The ovaries are a paired organ that belongs to the reproductive system. Their activities determine how a woman feels, as well as the characteristics of her condition and appearance. Ovarian wasting, a syndrome leading to problems with conception.
In this article we will talk about the features of premature ovarian failure syndrome (POF) and determine the main signs and causes of the disease.
General understanding of the problem of exhausted ovaries
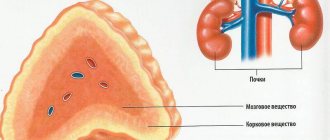
The function of the ovaries is to produce small amounts of hormones. The peak of activity is the period of childbearing age, which in most cases lasts 35-37 years.
At some point, the reproductive ability of the fair sex fades away. This is due to the onset of menopause, because over time the female body ages and wears out, and the genetic material that the descendants receive with the egg also undergoes changes. A consequence of age-related changes in germ cells is the appearance of multiple errors in DNA, and this is fraught with the development of serious diseases in the child.
Early ovarian failure syndrome is a failure of this organ that occurs before the aging process has begun. As a rule, such “early menopause” begins before the age of 40, while reproductive function still remains normal. It can occur in representatives of the fair sex who have not yet turned 44 years old.
Premature ovarian failure (clinical case)
ANNOTATION
Premature ovarian failure (POF) is a symptom complex characterized by secondary amenorrhea, symptoms of hypoestrogenism and increased levels of gonadotropins (FSH, LH) in women under 40 years of age. Among the reasons leading to the development of POI noted by patients are stressful situations, climate change, severe physical and psychological stress. The most widely used method for diagnosing POF is the determination of pituitary (FSH, LH), ovarian (E2, T) and adrenal (cortisol, DHAS, 17-OP) hormones in the blood plasma.
ABSTRACT
The Premature Insufficiency of Ovaries (PIO) is a symptomatic complex characterized by secondary amenorrhea, hypoestrogenic symptoms and increased level of gonadotropins (FSH, LH) at women under the age of 40 years. Among the reasons that lead to the development of the FPA, marked patients, are stressful situations, climate change, heavy physical and psychosocial loads. The most widely used method for diagnosis of PNJ is the determination of pituitary (FSH, LH), ovarian (E2, T) and adrenal (cortisol, DGAS, 17-OP) hormones in the blood plasma.
The incidence of this pathology ranges from 1 to 3% in the female population and is 10% in the structure of amenorrhea [1, p. 398]. This condition is described as a “multifactorial syndrome”, the development of which may involve chromosomal, genetic, enzymatic, autoimmune, infectious-toxic, iatrogenic, psychological factors, defects in the structures of gonadotropins [2, p. 991 – 994].
In our practice, we observed a clinical case of premature ovarian failure. Unfortunately, due to ignorance, emergency obstetricians and gynecologists use the wrong tactics for managing such patients [3, p. 292 – 302].
Woman 28 years old
was admitted to the urology department of a multidisciplinary hospital in Almaty with complaints of pain in the lumbar region, more on the left, fever up to 37.5C, frequent urination, general weakness, hot flashes up to 6-7 times a day, periodic headaches, absence of menstruation for 3 years and pregnancies for 5 years.
Anamnesis of life:
Somatically healthy. Denies operations or blood transfusions. Denies Botkin's disease, venereal disease, tuberculosis. Allergy history is not burdened.
History of the disease:
She fell ill due to hypothermia, when pain appeared in the lumbar region, more on the left, temperature increased to 37.5C, frequent urination, weakness, hot flashes up to 6-7 times a day throughout the year, absence of menstruation for 3 years and pregnancy within 5 years.
A year ago I was examined by an endocrinologist and had an ultrasound of the thyroid gland. Hormones in the blood:
T3-1.70 nmol, T4-80 nmol/l, TSH-2.29 nmol/l, ATPO-700 mU/ml, LH-38.3 mU/l, FSH-30.2 mU/l, Estradiol - 30 pg/ml
Conclusion of ultrasound of the thyroid gland:
Diffuse structural changes in the thyroid gland, characteristic of autoimmune thyroiditis. Node of the left lobe of the thyroid gland.
Diagnosis made
: Chronic autoimmune thyroiditis, euthyroidism
.
Hypergonadotropic hypogonadism. Ovarian wasting syndrome
Recommended: eutirox 25 mcg, 1 tablet, Duphaston 10 mg 2 times a day for 10 days, against the background of the menstrual cycle, control of LH, FSH, estradiol on the 5th day of the menstrual cycle, ultrasound of the pelvic organs on the 8th day of the menstrual cycle, clostilbegit 50 mg. 1 tablet x 1 time per day – 7 days, from the 5th day of the cycle.
On days 12-13 of the menstrual cycle, folliculometry
: Endometrium: 6mm. In the right and left ovaries, follicles are not visualized,
Ultrasound of the pelvic organs
Uterus in anteversio.
The dimensions of the uterus are 4.5x3.3x3.5 cm. The uterine cavity: not dilated, not deformed. Myometrium: without features. Endometrium: 0.36 cm Cervix of the uterus: the structure is not changed. Right ovary - 1.9x1.6 cm. Left ovary cannot be located; it was not possible to locate it due to pneumatosis intestinalis. Free fluid in the retrouterine space is determined in a significant amount.
Menstruation from the age of 14, established immediately, 4-5 days, after 28-30 days, regular, painless, moderate. Sexual life from the age of 18 (second marriage). Pregnancy-0. Contraception for 5 years, then no contraception, and no pregnancy for 5 years. According to the patient, she has been observed in the IVF center in Almaty since 2013 for polycystic ovary syndrome, primary infertility.
The last menstruation was from 06/15-06/18/2012, since 2013 she has had hot flashes up to 3-4 times a day, at the IVF center she was prescribed Femoston 2/10, Divigel, she takes it for 6 months. Past gynecological diseases: chronic salpingoophoritis.
Status
praesens
: General condition is satisfactory, the skin and visible mucous membranes are clean, of normal color. The mammary glands are soft and painless. Nipples are clean. Axillary lymph nodes are unremarkable. The abdomen is soft, painless in the lower sections. Pasternatsky's sign is positive on the left.
Status
genitalis
: The external genitalia are properly developed. Female pattern hair growth. On the mirrors: Mucous discharge. Cervix – clean, conical shape
PV:
The uterus is in anteflexio-versio, deviated to the left, dense, painless, not enlarged, the surface is smooth. The appendages on both sides are without features. The vaults are free.
Clinical diagnosis:
Acute pyelonephritis. There is no acute gynecological pathology. In the urology department she received antibacterial, infusion, and detoxification therapy
On the 3rd day of her stay in the urology department, the patient developed pain in the lower abdomen, more on the left with radiation to the left lumbar region, general weakness, and malaise. St. _ praesens :
The condition is of moderate severity.
Pulse -82 beats. per minute, rhythmic. BP-120/80 mm Hg. The tongue is moist and clean. The skin is pale in color. In the lungs, breathing is vesicular. Heart sounds are muffled, tachycardia. Pasternatsky's symptom is positive on the left. The abdomen is soft, painless, in the lower parts it is more painful on the left, where the symptom of peritoneal irritation is positive. Urination is frequent and painless. There was a chair. A series of computed tomograms dated April 2, 2014
did not reveal any evidence of stones or urostasis.
The pyelocaliceal system of the kidneys and ureter are not dilated. Accumulation of fluid in the pelvis in the posterior uterine space. Ultrasound of the pelvis from 04/03/14 -
Free fluid in the pelvis = 120.0 ml. Apoplexy of the left ovary?
Inspected in mirrors:
The cervix is clean, the discharge is mucous.
PV:
The cervix is conical in shape. The external os is closed. The uterus is in the correct position, of normal size. On the left there is a formation of a softish consistency, limited in mobility, painful. On the right, appendages are not identified. The posterior arch is painful and hangs over.
Diagnosis
: Intra-abdominal bleeding, ectopic pregnancy?
To determine the presence of further examination, a pelvic ultrasound was prescribed to determine the amount of fluid.
Pelvic ultrasound data
: The appendages are not located, free fluid = 300 ml in the pelvis.
General an. blood
: leukocytes-7.5 10▲8/l Hb- 117 g/l Ht- 32.5%, platelets-220000;
Blood coagulogram
: fibrinogen - 4.8 g/l;
Biochem.
an. blood : urea-8.0 total.
bilirubin - 16 mmol/l. General
urine test : leukocytes - 4.5 tv p/z, protein - 0.066 g/l, epit.
flat in large quantities; Urinalysis according to Nechiporenko
: leukocytes -13750, erythrocytes -250.
Considering the data from repeated ultrasounds in dynamics - an increase in free fluids from 120 ml to 300 ml., surgical treatment is indicated for the patient with an acute abdomen. Scope of surgery: decide intraoperatively.
Operation:
Laparotomy. Revision of abdominal organs.
Diagnosis before surgery:
Intra-abdominal bleeding.
Diagnosis after surgery:
Bilateral salpingitis.
Acute left-sided pyelonephritis. Anesthesia
: Intubation
Progress of the operation:
After appropriate treatment of the surgeon’s hands and the surgical field, the abdominal cavity is opened from the pubis to the navel with an infero-median incision. According to autopsy: Serous fluid in the amount of -400.0. Taken for bacterial culture and microscopy. The uterus is in the middle position and the size is not increased, the surface is smooth. The right fallopian tube is hyperemic, the walls are infiltrated, visible along its entire length up to 12.0 cm, the ampullary end is free, the fimbriae are pronounced. The right ovary measures 1.5 x 1.5 x 1.0 cm, whitish ovarian tissue with a dense capsule.
The left fallopian tube is hyperemic, the walls are infiltrated, visible along its entire length up to 12 cm, the ampullary end is free, the fimbriae are pronounced. The left ovary measures 1.5 x 1.5 x 1.5 cm, whitish ovarian tissue with a dense capsule.
Considering the absence of gynecological pathology, the responsible surgeon was invited to the operating room and the operation was continued together. The wound is extended upward, going around the navel on the right. When examining the abdominal organs, there is a serous effusion in the right and left lateral canals and in the pelvis. An examination of the abdominal organs was performed. No pathologies were detected in the stomach, small and large intestines, liver, gallbladder, spleen, or bladder. The pancreas and retroperitoneal space are unremarkable. The lymph nodes of the mesentery are not enlarged. The abdominal cavity was washed with chlorhexidine solution and dried. A drainage tube was installed in the small pelvis and brought out through the counter-aperture. Counting napkins and tools is everything. The abdominal cavity is sutured tightly in layers. An interrupted suture is applied to the skin. Aseptic dressing. Blood loss – 100.0 ml. Urine through a permanent catheter is light – 150.0 ml
Thus, patients with premature ovarian failure and infertility should be observed in urban human reproduction centers and IVF centers [4, p. 1028 - 1031].
If they turn to urgent surgery or urology, then related specialists should know that there is a category of patients who may have a peritoneal reaction in the form of excessive production of serous effusion, which can be regarded by urgent gynecologists and surgeons as ovarian apoplexy or ectopic pregnancy. Most often, these types of patients cannot become pregnant and give birth on their own [5, p. 505 - 510]. In some patients with early ovarian failure syndrome, pregnancy is possible due to the cyclical existence of the pathology. For this purpose, special hormone replacement therapy (gestagens plus estrogens) is carried out, after which the follicle matures, ovulation is restored and conception occurs. According to statistics, up to ¼ of women are able to become pregnant if favorable conditions are created. For the vast majority of women, the only chance to conceive is through IVF using donor oocytes [6, p. 539 - 545]. References:
1. Smetnik V.P. Non-operative gynecology. – M.: Medicine, 2006.- 398 p. 2. Licciardi FL, Liu HC and Rosenwaks Z. Day 3 estradiol serum concentrations as prognosticators of ovarian stimulation response and pregnancy outcome in patients undergoing in vitro fertilization. Fertil. Steril., 64, 2005, 991-994. 3. Lamp T., Schultz-Lobmeyr I., Obruca A., Huber JC et al. Premature ovar-ian failure: etiology and prospects. Gynecol Endocrinol 2000; 14: 292-302. 4. Lass A., Sealey R., Abrams DC et al. Follicular density in ovarian biopsy of infertile woman: a novel method to assess ovarian reserve. Hum. Re-prod., 12, 2005, 1028-1031. 5. Ming-Yang Chang et al. Use of the antral follicle count to predict the out-come of assisted reproductive technologies. Fertil. Steril, 69, 2008, 505-510. 6. Scott, RT, Leonardi, MR, Hofmann, GE et al. A prospective evaluation of clomiphene citrate challenge test screening in the general infertility population. Obstet. Gynecol., 82, 2003, 539-545.
Causes of pathology
The development of ovarian exhaustion, a syndrome that does not occur spontaneously, can be triggered by the following reasons:
- An autoimmune disorder or the presence of chronic abnormalities. A similar pathology is manifested by the fact that a woman has small ovaries, and, accordingly, a deficiency of the follicular apparatus, from the moment of her birth.
- In 50% of all known cases, patients suffering from ovarian depletion have a family history.
- A variety of factors in the antenatal and postnatal periods can influence the development of pathology. This is fraught with undesirable consequences in the form of damaged gonads and their replacement with connective tissue.
- Speaking about the depletion of the ovaries and the reasons that provoke them, we should mention the defective genome of any exogenous influences - drugs, radiation, influenza viruses and rubella. The influence of such negative factors is especially dangerous for babies developing in the womb.
- Often the root cause of the developing disease is stressful situations, inflammation of the pelvic organs, and infectious pathologies suffered earlier.
Etiology of primary ovarian failure and symptoms of the disease
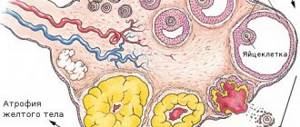
As is known, at birth, a girl’s ovaries have a certain number of primordial follicles, which are consumed over time. The rudiment of primordial cells proliferates in the female fetus until the 4th month of gestation. It has been established that the maximum supply of primordial follicles is 7 million. When this level is reached, their number decreases to 1-2 million at the time of birth and to 0.5 million by the period of puberty. With the depletion of potentially functional primordial follicles, menopause occurs.
In the etiology of POI, two main mechanisms can be distinguished: a decrease in the number (depletion of the pool) of follicles and their dysfunction. Typical causes of depletion of the follicular pool are Turner syndrome, chemotherapy and radiation therapy, and the causes of follicular dysfunction may be mutation of FSH receptors and autoimmune oophoritis.
Symptoms of ovarian failure
Primary symptoms of exhausted ovarian syndrome can occur as early as 37-38 years of age, when there are no problems with the functioning of the hypothalamic-pituitary system, but the ovaries stop working properly. The consequences are manifested by estrogen deficiency.
The onset of the disease can be recognized by the occurrence of disturbances in the menstrual cycle. The discharge is scanty and occurs less and less often. It all ends with persistent amenorrhea, that is, the complete disappearance of menstruation.
After some time, non-gynecological signs can be noted, which are evidence that estrogens no longer affect the girl’s body properly.
Exhausted ovarian syndrome can manifest itself with symptoms characteristic of menopause:
- sleep disorders,
- loss of strength and decreased performance,
- fatigue,
- causeless irritability,
- headaches,
- cardialgia,
- hot flashes and sweating that occur suddenly, even if it’s not summer outside,
- Not everything is going smoothly with the woman’s psycho-emotional status either. The patient exhibits excessive irritability, tearfulness, a tendency to depressive thoughts,
- disruptions that occur in the urogenital tract lead to the vaginal mucosa atrophying. In this area there is dryness, itching, the occurrence of chronic inflammatory processes is possible,
- Premature ovarian failure syndrome (POF) is often accompanied by aging skin, which loses its elasticity and becomes thin. Numerous wrinkles appear
- metabolic processes are disrupted, the content of other hormones in the blood also undergoes changes. The thyroid gland may become overactive or underactive. In some cases, type 2 diabetes mellitus, metabolic syndrome, and hyperadrogenism may develop.
If timely treatment is not taken care of, the pathology will progress and complicate the woman’s life.
Clinical picture of exhausted ovarian syndrome: main manifestations
The first symptom of ovarian depletion is the spontaneous occurrence of secondary amenorrhea, or oligomenorrhea with the gradual onset of persistent amenorrhea in women of reproductive age, as well as the development of infertility. Characteristic is the absence of menstruation and reproductive function disorders in the past, as well as the patient’s normal appearance: correct physique, lack of obesity. Subsequently, symptoms reminiscent of the clinical picture of menopause appear: increased weakness, headaches, impaired ability to work, sweating and periodic “hot flashes”. In parallel with this, atrophic processes develop in the genitals and mammary glands.
Diagnosis of the disease
The purpose of the examination procedure will depend on the characteristics of the clinical situation that the woman had to face. The doctor must determine the nature of the dysfunction in hormonal terms, and how much it can affect other systems and organs.
A visual examination of the woman does not reveal any phenotypic deviations - the patient still looks “feminine”, the development of the mammary glands occurs without failure. Upon examination, the gynecologist also does not detect any changes, except that the uterus and cervix decrease in size.
To clarify the degree of uterine hypoplasia, the patient will have to undergo a metrosalpingography procedure. In the vast majority of cases, it is possible to detect a thinned inner mucous layer of the uterine cavity, the size of the uterus will be smaller, and the same can be said about the patency of the fallopian tubes.
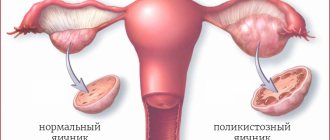
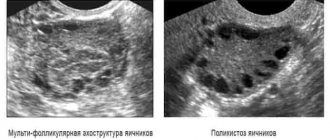
An ultrasound will clearly show that the size of the uterus and ovaries have changed and become smaller. The presence of small immature follicles can be seen on the echogram.
A diagnostic laparoscopy may be prescribed, which helps assess the condition of the problem organ. A characteristic sign of exhausted ovaries is a decrease in their size, acquiring a yellowish tint, and connective tissue replaces the cortical layer. It is important to correctly identify the characteristics of hormonal imbalances. For this purpose, special tests and samples are required. In addition, it is determined which of the main hormones are already present.
SPIA is characterized by the complete absence of estrogens. After receiving the results, the hormonal status is determined, a significant increase in the FSH content is noted, while estradiol and prolactin are contained in small quantities.
It is possible to prescribe a biopsy of the ovaries and endometrium.
Symptoms
In the vast majority of cases, ovarian wasting syndrome develops suddenly, and the main clinical manifestation is the complete cessation of menstruation. It is extremely rare that this is preceded by a rather short period of scanty and irregular menstrual flow.
In addition, ovarian wasting syndrome has the following symptoms:
- sudden flushes of heat throughout the body;
- secretion of a large amount of sweat;
- dryness of the genital organs, which provokes pain and discomfort in women during sexual intercourse;
- decreased sexual attraction to the opposite sex;
- frequent mood changes;
- irritability and tearfulness;
- depression and aggression;
- deterioration of concentration and memory;
- decreased ability to work;
- unmotivated anxiety;
- feeling of lack of air;
- headaches and heart pain;
- dry eye syndrome.
All of the symptoms described above lead to a decrease not only in the quality of life, but also in intimate relationships among representatives of the fairer sex. This means that if such signs appear, it is necessary to seek qualified medical help as quickly as possible.
Treatment of SPIA
Premature cessation of ovarian activity leads to early rapid aging of the body. This fact cannot but affect all aspects of a woman’s life. Psycho-emotional state is no exception.
The pathology strongly resembles physiological menopause, but at the same time it also differs from it. Therefore, you cannot do without consulting specialists.
Important! If a diagnosis of “premature ovarian failure” is made, then it is no longer possible to restore their lost physiological function.
Treatment is based on replacement therapy. Hormones that the body lacks will be replenished artificially. The purpose of these drugs is to “deceive” the female body by simulating the physiological function of the ovaries. This technique is somewhat reminiscent of the treatment of type 1 diabetes, when the lack of insulin in the body is compensated for by insulin therapy.
Drugs introduced into the body do not lead to the resumption of ovarian function.
Treatment of exhausted ovarian syndrome requires an individual approach. The choice of hormonal agents depends on the results of the examination, the age of the patient, and the degree of impairment of the functional capabilities of systems and organs.
Regardless of what therapy will be used, there are three main principles that are always followed by everyone:
- timely start of treatment,
- use doses to a minimum, but with sufficient effect,
- Hormones should only be used that are similar to natural ones.
The main goal of any hormone replacement therapy chosen should be to mimic normal menstruation. That is why combination therapy with estrogens and gestagens in cycles is usually used.
In patients who have undergone hysterectomy, estrogen monotherapy is used.
Hormone replacement therapy also involves concomitant symptomatic treatment aimed at eliminating unfavorable clinical symptoms: neurosis, autonomic, vascular disorders and other abnormalities.
Therapy for ovarian depletion syndrome is usually carried out until the patient reaches naturally occurring menopause - 50 years.
Treatment
Just 50 years ago, endocrine disorders of the ovaries were considered incurable. Despite the fact that with ovarian insufficiency, egg maturation is not possible, some women experience spontaneous ovulation. About 10% of patients diagnosed by doctors managed to get pregnant.
Treatment is restorative in nature. In most cases, doctors resort to hormonal therapy, which helps restore the balance of estrogen and progesterone in a woman. Gynecologists prescribe combined contraceptives if the patient has no contraindications. As an addition, gynecologists recommend a course of vitamin therapy. The main emphasis should be on vitamin D and calcium intake.
Please note: For young girls who want to become pregnant in the near future, doctors prescribe a low dosage of hormonal contraceptives. Small doses do not create a barrier to ovulation and do not mask it. In addition, these drugs are harmless in the early stages of pregnancy, since their composition is identical to that of the ovary.
Ovarian failure leads to infertility. Therefore, it is very important for women to follow all the doctor’s recommendations in order to get on the path to recovery.
We recommend you learn: Features of the ovarian cycle
Consequences and complications
The consequences of an unpleasant pathology are manifested in the fact that in any case, early aging of the body and infertility begin. Young patients faced with a similar pathology may experience arrhythmia, coronary artery disease, and a high risk of developing myocardial infarction.
The process of calcium absorption is disrupted, which means that the content of this element in the body decreases, resulting in increased bone fragility.
The development of early menopause affects the quality of sexual relationships. Often, a woman faced with such a pathology becomes depressed and her performance deteriorates.
Hormonal ovarian dysfunction: predisposing factors
Insufficiency of ovarian functionality can occur under the influence of a number of reasons and factors that contribute to disruption of the female reproductive system.
The etiology of the disease should be known in order to select optimal treatment methods.
These types of predisposing factors include the following:
- Hereditary predisposition . Hormonal disorders in close relatives, in particular in the mother, are very often transmitted genetically, which complicates the course of treatment.
- Effect of ionizing radiation . It can almost completely inhibit the production of all hormones, not just female sex hormones.
- Past infectious diseases (flu, rubella). Such viruses negatively affect the functioning of all organ systems, including the endocrine one.
- Exposure to toxic chemical compounds . They can have a destructive effect on both the hormones already present in a woman’s body and those that are just being produced. This, in turn, can lead to ovarian dysfunction.
- Long-term drug treatment . This could be chemotherapy, the use of antihormonal drugs, immunosuppressants, etc.
- Low body weight . Adipose tissue is a natural source of estrogens (female sex hormones). With its deficiency, their level decreases significantly, which affects the functioning of the ovaries.
- Carrying out in vitro fertilization (IVF). Any medical intervention is stressful for the body and can affect the level of female hormones.
Each of these factors determines the further course of treatment for a woman if the pathology is detected correctly and in a timely manner.
Possible complications
Such a disease, if not properly treated, can lead to the following complications and consequences:
- premature aging of the female body;
- cardiac ischemia;
- osteoporosis;
- myocardial infarction;
- atherosclerosis;
- female infertility – pregnancy with ovarian depletion syndrome will not occur naturally; conception will require IVF, while pregnancy management in this category of women is carried out in specialized reproductive centers;
- chronic depression and other psychological problems;
- progressive atrophic changes in the mammary glands and genitals;
- decreased quality of life and sexual relationships with the opposite sex.
In addition to ignoring the symptoms and lack of adequate therapy, independent elimination of such ovarian disease using folk remedies without consulting specialists can lead to the above complications.
Diagnostics
If you notice the symptoms listed above, it is recommended to consult a doctor as soon as possible. To make a correct diagnosis, the gynecologist will conduct a comprehensive examination.
If premature ovarian failure is suspected, the following is carried out:
- Anamnesis collection. The patient describes her complaints in detail.
- Inspection on the chair.
- Hormonal blood tests.
- Ultrasound examination of the pelvic organs.
- Laparoscopy with taking a tissue sample for biopsy.
As part of the study of biomaterial in a patient with the syndrome, an increase in the level of the hormones FSH and LH, a decrease in the concentration of progesterone and estrogen, and a low level of prostaglandin E2 are revealed. Tissue analysis shows cessation of follicle maturation.