Paresthesia, stiffness
- Paraesthesia, formicatio, myrmecismus.
Acroparesthesia
- Acroparaesthesia - an unpleasant sensation of goosebumps crawling over the body, stiffness, tingling (as if by an electric current), burning.
It is observed with neuritis, radiculitis, disorders of the blood supply to the nerves, diseases of the peripheral blood vessels, etc. Acroparesthesia
is a violation of the sensitivity of the extremities (usually at night): a feeling of crawling, stiffness of the hands and fingers or feet and toes, numbness of the extremities. The cause of these phenomena may be compression of the brachial nerve plexus or subclavian artery, inflammation of the coronary arteries, arthrosis of the cervical vertebrae, etc.
Treatment of pasteurization
:
1.
Take nettle leaves, viburnum bark, parsley fruits, goldenrod herbs, sweet clover and tricolor violet in the ratio 2:2:2:3:3:3.
Pour two tablespoons of the mixture into 0.5 liters of water, boil for 5 minutes, leave for 5 minutes, strain into a thermos; drink 1/2-2/3 glass 2-3 times a day after meals (Rewerski, 1980)
.
2.
Take a tablespoon of celery and valerian roots, common dubrovnik herb, pour in 0.6 liters of boiling diluted wine, leave for 2 hours, strain, add honey;
drink 100 g before and after meals (Zivotic, 1979)
.
3.
Mix horse chestnut bark, primrose flowers, yarrow herb and sweet clover in a ratio of 1:1:2:2.
Take 2-4 tablespoons of the mixture, pour 1 liter of water, boil for 5 minutes, strain, pour into a large bowl, add warm water and make baths for hands and feet, hold for 15-20 minutes, lightly massaging the limbs. In addition, it is recommended to massage them with a stiff brush and do contrasting water procedures: alternately hold them for 3-5 minutes in a hot (40° C) infusion of herbs, then 2-3 minutes in cold water (Rewerski, 1980)
.
4.
Homeopathic remedies for paresthesia: depending on its cause, aconite D6, agaricus (fly agaric) D4-D6, sekale cornutum (ergot) D3-D6, mezereum (common wolfberry) D3-D6, viscum (mistletoe) D1-D3, thuja occidentalis are prescribed D3-D10, Chamomilla D6, aesculus (horse chestnut) OZ, etc. (Quilisch);
for acroparesthesia, homeopaths recommend the following recipe: agaricus muscarius C4 (fly agaric), secale cornutum (ergot) C4 - 2 granules of each remedy 2 times a day (Pommier, 1985)
.
5.
Take one of the drugs containing ginkgo leaf extract: Craton, Memorll, Ginkgo-loges, Ginkgobil, Gingium, etc.
Descriptions of the treatment of paresthesia with folk remedies are presented for informational purposes. Before use, be sure to consult your doctor! Remember, self-medication can harm your health!
Paresthesia is a type of skin sensitivity disorder. Such conditions are characterized by spontaneous sensations of pins and needles, tingling, numbness or burning.
Description
Paresthesia is a type of sensitivity disorder that includes subjective sensations of tingling, burning, and “crawling.”
All these unpleasant sensations have bothered every person more than once; they could appear when sitting for a long time in an uncomfortable position, squeezing the arms or legs, or in case of a feeling of strong fear. However, this condition passes quickly and does not cause any particular inconvenience.
In the event that these sensations appear for no apparent reason and do not go away for a long time, you should consult a doctor to determine the cause and prescribe the necessary treatment.
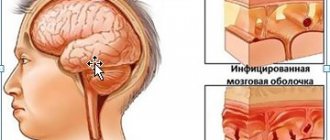
Paresthesia occurs when a nerve root, nerve ending, area of the spinal cord or brain is damaged or irritated. The localization of symptoms depends on the location of the nerve lesion.
The causes of paresthesia are varied and varied, depending on the location of the symptoms.
Paresthesia of the tongue occurs against the background of:
- irritation of its surface with sharp edges of teeth;
- rubbing with dentures used in dentistry;
- bite changes.
However, the development of paresthesia of the tongue occurs only when, against the background of the listed factors, there are also internal causes (diseases of the stomach, diseases of the ENT organs, arachnoiditis).
Paresthesia of the lower extremities occurs when:
- any medical intervention in the area of the spinal cord and spinal column;
- spinal cord injury;
- multiple sclerosis;
- polyneuropathy (mainly alcoholic and diabetic in nature);
- osteochondrosis of the lumbar spine;
- obliterating endarteritis;
- hypovitaminosis.
Paresthesia of the upper extremities appears against the background of:
- osteochondrosis of the cervical spine;
- the presence of formations of a malignant or benign nature;
- Raynaud's disease;
- multiple sclerosis;
- injuries to the cervical spine;
- stroke;
- inflammatory process affecting the neck muscles.
Lip paresthesia, which develops against the background of:
- osteochondrosis of the cervical spine;
- neuritis of the facial nerve;
- migraine;
- inflammatory lesions of the gums;
- hypertensive crisis.
In addition, there are reasons such as:
- poisoning by chemicals or heavy metals;
- prolonged exposure to stress factors;
- long-term and uncontrolled use of certain medications (isoniazid, cycloserine, ofloxacin, antiepileptic drugs, some antihypertensive drugs).
Paresthesia can occur equally in men and women.
Homeopathic medicines for the treatment of paresthesia
In the vast majority of cases, paresthesia can be quickly eliminated with medication. However, in some cases, this condition indicates serious abnormalities in the functioning of the body. In this case, therapy requires a long-term and comprehensive approach. Homeopathy shows very
. This is a treatment method based on the principle of similarity: a person takes a small dose of a substance that, in large quantities, can cause similar symptoms of the disease.
Most often, the following homeopathic preparations are used to treat paresthesia:
- Akonitum
(Aconitum) – relieves numbness of the forearm and left fingers caused by diseases of the cardiovascular system. - Alumina
– fights numbness in the legs when sitting for long periods of time in an uncomfortable position. - Causticum
- relieves difficulties in finger mobility when grasping. - Lycopodium
, Lycopodium - relieves numbness of the limbs caused by cardiovascular diseases. - Natrium muriaticum
– copes with tingling and goose bumps, returns normal sensitivity to the limbs. - Magnesia sulphurica
– relieves goosebumps on the fingertips and numbness of the limbs after waking up. - Phosphoric magnesia
(Magnesia phosphorica) – relieves stiffness of fingertips.
Photo 2. Homeopathy is the treatment of like with like.
The sensation of loss of normal sensation in the toes is considered common. The feeling of numbness in one or both feet, which arises from an uncomfortable posture, goes away without a trace. This happens to kids who “sit out” their legs, forgetting themselves while playing. A child's foot can be warmed, rubbed, and in this way the unpleasant tingling and painful numbness can be eliminated. But the absence of a skin reaction to touch also occurs as a result of a neuralgic disease, less often in children, much more often in adults.
Symptoms
"class="alignleft">
The appearance of paresthesia occurs when several electrical impulses of different potentials occur simultaneously in a sensitive nerve fiber. The impulses are layered on top of each other, and, as a result, information from the skin or mucous membrane enters the brain in a distorted form.
The location of symptoms depends on the location of the nerve damage. For example, during a stroke, paresthesia develops on the opposite side of the body (from the area of the brain where the circulatory disorder occurred). Migraine attacks may be accompanied by precursors in the form of paresthesia in the mouth. Polyneuropathy is characterized by localization in the area of the feet and hands.
Symptoms of paresthesia are:
- tingling or burning sensation;
- feeling of "crawling";
- pale skin in the affected area;
- feeling of numbness.
This condition can occur unexpectedly and suddenly, or it can develop gradually with an increase in symptoms. Typically, outbreaks of paresthesia go away over time, then attack again. But there is also a continuous course, for example, in multiple sclerosis with a long history of the disease, when paresthesia is a constant concern.
Diagnostics
"class="alignleft">
A therapist or neurologist is involved in identifying paresthesia.
Diagnosis is aimed at establishing the immediate cause that contributed to the development of paresthesia. During the conversation, the doctor finds out the onset of symptoms, their duration, and the presence of provoking factors. An important factor is to ensure that the workplace is designed to avoid exposure to chemicals.
After this, a neurological examination is performed, during which sensitivity impairment is determined.
The next stage is to search for the disease against which paresthesia developed. For this purpose the following studies are carried out:
- determination of blood sugar levels;
- blood test for toxins;
- blood chemistry;
- Ultrasound of the vessels of the lower extremities and brachiocephalic vessels;
- X-ray of the spine;
- CT, MRI of the brain and/or spinal cord.
An important research method is electroneuromyography, which shows the speed of excitation propagation along the nerve fiber, which makes it possible to identify disturbances in nerve conduction.
When paresthesia is caused by filling material entering the tooth canal, the dentist is involved in the diagnosis. Numbness develops in the chin, tongue, cheeks, lips, symptoms disappear after a few days or 2-3 months. In this case, there are no problems with diagnosis; the person independently associates the development of symptoms with a recent visit to the dentist.
Paresthesia is not a separate disease; it is always associated with concomitant pathology. Therefore, it is extremely important to carry out a full examination in order to prescribe the necessary treatment in a timely manner and prevent the development of complications.
Causes of paresthesia of the lower extremities
There are many reasons for the development of pathology. It is very important to find the right one, because the outcome of the entire treatment will depend on it.
- Doctors consider the most common causes of numbness in different parts of the legs osteochondrosis
.Traumatic and age-related deformations of the cartilage and bone tissue of the spine lead to prolonged compression of nerves and blood vessels, as a result of which metabolic processes slow down and paresthesia occurs.
The symptom is a companion to lumbar intervertebral hernias, and without treatment by a neurologist the patient risks being partially paralyzed.
- Paresthesia is found in patients who have undergone surgery to remove a spinal hernia
. If numbness is caused by postoperative paresis (paralysis) of the leg muscles, then the rehabilitation course is focused on overcoming the main complication. As the patient's condition improves, the symptoms soften or disappear altogether. - Heart disease
can cause a lack of blood supply to tissues. The legs suffer more often because they are farther than other parts of the body from the “central pump” - the heart. Peripheral vessels, deprived of the life-giving power of blood, reduce the lumen, lose tone and do not provide the correct skin reactions. - Cerebral circulation disorders
of any type and volume are fraught with the danger of paresthesia of the legs. It is not without reason that one of the common complications of strokes is paresis, accompanied by complete or partial loss of sensitivity in large areas of the body. Timely rehabilitation measures will help patients overcome complications. - Tumor processes in the spine and brain
lead to paresthesia. Special attention is not paid to the treatment of decreased sensitivity of the skin of the legs, since the patient’s condition usually requires surgical intervention. The patient's health depends on the outcome of treatment of the underlying disease. - Diabetes mellitus
in severe forms fatally affects the blood vessels of the lower extremities, leading to gangrene. Therefore, paresthesia in diabetic patients is almost inevitable. Treatment of diabetes is carried out comprehensively and includes measures to help blood vessels. - Diseases of the arteries of the legs
- obliterating endarteritis, Raynaud's disease - cause numbness of the limbs along the vessels. Multiple sclerosis is also associated with disorders of the skin reactions of the extremities. These diseases require long-term and highly professional treatment.
Causes of reversible paresthesia include:
- deficiency of B vitamins,
- seizures,
- repeated forced postures associated with prolonged compression of the limbs,
- a state of intense fear and anxiety,
- spicy
Treatment
Treatment is aimed at eliminating the cause of paresthesia and alleviating symptoms.
Blood sugar levels should be constantly monitored if you have diabetes. Careful monitoring will help prevent the development of complications such as diabetic polyneuropathy, which, in turn, is accompanied by paresthesia.
It is recommended to stop drinking alcohol, since prolonged use of alcoholic beverages provokes the development of paresthesia.
In case of poisoning by chemical substances, detoxification therapy is performed, aimed at removing toxins from the body.
Surgical treatment is used in cases where there is a tumor process that compresses the nerve.
Symptomatic treatment is aimed at reducing the manifestation of unpleasant sensations.
Physiotherapeutic treatment has a good effect. It is aimed at eliminating the subjective sensations of paresthesia. This treatment method includes:
- diadynamic currents;
- electrophoresis;
- magnetic therapy;
- mud therapy;
- massage;
- acupuncture.
Medicines are also prescribed to help eliminate the symptoms of paresthesia.
In cases where the mechanism of formation of paresthesia is associated with a violation of the conduction of excitation along the nerve fiber, the administration of B vitamins will have a good effect.
In addition, to eliminate the feeling of numbness, medications that improve blood circulation are prescribed. To achieve this effect, antiplatelet agents are used.
Groups of drugs such as antioxidants and antihypoxants are also used. They help improve metabolic processes in nervous tissue.
To prescribe a treatment regimen, you should consult a doctor who, individually, taking into account the cause of paresthesia and the presence of concomitant pathology, will prescribe the necessary medications. You should not wait for the symptoms to resolve spontaneously, but immediately make an appointment with a doctor to prevent the development of complications.
Diseases accompanied by paresthesia
The main cause of the development of paresthesia is disruption of the activity of the brain or peripheral nerves
. These organs are responsible for the functioning of the nervous system. The following diseases can provoke paresthesia:
- Tumors near the site of the lesion.
- Injuries to the head or limbs.
- Circulatory disorders.
- Spinal cord injuries.
- Nervous system lesions.
- Diabetes.
- Stroke, multiple sclerosis, migraine.
- Problems with the spine.
- Inflammation of the posterior muscles of the body.
- Avitaminosis.
- Poisoning by alcohol or toxins.
- Shingles.
Note! Doctors believe that most often paresthesia occurs due to cardiovascular diseases.
Medicines
Of the B vitamins, preference is given to thiamine (B1) and cyanocobalamin (B12). It is better to use it as intramuscular injections to achieve the required concentration of the vitamin in the blood.
If there is a concomitant disease that increases the risk of developing blood clots, antiplatelet drugs (for example, aspirin) are prescribed. The action of this drug is aimed at preventing the formation of a primary blood clot by inhibiting the process of platelet adhesion. This helps improve blood circulation, as a result, eliminating the feeling of numbness.
Of the antihypoxants, Actovegin has a good effect. This drug consists exclusively of physiological components that are normally present in the human body. The active substance is a deproteinized hemoderivative of calf blood. Every cell in the body needs oxygen, which is used as energy. Actovegin stimulates oxygen consumption by the cell, thus exhibiting its antihypoxic effect.
One of the representatives of antioxidants is vitamin E. It is the main fat-soluble antioxidant that protects fatty acids in and around cells from free radicals and lipid oxidation. Often used in combination with another antioxidant, vitamin C. This vitamin protects muscle and nerve tissue from the effects of free radicals.
Folk remedies
Folk remedies will not eliminate the cause of the development of paresthesia, but will help alleviate the symptoms and, thereby, improve the general condition of the person.
First of all, you should carefully monitor your lifestyle and diet. It is recommended to stop smoking and drinking alcohol, and not to abuse hot and spicy foods. Jerusalem artichoke has a good effect (helps eliminate numbness due to its beneficial effect on nerves and blood vessels).
Medicinal baths and contrast baths are also used. To prepare a medicinal bath, you can use herbs such as sage, chamomile, and string. The water temperature should not be hot, but comfortable for humans. Reception time is no more than 15 minutes. You can complement the effect with a massage with warming cream, which is performed immediately after taking a bath.
Contrast baths will help improve blood circulation and increase muscle tone. To carry out the procedure, you should prepare 2 basins with hot and cold water. The essence of the procedure is to alternately lower the feet into one and then into the other basin.
You can purchase a massage roller or brush for daily use. This kind of massage helps improve blood circulation and reduce the symptoms of paresthesia. But you should not massage areas of the body for too long and actively, so as not to injure the skin and cause irritation.
Soothing infusions of medicinal herbs have a good effect, since one of the reasons for the development of paresthesia is psycho-emotional stress. Herbs such as motherwort, mint, chamomile, adonis, and lemon balm are suitable for this. Decoctions are taken during the day in 3-4 doses. The course of herbal treatment lasts no more than 1 month, then a break is taken for several weeks, after which, if necessary, the course is repeated.
Source: yellmed.ru
Goosebumps all over my body...
The main feature is that the “goosebumps” can be localized in different places. This is influenced by the cause of the phenomenon and the characteristics of the course of the primary disease.
The following areas of the body are most often affected by paresthesia:
- hands;
- legs;
- fingers and toes;
- lips;
- language;
- head.
Some patients in dental clinics experience temporary paresthesia localized in the jaw, cheeks of the tongue or pharynx.
A decrease in sensitivity can occur as a result of improper treatment or tooth extraction. The dentist may snag or damage the nerve fiber. Usually the phenomenon goes away on its own within a few days. Sometimes re-treatment is required.
Causal complex
There are various causes of paresthesia, ranging from pinched nerves and neurological diseases to toxic poisoning and chronic illnesses. Usually the causes and place of manifestation of the phenomenon are interrelated.
Tongue on cheeks - blunder-blunder
Numbness and paresthesia of the tongue, as well as decreased sensitivity and the inability to distinguish tastes, occurs under the influence of external factors, neurological abnormalities and due to internal disorders in the body.
Most often, tingling and burning in the tongue occurs as a result of the development of the following pathologies:
- concomitant disease of the nervous system;
- disturbances in the gastrointestinal tract;
- cardiovascular diseases;
- disease of the endocrine system and so on.
In addition, the phenomenon may occur due to a lack of vitamin B or mechanical damage to tissue from teeth or artificial dental structures.
If your legs are taken away
Paresthesia of the limbs can occur as a result of the following factors:
- spinal cord injurieslocalized in the lumbar region or below, usually the patient also experiences other unpleasant symptoms: decreased sensitivity, weakness, pain, impaired motor function, and so on;
- surgery performed on the spinal cord, spinal nerves or spine;
- tumors on the spinal cord (nerve endings can be pinched, and the blood supply to nerve fibers and the spinal cord is also disrupted);
- multiple sclerosis , especially in cases where its foci are localized in the parietal part of the brain;
- polyneuropathy caused by taking medications, alcoholic beverages or chemical poisoning.
- Raynaud's disease;
- blood pressure disorders in the lower extremities.
Hand Wars
Unpleasant sensations in the hands can occur in the presence of the following pathologies:
- osteochondrosis (when intervertebral discs are destroyed, nerve endings become pinched);
- damage to individual nerves in the neck by an inflammatory process;
- disruption of the blood vessels that supply food to the brain (sometimes paresthesia is one of the first signs of a stroke);
- multiple sclerosis;
- neck muscle inflammation;
- decrease in calcium levels in the body.
With excessive alcohol consumption, certain infectious diseases, diabetes and intoxication, damage to nerve fibers can occur. As a result of the development of pathology, paresthesia in the hands may occur as one of the symptoms.
Loss of sensitivity in fingers
Often the phenomenon appears only on the fingers (hands or toes). The reasons for this phenomenon are usually no different from the reasons that cause paresthesia in the arms or legs. It could be:
- osteochondrosis;
- spinal cord injury;
- alcohol or other poisoning;
- Raynaud's disease;
- vitamin B deficiency;
- lack of calcium and other microelements.
The lips don't seem to be your own...
Tingling, burning or crawling in the lips may occur as a result of neurological or other diseases. Among the most common reasons it is worth noting:
- neuritis of the facial nerve;
- cervical osteochondrosis;
- multiple sclerosis;
- hypertensive crisis (a sharp increase in blood pressure is also accompanied by shortness of breath, severe headache, vomiting, loss of consciousness and other symptoms);
- lack of vitamin B;
- decrease in glucose.
When you have goosebumps all over your head
Neurological disorders can cause paresthesia of the entire head. The most common reasons include:
- neuralgia of the facial nerve;
- triple nerve neuralgia;
- Bell's palsy;
- transient ischemic attack.
Sometimes the phenomenon appears before a migraine attack.
Paresthesia can be a side effect of certain medications.
The phenomenon can be caused by taking medications to lower blood pressure and antieliptic drugs, as well as some other drugs.
Reasons for the development of paresthesia
Typically, this condition occurs due to prolonged compression, prolonged exposure to an uncomfortable position, overexertion and stress.
Moreover, the reason
Paresthesia
can be caused by vitamin deficiency, infectious nerve lesions, tumor formations
and other pathological conditions.
A neurologist diagnoses and treats the problem.
Hands
Hand paresthesia is the most common problem that causes patients to visit a neurologist. most often affects older people.
. The reason for this phenomenon lies in the slowdown of recovery processes in nerve cells.
Legs
Your legs may feel numb in the feet, calves, or thighs. The appearance of this condition indicates a deterioration in blood circulation
. Paresthesia can also be caused by vitamin deficiency. The most dangerous causes of this disease include brain tumors, osteochondrosis, intervertebral hernias or diabetes mellitus.
Language
Tongue paresthesia is an extremely rare occurrence.
, which occurs due to deterioration in the conductivity of nerve cells or due to mechanical damage. It can also be caused by pernicious anemia, head injury, laryngeal carcinoma, stroke or diabetes.
Doctors note that this condition occurs due to the use of medications, hormonal imbalances, and allergic reactions.
Lips
Osteochondrosis of the cervical spine can provoke paresthesia of the lips
. It is in this part that there are nerve endings that are responsible for the sensitivity of the face. This phenomenon can be recognized by a sharp deterioration in vision, hearing, and an unpleasant sound with any movement of the head. Inflammation of the facial nerve is also called the cause of lip paresthesia. It causes facial asymmetry and weakness of facial wrinkles.
Features of the clinical picture
Paresthesia is manifested by a decrease in sensitivity, which causes unusual sensations. The patient feels a tingling, slight burning sensation on the skin, as well as goosebumps.
The main feature is that a person experiences such sensations when different electrical impulses occur in the nerve fibers (or one fiber) that transmit information to the brain.
This happens most often due to disturbances in the functioning of the nervous system.
Establishing diagnosis
In case of prolonged or frequent paresthesia, you should consult a neurologist. After collecting an anamnesis and a detailed interview with the patient (complaints, chronic diseases, other symptoms, etc.), the doctor prescribes a series of clinical or instrumental studies that help establish the cause of the development of this phenomenon.
In most cases, the patient is prescribed electroneuromyography. Using this study, the passage of electrical impulses along nerve fibers is monitored. The method allows you to determine not only the location, but the degree of disruption of the passage of nerve impulses.
Depending on the accompanying symptoms, the doctor may also prescribe:
- ECG;
- MRI of the brain or spinal cord;
- Ultrasound of the heart;
- radiography of the spine;
- taking a blood test for toxins;
- EEG;
- Dopplerography of blood vessels and so on.
A complete examination allows you to determine the cause of the disorder and prescribe the correct treatment.
How to get rid of unpleasant symptoms
The treatment regimen is directly related to the disease or pathology that causes paresthesia. The main goals of therapy are to eliminate the irritating factor, as well as restore the functioning of the nervous system and blood supply.
Among the main goals it is also worth noting the stimulation of the transmission of nerve impulses in the affected area.
Methods used
Treatment of paresthesia depends on the location and cause of its occurrence:
- If tingling and burning of the skin occurs as a result of the appearance of a tumor, surgical intervention is recommended.
- If the functioning of peripheral nerves is disrupted or the spinal cord or brain is damaged , therapeutic actions are aimed at restoring performance (taking medications and prescribing procedures depends on each specific case).
- For diabetes mellitus, the patient takes medications to restore normal blood glucose levels. For metabolic disorders, medications may also be prescribed.
- When nerve endings are pinched, therapeutic actions are aimed at eliminating the problem. In case of deficiency of vitamin B or microelements, a special diet and vitamin complexes are prescribed.
Physiotherapeutic procedures are highly effective in the treatment of neurological diseases. The doctor may prescribe:
- electrophoresis;
- acupuncture;
- diadynamic currents;
- magnetic therapy;
- mud therapy and other procedures.
Physiotherapeutic procedures help restore normal transmission of electrical impulses, which helps get rid of unpleasant numbness and tingling.
Difficulties of therapy
The doctor is not always able to immediately determine the cause of the phenomenon, which delays the prescription of the correct treatment. In addition, it should be taken into account that in most cases, paresthesia is associated with disorders in the nerve fibers, spinal cord or brain.
Restoring the functioning of the components of the nervous system requires a special approach, and is not always possible in full. In some cases, surgery is required (tumors, pinching, etc.).
Sometimes diseases, the symptom of which is paresthesia, develop rapidly and can lead to dire consequences. That is why, if this phenomenon occurs repeatedly, it is necessary to consult a doctor.
Therapy for paresthesia in neuroses is complicated by excessive irritability and excitability of the patient. In this case, treatment is carried out comprehensively and includes medications, physical procedures and other methods.
Methods and methods of treatment
Treatment of this disease is successfully carried out using various physiotherapeutic methods. Using various types of massage gives good results. Treatment with the Darsonval apparatus and electrophoresis with nicotinic acid are also used. Galvanic mud applications, acupuncture, and physical therapy exercises are effective.
Treatment with medications in combination with physical therapy significantly improves the result. In these cases, medications are preferred that reduce blood viscosity and improve blood circulation in the brain and periphery. These are drugs such as nicotinic acid preparations, Piracetam, Cavinton, nootropics.
Antioxidants have a good effect: Actovegin, Mexidol, Berlition.
Treatment of the disease can also be carried out using traditional medicine. For this, infusions and decoctions of herbs such as sweet clover, horse chestnut, willow bark, and birch leaves are mainly used. They have the property of increasing blood circulation and having a vasodilating effect. It is only important to prepare and take decoctions correctly, without changing the recommended dosage.
Prevention of disease. Paresthesia can recur if there is an incorrect lifestyle and non-compliance with the regimen. Many patients take vasodilator medications for life. It is advisable to take medications based on herbal raw materials. Products with Ginkgo Biloba extract are often used: Tanakan, Bilobil, Memoplant.
In addition to taking medications, it is advisable not to sit still, lead an active lifestyle, and play sports. The optimal sport for this pathology is swimming, since all the muscles of the body work here, including the legs.
Of course, it must be remembered that smoking and excessive drinking of alcohol are the cause of many diseases and will certainly not be useful for paresthesia.
This is a term used to describe a burning or tingling sensation that usually occurs in the extremities. However, it can also occur in other parts of the body.
Often this feeling occurs suddenly, and this form is one of the most painless types of paresthesia. Surely, many have experienced it when, for example, they sat on their legs for a long time or crossed them, and then got up. Or if your hand was squeezed.
In such cases, muscles and nerves are compressed, and blood flow is hampered. That is why this tingling feeling comes. When the pressure eases, the unpleasant sensation goes away.
However, chronic paresthesia does not go away as quickly as temporary paresthesia and often causes more severe discomfort.
Anyone can experience temporary paresthesia, but the risk of developing this disease increases with age. Also at risk are people whose activities involve repeated compression and release of nerves: office workers who type a lot, musicians, athletes, in particular tennis players. The chances of suffering from paresthesia increase in people with type 1 and 2 diabetes, autoimmune diseases, neurological disorders...
Causes that provoke the occurrence of paresthesia
The main cause of paresthesia is pressure on the nerve. When it weakens, the unpleasant feeling goes away. But in some cases this does not help, the tingling feeling is constantly present. This is chronic paresthesia and may be a sign of nerve damage or disease. Chronic paresthesia is caused by the following factors:
- 1 Trauma or accident causing nerve damage.
- 2 Stroke or mini-stroke - when blood flow to the brain is restricted and causes damage.
- 3 Multiple sclerosis is a disease of the central nervous system.
- 4 Diabetes is a blood sugar disorder that can damage nerves over time.
- 5 A pinched nerve (often in the neck, shoulder or arm) from injury or overuse.
- 6 Sciatica – pressure on the sciatic nerve (which runs from the lower pelvis to the buttocks and legs), is a common problem during pregnancy and usually causes numbness and pain in the back or legs.
- 7 Lack of certain vitamins, especially low levels of vitamin B12, which is essential for maintaining nerves in good condition.
- 8 Alcohol abuse.
- 9 Taking medications – for example, some types of chemotherapy that cause nerve irritation or damage, some antibiotics, birth control pills.
Among other common causes of paresthesia, doctors name the following:
- malnutrition;
- menopause;
- dehydration;
- fibromyalgia;
- herpes zoster;
- hypoglycemia;
- Fabry disease;
- nervous irritation;
- immune deficiency;
- metabolic disease;
- lidocaine poisoning;
- taking anticonvulsants;
- lupus erythematosus ;
- neurological disorders;
- motor neuron diseases;
- autoimmune disorders;
- heavy metal poisoning;
- Guillain-Barre syndrome.
Symptoms of paresthesia
Paresthesia can affect any part of the body, but it usually appears in the arms, hands, legs, and feet.
The most common symptoms are numbness of a limb or other affected area, a feeling of weakness in it, tingling, burning, or vice versa - a feeling of coldness, muscle atrophy, restless legs syndrome, a crawling sensation on the skin.
Chronic paresthesia may cause stabbing pain. This may cause the affected limb to become clumsy. When paresthesia occurs in the legs and feet, it makes walking significantly more difficult.
If you experience symptoms of paresthesia that do not go away within a short time and impair the quality of life, you should definitely consult a doctor. This may be a sign that the person has an underlying medical condition that requires treatment.
Types of paresthesia
There are two types of paresthesia. Transient and chronic
. The first occurs briefly as a consequence of migraines, injuries, taking certain medications, as well as mechanical compression of nerves and muscles, which occurs when sitting on your feet or squeezing your hand.
Chronic paresthesia can result from disorders that affect the central nervous system. For example, such as transient ischemic attacks or strokes, multiple sclerosis or encephalitis.
Vascular lesions or tumor-like growths can put pressure on a person's spinal cord or brain and cause the development of paresthesia. However, the occurrence of the disease for these reasons is a fairly rare case.
More often, paresthesia develops after nerve damage from infections, injuries, inflammation or other conditions.
Complications of paresthesia
Paresthesia in most cases is a symptom that can cause complications of the primary or underlying disease that provoked its appearance.
For example, people with paresthesia may have difficulty walking or difficulty grasping objects with their hands, depending on which limb is affected.
People with decreased sensation may be unable to detect an injury (eg, burn, puncture wound), which can lead to infection of the extremities.
Loss of sensation in the legs can lead to an increased risk of falling.
Prevention of paresthesia
Paresthesia cannot always be prevented. After all, even temporary paresthesia can happen because you compress a nerve in your arm in your sleep. We have no control over this. But in order to avoid the unpleasant sensations of passing paresthesia, you can, for example, give up the habit of sitting on your feet. This way you won't feel any tingling sensations in them.
To prevent chronic paresthesia, follow the simple tips below.
- Avoid repetitive movements if possible.
- Rest often if you need to perform repetitive movements.
- Get up and stretch as often as possible.
- If you suffer from diabetes or any other chronic disease, get timely and regular checkups. Diagnosis and treatment of diseases will help reduce the risk of paresthesia.
Diagnosis of paresthesia
If a person experiences persistent symptoms of paresthesia for no apparent reason, he should definitely consult a doctor. It is important to give your doctor as complete a medical history as possible, as well as any repetitive movements that could cause pressure on the nerve. It is also important to talk about all the medications the patient is taking.
If a person with complaints suffers from diabetes, then additional examination will be needed to help determine the presence or absence of nerve damage. The doctor may perform a complete physical examination, including a neurological examination, as well as blood laboratory tests. A spinal tap may be prescribed, which will help rule out a number of diseases.
If the doctor suspects that the problem is in the neck or spine, he may send the patient for an X-ray, CT scan, or MRI. Depending on the results obtained, treatment may be continued by another specialist - a neurologist, endocrinologist or orthopedist.
Treatment of paresthesia in official medicine
Treatment of paresthesia depends on the diagnosis that provoked its occurrence. If your limbs are numb, you can restore their circulation through exercise, stretching, or massaging the affected area.
If paresthesia is caused by a chronic disease
diseases such as diabetes, or occurs as a complication of treatment (for example, after a course of chemotherapy), most treatments are aimed at relieving symptoms. Your doctor may prescribe anti-inflammatory medications to relieve mild discomfort.
For people with more severe paresthesia, antidepressants may be prescribed. Their dosage for the treatment of paresthesia is significantly lower than the dosage of antidepressants that a doctor may prescribe to combat depression. In this case, it is generally accepted that medications help change a person's perception of pain.
There are also a number of alternative treatments that can help relieve the symptoms of paresthesia. For example, a special diet that includes a B complex vitamin, especially vitamin B12. But vitamin supplements are something that should be taken with caution. Because an overdose of vitamin B6, for example, is one of the causes of paresthesia.
Doctors may prescribe acupuncture and massage, which are believed to help significantly alleviate the symptoms of the disease. Sometimes self-massage with aromatic oils is also useful.
Complications and prevention
Depending on the cause, paresthesia can lead to serious complications:
- paralysis;
- limb atrophy;
- numbness of tissues.
If you experience repeated or prolonged tingling or crawling, you should contact a neurologist to undergo an examination and find out the cause of this phenomenon.
A good prevention for this and other violations would be:
- proper nutrition;
- moderate physical activity;
- timely treatment of any pathological processes in the body;
- blood pressure control;
- rejection of bad habits.
Paresthesia itself does not pose a danger to the body. But unpleasant sensations may indicate the development of serious diseases and disorders of the nervous system, so do not put off visiting a doctor.
Source: NeuroDoc.ru
Etiology
Paresthesia acts as the body's response to damage or irritation of the nerve root or nerve endings located in the spinal cord or brain.
The disease can involve both the skin and mucous membranes, often the oral cavity. Depending on the affected segment, predisposing factors will differ. For example, paresthesia of the tongue occurs against the background of:
- irritation of its surface with sharp edges of teeth;
- incorrectly selected dentures by the dentist;
- changes in bite, which can occur due to the absence of several or all dental units;
- increased wear of the dentition;
- galvanization, which is a consequence of the installation of prostheses made of different materials.
However, involvement in paresthesia of the tongue occurs only in cases where the above reasons are supplemented by the following internal pathological factors:
- arachnoiditis or other pathologies of the central nervous system;
- ulcerative lesions of the duodenum or stomach;
- gastritis of any nature and other pathologies of the digestive tract;
- hypovitaminosis, in particular, lack of B vitamins;
- disruption of the functioning of the endocrine system;
- malignant hypertension;
- ailments of the cardiovascular system;
- diseases of the ENT organs, for example, sinusitis and rhinitis.
In addition, paresthesia of the oral mucosa can be caused by:
- wisdom tooth removal;
- entry of filling material into the tooth canal.
The lower and upper extremities are most often affected by paresthesia. In the first case, the provoking factor may be:
- any medical intervention in the spinal cord area, namely open surgery on the spinal nerves, spine or spinal cord, as well as improperly performed procedures such as lumbar puncture;
- injury to the lumbar spinal column;
- the course of diabetes mellitus;
- the formation of malignant or benign formations in the spinal cord in the lumbar region;
- Raynaud's disease;
- obliterating endarteritis;
- polyneuropathy of alcoholic, diabetic or intoxication nature;
- rabies and neurasthenia;
- multiple sclerosis.
Paresthesia of the upper extremities is often caused by:
- osteochondrosis;
- wide range of injuries;
- formations of a malignant or benign course;
- damage to the cervical spine;
- the presence of an inflammatory process in the neck muscles;
- banal overwork;
- acute or chronic circulatory disorders;
- stroke;
- abuse of alcoholic beverages;
- decreased calcium levels in the blood;
- multiple sclerosis and diabetes mellitus.
Paresthesia of the lips is not uncommon, and most often develops against the background of:
- hypovitaminosis;
- osteochondrosis of the cervical spine;
- neuritis of the facial nerve;
- lowering blood glucose levels;
- hypertensive crisis;
- inflammatory lesions of the gums. Most often, such paresthesia occurs after tooth extraction;
- chronic migraine;
- multiple sclerosis;
- herpes zoster;
- Bell's palsy.
Paresthesia of the fingers and toes most often results from:
- osteochondrosis;
- tunnel syndrome;
- vegetative-vascular dystonia;
- lack of vitamin B in the body, as well as substances such as calcium and magnesium;
- polyneuropathy of various nature;
- Raynaud's syndrome.
The most common causes of scalp paresthesia:
- neuralgia of the facial or trigeminal nerve;
- Bell's palsy;
- transient ischemic attack;
- migraine.
Involvement of the nose in the pathological process occurs against the background of frostbite, the formation of atherosclerotic plaques, and diseases affecting the cardiovascular system. However, most often a similar variant of paresthesia occurs with osteochondrosis in the area of the cervical spine.
It is extremely rare for testicular damage to occur; provocateurs for this may include:
- oncology in the scrotum area;
- inflammatory process of this localization;
- cauda equina syndrome;
- bladder dysfunction;
- benign tumors;
- testicular torsion.
In addition, the disease can be triggered by:
- prolonged stay in a forced and uncomfortable position associated with prolonged compression of the limbs;
- prolonged exposure to stressful situations;
- a state of intense fear;
- poisoning by chemicals or heavy metals;
- the influence of external factors, for example, squeezing the shoulder with a tight tourniquet;
- overdose of drugs, in particular antiepileptic drugs, as well as substances aimed at lowering blood tone;
- an inflammatory process localized in the vessels that provide blood supply to nerve fibers - a similar condition is also called vasculitis.
It is advisable to relate the above reasons for the appearance of such a disease to absolutely every person, regardless of gender and age category.
What it is
Paresthesia occurs in response to damage or irritation of a nerve root, nerve ending, area of the spinal cord, or brain. In this case, the symptom will be determined precisely in the area from which the impulse either travels along the damaged fiber or is processed by the affected central area.
It is paresthesia, and not a decrease in temperature or other sensitivity, that will occur if several isolated electrical impulses occur simultaneously in the sensitive nerve fiber (which carries information from the skin or mucous membranes to the brain).
Such potentials will be layered on top of each other, extinguishing or potentiating each other. As a result, the area of the skin or mucous membranes “does not know” how to react, which is manifested by goosebumps or a burning sensation.
Causes
Paresthesia can be caused by a variety of pathological conditions, the list of which will differ depending on the location of the symptom.
Language
Pathological sensations in this area arise due to:
- irritation of the tongue with sharp dental edges;
- rubbing with dentures;
- changes in bite due to the absence of several or all teeth;
- pathological abrasion of the dentition;
- galvanization phenomena if there are dentures made of different metals.
In this case, paresthesia will occur if, simultaneously with the above factors, there are one or more internal causes:
- diseases of the nervous system: arachnoiditis;
- Gastrointestinal diseases: gastritis, ulcers;
- endocrine pathologies: mainly menopause;
- vitamin deficiency B12;
- diseases of the cardiovascular system: atherosclerosis, hypertension;
- diseases of the ENT organs: sinusitis, rhinitis.
The symptom can develop with the following pathologies:
- Medical intervention in the spinal cord area: lumbar puncture, operations on the spinal nerves, spine or spinal cord. In this case, paresthesia will be accompanied by pain in one or two legs, impaired sensitivity in them, and weakness in the leg muscles.
- Spinal cord injury at the lumbar level. Symptoms for this pathology may be identical to those during surgical interventions.
- Impaired arterial circulation of the lower extremities, which developed, among other things, due to diabetes mellitus. The disease is accompanied by paresthesia and pain at night, muscle cramps, pale skin and decreased hair growth on the skin.
- Tumors of the spinal cord at or below the lumbar level cause symptoms similar to those caused by a spinal injury.
- Raynaud's disease, which will also manifest itself as chilliness and numbness in the fingertips.
- Multiple sclerosis . With this pathology, there are multiple lesions in the brain, and the “set” of these lesions is individual for each person. It is this combination of lesions that will manifest itself with various symptoms.
- Polyneuropathy: alcoholic, intoxication, diabetic. It is characterized by a decrease in sensitivity and motor activity from the tips of the fingers to a certain level on the leg.
- Rabies: Paresthesia will occur in the leg where the animal bit. In the future, sound, water and photophobia will develop.
Hands
The symptom develops due to:
- Osteochondrosis, trauma, tumor or spondylolisthesis of the cervical spine, instability of one of the cervical vertebrae. In this case, there will be pain in the muscles of the arms, a decrease in their strength, and a violation of deep and superficial sensitivity. In addition, with a widespread process, headache, neck crunch, dizziness, visual or hearing impairment may also develop.
- Overstrain or inflammation of the neck muscles. In this case, there will also be pain in the neck at a certain position, and the body temperature may rise.
- Circulatory disorders in the vessels that provide trophism to the brain - acute and chronic. In some cases, paresthesia in the hands may be the first sign of stroke, followed by loss of consciousness and the development of some kind of neurological deficit (paralysis, hearing impairment, understanding or speech reproduction).
- Damage to individual nerves due to chronic alcohol intake, diabetes, infectious and allergic causes. In this case, paresthesia is accompanied by impaired sensitivity and movement from the fingertips and above.
- Multiple sclerosis, if one of the lesions is in the sensitive area of the cerebral cortex. Additional symptoms can be very varied.
- Decrease in blood calcium levels. This condition is characterized by specific muscle cramps in the hands and face.
Lips
Paresthesia develops when:
- Hypovitaminosis B. In this case, there will be not only paresthesia in the lips, but also in other parts of the body, muscle cramps, and increased hair loss.
- Osteochondrosis of the cervical spine. Paresthesia is accompanied by headaches, lumbago in the neck, discomfort in the neck, back and shoulders, and numbness of the tongue.
- Neuritis of the facial nerve. In this case, there will also be a violation of salivation, facial asymmetry, and the inability to puff out the cheeks.
- Decreased blood glucose levels. This is also manifested by sweating, confusion, hunger, cold clammy sweat, and fatigue.
- Hypertensive crisis. A sharp increase in pressure to high levels is also manifested by headache, vomiting, and sometimes impaired consciousness, paralysis, chest pain, and shortness of breath.
- Multiple sclerosis.
- Migraine . Usually, in addition to paresthesia, a person is bothered by a severe headache in one half of the head.
- Inflammation of the gums. There is no violation of the general condition, there is only pain and discomfort in one of the areas of the oral cavity.
- Bell's palsy. In this case, numbness of the lips is the first sign of the disease; later paralysis numbs all facial muscles.
- Herpes zoster. In this case, an area of redness on the skin is visible, on which specific blisters subsequently appear.
Numbness and tingling may occur with:
- osteochondrosis;
- pinching of one of the nerves innervating the fingers, including with carpal tunnel syndrome;
- lack of vitamins B;
- lack of calcium or magnesium;
- Raynaud's disease;
- polyneuropathies of various origins.
Paresthesia of the entire head
Develop due to:
- Bell's palsy, followed by paralysis of the facial muscles.
- Trigeminal neuralgia, which also manifests itself as pain in areas of the face;
- Neuralgia of the facial nerve is accompanied by numbness and weakness of the face, lips, and tongue.
- Before a migraine attack, as an aura.
- Transient ischemic attack, which can manifest itself as a stroke, but the symptoms go away on their own within an hour.
Medications
The following can cause paresthesia as a side effect:
- "Methaqualone"
- "Isoniazid";
- "Protionamide";
- "Cycloserine";
- antiepileptic drugs;
- drugs to lower blood pressure.
Features of temporary paresthesia after dental treatment
Paresthesia can occur when a tooth is removed (especially a wisdom tooth), or filling material gets into the tooth canal. In this case, numbness develops in the chin, tongue, cheeks, and lips. Symptoms disappear after a few days (less often) or 2-3 months (more often).
This condition is treated with injections of Dibazol and Galantamine and B vitamins. If complaints persist, surgical treatment is used.
- Taking medications: Trental, Nicotinic acid, Piracetam, Actovegin, B vitamins;
- Physiotherapeutic techniques: electrophoresis, magnetotherapy, mud therapy, diadynamic currents.
Listen to your body and don’t put off visiting your doctor until the last minute!
Paresthesia of the lower extremities - what is it? This question worries patients with this problem. Paresthesia is numbness of various parts of the body, most often the limbs, and can also appear on the face, tongue, and lips. This is the result of irritation or damage to nerve fibers. In this case, you may feel a tingling sensation in the numb parts, the so-called “goosebumps”. The person does not experience pain. This phenomenon may be temporary or permanent. With temporary paresthesia there is no threat to health. Paresthesia is not an independent disease, but a symptom of some pathology.
- Feeling of numbness, tingling, goosebumps. Usually there is paresthesia of the arms and legs, face, neck, and tongue.
- This disease may cause symptoms such as pale skin and decreased temperature.
Paresthesia of the fingers. Sometimes a person feels his hand - who will pay attention to such a small nuisance? However, this symptom may indicate the presence of some disease, so this signal should not be ignored. Every person has probably felt numbness and tingling in their fingers at least once in their life.
They appear when there is compression of the nerve endings. This can happen if, for example, a person holds a heavy thing in his hands for a long time or at night presses his hand with the weight of his body. You just need to return your hand to its normal position, massage your hands, and your fingers will regain their sensitivity. But if discomfort in your fingers appears for no apparent reason, you should be wary - this may be one of the symptoms of the disease.
Our arms and legs are in a very close connection with the spine, and problems arising in it immediately affect the condition of the arms and legs.
Paresthesia of the fingers often appears with the following diseases:
- pinched nerve of the cervical spine;
- spinal injury;
- spina bifida;
- osteochondrosis;
- vertebral displacement.
The sensation of pins and needles in the fingers occurs during a stroke. Paresthesia of the fingers of the left hand in combination with pain on the left side of the body threatens a heart attack and requires immediate medical attention.
Regular manifestations of paresthesia occur in athletes who lift weights. In such cases, compression occurs, the so-called cubital syndrome. Paresthesia of the fingers often occurs in people who do monotonous manual work. For example, they work on a computer or play the piano. In such cases, compression of the median nerve of the wrist occurs - tunnel syndrome.
In addition to paresthesia, you may experience:
- general deterioration of health;
- confusion of consciousness;
- difficulty pronouncing words;
- dizziness;
- loss of body control;
- fainting;
- increased frequency of urination.
A combination of all or more of these symptoms is grounds for immediate medical attention.
Paresthesia of the lower extremities - what is it? The appearance of a symptom such as loss of sensation in the skin of the legs indicates this pathology.
It appears on different parts of the legs:
- most often this occurs in the feet;
- sometimes the calves cramp;
- necrosis also occurs on the thighs.
Sometimes leg paresthesia occurs at night. If you change your position, massage your leg and the symptoms go away, there is no reason to worry. The person simply slept in an awkward position and had a pinched nerve.
If paresthesias are regular, because of them a person sleeps poorly, pain and cramps appear, then it is necessary to consult a doctor and be examined.
The reasons for the appearance of this pathology:
- The most common cause is osteochondrosis. The spine becomes deformed with age due to injuries, as a result, nerves and vessels are subject to compression for a long time and paresthesia occurs.
- After removal of a spinal hernia, the leg muscles may be paralyzed, resulting in numbness. When the patient's condition improves, paresthesia disappears.
- In diseases of the cardiovascular system, there is a lack of blood supply to tissues throughout the body. The small vessels of the legs suffer the most from lack of blood and narrow the lumen. Therefore, numbness occurs.
- With paralysis, which is a consequence of a stroke, the sensitivity of some parts of the body is lost.
- Paresthesias are a consequence of tumors of the brain and spine. The treatment of paresthesia also depends on the treatment of the underlying disease.
- The blood vessels of the legs are affected in diabetes mellitus. Therefore, the occurrence of paresthesia in such patients will be inevitable. When treating diabetes, loss of sensitivity is also treated in combination.
- Diseases of the arteries of the legs, multiple sclerosis - these diseases also cause loss of skin sensitivity.
There are types of paresthesia that do not require treatment. This:
- lack of B vitamins;
- migraine;
- a pose with compression of the limbs, in which a person is forced to remain for a long time;
- excitement, emotional stress.
Symptoms
Paresthesia of the limbs or any other localization has a rather specific clinical picture. The main symptoms are presented:
- tingling or burning sensation of the skin;
- crawling feeling of “goosebumps”;
- blanching of part of the skin;
- hair loss in the affected area;
- a decrease in local temperature;
- numbness, which often spreads throughout the body;
- weakness of the muscles of the upper and lower extremities;
- convulsions that appear at night;
- chilliness of fingers and toes;
- headaches and dizziness;
- the appearance of a characteristic crunch during movements;
- pain syndrome of varying severity;
- disturbance of consciousness;
- pale skin;
- attacks of nausea and vomiting.
Attacks of paresthesia with the expression of similar signs can last from several minutes to 3 months.
Additional clinical manifestations will include symptoms of the underlying disease that provoked the development of paresthesia.
Symptoms and signs of paresthesia
Symptoms of paresthesia depend on the location of the lesion. Usually this disease can be recognized by the following manifestations:
- Feeling of coldness in the lower extremities
. - Numbness of the skin.
- Feeling of crawling sensations.
- Tingling
fingers and toes. - The appearance of allergic reactions
on the skin. - Reduced sensitivity.
Note! When the first signs of paresthesia appear, you should immediately consult a doctor. In the initial stages, it is much easier to get rid of this disease.
Diagnostics
If one or more of the above symptoms occur, you should seek help from a neurologist. The only exception is the localization of unpleasant sensations in the oral cavity - in such situations, diagnosis and treatment are carried out by a specialist in the field of dentistry.
Establishing a final diagnosis involves conducting a wide range of laboratory and instrumental examinations, which are preceded by manipulations performed directly by the clinician. Thus, the first stage of diagnosis includes:
- studying the medical history - to establish the most characteristic predisposing factor for a particular person;
- collection and analysis of life history - this is necessary in cases of the development of paresthesia due to reasons that do not have a pathological basis;
- a thorough neurological examination - aimed at assessing the condition of the skin and its sensitivity, as well as identifying areas of paresthesia and numbness;
- a detailed survey of the patient - to determine the severity of symptoms and compile a complete symptomatic picture.
Instrumental procedures involve the implementation of:
- electroneuromyography;
- radiography of the spine;
- Ultrasound of the peritoneum;
- ECG and EEG;
- CT and MRI of the spinal cord or brain;
- rheovasography.
Laboratory diagnostics are limited to:
- general clinical analysis and blood biochemistry;
- toxicological blood test.
Forecast
Most common causes of chest pain are fairly easy to treat and do not pose a serious health threat. However, chest pain can be a symptom of a life-threatening condition.
If you think you are having a heart attack or other heart or lung problems, seeking medical help right away can help save your life. After diagnosis, your doctor may recommend additional treatment to correct your condition.
- Diagnostic tests and procedures for heart attack
- Neck pain - what to do, causes, diagnosis, treatment, prevention.
- Chest pain. What to do if a patient has chest pain?
- Iron deficiency anemia: symptoms, signs, diagnosis and treatment
Treatment
Paresthesia of the face, limbs, lower jaw or any other localization is often eliminated using conservative techniques, which is based on the following:
- detoxification medications;
- hypoglycemic substances;
- vitamin complexes;
- antiplatelet agents, vasoactive drugs and other tablets aimed at improving blood rheology.
In addition, drug therapy also involves the use of warming ointments applied to the area of the injured nerve.
Treatment of paresthesia of the lower extremities or other types of illness using physiotherapeutic procedures includes:
- vacuum and underwater massage;
- darsonvalization;
- medicinal electrophoresis;
- galvanic mud applications;
- acupuncture.
Conservative therapy can also be aimed at:
- the patient undergoing a course of therapeutic massage;
- the use of folk remedies at home is indicated only after consulting with your doctor. The most effective are decoctions based on sweet clover and birch leaves, horse chestnut and willow bark.
If the above methods of treatment are ineffective, it is recommended to implement low-traumatic neurosurgical techniques. In addition, surgery is necessary in cases where the cause of paresthesia is tumors or hematomas.