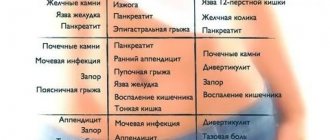
Types of hyperandrogenism in women
According to statistics, hyperandrogenism is diagnosed in 5-7% of women of reproductive age, of which about 20% experience problems with conception.
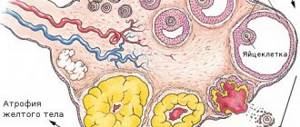
This is due to the fact that an excess of androgens interferes with the natural maturation of follicles. The ovaries begin to become overgrown with a dense membrane, which prevents the release of the egg from the follicle during the menstrual cycle. In addition, some patients experience problems conceiving and carrying a pregnancy. This disease can occur for various reasons, but most often the cause of the disease is a malfunction in the functionality of the pituitary gland-hypothalamus. Depending on the factor that provoked the development of the pathology, the following forms of the disease can be distinguished:
- central – occurs against the background of abnormalities in the functioning of the hypothalamus and the formation of a pituitary tumor,
- adrenal – the cause is a tumor of the adrenal glands,
- ovarian – a disease of this form is associated with the development of polycystic and ovarian hyperthecosis. And also this type of pathology is characterized by androgen-producing ovarian tumors,
- mixed - this form of pathology is characterized by several disorders at once (failure in the functionality of the adrenal glands, deviations in the functioning of the ovaries, etc.),
- peripheral – occurs against the background of diabetes mellitus and metabolic (fat) failure.
Experts note that the most common forms of hyperandrogenism are adrenal and ovarian.
Ovarian
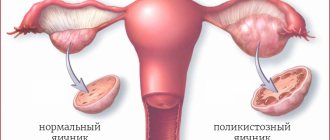
Most often, ovarian hyperandrogenism develops against the background of polycystic ovary syndrome, which is characterized by a deficiency of enzymes contained in these organs. This disease is considered hereditary. PCOS interferes with the conversion of androgens into female hormones.
In addition, experts note that this form of hyperandrogenism is caused by dysfunction of the pituitary gland and hypothalamus. Such deviations cause increased production of LH and deviations in the proportions of LH/FSH. High levels of LH cause the development of hyperplasia of the outer layer of the follicles. Ultimately, this leads to increased production of androgens and the appearance of the first signs of masculinization. And the lack of FSH affects the maturation of follicles. FLH is a type of hormone produced by the pituitary gland. In the human body, it is responsible for the functionality of the gonads and promotes the production of reproductive cells. In men, it controls testosterone levels and promotes the natural maturation of sperm, and in women it normalizes follicle maturation. Another factor in the development of the ovarian form of pathology is considered to be androgen-producing tumors. These neoplasms provoke increased production of male hormones and the further development of hyperandrogenism.
Experts note that the ovarian form of the pathology may be associated with the central one. Such cases occur against the background of certain factors: trauma and intoxication of the brain, pituitary tumors. This disease is accompanied by an increase in the level of prolactin in the blood.
Adrenal
According to experts, adrenal hyperandrogenism is a hereditary disease, since the risk of developing this pathology with a complicated genetic background is significantly high. The disease can occur even in childhood.
Among the main factors in the development of the adrenal form of the disease, one can highlight androgenital syndrome. It manifests itself in insufficient production of enzymes responsible for the production of hormones, which are located in the adrenal cortex. In medicine, these enzymes are called glucocorticoids. In the absence of the necessary enzymes, the human body begins to use substances that are normally processed to produce androgens. In this regard, an excess of androgens can also occur in children. Typically, symptoms of the adrenal form of pathology appear early. Menstruation begins quite late, and later becomes scanty or may disappear altogether. Women have a masculine figure, in which the pelvis becomes narrower and the shoulders, on the contrary, become wider. In addition, other symptoms of pathology appear:
- underdeveloped mammary glands,
- skin pigmentation,
- acne that is localized in the back and chest area,
- the clitoris hypertrophies slightly, and the size of the uterus decreases.
In the adrenal form of hyperandrogenism, patients are prescribed treatment with glucocorticoid drugs.
Treatment of hyperandrogenism syndrome
Since hyperandrogenism is not an independent disease, but occurs against the background of another pathology, treatment has an integrated approach.
According to clinical recommendations, depending on the cause of the disease, associated factors and the severity of symptoms, treatment is carried out in conjunction with eliminating the root cause or sequentially.
Drug treatment
Drugs are used that are designed to reduce the production of male sex hormones androgens:
- hormonal preparations containing progesterone;
- drugs that inhibit the production of androgens in the adrenal glands and ovaries;
- drugs that stimulate greater formation of female hormones estrogen.
Treatment of concomitant diseases
In order for therapy to give a real result that will not disappear soon, it is imperative to eliminate the root cause. These could be diseases of the thyroid gland and liver, the presence of hormone-producing neoplasms, etc.
To treat concomitant diseases, certain medication therapy or surgical intervention (removal of tumors, cysts, etc.) may be sufficient.
Lifestyle with hyperandrogenism
Any treatment must be accompanied by reflection on your lifestyle and daily habits.
Our diseases today are most often a consequence of our actions in the past.
For treatment to be effective it is necessary:
- bring the body to normal weight;
- physical exercise;
- balanced diet.
Forecast
If you are attentive to your body and its health, then with timely treatment and the absence of congenital pathologies, you can talk about a successful cure.
Women who have successfully completed treatment and follow the recommendations of doctors in the future do not have complications of hyperandrogenism, and can also become pregnant and give birth to a healthy child. Usually, pregnancy planning in such cases, as well as the entire period of pregnancy, the patient is under the strict supervision of doctors.
Causes of pathology
Hyperandrogenism usually occurs in two forms: absolute (increased levels of androgens in the blood) and relative (androgen levels are normal, but with increased metabolism into other types of hormones that have a negative effect on target organs - epithelium, sebaceous and sweat glands, hair follicles ). According to statistics, the number of people suffering from ovarian hyperandrogenism (of ovarian origin) is growing every year. Currently, every woman of reproductive age is diagnosed with this disease. To cure this pathology, it is important to identify the factor that provoked its appearance. Among the main causes of hyperandrogenism in women are the following:
- andrenogenital syndrome - in the process of producing androgens by the adrenal glands, there is an insufficient amount of enzymes to process the hormone. This leads to the accumulation of the hormone in the body,
- a tumor in the adrenal glands and ovaries - neoplasms that can provoke hormonal imbalance, in which there is increased production of androgen,
- polycystic disease is a pathological process in which the ovaries are covered with cysts,
- Cushing's syndrome - a deviation in the functionality of the adrenal glands, in which there is an increased production of glucocorticoids,
- pathologies of the thyroid gland - diseases there include hypothyroidism, which causes hormonal imbalance in the female body,
- increased body weight - excess weight can provoke hormonal imbalance. Obesity in childhood is especially dangerous.
- long-term use of hormonal contraceptives and steroid drugs,
- disturbance in the functionality of the pituitary gland or hypothalamus - such disturbances cause increased production of LH, against the background of which the proportion of LH/FSH is disrupted,
- ovarian hyperplasia - usually develops in women in old age,
- diabetes mellitus – with metabolic disorders, there is an increased production of certain hormones, in which hyperandrogenism may develop,
- pregnancy – during this period, hormonal changes occur in a woman’s body, which can cause an increase in androgen levels,
- congenital diseases of the adrenal glands and ovaries - this factor is common and is observed in 50% of patients with hyperandrogenism. With a complicated genetic background, it is almost impossible to cure the pathology.
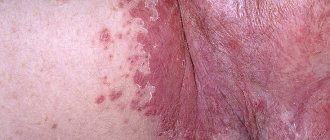
If the functionality of the ovaries is impaired, the pathology can develop in childhood. With congenital hyperandrogenism, problems may arise with determining the sex of the child. Girls are diagnosed with large labia and an enlarged clitoris, which may be similar in size to the penis. The internal genital organs are not modified. Their size is normal. With the development of hyperandrogenism at an older age, girls experience increased body hair growth.
It is worth noting that despite normal androgen levels, 70-85% of women show signs of hyperandrogenism.
Most patients suffer from acne on the body. Additionally, some women report hair loss on their scalp. In 40-80% of cases, this is due to increased production of androgens, and in the rest - increased processing of testosterone into a more active hormone that causes excess hair growth.
What is the danger of virilization for women?
Hyperandrogenism negatively affects not only appearance, but also reproductive function. In the absence of competent and comprehensive treatment, a woman faces many problems: social adaptation decreases, it is difficult to find a sexual partner, and difficulties arise with the level of fertility.
Disorders associated with viril syndrome:
- anovulation,
- infertility,
- scanty and infrequent menstruation,
- miscarriage,
- progression of hirsutism,
- development of alopecia,
- increased skin greasiness,
- increase in the area covered with acne,
- reduction in size or atrophy of the mammary glands,
- psychological problems.
How to treat fibrocystic mastopathy of the mammary glands?
View a selection of effective treatment options. Learn about the symptoms of a pituitary tumor in women, as well as methods for eliminating the formation, from this article.Go to https://fr-dc.ru/vnutrennaja-sekretsija/shhitovidnaya/kolloidnyj-zob.html and read about what colloid goiter of the thyroid gland is and how to get rid of it.
Symptoms of hyperandrogenism
Symptoms of ovarian hyperandrogenism in women of reproductive age are of two types: primary and secondary. The clinical picture of the disease depends on the severity of the pathology and the factor of its development. Among the main ones, experts identify the following signs of androgen excess in women:
- increased hair growth on the limbs and other areas of the body (chest, abdomen, back. In advanced cases, hair growth is observed on the face,
- formation of bald spots on the head,
- formation of acne and comedones on the face,
- cessation of mammary gland growth, the figure develops according to the male type,
- atrophy of muscle tissue.
Doctors also identify secondary signs of an increase in the amount of androgens, the appearance of which depends on the factor in the development of the pathology:
- high glucose content in physiological fluids (diabetes mellitus),
- rapid weight gain,
- increased libido,
- increased growth of muscle tissue,
- irregular menstrual cycle or amenorrhea,
- infertility or failure to bear a fetus.
Among the sexual signs of hyperandrogenism, one can distinguish the development of the woman’s reproductive organs according to the intermediate type and failure of the menstrual cycle (in some cases, the development of amenorrhea is possible). Increased activity of androgens causes the development of metabolic syndrome (hyperlipoproteinemia, type 2 diabetes), coronary artery disease, atherosclerosis, and arterial hypertension. Experts note that these failures lead to patients getting colds more often. This is explained by the deterioration of the functionality of the immune system against the background of hyperandrogenism. Many women with these diseases are prone to depression.
Viril syndrome in childhood
Intrauterine hyperandrogenism is a dangerous phenomenon that provokes the development of pseudohermaphroditism. The cause is dysfunction of the adrenal cortex. In severe cases, it is difficult for doctors to determine the sex of the newborn. To clarify, a genetic examination is prescribed: the combination of chromosomes YX is a male sign, XX is a female sign.
With congenital hyperandrogenism in a female fetus, the external genitalia are formed according to the male type: the clitoris is hypertrophied, the entrance to the vagina is smaller than the permissible size, is located close to the opening of the urethra, enlarged labia are similar to the scrotum
It is important to begin timely hormonal treatment to avoid severe complications and reproductive dysfunction in the future. Without correction, a girl's genitals will resemble a man's as she grows up. After 2 years, other external signs of hyperandrogenism appear: pubic hair is noticeable; at 89 years of age, facial hair is actively growing. Later, other signs of virilization develop: low timbre of voice, acne, hyperpigmentation of the epidermis. In adolescence, additional manifestations of virile syndrome are clearly expressed: the pelvis is narrow, the brow ridges are massive, the shoulders are wide, the muscles are well developed, and endurance is increased.
Diagnosis of pathology
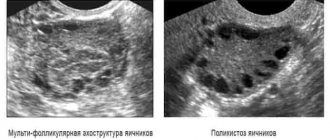
Mild hyperandrogenism of ovarian origin usually occurs latently and is almost impossible to diagnose.
As a rule, the level of androgens in mild hyperandrogenism of ovarian origin is within normal limits. If the patient experiences one or more symptoms of hyperandrogenism, then it is necessary to immediately visit a specialist. As a rule, the problem is diagnosed by a gynecologist. In addition, the woman will have to visit an endocrinologist. The specialist will prescribe a number of examinations:
- interviewing the patient (to establish an anamnesis of the patient’s life),
- MRI and CT,
- external examination of the skin,
- gynecological examination,
- tests using dexamethosone (carried out in order to establish the source of increased production of androgens),
- examination to determine genetic abnormalities,
- determination of globulin level,
- measurement of testosterone levels and 17 OP in urine,
- marker for the determination of hCG (prescribed if the androgen level is within normal limits.
If the presence of ovarian tumors is suspected, patients are referred for an ultrasound of the genital organs. All these examination methods will allow you to restore the clinical picture of the disease and select the optimal method of therapy.
Diagnostics
Ovarian hyperandrogenism is quite easy to diagnose. Sometimes a visual examination is enough to determine the presence of hair in uncharacteristic places to understand what exactly is happening to the woman.
The patient is examined and interviewed. The doctor (usually a gynecologist) tries to reject foreign diseases that have similar symptoms. Next is a series of laboratory tests.
Initially, the hormonal background is measured and it is established what changes it has been undergoing recently. The amount of androgen produced in a woman’s body is analyzed and then compared with the norm. For a more accurate clinical picture, the patient provides urine, in which the amount of ketosteroids-17 is measured.
If necessary, the patient is sent for a hardware and instrumental examination to draw up a detailed clinical picture and assess the damage caused to the body. It is worth clarifying that the disease has serious, irreversible consequences that can only be eliminated with timely, high-quality and complete treatment.
Therapy used
If a patient is diagnosed with an ovarian form of pathology, she is prescribed complex therapy using several treatment methods:
- medicinal (based on hormonal treatment with drugs containing the hormone TSH),
- therapy with traditional medicine,
- diet therapy.
If patients are diagnosed with a tumor of the ovaries or adrenal glands, surgical treatment is used. Such patients will undergo surgery to remove the tumor and further chemotherapy (if the tumor was malignant).
Conservative treatment methods
The principle of treatment for hyperandrogenism directly depends on the factor that provoked the development of the pathology. In addition, when prescribing therapy, the specialist must take into account the purpose of the therapy: elimination of signs of hirsutism, restoration of reproductive function, etc. If an excess of androgens is caused by excess weight, then patients are prescribed diet therapy and physical activity in order to reduce body weight. In addition, women are prescribed drug therapy using drugs of a certain group:
- for increased hair growth, Medroxyprogesterone is prescribed,
- To reduce the level of steroid hormones, patients are prescribed combination contraceptives. This therapy is prescribed only if the woman does not plan pregnancy,
- steroid production can be suppressed with Ketonozole,
- for symptoms of hirsutism, Spironolactone is prescribed. The course of therapy can last up to 6 months.
When a tumor is detected on the female ovaries, hyperandrogenism cannot be cured using a conservative method. In such cases, surgical intervention is prescribed.
Types and causes of occurrence
Based on the etiology of hyperandrogenism, the following forms are distinguished:
- ovarian;
- adrenal;
- mixed.
If the problem comes from the ovaries and adrenal cortex, it is primary hyperandrogenism. If dysregulation of androgen synthesis occurs due to pathologies of the pituitary gland, we are talking about a secondary form of the syndrome.
Hyperandrogenism can develop against the background of pathological conditions:
- polycystic ovary syndrome;
- adrenogenital syndrome;
- tumor hormone-producing formations;
- alpha reductase hyperactivity;
- hypothyroidism;
- Itsenko-Cushing syndrome;
- galactorrhea;
- amenorrhea;
- uncontrolled use of hormonal drugs, cyclosporine.
READ ALSO: How does high blood sugar manifest in women: symptoms and signs, effective treatment options
In some cases, hyperandrogenism is congenital. Most androgens are processed by special ovarian enzymes that transform them into glucocorticoids. But if a child is born with defects in these enzymes, then androgens begin to accumulate and are not transformed into glucocorticoids.
Folk remedies
According to experts, drug treatment of ovarian hyperandrogenism should be combined with the use of traditional medicine. Despite the effectiveness of such therapy, it is important to remember that long-term use of medicinal infusions can cause the development of negative consequences. Therefore, herbal remedies are taken only as prescribed by the attending physician.
- Uterus Borovaya - has a weak therapeutic effect for hyperandrogenism. Therefore, this plant should be used in combination with other herbs. In order for the treatment to be more effective, the course of taking Uterus boron should last at least 6 months. The recipe for preparing this medicinal infusion is simple: pour 1 tbsp into a glass of boiling liquid. spoon of dry herb and let it brew for 60 minutes. Drink a glass in small portions throughout the day. It is important to remember that the shelf life of this medicinal infusion is very short.
- Licorice root – helps reduce testosterone production in a woman’s body and has a calming effect. To make the treatment more effective, it is better to take licorice root in combination with Maryina root. Mix these ingredients in equal proportions (1 tablespoon each). Pour the resulting mixture with three glasses of boiling water and leave for 10-12 hours. Take 1 tbsp three times a day. spoon of decoction.
- Dandelion root is actively used not only in the treatment of hyperandrogenism, but also to remove waste and toxins from the body. Grind the dandelion root. After this, 4-5 tbsp. spoons of root pour 1 liter of hot liquid. Simmer over low heat for 30-40 minutes. After the time has passed, let the broth brew for an hour, and then strain thoroughly. Take 1 tbsp. spoons of the product 3-4 times a day.
- Mint – lowers androgen levels and has a relaxing effect. Add 1 teaspoon of the plant to tea. Pairs perfectly with any type of this drink.
- Medicinal decoctions are great for helping with hyperandrogenism, but they are by no means a panacea. As a rule, the effect of such therapy is not noticeable immediately, but only 3-4 months after the start of treatment.