Antibiotics are the greatest discovery of mankind. They have saved and are saving the lives of thousands of people, but despite their beneficial qualities, under certain circumstances an allergy to antibiotics is possible.
There is a certain category of patients in whom a drug allergic reaction can develop suddenly, regardless of compliance with all conditions for their administration.
Reasons for the development of the disease
Allergic drug reactions to antibiotics develop for various reasons. The most common are:
- the presence of concomitant pathological processes in the body (cytomegaloviruses, mononucleosis, etc.);
- the presence of an allergic reaction to pollen, food, etc.;
- genetic predisposition;
- Allergy to antibiotics can be caused by long-term use of medications;
- long-term drug therapy with a single drug.
In addition, an allergy to an antibiotic can occur when the patient’s immune system is weakened. This is especially common in children.
Manifestation of allergic reactions
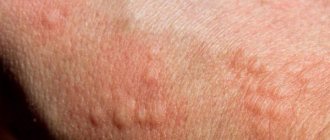
If you are allergic to antibiotics, skin rashes can occur on any part of the body; they develop both during the first doses and towards the end of the treatment course.
Urticaria is characterized by the appearance of reddish spots on the body. They protrude slightly above the skin, itch and can cover large areas of the body.
It is located symmetrically on the limbs or in places of greatest pressure, rarely on the hands.
The form of the rash is erythematous papules and pustules, which tend to merge adjacent spots.
The rash appears in the first week of antibiotic treatment and may disappear on its own without stopping the drug.
Another option is to transform the pustules into erythematous dermatitis. Therefore, in any case, if a rash appears, discontinuation of the drug is recommended.
Contact allergic dermatitis.
Contact allergic dermatitis is expressed as a delayed reaction. It occurs after a few days of using antibiotics; if it is used repeatedly, contact dermatitis may occur on the first day of treatment.
Dermatitis manifests itself as redness of the skin, itching, irritation, and weeping spots. The chronic course of contact dermatitis subsequently leads to infiltration and the appearance of pigmented spots.
A skin reaction occurs after exposure to ultraviolet radiation. The symptoms are similar to solar dermatitis - a burning sensation and red spots appear on areas of the body exposed to sunlight.
Vesicles appear - bubbles of different sizes filled with serous contents.
Manifestation of allergies to antibiotics
Allergic reactions to antibiotics largely depend on how long the medications are taken. As a rule, the first allergy symptoms appear within 24 hours. There are also immediate-type reactions, when an allergy to antibiotics can develop a few hours after using the drug.
Symptoms of an allergy to antibiotics most often manifest themselves:
- a hyperemic rash appears;
- quite often the rashes on the body resemble burns;
- swelling of the tissue and painful itching;
- in severe cases, difficulty breathing may occur;
- painful cough with wheezing;
- the patient is haunted by nausea, which turns into vomiting;
- there are difficulties with swallowing food.
The most dangerous symptoms are the development of anaphylactic shock and Quincke's edema. These conditions can be fatal if the situation is not stabilized in a timely manner.
Symptoms
It is important to understand that delay or reluctance to go to the hospital can lead to serious problems and even death
Most often, an allergy appears within an hour, but sometimes a reaction develops after three days or more. Antibiotic allergies manifest themselves in different ways. These may be common symptoms that a person immediately associates with allergies: rash from various antibiotics, itching, redness, swelling, cough. Most often they are not dangerous, but they bring a lot of discomfort. There is a possibility that they will develop into complications; help should be provided immediately.
There is a group of specific and more serious symptoms. Some are new to a person, and he does not understand what is happening to him.
Serum sickness. This is the name of the systemic immunopathological reaction that manifests itself after the introduction of a parenteral foreign protein. Symptoms in adults and children manifest themselves in the form of swelling and pain in the injection area, and after a week or more. Other signs of serum sickness are fever, swelling of regional lymph nodes, rash with itching on the skin, conjunctivitis.
Lyell's syndrome. A serious polyetiological disease, which is characterized by an acute deterioration in a person’s condition, bullous lesions of the skin throughout the body and mucous membranes. Due to rapid dehydration, toxic kidney damage, disruption of other internal organs, and infection, the patient may die.
Drug photosensitization. Allergies to antibiotics in this form are associated with the sun. This is a perverted skin reaction to ultraviolet rays due to the action of medications. The reaction occurs in one of the forms. The phototoxic reaction is similar to a sunburn, that is, blistering, swelling, and erythema appear. A photoallergic reaction manifests itself in sensitized people in the form of rashes, papules, loss of natural skin color, and water cavities raised above the skin.
Anaphylaxis. It refers to an acute allergic skin condition. This is an immediate reaction of the body, although sometimes symptoms appear several hours later. Anaphylactic shock is characterized by a decrease in blood pressure, dizziness, arrhythmia, weakness, fainting, and discomfort in the chest area. This is how an allergy to antibiotics manifests itself in severe cases. Without help, death can occur.
Quincke's edema. Most often develops within a few minutes. It manifests itself as swelling of areas of the body with loose tissue - lips, cheeks, oral mucosa, eyelids, scrotum. Swelling may appear in the larynx. Other symptoms are speech impairment, wheezing, hoarseness. Intestinal obstruction may develop, which is manifested by vomiting, nausea, and stool upset.
If you are allergic to certain antibiotics, the symptoms require urgent attention. Some of them are difficult to associate with an allergic reaction to antibiotics. A person may think of something else. Regardless of your assumptions, if your health worsens, you should consult a doctor. The serious condition requires the intervention of an ambulance team. It is important to understand that delay or reluctance to go to the hospital can lead to serious problems and even death.
Diagnostics
An allergy to antibiotics requires a diagnostic examination using special tests. First of all, the patient is asked about his allergic history, after which the doctor prescribes laboratory tests to identify an allergic reaction to antibiotics:
1. Skin analysis. A patch of medication is placed on an area of skin. It is recommended to check for an allergic reaction to antibiotics no earlier than 2 days.
2. Prick test for allergies. The final test appears after 15-20 minutes. If the papule is less than 3 mm, the result is considered negative and an intradermal test may be recommended.
3. Intradermal test. This test is recommended to be done by administering an antibiotic (0.02 ml) intravenously. After some time, an allergic reaction appears (or is absent) on the skin, after which the doctor interprets the result.
It is important to remember that almost every antibiotic allergy skin test should be analyzed within 72 hours. Subsequently, it is necessary to treat the disease taking into account the diagnosis.
Treatment of allergic rash
Treatment of antibiotic rash includes the following:
- replacing an antibiotic-allergen with a similar medicine from another group;
- prescribing antihistamines to reduce the severity and further eliminate symptoms;
- the use of enterosorbents to remove the allergic component.
In the presence of pronounced changes, it is advisable to prescribe hormonal drugs. In mild cases (especially in children), just stopping the antibiotic that caused the allergy may be enough for the symptoms to go away on their own. If taking an allergenic antibiotic is vital, desensitization is used. It is also recommended to use traditional medicine recipes along with pharmaceuticals.
Allergen replacement
A prerequisite for successful treatment of any allergy is avoiding contact with the allergen. If redness of the skin, itching or rash appears on the skin from taking an antibiotic, you should stop using this drug. In this case, cancellation applies only to antibiotics of this group, and further treatment is carried out using a similar medicine of a different class that does not contain an allergenic component.
A peculiarity of the treatment of allergies to antibiotics is that the elimination of contact with the allergen is done not by complete withdrawal, but by replacing the drug, since antibiotic therapy cannot be stopped. However, the possibility of cross-allergy should be taken into account, especially since its likelihood increases due to the presence of intolerance to antibiotics of any one class. Therefore, you need to choose a drug from the next group after testing for the reaction.
After successful replacement, symptoms usually begin to decrease as the allergenic drug is removed from the blood. In such cases, there is no need to continue further treatment of the rash and other manifestations of allergies. If the signs do not disappear, antihistamines are prescribed.
Antihistamines
Symptoms of an allergy to the use of antibiotics in the form of a skin rash develop under the influence of free histamine released into the blood. Antihistamines help reduce the production of this substance and eliminate signs of a reaction.
Depending on the severity of symptoms and the individual characteristics of the patient, the following drugs can be used:
- "Loratadine";
- "Cetirizine";
- "Diphenhydramine."
The dosage is also prescribed taking into account the above factors. Taking any drug must be carried out in strict accordance with the doctor’s recommendations and the accompanying instructions.
Antihistamines are not used to treat allergic rashes in children under 4 years of age and in older adults, as they can cause increased irritability, drowsiness or dizziness. In addition, taking antihistamines with a pronounced sedative effect cannot be combined with antidepressants and strong analgesics.
Attention! Antihistamines are contraindicated during pregnancy and breastfeeding. They can cause fetal defects or side effects in the newborn.
Desensitization
This method of eliminating allergic reactions is used when long-term antibiotic therapy is necessary or in cases where other allergy treatment options have been ineffective. The technique consists of subcutaneous injection of small doses of the allergenic component over a long period of time. At the same time, the dosage of the allergen is gradually increased, which helps the body get used to it.
The negative side of desensitization is that it does not completely eliminate allergies, but only reduces the level of susceptibility to the antibiotic-allergen. Treatment in this way can last 6–7 years. But the first 2 years are indicative - if during this time there is no visible improvement, then desensitization stops.
Course of the disease in childhood
Allergic reactions to antibiotics in children are practically no different from the reactions of adults. The most common drugs that cause acute allergic reactions are Ampicillin and Amoxicillin, especially if the doctor prescribes them to treat small children.
In addition, due to an immature immune system, an allergic reaction to the following antibiotics is possible:
- penicillins;
- tetracyclines;
- sulfonamides;
- chloramphenicol, nitrofurantoin;
- ciprofloxacin, vancomycin, etc.
For infants, antibiotics are prescribed with extreme caution and only when treating a bacterial infection. It is not recommended to take medications if the baby simply has a stomach ache or diarrhea. In this case, it is recommended for infants to take the least toxic drugs in the form of solutions and suspensions, since in children, after taking antibiotics, various complications are possible, and first of all, disturbances in the functioning of the digestive system.
In addition, under no circumstances should infants or older children be treated independently. If a child develops an allergy to an antibiotic for the first time, you should immediately consult a doctor to avoid complications.
Possible complications
Most often, drug allergies can appear suddenly and be accompanied by concomitant diseases. For example, if a child has an allergic reaction to antibiotics, dermatoses and dermatitis may worsen, psoriasis and acne may appear.
In addition, the following complications are observed quite often:
- a hyperemic rash appears;
- there is a violation of cardiac activity in the form of arrhythmia;
- the development of Lyell's syndrome is possible, the onset of which is accompanied by slight redness, gradually increasing in size, after which watery blisters appear, which subsequently burst. The rash may resemble a post-burn condition, and such a manifestation should be treated;
- drug allergies can provoke the development of angioedema and anaphylaxis, especially in children. In this case, tachycardia, hyperemic skin rash and suffocation are observed. This condition is considered extremely serious and requires immediate qualified assistance.
It is important to follow the dosage, since if it is violated, the patient may experience dizziness, vomiting and nausea. As a rule, immediate discontinuation of the drug is required.
Frequent allergic reactions to antibiotics
Anaphylactic shock develops in the shortest possible time. When administering an antibiotic in the form of an intramuscular or intravenous injection, the reaction develops within 5 to 30 minutes. When treated with tablets, anaphylactic shock may occur within the first three hours.
Skin itching, urticaria in all parts of the body, and lacrimation appear. Bronchospasm is considered the most dangerous; its appearance is preceded by swelling of the throat and glottis, the patient develops shortness of breath, the face and neck swell, problems with the heart, and tachycardia occur.
The occurrence of anaphylactic shock requires immediate medical assistance; this condition is especially dangerous in young children.
Before the ambulance arrives, when introducing an antibiotic into a vein, apply a hemostatic tourniquet above the injection site, lay the patient down, turn his head to the side, this is necessary so that the patient does not suffocate if vomiting occurs.
Medical therapy
Treatment of negative symptoms is primarily aimed at getting rid of rash, itching, general intoxication, etc. Drug therapy for antibiotic allergies involves prescribing the following drug groups:
- antihistamines (Suprastin, Zyrtec, Zodak, Loperamide, Suprastin, etc.) eliminate swelling of the skin, itching and neutralize skin rashes. Antihistamines are prescribed in the form of sprays, tablets and injection solutions;
- glucocorticosteroids (Elocom, Prednisolone, Dexamethasone, Lokoid, etc.) are prescribed if the therapy is ineffective. As a rule, treatment involves the use of external hormonal agents, but in the absence of positive dynamics, it is recommended to do intramuscular and intravenous injections with hormonal drugs;
- in severe cases, treatment with Adrenaline is prescribed, which helps relieve the toxic effects on the body. The drug relaxes the muscular system, which is important if the patient has difficulty breathing. However, it should be remembered that it is not recommended to give injections with adrenaline for hypertension, as it increases blood pressure.
To accelerate the removal of toxins from the body, it is recommended to use enterosorbents (Entorosgel, Polypefan, etc.). Allergies to antibiotics in children, as in adults, proceed in almost the same way. In this case, the treatment differs only in the selection of the required dosage. In the absence of aggravating circumstances, it is better for a child to be treated with external medications.
How will we treat?
To cope with the disease and eliminate allergy symptoms, the following remedies are used:
- Antihistamines are medications that will cope with rashes, itching, and swelling.
- Glucocorticosteroids (hormones) are drugs that have a powerful anti-edematous and anti-inflammatory effect.
- Adrenaline increases blood pressure and helps quickly relieve spasms in the bronchi. This is important in the development of anaphylactic shock.
All of the listed drugs in case of acute reactions can be administered by injection, only as prescribed by a doctor.
To remove the remaining antibiotic from the body, the doctor may prescribe sorbents - activated carbon, enterosgel.
The material was prepared by first category allergist Olga Gromada.
Diet for allergies to antibiotics
If you have an allergic reaction to antibiotics, you must follow a special diet. This is necessary to restore intestinal microflora and strengthen the immune system, especially when allergic reactions from antibiotics occur with frequent vomiting and diarrhea.
- In the first few days, it is preferable to drink a large amount of liquid, after which some cereals and bread are added during the course.
- In conclusion, fermented milk products must be introduced.
- At this time, it may be necessary to restore mineral and vitamin complexes in case of allergies from antibiotics.
- After 7 days, it is recommended to add boiled lean meat and low-fat fish, eggs, etc. to the diet.
It is important to remember that it is strictly forbidden to independently treat any disease with antibiotics, as this can disrupt the intestinal microflora and lead to serious consequences.
What to do if you develop an allergy to medications:
- Tell your doctor if you are intolerant to the drug. Any antibiotic should be prescribed exclusively by a specialist. Moreover, this must be done taking into account age, the presence of concomitant diseases and the general condition of the body;
- Take antibiotics only for pathologies that are associated with a bacterial infection. It is important to remember that viral diseases are not treated with such drugs;
- If you cannot avoid the use of antibiotics, you need to choose a remedy that has a local effect. You should not use medications for a wide range of diseases;
- When using antibacterial drugs, it is important to take agents that restore normal microflora. In addition. You should include more fruits and dairy products in your diet.