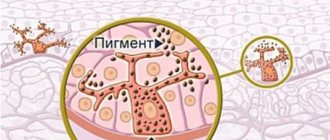
Melasma, also called chloasma, is a common skin condition in adults that develops light brown or grayish pigmentation, often affecting the face. The problem can arise for anyone, regardless of race or gender. Dermatologists note that a larger percentage of patients with this problem are women, as well as dark-skinned people living in sunny climates. The pathology is often observed in Asia, the Middle East, South America, Africa and the Indian subcontinent.
Melasma usually becomes more noticeable in the summer, with improvement observed in the winter months. This is not an infection, it is not contagious and is not associated with allergies. It is also worth noting the nature of the problem. This is not a malignant phenomenon, therefore it cannot turn into skin cancer.
Melasma and chloasma - is there a difference?
There is no definite opinion among scientists regarding whether these concepts are synonyms of one disease or not. The difference in definition lies in the causes of hyperpigmentation. That is why the concepts of “Melasma” and “Chloasma” are somewhat different.
- Melasma is a broader concept that does not include the cause of its occurrence.
- Chloasma is a simplified manifestation of melasma, which is a pathological hyperpigmentation caused by pregnancy. The second concept is popular among European dermatologists.
The occurrence of chloasma is a consequence of the following disorders:
- the amount of melanin production is exceeded;
- hormonal disbalance;
- diseases of the reproductive system;
- diseases of the liver, gastrointestinal tract.
There are specialists who separate the two concepts, taking into account the areas of damage and the nature of the localization of pigmentation. Practice indicates the same type of manifestation, treatment methods, and prevention methods, which allows these two concepts to be equated.
Mechanical and chemical methods
Chemical peels are used to treat moderate to severe melasma. Prescribed in cases where whitening agents do not have an effect.
During the procedure, the upper epidermal layer is removed. This starts regenerative processes. Thanks to the active components of peels (resveratrol, concentrated 50-70% glycolic, kojic and mandelic acids, resorcinol, salicylic acid), the process of melanocyte proliferation slows down. To correct melasma, deep peeling is not used; only superficial and medium peeling is necessary.
In order to ensure deeper penetration of substances that suppress melanocyte activity, mesotherapy can be used - injections of special cocktails of acids. This method allows you to gradually destroy the pigment, lightening the melasma spots.
Dermal melasma is not corrected by chemical and laser peels. In this case, even by removing part of the dermis (and this is guaranteed to leave scars), a positive effect cannot be achieved. Melanin in the dermis can be affected using neodymium or fractional laser therapy. Fractional laser has been practically not used lately, due to its traumatic nature for the tissues surrounding the lesion. Neodymium laser has a softer effect and is popular among clients of beauty salons.
According to Dr. Moshe Lapidot (President of the European Association of Laser Therapy in Dermatology), laser therapy for melasma and chloasma cannot be considered an effective treatment method. Based on clinical studies, he concluded that six months after stopping all procedures, the results are approximately the same as after using conventional external UV protection products.
It is noted that a large percentage of patients who have undergone laser therapy complain of a complete return of hyperpigmentation.
A positive effect can be achieved only by using hardware techniques and physiotherapy in combination with cosmeceuticals.
Folk remedies
Natural herbal remedies can not only reduce/eliminate pigmentation, but also start skin regeneration processes, soften it and increase elasticity, and cleanse pores.
Recipes for folk remedies:
If after regular use of folk remedies no positive changes are observed, it means that melanin lies deeper, and a superficial effect does not make sense. In this case, it is worth turning to drug therapy or mechanical treatment methods (peeling, laser therapy).
What is melasma (chloasma): the essence of the problem, possible causes
Melasma is often referred to as visual changes to the skin. In this case, the affected areas become covered with spots that have a darker shade (from light tan to deep brown). Doctors call this symptom hyperpigmentation. Usually the spots are located on both sides of the face, almost symmetrically: forehead, cheeks, above the upper lip. There are cases when the spots cover other parts of the body that are exposed to the sun, such as the forearms and neck.
Since the disease is often caused by hormonal imbalances, it occurs more often in the female half of the population. Since during pregnancy and during hormonal therapy (HRT) the level of hormones cannot be called stable, the disease manifests itself precisely at this time. Melasma can also often be found during the period of taking oral contraceptives.
The cause of the occurrence is quite difficult to determine, since they vary and mix. However, a number of main reasons can be identified:
- Stress: Any fluctuations in emotional balance can trigger a period of hyperpigmentation.
- Thyroid disease. The body is unable to properly create or regulate hormone levels and this skin condition can result.
- Sunbathing: When skin cells are exposed to solar radiation, it can also affect the pigment that makes up the body's cells, resulting in darker spots.
- Genetic predisposition. Some evidence has been found that melasma is genetically linked, but this area still requires more research and the condition is not thought to be widespread.
- Hormonal Fluctuations: The reason pregnancy mask is often seen in pregnant women is because hormonal fluctuations can cause the condition to flare up. It may also result from the use of steroids, certain medications, or changes in birth control.
Chloasma during pregnancy
Pigmentation increases during pregnancy; this is a normal phenomenon that should not be dealt with. The areolas and the line at the bottom of the abdomen darken, and freckles become more noticeable. Hormonal changes in the body working with double load provoke the appearance of melasma.
It is advisable for pregnant women to protect themselves from the sun, take vitamins on time, and consider a diet rich in sea fish, herbs, vegetables and fruits.
If spots do appear, they will disappear on their own 3-5 months after birth. If they do not go away, you should consult a doctor. Pigmentation can signal internal problems in the body; after pregnancy, it is especially important to check the proper functioning of the ovaries and thyroid gland; the functioning of these organs may change during pregnancy.
According to the observations of practicing dermatologists, an average of about ten patients consult them about pigmented formations on the skin within 1 month. Excessive pigmentation (hyperpigmentation) of a non-tumor nature accounts for 22.3% of all pigmented formations. Of these, 15.3% is chloasma, the rest is due to post-traumatic pigmentation and lentigo.
In recent years, the attention of dermatologists and cosmetologists to disorders of pigment formation (melanosis) has increased significantly due to two reasons:
- melanocytes that produce the pigment melanin are the founders of melanoma, the most malignant tumor;
- Despite the lack of influence of benign hyperpigmentation on health, they are a cosmetic defect that is difficult to correct and often cause serious psychological disorders.
Symptoms
Since the disease is manifested by the appearance of spots, it is worth noting their possible location:
- forehead;
- whiskey;
- cheeks;
- area above the upper lip;
- forearm;
- neck.
The symptoms are purely cosmetic in nature and therefore do not cause pain.
The duration of the manifestation directly depends on the cause of its occurrence. So, during pregnancy, dark spots occur until the end of the pregnancy, then after a couple of months, the disease gradually goes away on its own. If melasma is caused by taking hormonal medications, then stopping them may be the beginning of the disappearance of unpleasant symptoms.
Diagnosis of the problem
Diagnosing melasma on your own is not difficult. However, it is better to contact a specialist. Diagnosis consists of examining the skin and assessing the general medical history. Since it is history that will help a specialist determine the possible causes of such a condition. The exact cause of the disease is the first step towards recovery.
During the examination, the doctor may need a special lamp. The principle of its operation is ultraviolet radiation. With the help of this lamp, it becomes possible to determine the exact degree and depth of deformation of skin areas, the boundaries and contour of the pattern.
After the examination, it will be easier for the doctor to determine the type of pathology:
- Epidermal. This type is characterized by damage exclusively to the upper layer of the skin. The spots have a clear outline and are dark brown in color. Using fluorescent lighting, the doctor sees a sharp contrast.
- Dermal. The location of age spots under healthy skin is characteristic. The spots are characterized by certain contours and a light brown tint. When exposed to fluorescent light it does not contrast.
- Mixed. During examination, the doctor sees both contrasting and non-contrasting spots, which indicates the effect of melanin on the epidermis and dermal layer of the skin.
The epidermal type of the disease is best corrected.
Melasma classification
There are several types of melasma. Depending on the depth of occurrence in the skin, the following types of melasma are distinguished:
- Epidermal. In this case, melasma is located in the epidermis. As a rule, in this case, the pigment formation has a light shade and clear boundaries, which are very easy to identify under the rays of an ultraviolet lamp. Epidermal melasma is most treatable.
- Dermal. In this case, pigment production occurs throughout the dermis. In this case, the contours of the spots are quite blurry, and the contours acquire a dark brown tint. Dermal melasma is the most difficult to treat.
- Mixed. In this case, melasma is characterized by the presence of heterogeneous spots of various tones and varying degrees of clarity. In this case, some areas respond quite well to treatment, while others respond less well.
Depending on the nature of the course, melasma can be of the following types:
- Passing. In this case, after eliminating the factor that caused the pigmentation, the spots completely disappear.
- Persistent. Over time, the spots become smaller and lighter, but do not go away completely.
Depending on the clinical signs, melasma can be of the following types:
- Painting - the main pigment foci are localized in the cheeks and nose.
- Central facial - pigment spots are mainly localized in the forehead, upper lip, nose and chin.
- Mandibular - pigment spots affect the arch of the lower jaw.
According to the depth of skin damage
- Epidermal - hyperpigmentation occurs in the outer layer of the skin - the epidermis; with this form of the disease, the spots are usually light and have smooth contours. This form is the easiest to treat.
- Dermal - increased production of melanin occurs in the deeper layer of the skin - the dermis, in which case the spots have a more saturated color and unclear outlines. Dermal melasma is quite difficult to treat.
- Mixed - there are light spots on the skin affecting the epidermal layers of the skin and darker spots on the dermal layers.
According to the course of the disease
- Transient - spots disappear completely after eliminating the factors that provoke their appearance.
- Persistent - areas of hyperpigmentation may become lighter, but the spots do not completely disappear, the disease proceeds according to the “exacerbation-improvement” principle.
By location of melasma
- Mandibular – excessive pigment production is observed in the area of the mandibular arch.
- Centrofascial - spots are located along the midline of the face (conditionally), the lesion affects the forehead, nose, upper lip and chin.
- Painting - age spots are mainly located on the cheeks and nose.
Chloasma most often affects the face, hips, and chest.
Chloasma has the appearance of an irregularly shaped spot, which has clear boundaries. Color - brown and its shades, even brown.
This skin pathology does not rise above the epidermis. One chloasma or several at once can form.
Chloasmas close to each other are combined into a single spot. Hyperpigmentation most often appears on the face, and depending on the affected area, there are 3 types:
- Centrofacial. The lesion appears on the lips, forehead and nose.
- Molar. Pigmentation affects the cheeks, cheekbones and sides of the nose.
- Mandibular. Chloasma forms on the skin in the lower jaw area.
Prevention
When using cosmetics, you should carefully choose care products. Give preference to only gentle products that do not irritate or cause inflammation, since products that irritate the skin can worsen the severity of melasma.
The main thing that requires attention when treating melasma is limiting sunbathing. Do not neglect all the advice known to everyone since childhood:
- It is worth taking care of your headdress, preferably a hat with a wide brim. Don't forget about sunglasses.
- People with melasma should be especially careful when choosing sunscreen, following the rules for its use. So, the SPF of such a cream cannot be lower than 30. It is better to treat the skin 15 minutes before going out. It is also important to re-treat the skin every 2 hours.
- It is worth remembering that even in cloudy weather, the sun continues to be active. In any case, when going outside, it is best to stay on the shady side.
Dermatologists around the world recommend using solar blocks such as zinc oxide or titanium dioxide. They are applied exclusively to areas subject to deformation.
Discussion
This study is the first report of the use of fractional photothermolysis in the treatment of melasma on large anatomical surfaces, such as the entire face or neck.
Chart 1. Percentage improvement in melasma as assessed by experts
Chart 2. Percentage improvement in melasma as rated by patients
We have known for a long time that CO2 laser resurfacing causes significant improvement or even complete resorption of melanotic areas. This point of view has been confirmed in many recent studies. It was natural to assume that a fractional approach to the grinding method would achieve an even more significant improvement in results. Therefore, we undertook this study with the publication of experimental data and their evaluation. We took 10 patients for the study.
Fractional photothermolysis is based on a new principle of laser application, when the laser beam acts on numerous microscopic areas, causing thermal damage in them, leaving most of the skin tissue intact. Areas of skin not involved in irradiation serve as a further source of reparation. The depth and diameter of each microthermal zone is determined by the specified energy parameters. An energy dose of 6 mJ corresponds to a microthermal zone with a diameter of 80 microns and a depth of 360 microns according to histological examination. Similarly, an energy dose of 10 mJ corresponds to a microthermal zone with a diameter of 110 microns and a depth of 500 microns (Reliant Technologies, own communication, March 2001). The size of the surface exposed to irradiation depends on the power flux density and the number of irradiation sessions.
The Fraxel laser is currently approved by the US Food and Drug Administration (FDA) for the improvement of periorbital wrinkles, lentigines and dyspigmentation. The results of a study on the safety and effectiveness of fractional photothermolysis in the periorbital region were recently published by Manstein and colleagues. Researchers noted smoothing of periorbital wrinkles in 96% of patients and an average improvement of 0.9 on the Fitzpatrick wrinkle scale in 30 people. According to our observations, denaturation of the epidermis and dermis occurs in microthermal zones, which look like “columns” on histological pictures. Microepidermal necrotic debris (MENDS) are spherical or biconvex lens shaped, clustered, and located directly beneath the intact stratum corneum that covers each microthermal zone. These debris are sloughed off approximately a week after the procedure. Just below the MENDS layer is a layer of denatured collagen.
The fractional grinding method has many advantages both in theoretical and practical aspects. The first and main advantage is that patients do not develop a wound surface, which reduces the recovery period to a minimum. The second advantage is that anatomical areas that are prone to scarring after traditional resurfacing can now be treated in a gentle manner, avoiding this complication. Thirdly, complications accompanying an open wound surface, such as infection, hyper- and hypopigmentation, are minimized. Fourthly, the method opens up new possibilities for the treatment of deep skin pathologies. Typically, when resurfacing with a carbon dioxide laser, a layer of approximately 200–400 microns is removed over several procedures. This increases the risk of scar complications. When using the Fraxel laser, you can safely penetrate much deeper because it does not remove the entire epidermal and dermal layer. Thus, the method reveals additional prospects in the treatment of melasma.
This pilot study represents the first positive review of a new approach to treating cutaneous melanosis using fractional photothermolysis.
The patients themselves who took part in this study noted that their skin condition improved by 75%–100%. This is consistent with the experts' assessment in the report that 60% of patients experienced 75% to 100% lightening of their affected areas. The patient who did not benefit from the new resurfacing technique and those who showed slight improvement (n = 2) were of Spanish origin and skin type V. Perhaps the persistent course of melasma in patients in this group is caused by factors that have not yet been sufficiently studied. It can be assumed that in these patients the melasma was quite deep. Therefore, to achieve a therapeutic effect, one should look for ways to penetrate deeper into the skin to destroy the melanin located there. When comparing the results of the Fraxel laser and traditional resurfacing techniques, it is interesting that in the first case the degree of depigmentation is significantly lower. However, it should be kept in mind that when resurfacing with a CO2 laser, hypopigmentation, as a complication, may appear 6–24 months after the course of treatment. Therefore, it is necessary to conduct longer monitoring of patients after the course of treatment. Only after this can we draw objective conclusions that the reason for the destruction of the pigment is the fractional grinding technique itself. We advise against using the Fraxel laser in patients with active herpes, as their condition may worsen during fractional photothermolysis. If the patient knows that he is a carrier of herpes, it is recommended that he undergo preventive treatment before starting laser resurfacing.
The patients who took part in the experimental study rated pain an average of 6.3 points on a ten-point scale. All patients in this group were able to undergo the procedure only under local anesthesia. In our practice, there have been cases when local anesthesia alone was not enough, especially in cases of exposure to the oral area. Nerve blockade was then successfully used. The method of choice is to use cold air supply devices. But practice shows that in cooled tissues the diameter and depth of each microthermal zone can decrease, so energy parameters should be adjusted.
A limitation of this pilot study is that our patients were not classified into melasma types based on biopsy findings or the approximate Wood classification. However, the purpose of our pilot study was to try to answer the question of whether this method can cause improvement in the treatment of melasma itself. Perhaps dividing patients into such groups will help more accurately assess the results of treatment and select treatment parameters for each type of melasma so as to achieve a greater therapeutic effect. The presence of a small number of patients in the group allows for more detailed observations with a larger number of studied parameters in order to study this method in more depth. The difficulty also lies in the fact that melasma, regardless of the chosen therapeutic technique, produces a high percentage of relapses. Since this study is experimental, we were not able to conduct long-term postoperative follow-up of the patients. To assess how durable the effect of the applied resurfacing method will be, longer follow-up of patients is necessary. In order to use all the possibilities of this therapeutic method for the treatment of melasma, it is necessary to further study it, select the most effective parameters and modes of operation of this new laser technology.
Figure 1. (A) Melasma on the face of an Asian patient after one irradiation session (no preoperative image) (B) Complete resolution of melasma after five sessions of Fraxel laser irradiation
Figure 2. (A and B) Profile photographs of the same patient.
Figure 3. (A) Melasma in a patient with skin type V. Photo before surgery (B) Improvement after five radiation sessions
Figure 4. (A) Melasma on the cheeks and forehead before treatment (B) Significant improvement after six radiation sessions
Figure 5. (A) Melasma on the patient’s cheeks and neck before treatment (B) Significant improvement in dyspigmentation areas after five radiation sessions
Bibliography
1. Grimes PE. Melasma: etiologic and therapeutic considerations. Arch Dermatol 1995; 131:1457–6.
2. Srkar R, Charandeep K, Bhalla M, Kanwar A. The combination of glycolic acid peels with topical regimen in the treatment of melasma in dark skinned patients: a comparative study. Dermatol Surg 2002; 28:1120–3.
3. Hurley ME, Guevara IL, Gonzales RM, Pandya AG. The efficacy of glycolic acid peels in the treatment of melasma. Arch Dermatol 2002; 138:1578–82.
4. Fitzpatrick RE, Goldman MP, Ruiz-Esparza J. Laser treatment of benign pigmented epidermal lesions using a 300 nanosecond pulse and 510-nm wavelength. J Dermatol Surg Oncol 1993; 18:341–7.
5. Taylor CR, Anderson RR. Ineffective treatment of refractory post inflammatory hyperpigmentation by Q Switched ruby laser. J Dermatol Surg Oncol 1994; 20:592–7.
6. Wang C, Hui C, Sue Y, et al. Intense pulse light for the treatment of refractory melasma in Asian patients. Dermatol Surg 2004; 30:1196–200.
7. Nouri K, Bowes L, Chartier T, et al. Combination treatment of melasma with pulsed CO2 laser followed by Q switched alexandrite laser: a pilot study. Dermatol Surg 1999; 25:494–7.
8. Angsuwarangsee S, Polnikorn N. Combined ultrapulse CO2 laser and Q switched alexandrite laser compared with Q switched alexandrite laser alone for refractory melasma: split face design. Dermatol Surg 2003; 9:59–64.
9. Manaloto RM, Alster. Erbium:YAG laser resurfacing for refractory melasma. Dermatol Surg 1999; 25:121–3.
10. Manstein D, Herron GS, Sink RK, et al. Fractional photothermolysis: a new concept for cutaneous remodeling using microscopic patterns of thermal injury. Lasers Surg Med 2004; 34:363–7.
Treatment
The main cause of melasma is unstable hormone levels. However, it tends to stabilize. As a result, the pigmentation goes away. Therefore, women who develop a similar disease during pregnancy should not worry about treatment; the spots disappear a couple of months after the birth of the baby. If the disease is caused by taking medications or undergoing a treatment course, you should expect a full recovery after completing the course.
The following recommendations will help your skin look natural:
- Hydroquinone. A cream that helps the process of removing pigment from the skin. It also plays the role of a blocker of the natural chemical process - the final stage of which is the production of melanin.
- Tretinoin is a type of vitamin A. It plays the role of an assistant, increasing the rate of replacement of old dead cells with new ones. This process gradually removes cells damaged by melanosis.
- Azelaic acid. The effect of the drug is to slow down and stop the production of pymentum, which makes the skin darker.
- Chemical peels. The procedure is based on the use of liquid solutions that act on the skin. The principle of exposure is to cause mild chemical burns to the affected areas of the skin. Then, like a sunburn, after a certain period of time, the burned area of skin peels off, allowing a new, clean one to emerge. This method is divided according to strength. Dermatologists recommend using glycolic acid. Its use is the safest, due to the mildness of its effects. Subsequently, there are no scars or discolored areas left on the skin. Chemical peeling is prescribed exclusively if other methods have failed.
- Intensive pulsed light therapy. Removing stains using this method is possible by using different wavelengths of light.
Treatments for melasma include not only chemical peels, but also microdermabrasion, dermabrasion, laser treatment or a light procedure. Only a dermatologist should perform these procedures.
You should carefully choose the method for removing unwanted hair. Many methods cause inflammation, which can subsequently negatively affect the course of a phenomenon such as melasma, worsening the general condition. It is better to consult a dermatologist.
How to remove chloasma on the face
Successful treatment of chloasma is possible after an accurate diagnosis of the diseases that caused it. Once metabolism and hormonal balance are restored, pigmentation of areas of the skin becomes a cosmetic problem that can be easily corrected. For successful recovery you need to follow several rules:
- avoid being in bright sun;
- use sunscreen;
- take vitamins prescribed by the doctor: aevit, acid, methionine, riboflavin, injections of B vitamins.
- stop visiting the solarium;
- Avoid using essential oils in cosmetics; they increase sensitivity to the sun and cause pigmentation.
Methods of cosmetic facial correction
A visit to a cosmetologist gives lasting results in the treatment of hyperpigmentation on the face. The work of a cosmetologist on chloasma comes down to the following actions:
- Protection from direct sun exposure. For this purpose, suitable protective equipment is selected for the patient.
- Removing the layer of dead cells. Thus, some of the dark cells are mechanically removed and the spots become lighter. The skin begins to renew itself more actively, and the stain gradually disappears.
- Suppression of melanin production in certain areas. For this, whitening cosmetics with traditional and modern components are used: acids, plant extracts, omega-3 and others.
In addition to cosmetics, hardware procedures are used for correction: dermabrasion, laser corrections, massages, injections.
Medicines
Drugs prescribed for the treatment of chloasma require careful adherence to instructions, dosages and specialist supervision. Overdosing or increasing the time of procedures can lead to the opposite effect: the skin in the affected area will be excessively whitened, and this area will also stand out on the face. In addition, in some cases, actively targeting melasma can cause increased melanin production, causing the spot to darken even more.
To control the production of melanin, doctors prescribe vitamins that affect its production and excretion:
- The essential amino acid methionine
effectively lightens chloasma. It is prescribed three times a day, 0.5 g. - Ascorbic acid,
when applied to the skin, easily penetrates the external barrier, stops the formation of melanin, promotes active collagen production and whitens the skin. To enhance the effect, ascorbic acid is prescribed for oral administration. - Folic acid
(vitamin B9) has a beneficial effect on the skin. Among its many beneficial properties is the ability to create invisible protection against UV radiation. Take 0.1 g per day. - Skinoren cream
not only solves the problem of excess pigmentation, it cleanses the skin of inflammation and helps remove traces of acne. The active ingredient of the cream is azelaic acid. It suppresses the development of excess melanocytes, making them non-viable. To get rid of pigmentation, a course of about three months is required. A 2.5 cm strip of cream is enough to apply to the entire face.
Which doctors should I contact for this problem?
Skin problems are dealt with by specialists - dermatologists. You can also start treatment by making an appointment with a therapist, who will write a referral to a dermatologist and specialists in major chronic diseases. Based on the test results and taking into account your medical history, you can receive a referral to a gastroenterologist, gynecologist, oncologist, neurologist and other specialized specialists.
Treatment with traditional methods
Supporters of natural methods of treatment can resort to traditional methods. As a rule, these are whitening masks. The majority of masks contain exclusively natural ingredients.
Among the most common are:
- Whitening mask. To prepare it, dilute hydrogen peroxide (3%) and lemon juice at a ratio of 2 to 1. Moisten a pre-prepared piece of gauze generously in the resulting solution. Apply to the affected area. Application time – 15 minutes. Remove the gauze and then wipe your face with clean, warm water.
- Watermelon mask. Before using it, you need to prepare your face. To do this, brew medicinal chamomile and steam your face over the decoction. Watermelon pulp is pounded into puree and applied to places where there are stains. Wash off after 20 minutes.
- You can also use the whitening properties of grapefruit juice, kefir, and parsley decoction. To increase the effect, it is recommended to wash your face with it daily. In summer, you can remember such a plant as celandine. Its juice can be used to treat areas with stains. In order not to interrupt treatment, you can prepare an alcohol tincture of celandine for the winter.
Who is at risk?
Anyone can experience melasma, but young women are more susceptible to it. Melasma often develops during pregnancy, around the second or third trimester. Because of this, it is sometimes called the “pregnancy mask.”
Doctors do not know the exact causes of melasma, but many tend to associate it with the female hormones estrogen and progesterone. That is why the risk group includes women taking contraceptives and certain medications or undergoing hormone replacement therapy.
Melasma is also common in people who live in a region with a tropical climate. Regular long-term exposure to open sun significantly increases the risk of developing this disorder. People with dark skin color are also more prone to melasma.
When to call a specialist
If any health-related problem arises, you should contact the right specialist. Skin discoloration is no exception. Especially if there is no reasonable explanation for such a phenomenon.
With the help of an experienced specialist, a number of other skin diseases can be ruled out.