Myasthenia gravis is a neuromuscular disease of an autoimmune nature, the main symptom of which is pathologically rapid fatigue of striated muscles (those that form skeletal muscles). The pathology is very serious, often accompanied by dangerous crises. Recently, the incidence rate has been increasing - there are 7-8 cases per 100,000 people.
Why does myasthenia gravis occur? What symptoms indicate it? How is she treated? This is worth talking about now.
Causes
Doctors have not fully figured out why exactly the disease occurs. Many are inclined to believe that there is a hereditary factor, but this has not been proven. But it is a fact that this disease is combined with a tumor of the thymus gland or with hyperplasia.
Also, the causes of myasthenia gravis, the symptoms of which are listed below, include:
- Organic diseases affecting the nervous system (for example, amyotrophic lateral sclerosis).
- Dermatomyositis. This is a disease of the entire muscular system of the body, accompanied by inflammatory and degenerative changes occurring in it.
- Breast, ovarian, prostate and lung cancer.
- Sleeping sickness.
- Thyrotoxicosis.
It is important to note that myasthenia gravis most often affects women. There are half as many men suffering from this disease. As for the age category, people from 20 to 40 years old are at risk.
Etiology
Myasthenia gravis can be either congenital or acquired. The cause of congenital myasthenia gravis is mutations in the genes of various proteins responsible for the construction and functioning of neuromuscular synapses. At synapses (particularly at the end plates of neuromuscular junctions), acetylcholinesterase is present as a tetramer of the T isoform attached to a collagen-like protein, which is encoded by a separate gene, COLQ[1]. A mutation of this gene is one of the most common causes of hereditary myasthenia gravis [2]. Another common cause of myasthenia gravis is various mutations in the nicotinic acetylcholine receptor subunits[3].
Sometimes, more often in young people, a tumor of the thymus gland occurs, which is removed surgically.
Manifestations of the disease
The symptoms of myasthenia gravis are specific, so they are difficult to confuse with signs of any other disease. They begin to manifest themselves in stages, and here is what usually happens and in what order:
- Weakness of the facial, pharyngeal and masticatory muscles.
- Fast fatiguability. A person gets tired even after the simplest manipulations with his hands or walking.
- Low mobility.
- Weight loss and physical exhaustion.
- Swallowing problems (dysphagia).
- Changes in facial expressions and gait.
- Weakness of the neck and respiratory muscles.
- Impaired sensitivity of the tongue, pharynx and lips.
- Weightening of the eyelids and deterioration of vision.
During the day, the severity of symptoms changes, and a person’s well-being after prolonged muscle tension worsens significantly. In the morning a person may feel healthy and energetic, but after a few hours he begins to feel tired, which progresses very quickly.
Myasthenia gravis: symptoms that often go unrecognized
Unfortunately, most often myasthenia gravis is diagnosed in cases where the disease continues for several years in a row and becomes advanced. For this reason, any unexplained fatigue, muscle flaccidity, or weakness that increases sharply with repeated movements should be regarded as a possible symptom of myasthenia gravis until this diagnosis is completely refuted.
Early symptoms include:
- when talking - “fading of voice”,
- difficulty chewing solid food to the point of refusing to eat,
- swallowing disorder
- fatigue when combing, climbing stairs, normal walking,
- the appearance of a shuffling gait,
- drooping eyelids.
The most often affected are the oculomotor, facial, and masticatory muscles, as well as the muscles of the larynx and pharynx. The following tests help identify latent myasthenia gravis:
- If a patient is asked to quickly open and close his mouth within 30 seconds, a healthy person will make about 100 movements, and a person suffering from myasthenia gravis will make less.
- Lie on your back, raise your head and hold it in this position for 1 minute, while looking at your stomach.
- Extend your arms and stand there for 3 minutes.
- Do 15–20 deep squats.
- Quickly clench and unclench your hands - this often causes drooping eyelids in a patient with myasthenia gravis.
The local form of myasthenia gravis is characterized by the manifestation of muscle weakness of a certain group of muscles, and in the generalized form, the muscles of the trunk or limbs are involved in the process.
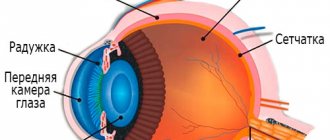
Eye shape
Symptoms of this type of myasthenia should be considered separately. In this form of the disease, the following are affected:
- Oculomotor muscles.
- The muscle that lifts the upper eyelid.
- Orbicularis oculi muscle.
Therefore, the main manifestations are:
- Inability to look for a long time at objects that are too far or close.
- Strabismus.
- Double vision.
- Difficulty focusing.
- Drooping of the upper eyelid (ptosis).
The disease of the ocular form can be localized. That is, it will not transfer to other muscle groups and organs. Experts say that if over the next two years the process does not spread to other anatomical zones, then the patient’s life is not in danger.
However, the prognosis for myasthenia gravis is not always so positive. Often the disease progresses, and this manifests itself in the frequent onset of muscle fatigue and taking too long to gain strength.
Pathologies of other types
Fatigue of the chewing and facial muscles, as well as the muscles responsible for speech, leads to unpleasant consequences. Among them:
- Voice change.
- Difficulty eating.
- Difficulties related to speech and pronunciation.
- The voice becomes dull, “nasal”. It seems that the person is speaking with his nose held.
- Fatigue, which occurs even from a short conversation. After a five-minute conversation, a person may need several hours to rest.
- Weakness of masticatory muscles. The person is unable to eat solid food.
The type of myasthenia gravis in which the muscles of the pharynx are affected is more dangerous. Because a person with such a pathology is not able to take liquid food. Every attempt to drink ends with the person choking on it. If the patient chokes, water enters the respiratory tract, as a result of which aspiration pneumonia begins to develop.
But the most dangerous condition is generalized myasthenia gravis. It is this that accounts for 1% of the mortality rate among people suffering from this pathology. A symptom of this form of myasthenia is weakness of the respiratory muscles, which causes breathing disorder. As a result, acute hypoxia may occur and, as a result, death.
Symptoms of myasthenic crisis
Myasthenic crisis is a sharp deterioration in the general condition of the body, associated with a sharp weakness of muscles up to their paralysis. The most characteristic symptoms of a crisis are the following:
- Breathing: at first it is frequent, superficial, involving the intercostal muscles in the act of breathing, and then rare and intermittent. The face becomes red and subsequently acquires a bluish, cyanotic hue. The patient is agitated and anxious. After a complete stop of breathing, loss of consciousness occurs and without timely assistance, clinical death occurs very quickly.
- Cardiovascular system: pulse increases to 180 beats per minute, blood pressure reaches 200 mm Hg. Art. Then the pulse slows down, becomes thread-like and weak.
- Autonomic nervous system: excessive salivation, increased sweating.
If help is not provided in a timely manner, brain damage occurs due to oxygen starvation.
Diagnostics
Well, the classification of myasthenia gravis is clear, now we can talk about what studies are carried out to determine this disease.
The most revealing procedure is the proserine test. It is this study that provides the neurologist with the greatest amount of information about the disease. How is everything going? First, the person is examined to assess the condition of his muscles. Then Proserin, a synthetic drug whose active substance is neostigmine methyl sulfate, is injected subcutaneously.
This medication prevents the destruction of acetylcholine, which releases neurons. As a result, the impulse reaches the muscles and the patient’s strength is restored. Usually the effect occurs after 30-40 minutes - then the doctor examines the patient again to find out how his body reacted to the drug.
In addition, electromyography is performed, during which the electrical activity of the muscles is recorded. It is carried out twice - before the introduction of Proserin into the blood and an hour after that. This test can determine whether the problem is actually a disorder of neuromuscular transmission, because the cause may lie in the dysfunction of an isolated nerve or muscle.
If after electromyography the doctor still has doubts regarding the nature of the disease, the patient is sent for electroneurography, aimed at studying the conductive ability of the nerves. In addition, a specialist cannot diagnose myasthenia gravis in adults without studying the results of a blood test (general and biochemical).
Computed tomography of the mediastinal organs also provides a lot of valuable information. It is carried out frequently, since the appearance of myasthenia gravis is often associated with volumetric processes in the thymus gland. And, of course, the patient will definitely need to undergo differential diagnosis so that the doctor can exclude all diseases that have similar symptoms.
Modern drugs
Now we can move on to the topic of treating myasthenia gravis. There are many modern medications that help maintain ability to work, improve quality of life and avoid disability. Which exactly a person will need to take is determined by the doctor, based on the diagnostic results.
As a rule, the following drugs are prescribed:
- "Sonapax". Affects the peripheral and central nervous system, has a tranquilizing, antipsychotic, antidepressant effect. Reduces feelings of anxiety and tension.
- "Chlorophyll". A natural remedy that helps raise vitality and saturate tissues with oxygen.
- "Actovegin". Improves the functioning of the central nervous system and dilates coronary vessels.
- "Spazmalgon." It has a direct effect on the smooth muscles of internal organs, relaxes it, and relieves pain.
- "Fortalgin." Inhibits platelet aggregation, has antipyretic, analgesic and anti-inflammatory effects.
- "Voltaren." Used to eliminate inflammation and pain, increase joint and muscle mobility.
- "Ibuprofen." Increases range of motion in joints, reduces morning stiffness.
- "Ketoprofen". Inhibits the activity of neutrophils, stabilizes lysosomal membranes, and has anti-bradykinin activity.
- Coldrex. Reduces swelling of the mucous membranes and sinuses, facilitates breathing, has a tonic effect, and replenishes vitamin C reserves in the body.
- "Tempalgin". It has a sedative, analgesic and anti-inflammatory effect.
Only a doctor can prescribe treatment for myasthenia gravis. Self-indulgence in this regard is very dangerous. A person, having listened to the recommendations of people who are not doctors, may take the wrong thing - Aminazine, for example, or Amitriptyline. They, like Sonapax, are also antipsychotic drugs. But these drugs have a completely different effect. They relax, stop psychomotor agitation and reduce motor activity. And this will greatly aggravate the course of the disease.
How to increase the body's strength?
With myasthenia gravis, a person's immunity is greatly reduced. And you can’t do without increasing the body’s defenses, otherwise there is a risk of functional changes.
As a rule, patients are prescribed infusions of immunoglobulins, which are obtained from donor blood. The most harmless drugs are:
- "Intraglobin".
- "Pentaglobin".
- "Gamimun-N".
- "Octagam 10%."
If a patient suddenly experiences a crisis, immunoglobulins are prescribed to him only after emergency resuscitation measures have been carried out. But regular use of these medications can prevent the development of serious complications. They are usually administered once every two days. The exact dosage is prescribed by the doctor.
You need to take these drugs with caution. Often patients to whom they were prescribed complain of headache and nausea. Typically, this is the body's reaction to a change in the number of T cells in the blood. After conducting the study, one can notice defects in immune particles, as well as increased activity of humoral thymic factors.
Diet
It is very important to maintain proper nutrition during myasthenia gravis. After all, along with food and drink, a variety of substances and elements enter the human body. With such a serious illness, they should be useful.
Your doctor will provide nutritional recommendations after diagnosing myasthenia gravis. But in general, with this illness, a person needs to consume as much potassium as possible, since it helps restore muscle function. Its sources are:
- Fresh fruits: melon, bananas, oranges, avocados.
- Fresh vegetables: pumpkin, potatoes, rutabaga.
- Legumes: lentils, lima and beans.
- Grain (not crushed).
- Parsnip (you can make infusions from it).
- Raisins and dried apricots.
The body also needs calcium. It increases the excitability of nerve tissues, muscle contractility, and strengthens teeth and bones. This is important because people suffering from myasthenia gravis are susceptible to injury. The body obtains calcium from the following foods:
- Dairy products.
- Cauliflower and turnips (and their leaves).
- Lentils, legumes, asparagus.
- Nuts.
- Egg yolks.
- Figs
- Soft salmon and sardine bones.
In order for calcium to be better absorbed, it is recommended to consume its sources together with foods that contain phosphorus. These are cottage cheese, meat, brains, cheese, beef liver, fish, walnuts, eggs, as well as oatmeal, pearl barley and buckwheat.
Contraindications for myasthenia gravis
There are a number of things that are prohibited to do with this disease. The main contraindications include:
- Serious physical activity.
- Use of curare-like muscle relaxants.
- Extended exposure to direct sunlight.
- Use of tranquilizers. The exception is Grandaxin.
- Taking medications that contain magnesium.
- Use of diuretics. The only exception is Spironolactone.
- Use of antipsychotics.
- Use of fluoride-containing corticosteroids.
- Taking antibiotics belonging to the group of aminoglycosides or fluoroquinolones.
- Use of drugs that are derivatives of quinine.
- Taking medications with D-penicillamine.
And, of course, it is forbidden to ignore medical recommendations. If a patient wants to improve their quality of life, then they should not self-medicate.
Treatment
The complex of diagnostic measures for myasthenia gravis includes electroneuromyography.
Treatment of myasthenia gravis is carried out by prescribing hormonal drugs, as well as anticholinesterase drugs. In severe cases, cytostatics may be prescribed. During a cholinergic crisis, the patient is given mechanical ventilation until his condition stabilizes.
Forecast
Much has been said about the symptoms of myasthenia gravis. What are the prognosis for such a serious disease? Unfortunately, it cannot be cured completely. And if a person ignores its manifestations and does not turn to a neurologist to receive adequate treatment and clinical recommendations, myasthenia gravis will develop further. This can result in complete atrophy of the muscular system, which is fatal.
Also, as the disease progresses, the risk of sudden cardiac arrest increases. Fortunately, in our time there are many proven methods that allow you to maintain a person’s quality of life at the proper level and even put myasthenia gravis into a stage of long-term remission.
Forecast and prevention of myasthenia gravis
It is almost impossible to predict the exact outcome of this disease, since it depends on many factors: time of onset, clinical form, gender and age of the patient, as well as the presence or absence of therapeutic measures. The most favorable course occurs in the case of the ocular form of myasthenia, and the most severe course of the disease accompanies the generalized form. With proper treatment and constant medical monitoring, almost all forms of this disease have a favorable prognosis.
Since myasthenia gravis in most cases is a chronic disease, in order to prevent exacerbations, patients need to take medications almost all the time. Constantly taking medications causes some inconvenience, but in general the quality of life of patients remains at a satisfactory level. The key to combating this disease will be timely diagnosis and treatment before irreversible processes develop.