Abdominal ascites is a pathology characterized by the accumulation of fluid in the abdomen. Such a disorder is considered a complication of a number of extremely life-threatening diseases. Ascites usually occurs in a progressive form. If the volume is small, the fluid in the abdomen may resolve on its own if treatment of the primary disease is effective.
In severe forms of this disorder, more than 15 liters of transudate may accumulate in the abdomen, which will no longer be able to find a way out on its own.
[toc]The reasons why this phenomenon occurs can be very diverse. For example, ascites can develop against the background of fungal, tuberculous and parasitic lesions of the abdominal cavity.
Gradually, the accumulation of fluid in the abdominal cavity not only causes mechanical compression of organs, but also predisposes to a number of dangerous complications. Often, patients with a severe form of edematous-ascitic syndrome develop obstruction due to intestinal compression, as well as peritonitis, since transudate, the amount of which increases in the abdomen, is an ideal nutrient medium for microflora.
Etiology of abdominal ascites
Many diseases can cause pathological fluid accumulation. Men who are susceptible to alcohol addiction often suffer from this disorder. Alcohol cannot directly provoke edematous-ascitic syndrome, but its breakdown products quickly destroy the liver. This organ is a multifunctional natural laboratory. It is the liver that is responsible for the production of proteins that regulate the degree of permeability of both blood and lymphatic vessels. Frequent consumption of alcoholic beverages contributes to the destruction of the tissues of this organ. Most people who have suffered from alcohol addiction for many years are diagnosed with severe forms of cirrhosis. In this case, the liver tissue is so destroyed that it cannot cope with its functions.
Causes and risk groups
In 70% of cases of ascites, cirrhosis plays a major role. In severe cases of liver damage, accompanied by accumulation of fluid in the abdomen, the prognosis is unfavorable.
Often, abdominal ascites develops against the background of diseases accompanied by portal hypertension. Such pathological conditions include:
- sarcoidosis;
- hepatosis;
- hepatic vein thrombosis due to cancer;
- widespread thrombophlebitis;
- stenosis of the inferior genital or portal vein;
- venous stagnation;
- alcoholic hepatitis.
The accumulation of fluid in the abdomen can be a consequence of various diseases of the kidneys, gastrointestinal tract and heart. This complication often accompanies pathological conditions such as:
- myxedema;
- glomerulonephritis;
- nephrotic syndrome;
- heart failure;
- pancreatitis;
- diarrhea;
- Crohn's disease;
- lymphostasis.
Often, edematous-ascitic syndrome develops against the background of oncological processes occurring in the body. Often such a complication is observed when malignant tumors of the large intestine, stomach, ovaries, breast and endometrium are affected.
Sometimes pathological accumulation of fluid in the abdomen develops as a result of diffuse peritonitis, Crohn's disease, tuberculosis, fungal infection and parasitic infestation. Ascites can be observed against the background of polyserositis caused by systemic lupus erythematosus, rheumatoid arthritis, Meigs syndrome, uremia, etc.
There are a number of factors predisposing to the appearance of ascites. Significantly increase the risk of developing such a problem by chronic hepatitis, alcohol abuse, injection drug use, blood transfusions, living in areas with unfavorable environmental conditions, obesity, tattooing, high cholesterol and type 2 diabetes. This is not a complete list of factors contributing to the development of ascites.
In newborns, ascites often occurs with the development of hemolytic disease of the fetus, which occurs during pregnancy. In young children, fluid in the abdominal cavity may begin to accumulate due to hemolytic disease, exudative enteropathy, malnutrition, and congenital nephrotic syndrome.
To effectively treat ascites, identifying the root cause of the problem is extremely important.
To prevent the re-accumulation of fluid in the abdomen, it is necessary to direct efforts to eliminate the underlying disease.
Causes of dropsy
Dropsy in the abdomen is a serious disease. If you do not pay attention to the problem in a timely manner, the process may drag on and lead to serious complications.
The causes of abdominal dropsy are divided into several groups.
The first type of provoking factors is accompanied by swelling of the abdomen and legs. This group includes:
- myocardial infarction;
- pathological process in the respiratory system;
- myocarditis;
- abnormalities with the heart valves.
The second group of reasons is the progression of cancer. Once harmful cells enter the liver, they lead to obstruction of fluid outflow.
Doctors talk about the third type of factors as the terminal phase of renal failure. The causes of the pathological process are hidden in hypoplastic pyelonephritis, cancer, intoxication of the body, tuberculosis, and urolithiasis.
The causes of the fourth group include serious liver diseases in the form of cirrhosis and hepatitis.
Pathogenesis of ascites development
The peritoneum performs several important functions at once, including fixing the organs located in this area in their anatomical places, and also protects them from injury. Any healthy person has some fluid between the layers of the peritoneum, the volume of which is maintained at normal levels by an extensive network of lymphatic vessels. There is constant circulation of transudate here, that is, the old one is absorbed, and a new one comes in its place. However, certain serious diseases and pathologies can disrupt this delicate natural mechanism.
Ascites develops when the release of fluid into the abdominal cavity, the process of its reabsorption is impaired, or there is a decrease in the barrier to toxins.
Gradually, the volume of fluid increases, which leads to a number of complications. First, compensatory mechanisms are launched, so the lymphatic system begins to work at the limit of its capabilities, pumping more than 15 liters of fluid per day, removing it from the liver. Normally, the volume of pumped lymph when it is removed from this organ is about 7-8 liters. The venous network is unloaded, which contributes to a temporary improvement in the general condition. Subsequently, the overloaded lymphatic system can no longer cope with this task. Oncotic pressure decreases significantly and interstitial fluid volume increases. Due to these pathological processes, transudate sweats, where it accumulates.
Prevention
The main preventive measures are avoiding alcohol, maintaining a proper and balanced diet, and playing sports. But the most important thing is timely treatment of any disease, as well as regular routine medical examinations.
Author: Nasrullaev Murad
Candidate of Medical Sciences, mammologist-oncologist, surgeon
Ascites, which is sometimes called abdominal dropsy, is not a separate disease, but a complication of a number of independent diseases. And almost all of them are extremely dangerous to health and life. How is abdominal ascites diagnosed, what causes it and can it be cured?
Symptoms of fluid accumulation in the abdomen
Despite the gradual development of edematous-ascitic syndrome, a rapid variant is also possible. There are 3 main stages of pathology: transient, moderate and intense. The nature of symptomatic manifestations depends entirely on the amount of accumulated fluid.
- With transient ascites, the volume of transudate does not exceed 400 ml. In this case, only swelling is observed.
- With moderate ascites, about 5 liters of fluid can accumulate in the abdomen. In this case, the manifestations become pronounced. The patient begins to notice problems with the functioning of the digestive organs and increasing signs of cardiac and respiratory failure.
- Tension ascites is diagnosed when the volume of fluid accumulating in the abdomen varies from 5 to 20 liters. At this stage of development of the pathology, the patient’s condition becomes extremely serious, as disruptions in the functioning of a number of vital organs increase.
Typically, edematous-ascitic syndrome develops gradually. With this classic version, the patient notices that his stomach is slowly increasing in size. As a rule, no obvious signs of a problem are observed at first, but the clothing size gradually increases. In some cases, the patient may be bothered by causeless weight gain. A noticeable increase in size is observed exclusively in the abdominal area. When more than 3-5 liters of fluid accumulates in the abdominal cavity, pronounced signs of ascites appear. These include:
- feeling of fullness;
- nausea;
- belching,
- abdominal pain;
- heartburn;
- protrusion of the navel;
- heartache;
- swelling of the abdomen in the sides;
- swelling of the legs;
- dyspnea;
- difficulty turning;
- gurgling noise during sudden movements.
The accumulation of a significant volume of transudate in the abdominal cavity is accompanied by a number of complications.
Often, due to increasing pressure, umbilical and femoral hernias develop. In addition, severe ascites can lead to rectal prolapse. In some cases, edematous-ascitic syndrome leads to the appearance of hemorrhoids and varicocele in men. Compression of organs located in the abdominal cavity often causes the development of obstruction and accumulation of feces. Accumulating fluid creates the preconditions for the development of peritonitis. Transudate contains a large amount of protein, therefore it is an excellent breeding ground for pathogenic microflora. The development of peritonitis against the background of ascites usually leads to death. A significant increase in the volume of transudate causes disruption of the functioning of all vital organs.
Treatment of dropsy of the abdomen
Dropsy in men, women, children, and pregnant women is dangerous when the volume of fluid exceeds eight liters. In many cases, modern treatment methods are used. Drug therapy involves the use of diuretics, which help correct the water-salt balance.
If medications do not give the desired result, then surgical treatment is performed. Dropsy in the abdomen is eliminated by drainage using local anesthesia.
Pathology can be treated with massage. It is recommended to do it 2-3 times a day. In this case, sunflower or linseed oil is rubbed into the abdominal area.
If a patient has symptoms of abdominal hydrops, the causes and treatment should be recognized as soon as possible. There is no need to delay this process.
Treatment often involves following a strict diet. Soups and borscht should be completely excluded from the diet. All salty, fatty, smoked and sweet foods are also prohibited.
The following additions in the form of marjoram, parsley, cinnamon, ginger, celery, and fennel will help diversify the menu. Soups are replaced with broths made from chicken or fish.
The disease can also be treated with flaxseeds. They contain beneficial acids that help remove excess fluid from the body. To prepare the medicine, take two spoons of seeds and add a liter of water. Cooks on the stove for 15 minutes. After this, the medicine is removed from the heat and wrapped in a towel. After an hour, the product is ready.
Seeds should be consumed up to six to eight hours a day. At the same time, drink plenty of water. The duration of treatment is 14 days.
Diuretic tea based on skier and bearberry will help cure the disease. For cooking, ingredients are taken in equal proportions. Mix thoroughly and then add 20 milliliters of boiled water. Infuses for about two hours. The finished product should be taken in the morning and evening on an empty stomach.
Birch leaves will help eliminate the symptoms of ascites. You need to take young leaves and put them in a large container. Cover with film and place in a sunny place. The dried leaves are placed in a hot bath. The patient needs to sit in such a bath for at least 30-40 minutes.
Wraps are another good treatment method. The leaves are not placed in the bath, but placed on the patient’s stomach. A plastic bag and a warm blanket are placed on top. The duration of the procedure is 30 minutes.
There are other effective recipes for treating dropsy at the initial stage.
- Plant juices can stop signs of a progressive disease. Juices from black radish, onion and pumpkin will provide good benefits. They can be mixed with honey to give a pleasant taste.
- Elderberry with grapes relieves anxiety symptoms. To do this, you need to take a decoction of elderberry or fresh grapes every day. All manipulations are carried out on an empty stomach.
- Parsley is soaked in milk or boiled water.
- Decoctions based on medicinal herbs eliminate inflammation. Horseradish with lemon juice, corn silk, nettle tea, plantain and meadow clover have proven themselves well.
Traditional methods can be used only when the disease is at the initial stage of development. If such methods do not help, and the disease progresses further, then you should urgently consult a doctor. He will prescribe drug therapy. The lack of effect within 3-6 months indicates that surgical treatment is urgently necessary. Remember, dropsy is dangerous due to its complications, so you cannot delay treatment.
Source: zivot.ru
Methods for diagnosing abdominal ascites
The process of identifying fluid accumulation in the abdomen is currently not difficult. First of all, the doctor gets acquainted with the medical history to identify diseases that can provoke the development of such a pathology, and also performs percussion, that is, tapping.
Even light clicks on the stomach cause oscillatory movements of the fluid located inside. When a large amount of transudate accumulates, if you place your palm on one side of the abdomen and clap on the other, a pronounced fluctuation is observed.
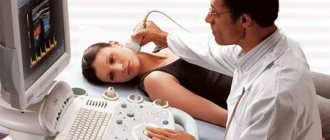
Computed tomography and ultrasound are performed to confirm the presence of fluid in the abdominal cavity. In addition, general and biochemical blood and urine tests are done to make a diagnosis. Depending on the patient's medical history, chest X-ray, examination of abdominal fluid, Doppler sonography, selective angiography, and hepatoscintigraphy may be necessary. If the root cause of the complication cannot be identified, a diagnostic laparoscopy is performed, which allows all the fluid to be removed and a biopsy of the peritoneum to be performed.
Diagnostics
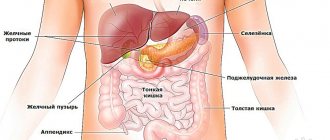
It is the violation of the absorption of fluid by the peritoneum, the difficulty of outflow, that leads to its accumulation in the abdominal cavity during cancer, and here’s why. All venous blood from the internal organs enters the portal vein system of the liver.
Why the portal - because it is formed at the gate of the liver, this is the area on its lower surface where the vessels and bile ducts enter and exit. The portal vein branches into the liver, passing all the blood through its hepatocyte cells, where toxins are removed.
Next, the blood collects in the hepatic veins and enters the inferior vena cava, which carries blood to the heart.
Incipient ascites is usually not a cause for concern. When the amount of free fluid exceeds 500-600 ml, an unpleasant feeling of heaviness appears in the abdomen, a feeling of pressure in the pelvis in an upright position.
As its amount increases, the symptoms increase. Dull pain in the abdomen without clear localization occurs, the abdomen becomes convex and hard.
This is especially noticeable in people with low nutrition.
The abdominal area in normal condition contains a certain amount of fluid, which prevents friction of the internal organs. The body controls the production and absorption of exudate through the peritoneum.
Some malignant neoplasms have a tendency to spread cancer cells into the visceral layers of the peritoneum. Further growth of metastasis disrupts the function of this system. As a result of this, the abdominal cavity is filled with fluid that the cancer patient’s body is unable to remove.
Etiological factors may also include:
- Dense arrangement of peritoneal sheets.
- The presence of a dense network of blood and lymphatic vessels.
- Transfer of mutated cells to the peritoneum during radical surgery.
- Multiple metastases of tumor formations.
- Carrying out a course of chemotherapy in late stages of cancer.
In the initial period, this pathology is practically impossible to diagnose. Pathological accumulation of fluid can initially be suspected only by the symptoms of a primary cancerous tumor.
Ascites in gastric cancer is manifested by progressive nausea and periodic vomiting. At this time, the patient feels discomfort and pain in the epigastrium.
In addition to the external examination, a cancer patient must undergo the following examinations:
- Ultrasound examination, which determines the presence of a tumor and its structure.
- Tomography - X-ray scanning reveals fluid and its amount in the peritoneum.
- Laparocentesis is a medical procedure that includes a puncture of the anterior abdominal wall and collection of liquid biological material for histological analysis.
The formation of abdominal ascites in most patients with cancer occurs gradually, over several weeks or even months. Therefore, the first signs of this formidable complication remain unattended.
Clinically, ascites begins to manifest itself after a sufficiently large amount of fluid has accumulated in the abdominal cavity; this complication manifests itself:
- Feeling of fullness in the stomach.
- Abdominal pain of different nature and duration.
- Belching and heartburn.
- Nausea.
You can visually pay attention to the gradually increasing belly; in a vertical position it hangs down, and in a horizontal position it spreads out to the sides. Stretching the skin of the abdominal wall allows you to see the network of blood vessels and the protruding navel.
Pressure on the chest causes shortness of breath and irregular heart function. With ascites, it is difficult for a person to bend over, fasten shoes, or put on trousers.
Photo of abdominal ascites in a man
Patients with cancer should always be monitored by a doctor, and the oncologist, depending on the location of the tumor, should already assume the likelihood of complications.
Ascites can be suspected based on external signs and patient complaints; palpation and percussion of the abdomen is of no small importance.
It is mandatory to assign instrumental methods:
- Ultrasound. In addition to fluid, this study can reveal the presence of tumors, their location, and changes in the structure of internal organs.
- Tomography. This method is necessary to determine the amount of fluid and its location in the abdominal cavity.
- Laparocentesis. After anesthesia, the abdominal wall is punctured just below the navel and the fluid is pumped out. The procedure is prescribed for therapeutic and diagnostic purposes. Part of the exudate is sent for analysis, where the presence of albumin, glucose, types of cellular elements, and pathogenic microflora is determined.
Ascites manifests itself depending on the amount of accumulated fluid. Its symptoms may be completely absent if a small amount of transudate is present. The pathological process can only be detected by examining the patient.
Symptoms of ascites:
- 1. Increase in body weight.
- 2. Increase in abdominal circumference. This becomes noticeable when more than 1 liter of fluid accumulates.
- 3. Feeling of fullness in the stomach.
- 4. Protrusion of the navel.
- 5. Dyspeptic disorders in the form of diarrhea, nausea, vomiting.
- 6. Decreased appetite.
- 7. Abdominal pain. They can be very strong and lead to a woman adopting a forced position in the form of a fetal position.
- 8. Edema.
- 9. Increase in temperature.
- 10. Shortness of breath.
- 11. Hemorrhoids.
- 12. Frequent urge to urinate.
- 13. Dilatation of the saphenous veins on the abdomen - “jellyfish head”.
- 14. Jaundice.
With ascites, fluid accumulates in the abdominal cavity and has no outflow. In most cases, doctors associate this pathology with impaired water-salt balance and edema. It is difficult to guess that a person has ascites. A person continues to live as usual until the first serious symptoms appear, until the pathology begins to negatively affect the patient’s well-being.
Dropsy can develop gradually, over 1-3 months or even six months or more, or spontaneously, for example, with thrombosis of the portal vein. The first signs of abdominal ascites appear after the accumulation of 1000 ml of fluid or more, among them:
- Pain and feeling of fullness in the abdomen;
- Flatulence and belching;
- Increase in body weight and abdominal volume;
- Heartburn;
- Swelling of the legs, sometimes in the scrotum in men;
- Shortness of breath and tachycardia when walking;
- Difficulty when trying to bend the body.
If a person stands, the stomach takes on a spherical shape, and in a horizontal position it blurs. Over time, the skin becomes covered with light striae (stretch marks), and the navel bulges out as fluid accumulates in the abdominal cavity.
With increased pressure in the portal vein on the sides and in front of the abdomen, the saphenous veins expand, becoming noticeable - this symptom is called “head of the jellyfish”.
Symptoms of abdominal ascites such as jaundice, nausea and vomiting appear with portal hypertension due to blockage of the subhepatic vessels.
With tuberculosis, a person quickly loses weight, feels headaches, severe weakness, and the pulse becomes rapid. The abdomen enlarges very quickly if the outflow of lymph is impaired, and slowly if the cause of ascites is protein deficiency. In the latter case, edema is pronounced, which also occurs with cardiac, liver and kidney failure.
An increase in body temperature is not a direct sign of ascites and occurs only in some diseases that cause dropsy:
- liver cirrhosis;
- tumors;
- peritonitis;
- pancreatitis.
If ascites develops due to myxedema, then the temperature, on the contrary, drops below normal - to 35°C. This is due to insufficient production of thyroid hormones, which affect the intensity of metabolism and the body's production of heat.
Every tenth cancer patient experiences dropsy. Patients with this complication have a significantly reduced chance of surviving more than two years.
In addition, if peritoneal carcinomatosis develops simultaneously with ascites, surgical intervention will no longer help cancer patients. Therefore, treatment consists of maintaining the patient’s stable condition.
Specialists prescribe medications to reduce pain and discomfort.
Ascites is a symptom of many serious diseases, one of which is cancer. Disturbances in the normal functioning of organs lead to a pathological accumulation of exudate in the abdominal cavity. If not treated promptly, this disease can cause death.
The main task of diagnosing ascites is its timeliness. Therefore, every cancer patient is regularly examined and questioned about the appearance of new symptoms.
The oncologist prescribes a general blood test, urine test and exudate sample to the patient. A fluid sample is obtained using abdominal laparocentesis.
During examination, the enlarged abdominal cavity is palpated and tapped. The doctor must clarify all the symptoms of the disease, the severity and approximate time of abdominal enlargement.
An ultrasound and tomography should also be done. Such instrumental methods make it possible to determine the size of the tumor, its location, and the amount of fluid in the abdominal cavity.
Preventive measures are primarily related to the timely treatment of any diseases. Moreover, if a person has problems with the liver, kidneys, or heart, it is worth visiting a doctor regularly, getting tested and monitoring the appearance of new symptoms, even the most minor ones.
It is advisable to minimize alcohol consumption and quit smoking. After 60 years, try to move more and walk. It is important that the patient’s diet includes enough fresh vegetables and fruits. Diet for ascites should be rich in potassium.
When the stomach begins to grow during cancer, shortness of breath and pain in the abdominal cavity appear, you should think about how to treat ascites. After diagnosing the abdominal cavity, the doctor will prescribe therapy, which will include medication, surgery and diet. The main means used in drug therapy are diuretics.
You cannot cope with this disease on your own, and even with timely treatment, the prognosis is disappointing. Therefore, this consequence of cancer is easier to prevent than to overcome.
Diagnosis of ascites is based on clinical examination data. If necessary, instrumental tests are prescribed:
- Ultrasound of the abdominal organs;
- computed tomography;
- R-graphy (radiography) for differential diagnosis with other diseases;
- diagnostic puncture with cytological examination of the liquid contents of the stomach - unlike other diseases, cells with signs of malignancy will be found in the puncture.
Abdominal ascites in oncology develops slowly. Dropsy may be noticeable after several weeks or even months. At the initial stage, when the volume of fluid does not exceed 1.5 liters, there are no symptoms. Since there are no complaints, the patient is not aware of the problem. Dropsy can only be detected by ultrasound.
As the volume of fluid in the abdominal cavity increases, the following signs appear:
- heaviness, a feeling of fullness, the stomach becomes hard like a drum;
- decreased appetite;
- nausea after eating food;
- dull nagging pain in the lower abdomen;
- heartburn and belching;
- disturbance of stool and urination;
- weakness;
- shortness of breath, tachycardia.
The examination is carried out based on the patient's complaints. The doctor palpates the abdomen, and already at this moment you can guess the development of a complication.
To make an accurate diagnosis, the following diagnostic techniques are used:
- Ultrasound. In addition to the fluid, tumors and the structure of internal organs are visible. The most accurate data is provided by endoscopic ultrasound. The endoscope is inserted through the probe.
- CT. Allows you to accurately determine the volume of liquid.
- Laparocentesis. This is both a diagnostic and therapeutic procedure. A puncture is made in the abdominal cavity below the navel, and the fluid is pumped out. The exudate is sent for examination. The presence of cancer cells, albumin, glucose and pathogenic microflora is determined.
The accumulation of fluid in the abdominal cavity occurs differently in each body. In order to better understand the mechanism itself, you need to understand a little about human anatomy.
Inside, the abdominal cavity is covered with a membrane of connective tissue, which completely envelops some organs, and partially or does not touch others at all. This tissue ensures the normal functioning of all organs, because a special liquid is released from it, which does not allow the organs to stick together. During the day, it is repeatedly released and absorbed, that is, it is regularly renewed.
Ascites causes disturbances in the basic function of the abdominal cavity: the release and reabsorption of fluid, as well as barrier protection from various harmful substances.
Cirrhosis is the main cause of ascites:
- the liver synthesizes less protein;
- healthy liver cells are gradually replaced by connective cells;
- a decrease in the amount of albumin protein leads to a decrease in plasma pressure;
- the fluid leaves the walls of the blood vessels and enters the body cavity and tissue.
Liver cirrhosis provokes an increase in hydrostatic pressure. The fluid cannot remain in the walls of the vessels and is squeezed out - ascites develops.
Trying to reduce the pressure in the vessels, the body increases lymphatic drainage, but the lymphatic system does not have time to do its job - a significant increase in pressure occurs. Fluid entering the abdominal cavity is absorbed for some time, but then this also stops happening.
Oncological or inflammatory diseases lead to the fact that the peritoneum begins to secrete too much fluid, which cannot be absorbed back, and lymphatic drainage is disrupted.
To make a diagnosis, a complex of various procedures is required, the results of which can accurately indicate the amount of fluid inside the abdominal cavity and the presence of various complications.
- Inspection - depending on the position the person is in, when tapping movements, a dullness of sound can be detected. When pushing to the side with one palm, the second palm, which fixes the stomach, feels noticeable vibrations of the fluid inside.
- X-ray examination - allows you to detect ascites with an amount of fluid of more than half a liter. If tuberculosis is detected in the lungs, a preliminary conclusion can be made that the disease has a tuberculous etiology. If pleurisy and expansion of the borders of the heart are detected, it can be assumed that the cause of the disease was heart failure.
- Ultrasound examination - allows you to determine the presence of ascites, as well as detect cirrhosis of the liver or the presence of malignant tumors in the abdominal cavity. Helps assess blood flow through veins and vessels. Examination of the chest area can detect heart disease.
- Laparoscopy is a puncture of the abdominal cavity, which allows you to take fluid for laboratory testing to determine the causes of the disease.
- Hepatoscintigraphy - allows you to determine the degree of damage and the severity of changes in the liver caused by cirrhosis.
- MRI and CT scans allow you to determine all the places where the fluid is located, which could not be done by other means.
- Angiography is an X-ray examination performed along with the administration of a contrast agent. Allows you to determine the location of affected vessels.
- Coagulogram is a blood test that allows you to determine the rate of its clotting.
- The following indicators are determined in the laboratory: globulins, albumins, urea, creatine, sodium, potassium.
- 10. Determination of the level of α-fetoprotein is carried out to diagnose liver cancer that can lead to ascites.
Conservative treatment of ascites
To prevent the accumulation of transudate in the abdomen, the primary disease must be treated first.
Complex therapy is especially important for heart failure, tumors and liver damage.
If there is transient ascites, clear improvement can be achieved with conservative measures. The patient is prescribed a strict salt-free diet for abdominal ascites. It is imperative to include foods high in potassium in your diet. These include:
- baked potato;
- dried apricots;
- spinach;
- raisin;
- grapefruit;
- asparagus;
- green pea;
- carrot;
- oat groats.
Despite the fact that the diet has a lot of restrictions, it must be designed so that the patient’s body receives all the necessary proteins, fats, vitamins and minerals. Depending on the characteristics of the primary disease, the list of foods that are recommended to be excluded from the diet may vary significantly.
The amount of liquid consumed per day should be limited to 1 liter.
In addition, medications are prescribed to help restore water and electrolyte balance.
Diuretics can have a significant positive effect, but they should be used with extreme caution. At a moderate stage of ascites, in addition to medications and diet, puncture removal of fluid from the abdomen is used to a limited extent.
Abdominal laparocentesis for ascites can very quickly improve the patient's condition. Up to 5 liters of transudate can be eliminated in one puncture. It is not recommended to immediately remove large amounts of fluid, since collapse may develop due to a rapid decrease in intra-abdominal pressure. In addition, this treatment method creates optimal conditions for inflammatory processes, infection, the formation of adhesions and the occurrence of other complications. This method of treatment is effective when there is non-strain ascites. In severe cases, when frequent evacuation of fluid from the abdomen is required, a permanent peritoneal catheter is installed. When ascites progresses, treatment can only slow down the process.
Symptoms of abdominal dropsy
The main symptom of this disease is an increase in abdominal volume due to the accumulation of free fluid. Ascites can occur either acutely or long-term. In the first case, the cause is thrombosis of the portal vein. Complete closure of its lumen leads to a sharp increase in pressure and rapid leakage of plasma into the abdominal cavity.
In most cases, abdominal enlargement occurs gradually over several months or even years and is unnoticed by the patient.
Flatulence accompanies this pathology, and very often it comes first among patients’ complaints.
At the initial stages, the stomach increases imperceptibly and patients think that they are gaining weight. Then it begins to round and take the shape of a ball, the anterior abdominal wall stretches and becomes tense, and the navel may even protrude. Due to the sharp stretching of the skin, stretch marks are formed (from the navel to the periphery in the form of sun rays).
With advanced ascites due to cirrhosis of the liver, the abdomen resembles the head of a jellyfish. The saphenous veins thicken and are clearly visible through the skin, and the abdomen itself becomes enormous in size and the anterior abdominal wall becomes very thin.
A complication of abdominal ascites is the formation of various types of hernial protrusions due to increased pressure in the abdominal cavity. Since diseases leading to the occurrence of abdominal dropsy affect the entire body and transudate accumulates not only in the abdominal cavity, but also in the pleural cavity, leading to respiratory and then cardiovascular failure. In addition, swelling develops throughout the body, especially in the lower extremities.
The consequences of ascites with large volumes of the abdomen, compression of the chest cavity organs occurs and patients develop complaints from the respiratory system. Shortness of breath develops during physical activity and at rest, worsening when lying down. Pressure on the heart leads to rhythm disturbances and difficulties in the contractile activity of the heart, which further aggravates the course of the underlying disease and increases the manifestations of abdominal dropsy.
The accumulated liquid is transparent and has a slightly yellowish tint. Cloudiness or the presence of pus and blood are very rare. The abdominal cavity can accommodate up to 30 liters of transudate, and sometimes more. The diagnosis of ascites is established when the amount of fluid exceeds 1 liter, since normally the abdomen contains a certain amount of fluid, which is necessary for the normal sliding of organs relative to each other.
Source: pancreatus.com
Surgical treatment of ascites
Surgical interventions to eliminate fluid from the abdominal cavity are used only in severe cases, when other methods are not effective or there are complications of the pathology. For example, if the transudate becomes infected with microflora and peritonitis develops, all accumulated fluid is removed and the intestines and abdominal organs are treated with special solutions. Such a radical method of treatment does not always save the patient’s life, but there is no other method of eliminating infected exudate.
Among other things, if a patient is diagnosed with severe ascites, a peritoneovenous shunt is installed or deperitonization of the abdominal walls is performed. This allows liquid to be removed directly. In addition, surgical interventions can be performed that indirectly help eliminate ascites. In some cases, measures are necessary to reduce pressure in the portal system. For this purpose, lymphovenous anastomosis or reduction of splenic blood flow is often performed. In addition, intrahepatic bypass can be performed. In rare cases, splenectomy is performed. When ascites develops against the background of cirrhosis, only liver transplantation can improve the patient's condition and prevent the accumulation of transudate.
Diagnostic measures
If the patient has signs of ascites, then first you need to consult a specialist. When examining a patient, the doctor pays attention to the following indicators:
- Liver cirrhosis manifests itself as bleeding. It arises from the veins of the esophagus and spreads further throughout the abdominal cavity.
- In heart failure, swelling of the ankle area develops.
- With renal failure, swelling of the skin and subcutaneous tissue occurs.
To make a correct diagnosis, the doctor performs a puncture from the abdominal cavity and carefully examines the contents.
If heart failure progresses or liver cirrhosis rapidly develops, the fluid will become colorless. It will also contain endothelial cells and an increase in protein up to 2.5 percent.
Prognosis for abdominal ascites
The accumulation of fluid in the abdomen is a serious complication of any disease. The survival prognosis depends on the general condition and the primary pathology that provoked the development of the problem. In addition, peritonitis, hepatorenal syndrome, hepatic encephalopathy and bleeding can significantly aggravate the situation. Unfavorable factors that worsen the prognosis include:
- elderly age;
- liver cancer;
- increased albumin levels;
- decreased glomerular filtration of the kidneys;
- diabetes;
- hypotension.
In older people with the pathologies presented above, the prognosis for the development of ascites is unfavorable. In this case, even with targeted therapy, the life expectancy of patients rarely exceeds 6 months, and in the most favorable case - no more than 2 years.
Ascites is a serious complication, indicating that the primary disease is severe.
Currently, new techniques are being actively developed to improve the condition of patients with this complication, but, as a rule, a good survival prognosis is observed only in cases where the pathology was identified at an early stage of development.
Signs of ascites [edit | edit code]
With large ascites, the abdomen is evenly enlarged, swollen, its skin is tense and shiny; with portal hypertension, ascites can be combined with dilation and tortuosity of the saphenous veins of the anterior abdominal wall (“head of the medusa”). Protrusion of the navel is often observed due to a significant increase in intra-abdominal pressure and the development of an umbilical ring hernia. When a small amount of fluid accumulates in a horizontal position of the patient, the peri-umbilical region flattens and the flanks of the abdomen protrude (frog belly). To confirm the diagnosis, imaging (x-ray, ultrasound) research methods are used.
The most common complication of ascites is spontaneous bacterial peritonitis. It occurs when ascitic fluid becomes infected, which occurs spontaneously in 90% of cases. Patients develop abdominal pain and body temperature rises.