobacteria and lactobacilli (lactic acid bacteria), as well as other, less known “good” microbes. At the same time, pathogens multiply intensively, which is associated with intoxication and putrefactive processes.
Causes and symptoms
The number of so-called good bacteria in the intestines decreases with changes in diet , vitamin deficiency, stress, infectious diseases, and fasting. Parasites and tumor processes also change the normal microflora.
Reference. Dysbacteriosis occurs especially quickly when taking penicillin and tetracycline antibiotics, chloramphenicol, and sulfonamides.
The causes of vaginal dysbiosis in gynecology are sexually transmitted infections, too frequent douching, and improper washing. Sometimes the same effect is associated with contraception.
Methods for treating disturbed microflora
To normalize the microbiota, pro- and prebiotics and symbiotics are used .
Ideally, a doctor should prescribe these medications for dysbiosis after examining the composition of the microflora. In practice, they often do without expensive examinations.
Experts pay attention to the composition of the drugs and indications , as well as reviews from colleagues. Most often, agents are prescribed that include beneficial strains of Bifidobacterium, Lactobacillus, Saccharomyces, and Escherichia coli.
Symptomatic therapy consists of the use of intestinal sorbents and drugs that regulate stool. Functional disorders in the gastrointestinal tract are corrected by digestive enzymes.
Important! Complex treatment of dysbiosis - use of at least 3-5 groups of drugs.
Classification of drugs for dysbiosis
Probiotics alone are not enough to improve microflora . They take medications for rumbling and bloating, heaviness in the abdomen, and heartburn. The goal of symptomatic therapy is to relieve the patient of discomfort. Next, it is necessary to normalize the functioning of the intestines - our “second brain”, an organ on which the functioning of the immune system depends 80%.
How do probiotics work?
The more diverse the microflora, the better for the body . Therefore, medications and dietary supplements with different types and strains of beneficial microorganisms are preferable.
How probiotics work:
- They stop the depletion of intestinal microflora during antibiotic therapy, help increase the number of “good” microbes and suppress “bad” microbes.
- Lactobacilli act predominantly in the small intestine, bifidobacteria - in the large intestine. They enrich the intestines of a child and an adult with beneficial microorganisms if there is an imbalance due to changes in diet or stress.
- In addition to the direct effect on the composition of microflora, they have an indirect positive effect on the body. After developing healthy intestinal flora for several weeks, digestion improves and the immune system is strengthened.
- “Good” bacterial strains reduce intestinal inflammation and prevent its development.
It is not easy for bacteria from a drug to take root in the intestines of a particular person. Therefore, experts recommend taking a probiotic from 2 weeks to 1.5 months.
Attention! It is more difficult to restore the microflora of a child’s intestines than an adult.
The probiotic in powder form contains specially dried microorganisms . They resume their vital functions when mixed with liquid. It is important that beneficial bacteria are viable, colonize the intestines and begin to participate in metabolism.
The ampoules are opened and the powder is dissolved before use . You cannot store the already prepared solution. Liquids are easier to dose and give to young children. Reviews from parents and pediatricians about probiotic drops are most favorable.
Original imported medicines are more expensive. There are inexpensive, but no less effective domestic drugs. The possibility of replacement should be discussed with your doctor or pharmacist.
Sorbents
This group is prescribed for flatulence, overeating, dyspepsia, allergic diseases, dysbacteriosis, and parasite infestation.
The cheapest intestinal sorbent is activated carbon. White coal is produced not from carbon mass, but from silicon dioxide. The drug is affordable, acts quickly and effectively. A relatively expensive intestinal sorbent, Enterosgel, absorbs cholesterol, bacteria, some viruses and fungi .
The selective effect is manifested in the preservation of the molecules of most vitamins, proteins, and enzymes. Medicine for diarrhea, allergies and dysbiosis for adults is produced in the form of an unsweetened paste, for children - in the form of a fruit-flavored gel. Adsorbents retain toxins, microbes, and gases in the pores. Excretion is carried out naturally - through the rectum. Enterosgel and Polysorb MP have the greatest absorption capacity . These drugs are 50-100 times more expensive than activated carbon. Smecta is often prescribed to a small child. A cheap domestic analogue is Neosmectin (140 rubles).
Enzymes
The preparations contain pancreatin . The pancreatic enzyme complex improves digestion and absorption in the intestine. With dysbacteriosis, both processes are disrupted.
"Festal", in addition to pancreatin, contains bile acids . It is recommended for use in cases of enzyme deficiency resulting from dysbacteriosis, in combination with cholecystitis.
My choice of probiotics for children and adults
Our pharmacy probiotics do not meet the standard - the dosages are very small and are not tested. Therefore, I prefer American thermostable high-quality probiotics from the iHerb store:
ADULTS
✿ Jarrow Formulas, Saccharomyces boulardii + MOS, 5 billion, 30 pcs. Ingredients: Saccharomyces boulardii already with prebiotic fiber.
✿ Solgar, Advanced Multi-Billion Dophilus, 60 drops. — 5 billion CFU, 4 strains of bacteria, not many, but the most important for the intestines.
✿ Nutrition Now, PB8, original recipe, 120 drops. — 14 billion bacteria per serving, 8 strains of lacto and bifidobacteria + prebiotics.
✿ California Gold Nutrition, LactoBif Probiotics, 60 drops. is an iHerb brand, 30 billion CFU, 8 strains of lacto and bifidobacteria.
✿ Garden of Life, Primal Defense, HSO Probiotic Formula, 90 drops. - the source of probiotics is homeostatic soil organisms, in other words, bacteria that live in good healthy soil and should, in theory, be supplied to the body with high-quality organic vegetables and herbs. It has an exemplary composition: Saccharomyces Boulardii + 12 strains of lacto and bifidobacteria. High bioavailability.
✿ Garden of Life, For children, probiotic formula with banana flavor, 76.8 g Ingredients: a mixture of probiotic Boulardi mushrooms with probiotic bacteria of 6 cultures + prebiotics, including inulin. 4 billion CFU.
✿ Nature's Plus, Animal Parade, 90 Chewable Tabs. in animal form - 1 billion CFU, 8 probiotic strains + fructooligosaccharides with grape seed.
For small children under 2 years old, it is better to use drops, 2 options:
✿ Mommy's Bliss, Probiotic Drops, 15-day course, for newborns, 6 ml - Lactobacillus rhamnosus GG, 1 billion cells per serving. ✿ Jarrow Formulas, Probiotic Drops for Infants, 15 ml - Bifidobacterium Longum Subsp. Infantis M-63, 1 billion CFU. Both types of probiotics help babies easily switch from breastfeeding to complementary foods.
How to choose probiotics for the intestines: list of drugs
Probiotics are live bacteria - microorganisms that live in the human body and have a positive effect on its vital functions.
Probiotic preparations contain different strains of bacteria. There are bifido-containing, coli-containing, and lactose-containing preparations. The composition may also contain yeast-like fungi, enterococci, aerococci, depending on the manufacturer and purpose. Probiotics are available in liquid and dry form.
Probiotics not only allow you to populate the intestines with the right microorganisms and overcome pathogenic flora that causes various unpleasant symptoms, but also make it possible to increase immunity and effectively fight ailments. In this article, we look at inexpensive yet effective gut probiotics. You will find reviews, as well as a list of drugs with prices, just below.
Eubiotics, probiotics, prebiotics, synbiotics: mechanism of action
Probiotics are living organisms that:
- when introduced into the human body in sufficient quantities, they have a positive effect on health;
- can be included in foods and medicines.
There are many microorganisms that theoretically have health benefits, but there is little practical evidence of these benefits through evidence-based research.
Prebiotics are substances that are not absorbed from the gastrointestinal tract and stimulate the growth and activity of beneficial intestinal microflora and thus have a positive effect on health.
In other words, prebiotics are food for beneficial microbes.
Synbiotics are medicines and foods that contain probiotics and prebiotics. Everything is clear here and no more detailed explanation is required.
Eubiotics. The concept of “eubiotic” is more complicated. Some scientists consider the terms "probiotic" and "eubiotic" as synonyms. But most believe that eubiotics are biologically active food additives containing live microorganisms and (or) their metabolites. The difference here is huge and fundamental! In order to be called a eubiotic, it is not at all necessary to bring scientifically proven benefits; it is not at all necessary to enter the intestines alive and “in sufficient quantities.” Obviously, all probiotics are eubiotics, but the opposite is not always true (to put it mildly).
When are probiotics prescribed?
According to the American Gastroenterological Association, probiotics are currently most commonly prescribed to treat the following diseases and conditions:
- Infectious diarrhea caused by rotavirus infection, including in infants and young children - strains of lactobacilli of the species Lactobacillus rhamnosus and Lactobacillus casei.
- Irritable bowel syndrome - probiotic strains of lactic acid bacteria Bif > Antibiotic-associated diarrhea - Saccharomyces boulardii can prevent relapses of the most dangerous and most common antibiotic-associated diarrhea caused by Clostridium difficile.
In addition, a gastroenterologist can prescribe probiotics if the patient complains of stool problems, colic and frequent bloating and flatulence, a feeling of heaviness in the stomach, as well as other conditions.
How to take it correctly?
It is very important to choose the right probiotic to treat a specific condition. To select a probiotic, you can use the following simple rules:
- If bacterial damage to the intestines is suspected (acute or chronic), it is recommended to take complex preparations containing lactobacilli and bifidobacteria at the same time (for example, Bacteriobalance, Bifidin, Linex, etc.).
- If you suspect a viral infection of the intestines (acute or chronic), it is recommended to take medications containing lactobacilli (for example, Lactobacterin, Narine, Biobakton, Primadophilus, etc.).
- If you suspect a fungal infection of the intestines and genitals (intestinal and vaginal candidiasis), it is recommended to take medications containing bifidobacteria (for example, Probiform, Biovestin, Bifidumbacterin, etc.).
When treating intestinal dysbiosis, it is recommended to first take drugs with lactobacilli, then with bifidobacteria, and only after that with colibacteria (for example, Colibacterin). You can immediately start taking complex medications that simultaneously contain bifidobacteria and lactobacilli.
Probiotics and prebiotics: what's the difference?
The names of these two groups of drugs are very similar, so they are often confused.
- Probiotics are live microorganisms that belong to the normal intestinal microflora.
- Prebiotics are organic chemicals that have the ability to create excellent conditions for the proliferation of normal intestinal microflora.
It should be noted that the effect of both prebiotics and probiotics is similar, because each of the groups of these drugs normalizes the intestinal microflora.
Beneficial features
Most probiotic bacteria belong to two genera: lactobacilli (Lactobacillus) and bifidobacteria (Bifidobacterium), although you should know that there are many other types of probiotic bacteria.
These drugs are capable of:
- Produce substances that prevent various infections.
- Prevent bacteria harmful to humans from attaching to the intestinal wall and inhibit their growth.
- Inhibit the secretion or destroy toxins secreted by some bacteria that are “bad” for the human body.
- Stimulate the strengthening of the mucous layer in the intestines as a barrier against infections.
- Increase the effectiveness of the immune system by secreting antibodies to certain viruses.
- Produce B vitamins necessary for food metabolism, preventing anemia that occurs due to vitamin deficiency
- B6 and B12, as well as maintaining skin and nervous system health.
The described effects are, to a greater or lesser extent, characteristic of all microorganisms related to probiotics. However, the mechanisms of these effects have not yet been fully elucidated.
Probiotics for the intestines: list and prices
To maintain intestinal health, the following medications may be prescribed:
- Linex is one of the most famous probiotics that are common in Russia. It contains three components of microflora, which are located in different parts of the intestine. Price 350-500 rub.
- Bifidumbacterin forte. It is often used in pediatrics for conditions characterized by disturbances in the colonization of the intestinal flora, in combination with antibiotics and other drugs. Contains Bifidobacterium bifidum N1 in dry powder form. Price 350-400 rub.
- More concentrated bifidobacteria are contained in Probifor - one sachet contains about 10 servings of bacteria that are found in Bifidumbacterin. Price 500-600 rub.
- Bifiform. In addition to probiotic strains of lacto- and bifidobacteria, it contains Escherichiacoli. Combined with antibiotic therapy, thanks to the protective capsule it easily overcomes the acidic environment of the stomach. It is one of the best capsule probiotics for adults. Price 350-400 rub.
- Florin forte. It is a powder containing lacto- and bifidobacteria. It is prescribed for both adults, children and newborns. Thanks to the combination of bacteria, it has a complex effect, but does not combine well with some antibiotics. Price 500-550 rub.
Depending on the time of creation and improvement, several generations of probiotics are distinguished:
- I generation - classic monocomponent preparations, consisting of one strain of microorganisms - typical inhabitants of the intestines (bifidumbacterin, lactobacterin, etc.);
- II generation - self-eliminating antagonists (bactisubtil, enterol, biosporin, etc.);
- III generation - multicomponent preparations (symbiotics), consisting of several (from 2 to 30) strains of bacteria (Bifilong, etc.) or several types of bacteria (Linex, Bifikol, etc.);
- IV generation - combined preparations (synbiotics), consisting of a strain of bacteria and ingredients that promote their growth, reproduction and metabolic activity (bifiliz, kypacid, etc.);
- V generation – multicomponent combination preparations (synbiotics), consisting of several types of bacteria and ingredients that promote their growth, reproduction and metabolic activity (floristin, bifiform, etc.).
In addition, the form of the probiotic must be taken into account. They are all divided into:
- Dry probiotics (lactobacterin, bifidumbacterin, colibacterin, etc.);
- Liquid forms (biovestin, biovestin-lacto, floristin, trilact, bifidum No. 791 BAG, liquid bifido- and lactobacterins, lactoflor, etc.);
- Sorption forms (ecoflor, probifor, bifidobacterin forte, bificol forte, etc.);
- Capsules with enteric coating (Linex, Bifiform).
Maxilak for the intestines
The intestinal microflora performs several functions: strengthens the immune system, prevents the colonization of the intestines by foreign bacteria, synthesizes vitamins, reduces intoxication of the body, enhances the production of interferons, and eliminates the development of allergies and inflammatory processes in the intestines. Disruption of the intestinal microflora can be caused by food poisoning, the use of antibiotics or diseases of the gastrointestinal tract. One way to restore microflora is to use synbiotics - dietary supplements that are a combination of pre- and probiotics. Such dietary supplements include the drug Maxilac. It is sold in both Russia and Ukraine.
Maxilac is allowed to be taken by adults and children over 3 years of age.
The daily dose is one capsule, taken once a day during meals (preferably in the evening). If the drug is prescribed to a child under five years of age, before administration, the capsule is opened and its contents are poured into a liquid (milk or water) at a temperature of up to 40°C. The contents of the capsule are mixed with liquid and immediately given to the patient.
There have never been any cases of overdose with Maxilac during the entire period of its clinical use. Exceeding the dosage specified in the instructions may result in the development of one or two diarrhea. In such cases, it is recommended to monitor your stool.
Probiotics in foods
Sources of prebiotics are: dairy products, bread, cereals, peas, corn flakes, garlic, bananas, onions, beans and some other types of foods. One of the most popular foods that provides probiotic intake is yogurt.
In addition, their sources are: most dairy products, for example, cheese, kefir, cottage cheese, buttermilk. Some other examples of probiotics include sauerkraut, kimchi, pickles, bread, wine, soy sauce.
Can I take probiotics after a course of antibiotics?
Antimicrobials, or antibiotics, are used in medicine to fight bacterial infections. In almost a hundred years since the discovery of penicillin, antibiotics have saved more than one million lives, successfully coping with many dangerous diseases, for example, pneumonia, cholera, and tuberculosis.
However, the unjustified prescription of antibiotics, their independent use by patients without the supervision of a doctor, as well as the ability to purchase drugs in pharmacies without a prescription lead to the fact that humanity will soon face the so-called post-antibiotic apocalypse.
This phenomenon is caused by the growth of antibiotic-resistant bacteria (superbugs). According to scientists, soon even a slight ailment can develop into a fatal disease. Another problem associated with antimicrobial drugs is their ability to inhibit intestinal microflora, increasing the manifestations of dysbiosis. Below we will look at how to avoid unnecessary use of antibacterial drugs, and whether it is worth taking probiotics after a course of antibiotics.
Contraindications
Although probiotics do not interfere with antibiotics, they may interfere with other medications. For example, scientists have observed that a species of bacteria called Lactobacillus acidophilus speeds up the absorption of the drug sulfasalazine by the body. At this stage, doctors cannot say whether this interaction is harmful or not.
They may cause an allergic reaction and mild stomach problems, especially in the first few days you start taking them. But stomach symptoms usually go away once your body gets used to the probiotics, which is not the case with an allergic reaction.
Additionally, an autoimmune condition such as celiac disease (which causes the immune system to attack its own tissues) may require immunosuppressive medications. By suppressing your immune system, immunosuppressants make your body more susceptible to disease. In this case, probiotics may backfire and cause bacterial or yeast infections. Therefore, be sure to consult with your doctor before taking probiotics to reduce the risk of harmful reactions.
How to properly take probiotics with antibiotics?
Even the healthiest of us may need to take an antibiotic at some point in our lives. I don’t treat them very well, but what to do if a bacterial infection takes you by surprise...
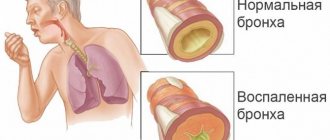
Antibiotics are very important and effective in treating serious infections, but they can cause a lot of unpleasant side effects, from diarrhea and thrush to more serious inflammatory and immune conditions.
It turns out that just one week of taking antibiotics can change the composition of the gut microbiota for up to a year.
Another serious problem after a course of antibiotics is the appearance of clostridia (Clostridium difficile) , an opportunistic pathogen that thrives in an intestine empty of beneficial bacteria and rich in carbohydrates. The number of these bacteria can increase greatly and completely replace the natural environment of the intestines, causing inflammation, diarrhea and fever. At the same time, clostridia produce a lot of toxins and are difficult to treat.
Taking probiotics with antibiotics may help
One recent study confirmed that patients taking probiotics during a course of antibiotics had a dramatic reduction in the risk of clostridial infections .
Probiotics not only quickly restore the original intestinal microflora, prevent diarrhea and the colonization of pathogenic bacteria instead of beneficial ones , but also reduce resistance to antibiotics, ensuring people take the full course of prescribed antibiotics.
Why take probiotics after antibiotics?
Since antimicrobial drugs usually destroy all microorganisms, this can lead to an imbalance of the microflora, which is manifested by the following symptoms:
- antibiotic-associated diarrhea;
- nausea, loss of appetite, bloating;
- manifestations of thrush in women;
- skin rash.
Pathogenic microbes can take the place of beneficial bacteria. And then long-term consequences of taking antibiotics associated with immunodeficiency conditions occur. A person may be bothered by allergies, frequent colds, and sometimes autoimmune diseases develop due to uncontrolled use of antibiotics. This pathology can affect any organ system.
To avoid negative consequences, it is important to take probiotics after a course of antibiotics. They will prevent harmful consequences for the intestinal microflora and accelerate the disappearance of pathological symptoms. Beneficial bacteria secrete postbiotic substances that are involved in hundreds of biochemical reactions in our body. Their benefits are difficult to overestimate, since microbes directly or indirectly regulate everything that happens in the human body.
How probiotics cope with the problem
Research shows the effectiveness of probiotics in preventing diarrhea (caused by antibiotic use). Additionally, studies have confirmed that probiotics rarely cause side effects, even in children. Taking probiotics before, during, and after a course of antibiotics will help maintain balance in your digestive system. The main thing is to know how to take antibiotics and probiotics correctly.
Here are some benefits of probiotics:
- Probiotics restore microflora disturbed by antibiotics;
- Taking a probiotic helps repopulate your digestive tract with beneficial bacteria;
- They reduce symptoms of antibiotic-associated diarrhea;
- They inhibit bad bacteria and prevent them from sticking to the intestinal walls.
Rules for taking probiotics with antibiotics
Since probiotics and antibiotics are essentially antagonists, it is important to follow the rules for taking these medications. Otherwise, the results from probiotics will be neutralized. Remember 5 simple rules for taking probiotics during a course of antibiotics:
- take medications at different times of the day. The recommended period is at least 2 hours. However, it is better if you take the medicine in the morning and the dietary supplement in the evening. For example, you can drink an antibiotic at 9 o’clock in the morning, and a probiotic at 7 o’clock in the evening, after dinner. This way you can avoid the neutralization effect.
- Read the instructions for the medications to follow the recommendations. For example, OM-X® probiotics from Dr.OHHIRA are taken 1 capsule twice a day, after meals, with a small amount of water.
- Take care of your nutrition. Experts recommend eating as many vegetables of different colors as possible that contain fiber. Avoid sweets, baked goods, gluten and whole milk, which contribute to the development of leaky gut syndrome.
- Add probiotics to your diet in food form. Pickled vegetables, fermented milk products, miso soup, kimchi, kombucha - choose what suits your taste and consume at least one serving per day.
- Minimize toxic exposure. If you are taking antibiotics, your immune system is already overworked. Help her by giving up cigarettes and alcohol.
If you have not previously taken probiotics, start taking them on the first day of your antimicrobial course.
A few words about probiotics
A lot has been written and said about them, because without these bacteria it is very difficult for any organism. Today, there are many medicines containing probiotic microorganisms, and some food products contain them in large quantities and support the intestinal and stomach microflora in the desired condition.
For example, I drink sauerkraut juice 2 times a day: in the morning on an empty stomach and in the evening before bed. 2-3 sips are enough for me. There is also an article where more is written about kombucha, kimchi, natural yogurt and beet kvass.
- Probiotics consist of 5 groups of microorganisms: aerobes, anaerobes, bifidobacteria, yeast fungi and lactobacilli.
- We can use them both in dry form (tablets, powders, capsules) and in liquid form (suspensions and emulsions). Yes, they are also in products. It is important to know that in dry form there are no living microorganisms, but only strains that are activated several hours after entering the stomach.
- Of course, it is better to take probiotics in liquid form, as they begin to act instantly. But in dry conditions only after 2 - 4 hours.
- Another important detail: probiotics should not be confused with prebiotics, since the latter are found in vegetables and fruits and provide “food” in the form of carbohydrates for beneficial bacteria: garlic, onions, asparagus, chicory, bananas and tomatoes. You can find out more in the article written on this topic.
When there are not enough beneficial bacteria in the intestines, various problems begin: dysbiosis, allergic reactions, constipation or, conversely, diarrhea, as well as weakness, nausea, stomach pain, and the general condition is not very good. How to take probiotics correctly, and do you need to take them constantly? Let's look at the main cases when you really need beneficial bacteria.
Should I take antibiotics and probiotics together?
Often, the doctor prescribes medications for treatment that help get rid of one disease, but very hard on the stomach and intestines. This happens because along with harmful bacteria and viruses, infections also kill those very necessary microorganisms. Moreover, an imbalance in the intestines appears after a few weeks in the form of the above symptoms.
Don't forget that you can eat meat loaded with antibiotics or eggs that also contain them. After all, chickens are fed food with antibiotics so that they don’t get sick.
Probiotics must be taken along with antibiotics.
- If you are prescribed to take them at the same time as antibiotics, take the beneficial bacteria 2 hours before the medicine and 2 hours after the antibiotics. It is this period of time that protects the vital activity of beneficial bacteria from being destroyed by antibiotics.
- When the course of antibiotics has been completed, carefully read the instructions. Probiotics are taken half an hour before meals.
- After completing a course of antibiotics, you need to take probiotics for another 2 weeks.
- It is important to take a full course of microflora restoration, and not drink probiotics from time to time. Then you may not be able to see the effect, since our smart body reacts very subtly to any actions, and simply cannot get used to the fact that you are helping it.
As for medical preparations, you can use the drug Biobalance B produced or analogues. It is important that the composition contains the following bacteria: Lactobacillus acidophilus, Lactobacillus rhamnosus and Bifidobacterium lactis.
What to do if you have thrush?
There are many drugs that can be used to treat this disease. Probiotics not only support the gastrointestinal tract and the body as a whole, but also help get rid of this disease.
Depending on your test results, your doctor will prescribe the most appropriate thrush remedy for you. In addition, the instructions always indicate the dosage.
Here are examples of the most famous drugs:
- There are products containing both probiotics and prebiotics: Bifiform, Polybacterin, Bifidumbacterin forte. Here the course of treatment is 5 - 10 days, 1 suppository.
- Linex, Yogulakt, Maxilak. Here one capsule is taken three times a day.
- Top items on the list are garlic and unsweetened sourdough yogurt. A day is enough to eat at least one clove of garlic and drink one serving of yogurt in the morning and evening. They carry the necessary supply of microorganisms into the body to strengthen the immune system.
- You need to exclude all yeast products containing sugar, white bread, white potatoes and white rice.
Probiotics versus antibiotics: which is healthier?
According to a recent study led by Daniel Merenstein, patients who regularly took probiotics received 29% fewer antibiotic prescriptions. Based on the findings, Dr. Merenstein declared, “Consumption of probiotics reduces the duration and severity of certain types of acute respiratory and intestinal infections.” These findings are particularly important in light of the rapid increase in antibiotic-resistant bacterial infections.
The positive effect of probiotics on the immune system is due to postbiotic substances, which are the “secret of the microbiome.” Postbiotics are currently under close research attention.
Renowned integrative medicine physician Ross Pelton argues that a greater variety of microbiome is the key to health. “Greater microbiome diversity” means that your gut is home to a wide range of different types of bacteria, which in turn produce a variety of postbiotic metabolites.
Why are probiotics needed?
Author KakSimply!
A probiotic preparation is a certain amount of live microorganisms that have a positive effect on the immune system and intestinal microflora. Probiotics prevent the proliferation of bad bacteria and restore the balance of good bacteria after taking antibiotics or a long-term illness that has weakened the body.
This remedy has a positive restorative effect in the presence of acute intestinal infections, reducing the duration of the disease and healing the intestinal mucosa. They are also effective for diarrhea caused by taking antibiotics or various types of poisoning.
Research on the use of probiotics for various diseases of the gastrointestinal tract gives the most positive results.
Doctors recommend taking this medicine for persistent constipation, chronic intestinal inflammation, lactose intolerance, and irritable bowel syndrome. In addition, probiotics can be taken for upper respiratory tract infections, and can also be taken as an additional therapeutic agent for atopic dermatitis. Remember that before taking probiotic medications, it is advisable to consult with your doctor, who will accurately determine the type and dosage of the medication.
If a person’s health does not concern him, he does not need probiotics to support optimal intestinal microflora. Healthy people can do this through diet—natural probiotic nutrients are found in many foods. So, a sufficient amount of them can be obtained from fermented milk products, juices, chocolate, tomatoes, asparagus, bananas, onions, garlic and whole grain wheat. These products act as a nutrient medium for these beneficial bacteria and increase their content in the small intestine.
The maximum amount of natural probiotic substances is contained in the exotic fruit – kiwi.
Some people ask the question: “in what form is it best to take probiotics?” Nutritionists say that each form of probiotics serves a specific role. For example, it is advisable to take fermented dairy products with beneficial lactobacilli as a preventive measure or for uncomplicated disorders of the gastrointestinal tract. Probiotics in dosage form (drops, capsules, tablets) are prescribed by a doctor in the presence of acute diseases or in case of prolonged complaints of a person about intestinal problems. The main rule for taking probiotics is to take enough of them so that they can fully provide a good and long-lasting therapeutic effect.
Video on the topic
Why are probiotics needed?
www.kakprosto.ru