Tonsillitis is an inflammation of areas of lymphoid tissue (tonsils) located on the back wall of the pharynx. They protect the body from the penetration of potentially dangerous viruses or bacteria, but in some cases they themselves can become infected. In many acute cases, the disease is viral in nature, so tonsillitis can be treated without the use of antibiotics. The chronic form of the disease is associated with the long-term existence of bacteria in the tonsil tissue. It requires complex therapy, and in some cases, surgical intervention. Tonsillitis most often affects children, but it can develop in people of any age.
Chronic tonsillitis: symptoms in adults and children
Tonsillitis is a disease caused by infection that affects the tonsils - organs that are located in the nasopharynx and form a ring barrier that protects the body from the penetration of viruses and bacteria, triggering the action of the immune systems.
The surface of the tonsil is covered with depressions - lacunae. These depressions can cause chronic inflammation, as food debris and dead cells settle there, which are a favorable environment for pathogens.
When the self-cleaning process of lacunae is disrupted, pathogenic microflora multiplies, causing chronic inflammation.
When damaged by microbes, the tonsils themselves turn into a source of infection and contribute to the spread of pathogenic flora throughout the body.
The main causative agents of tonsillitis are:
- Pneumococcus
- streptococcus
- staphylococcus
- hemophilus influenzae
According to the nature of the disease, tonsillitis is distinguished:
- acute , which is characterized by high fever, sore throat when swallowing, chills, general malaise chronic , when microbes affect the tonsils for a long time, resulting in inflammation in the palatal area
Chronic tonsillitis can be of various types:
- follicular - small pustules predominate on the affected tissue
- lacunar – widened lacunae predominate
- catarrhal - enlarged tonsils are covered with plaque
- fibrous-membranous - tissues covered with a film
- phlegmonous - the most severe and dangerous form with purulent inflammation
In addition, doctors distinguish between the following forms of tonsillitis:
- simple – inflammation of the tonsils is slight, and the body’s reaction is not significant
- toxic-allergic – inflammation is widespread, in which disturbances are observed in other systems in the body
The main symptoms of chronic tonsillitis can be:
- sore throat causing dry cough
- pain of a constant nature, which periodically decreases or intensifies
- swelling of the nasopharyngeal area
- negative reaction of the throat mucosa to cold
- pus is released from the tonsil when pressed
- general weakened state and fatigue
- body temperature is increased
- in some cases there is aching in the joints
- specific odor from the mouth due to purulent plugs
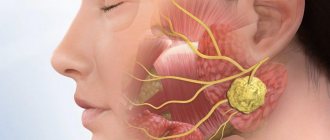
- submandibular lymph nodes enlarge, become dense and sensitive to palpation
Reasons that provoke the development of the disease:
- nasal polyps
- frequent inflammation of the tonsils
- chronic adenoiditis
- purulent sinusitis
- deviated nasal septum, which interferes with proper breathing
Chronic tonsillitis seems to be a very serious disease, since the human body is exposed to toxic components of the infection for a long time, which can cause damage to internal organs. In addition, purulent discharge from the tonsils enters the gastrointestinal tract.
These factors can lead to various complications
- diseases of the cardiovascular system
- kidney damage
- dysfunctions of the genitourinary system
- rheumatism
- dysbacteriosis
- polyarthritis
- nervous system disorders
- pneumonia
- psoriasis
- exacerbations of allergic reactions
- in cases of prolonged absence of treatment – the development of an autoimmune disease
Causes of tonsillitis
Depending on the nature of the course, tonsillitis can be:
- acute (also called sore throat),
- chronic1,2,3.
The cause of acute inflammation of the tonsils is infection1. It can be viral, bacterial or mixed1,2.
The viral nature of sore throat predominates in adults and children over 15 years of age1,2. It usually develops with ARVI, which is caused by rhinoviruses, adenoviruses, and parainfluenza viruses1. In this case, tonsillitis is accompanied by rhinitis, pharyngitis, laryngitis and other respiratory tract diseases1.
In children 5-15 years old, bacterial tonsillitis is more common, and in first place (up to 30% of cases) among them is the most dangerous type of sore throat, caused by beta-hemolytic streptococcus of group A1. In adults, this type of tonsillitis is much less common1, and among the bacteria that cause the disease, streptococci of other groups, corynebacteria, Haemophilus influenzae, Neisseria, and staphylococci predominate1.
The cause of chronic tonsillitis is also an infection, but, unlike acute processes, it is caused by less aggressive pathogens2. In this case, there may be no acute inflammation of the tonsils; the process is initially chronic in nature and is hidden behind frequent acute respiratory viral infections and inflammatory diseases of the oral cavity and pharynx (non-anginal form of chronic tonsillitis)2.
Chronic inflammation leads to the death of functional, that is, lymphoid, tissue of the tonsils and its replacement with connective tissue1. The tonsils gradually lose their protective functions, often become easy prey for microbes and viruses, become inflamed and turn into a breeding ground for infection1 and an irritant for the immune system. As a result of chronic tonsillitis, immune disorders often occur, leading to the development of infectious-allergic and autoimmune diseases1,2.
Chronic tonsillitis - treatment in adults
Diagnosis of chronic tonsillitis is often difficult. An otolaryngologist treats tonsillitis. Using tests, he determines the degree of inflammation and tissue damage.
As a rule, the following tests are prescribed:
- swab from the throat and nasal mucosa
- general blood and urine test
- biochemistry of saliva
- immunogram
Treatment methods for this disease depend on the nature of its course:
- conservative – drug therapy aimed at treating inflammation, the infection that caused it, as well as diseases that can provoke exacerbation.
- surgical - complete removal of the tonsils or only their affected parts.
Treatment of chronic tonsillitis always begins with a conservative method. In cases where no positive dynamics are observed after 3 courses of therapy, a decision is made to remove the tonsils - tonsillectomy. The toxic-allergic stage requires a surgical method after 2 courses of unsuccessful drug treatment.
The main condition for achieving a positive result is an integrated approach, which, in addition to eliminating the source of infection, includes:
- sanitation of the oral cavity (treatment of caries)
- elimination of chronic inflammation of the nasal cavity (rhinitis, sinusitis, adenoiditis)
- strengthening the immune system
Conservative treatment of chronic tonsillitis
Using a conservative method, chronic tonsillitis is treated in courses, preferably in spring or autumn.
This therapy includes several stages:
- cleansing the tonsils from pathological flora, pus and plugs (rinsing with antiseptics, using ultrasound);
- introduction of medications into cleaned lacunae in the form of ointments, solutions, emulsions, pastes
- taking anti-inflammatory drugs;
- if necessary, prescribing antibiotics;
- elimination of secondary allergization of tissues;
- relieving large swelling with antihistamines;
- prescription of immunostimulating drugs;
- irrigation of mucous membranes with complex salt solutions, which eliminates allergic reactions and strengthens the immune system;
- medical physiotherapeutic procedures (UHF, ozokerite compresses on the lymph node area, UV irradiation of the tonsils);
- reflex therapy (cervical spine massage, acupuncture);
- inhalations using medications;
- gargling with decoctions of medicinal plants.
The success of conservative treatment lies in an integrated approach and regularity of procedures.
If you have tonsillitis, you should not self-medicate. Even inhalations must be prescribed by a doctor, since any treatment methods often have a number of contraindications.
Chronic tonsillitis: surgical treatment
If there is no positive result after conservative treatment, a decision is made on a surgical operation to remove the tonsils (tonsillectomy), when the affected tissue is removed and the areas in contact with it are cauterized. The procedure is performed under anesthesia (general or local).
Indications for surgical intervention are:
- paratonsillar abscess
- toxic-allergic form
- chronic or acute sepsis
- excessive enlargement of the tonsils, which interferes with the mechanical process of swallowing
- apnea
- dysfunction of internal organs
Modern clinics offer various methods of performing tonsillectomy:
- Classic: using surgical instruments - the procedure is quite painful, accompanied by blood loss. This method is considered obsolete.
- Laser is the least traumatic method, making it possible to remove not the entire tonsil, but only the affected part.
- Electrocoagulation is exposure to high-frequency current.
- Ultrasonic – uses the energy of ultrasonic vibrations.
- Radiofrequency ablation - tissue is cut without thermal energy. Trauma and blood loss are minimal.
- Cold plasma - exposure to the source of the cold plasma component. It is considered one of the safest methods for removing tonsils.
The nature of the operation is determined based on:
- the size of the growth of pathological tissues
- presence of scars
- the degree of fusion of the tissues of the tonsils with the tissues of the nasopharynx
Contraindications to tonsillectomy are:
- acute inflammatory process
- tuberculosis
- diabetes
- blood and vascular diseases
- acute renal failure
- heart disease
- menstruation period
Doctors give the following recommendations to patients on how to behave in the postoperative period:
- If possible, do not talk for 24 hours
- keep bed rest
- sleep on your side
- exclude rough foods
- Hot baths and saunas are prohibited during the week
- exclude the pool for 4 weeks
Complications after surgery are rare. To avoid this, you must strictly adhere to your doctor’s recommendations.
Many people fear that after removal of the tonsils, the body’s protective properties will noticeably decrease. This fear is completely justified. However, there is no significant decrease in immunity in patients after surgery. A number of experts believe that the remaining tonsils of the pharyngeal ring continue to successfully serve as a barrier against infections.
Chronic tonsillitis in a child: treatment
Tonsillitis is quite common among children. According to statistics, more than half of frequently ill children have a chronic form of the disease. Tonsillitis can develop and become chronic in a child at any age.
Children with:
- allergies
- chronic rhinitis
- hypovitaminosis
- rickets
- low immunity
Sometimes it is possible to develop chronic tonsillitis without a cold. This is due to congenital pathologies of the palatine tonsils. In such cases, tonsillitis, as a rule, is provoked by diseases of the oral cavity (caries, stomatitis), and the tonsils are involved in the general inflammatory process.
Pediatricians give the following recommendations for parents of a child with chronic tonsillitis:
- undergo preventive treatment at least 2 times a year
- It is preferable to use homeopathic remedies
- at an early age, when the child cannot yet gargle, let him drink chamomile decoction
- teach your child to keep his mouth clean
- Provide your baby with a nutritious diet enriched with vitamins and minerals
- take a walk in the fresh air every day
- avoid severe hypothermia
- toughen up the child
- accustom your tonsils to cold (during remission, drink chilled drinks in small portions)
- If possible, provide your child with a vacation on the seashore
- Give your baby a gentle throat massage from top to bottom using stroking movements
- Keep in mind that ultrasound and microwave physiotherapy is indicated from 6 to 7 years of age
Exacerbation of chronic tonsillitis: treatment
During an exacerbation of chronic tonsillitis, pathogenic microflora is activated. This condition can be triggered by the following factors:
- ARVI
- severe hypothermia
- stressful situation
- low immunity
- allergies
- fungal and viral infections
During an exacerbation, infectious agents begin to actively penetrate the vessels and tissues of the tonsils. And the release of toxins causes an acute allergic reaction.
Exacerbation of this disease can lead to negative changes in the structure of the tonsils:
- hyperplasia - fibrous tissue grows, cysts form, and the tonsils enlarge
- atrophy - lymphoid tissue is replaced by fibrous tissue, and the size of the tonsils decreases
In cases of exacerbation, the following treatment methods are usually used:
- antibiotic treatment
- the use of bacteriophages, especially in cases where the infectious agent is not sensitive to various antibiotics
- Irrigation of the tonsil area with disinfectants
- use of antimicrobial drugs
- physiotherapeutic procedures
Prevention
Prevention is based on:
- giving up bad habits, smoking;
- carrying out hardening procedures;
- establishing a balanced diet;
- avoiding hypothermia and drinking cold drinks;
- timely release of nasal breathing and clearing of the nose from purulent accumulations;
- proper treatment of tonsillitis and sore throat, avoiding complications.
If primary signs appear, do not hesitate to consult a doctor, otherwise inflammation of the tonsils, especially in a child, can lead to cardiovascular diseases, rheumatism, and the consequences may well become irreversible
Next Post
Previous Post
Chronic tonsillitis: treatment with antibiotics
To treat chronic tonsillitis, antibiotics are often prescribed to stop the infection and prevent it from spreading further. These funds can be:
- wide range
- local action
Antibiotic drugs belong to different groups:
- Cephalosporins – Cefix, Cefodox, Cefazolin, Tricaxon, Ceftriaxone
- Penicillins – Amoxiclav, Flemoklav, Unazin, Timentin, Penicillin, Amoxicillin
- Macrodids - Erythromycin, Azithromycin, Clarithromycin, Roxithromycin
- Lincosamides – Lincomycin, Clindamycin
The choice of an antibiotic of one group or another is determined only by a doctor after an appropriate examination. It is strictly prohibited to start taking these medications on your own and without medical supervision.
When taking these medications, consider the following:
- antibiotics are taken in a course;
- taking medications is stopped after 3-5 days of normalization of the condition;
- the use of reduced antibiotic standards can lead to resistant strains of microorganisms, which will complicate treatment in the future.
Possible complications
Despite its apparent harmlessness, tonsillitis is a rather dangerous condition that can lead to the following consequences:
- Inflammation in the middle ear area, which in turn will provoke decreased or complete loss of hearing (in the absence of adequate and timely therapy).
- Acute rheumatism of the heart and joints.
- Formation of prolapses in the heart valves.
- Glomerulonerite.
- Purulent inflammation of the tissues in the pharynx.
- Peritonsillar abscess.
- Severe pneumonia (unilateral or bilateral).
- Exacerbation of allergic reactions.
Komarovsky: treatment of chronic tonsillitis
The famous children's doctor Evgeny Komarovsky draws the attention of parents to the fact that many confuse sore throat with chronic tonsillitis. These are two different illnesses. Sore throat is an acute infectious disease that is always caused by microbes and cannot appear only after hypothermia. Damage to the tonsils in such cases is an indicator of the severity of the disease. And chronic tonsillitis is a disease of the palatine tonsils themselves, in which various factors can provoke an exacerbation.
Komarovsky considers the main cause of exacerbations of chronic tonsillitis to be a decrease in the body’s protective properties. Therefore, the main task is to strengthen the immune system. In addition, the doctor recommends:
- do not use Lugol’s solution to lubricate the tonsils in children, as it contains a high concentration of iodine;
- avoid dryness of the mucous membranes of the mouth and nose;
- humidify the air in the room;
- limit the use of local antiseptics;
- do not forbid your child to eat cold foods, since cold stimulates blood circulation and thereby improves immunity; be sure to treat caries;
- teach your child to rinse his mouth after eating.
Enlarged tonsils - the reason?
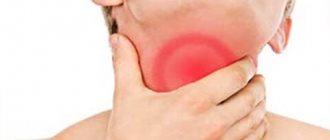
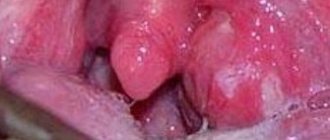
There are several reasons why your tonsils start to hurt. Consider the inflammation of the tonsils in the throat in the photo. This picture can be seen if microbes that cause abnormalities - streptococci, staphylococci and others - settle in the throat. Another reason may be the invasion of viruses or fungi into the oral cavity.
The tonsils consist of a large concentration of lymph nodes. Their product is lymphocytes, which fight all infections that penetrate us. If there are not enough lymphocytes, or they are unable to overcome the infection themselves, then the tonsils become inflamed.
In what cases should you be wary of a painful reaction of the tonsils:
- If immunity is lowered, this can happen not only in the off-season. A fairly long period of stress is enough for the body to stop protecting itself from enemies.
- The presence of inflammation that has become chronic.
- Irritation from allergens, chemicals, spicy foods or drinks.
Treatment of chronic tonsillitis with laser
Laser tonsillectomy is one of the progressive methods of treating chronic tonsillitis. Unidirectional laser radiation is used in both conservative and surgical treatment. With conservative therapy, the laser beam has an anti-inflammatory effect.
Features of this method:
- laser is applied in courses 2 times a year
- the course includes an average of 10 procedures
- Process duration: about 4 minutes
- after removal of tonsils, this procedure has a healing effect
- local irradiation of lacunae is possible
- goes well with drug therapy
The surgical treatment method, in which tonsils are removed using a laser, has its own characteristics:
- Before surgery, immunomodulators are prescribed to increase the resistance of body cells to bacteria
- the procedure is performed under local anesthesia
- Typically the operation takes about 20 minutes
- no pain or other discomfort
- the likelihood of bleeding is quite low
- the rehabilitation period lasts about a week
With the help of a laser, 2 methods of surgical treatment are possible:
- complete removal of tonsils
- partial excision
Contraindications to laser tonsillectomy are:
- age up to 10 years
- oncological diseases
- exacerbation of chronic diseases
- blood and vascular diseases
- pregnancy
Treatment of sore throat
When treating angina, it is important to begin symptomatic treatment at the first signs of the disease and carry out all procedures regularly and as often as possible.
Drug treatment should be prescribed only by a doctor, after examination and consultation of the patient.
At the first signs of a sore throat you should:
- gargle as often as possible - this helps to mechanically remove microorganisms, suppress their activity, reduce inflammation and pain. You can gargle with any antiseptic solutions - furatsilin solution, decoctions of chamomile, sage, soda-salt solution (0.5 tsp of salt and soda per 1 cup of water), iodine solution (1-2 drops per 1 cup of water), 1% solution hydrogen peroxide (10-30 drops per 1 cup of water), propolis solution (2-5 drops per 1 cup of water) and so on. Such rinses should be carried out as often as possible, up to 10-12 times a day, but at least 4-6 times a day;
- drink more alkaline liquid - the patient needs to drink 2-2.5 liters of liquid per day. This could be warm milk, an hour with lemon and honey, broth, mineral water, compotes, jelly, and so on;
- do inhalations - such procedures can only be carried out at normal body temperature. Inhalations are done with sage, chamomile, boiled potatoes or special preparations;
- take lozenges and tablets - various cough lozenges help soothe the throat and reduce inflammation; for sore throat, they can be used as an adjuvant. Such drugs as Adjisept, Travisil, Faringosept, Sprepsils, Septolete, Angisept and others have a good effect;
- use sprays - to treat sore throat in young children, you can use spray medications; they help reduce inflammation and destroy microorganisms. For the treatment of sore throat, Ingalipt, Yox, Bioparox, Stopangin and others are used.
Chronic tonsillitis: treatment, drugs
For chronic tonsillitis, medications are selected after determining the cause of the disease. Taking into account the type of pathogens of the disease and the form of its course, the following remedies can be prescribed:
- Local and broad spectrum antibiotics.
- Augmentin is a penicillin series, quite effective and popular
- Sumamed is a group of macrolides, widely used in the treatment of the respiratory tract.
- Ceftriaxone (powder for injection) – administered intramuscularly or intravenously
- Bioparox (aerosol) – has an antiseptic, antifungal and anti-inflammatory local effect
- Miramistin is a mild antibiotic used for inhalation
- Antiseptics that affect the pathogenic flora of the tonsils, disinfect and disinfect the nasopharyngeal area:
- Faringosept (lozenges) – has a bacteriostatic effect on most pathogens.
- Falimint (tablets) – in addition to being antiseptic, it has a slight anesthetic effect.
- Tonsilgon (drops and tablets) is a plant-based antiseptic with an anti-inflammatory effect.
- Chlorophyllipt – has antibacterial properties against antibiotic-insensitive pathogens. An alcohol solution is used for rinsing, and an oil solution is used to lubricate the tonsils.
- Chlorhexidine (solution, spray) – used as a rinse and irrigation.
- Lugol (spray, solution) – for treating tonsils.
- Decasan - has an antiseptic effect, increases the sensitivity of microbes to antibiotics.
- Decathylene (lozenges) – has a bactericidal effect, eliminates pain symptoms.
- Trachisan (lozenges) – has an antimicrobial effect.
- Anti-inflammatory, promoting tissue regeneration and eliminating inflammation:
- Tantum verde (tablets, spray, solution) - also has analgesic properties.
- Ingalipt (aerosol) – has an antimicrobial and cooling effect on the mucous membrane.
- Strepfen (lozenges) - belongs to the group of local non-steroids. Eliminates inflammation, relieves sore throat.
- Septolete (lozenges) – indicated for inflammatory and infectious diseases.
- Painkillers - to relieve pain in the throat:
- Grammidin (tablets) – also have an antiseptic and anti-inflammatory effect
- Strepsils (tablets) – fungicidal and antibacterial medicine containing menthol and vitamin C
- Stopangin (rinse solution, spray) – has analgesic and antimicrobial properties
- Acetaminophen (tablets) – relieves pain and fever symptoms, has an anti-inflammatory effect
- Combined, affecting the body in several directions:
- Proposol (spray) is an antimicrobial, wound-healing and anti-inflammatory drug.
- Tonsilotren (tablets) is a homeopathic remedy that restores tissue structure and has anti-inflammatory and immunomodulatory properties.
- Aqualor – has an antiseptic, anti-inflammatory and restorative effect, improves immunity.
- Givalex (irrigation solution) – has antibacterial, antifungal, analgesic effects.
- Tera-Flu (spray) is a product with antiallergic, antipyretic, and analgesic effects.
- Lizobakt (lozenges) – on a natural basis, has antiviral, antifungal and antiseptic effects, regulates the immune system.
If necessary, antiviral auxiliary agents can be prescribed, which are prescribed in cases where the disease is caused by a viral infection:
- Acyclovir
- Valaciclovir
- Pharmciclovir
- Viferon
- Arbidol
Antipyretics for high temperatures:
- Ibuprofen
- Paracetamol
- Aspirin
Immunomodulatory, helping to normalize the immune system:
- Imudon (lozenges) – increases the body’s resistance, eliminates bacterial infections
- IRS-19 (nasal spray) – can be used from three months of age
- Ribomunil (tablets, granules) – used as a therapeutic and prophylactic agent
- Broncho-munal (capsules) – reduces the frequency and severity of infectious diseases
Antihistamines – in case of allergic reactions:
- Tsetrin
- Loratadine
- Suprastin
- Tavegil
Chronic decompensated tonsillitis: treatment
Experts distinguish the following types of chronic tonsillitis:
- compensated – the inflammatory process does not extend beyond the area of the palatine arches, the person’s general well-being is not disturbed
- decompensated - the inflammatory process is combined with a disruption of the functioning of other body systems, an increase in temperature
This stage is the most severe form of the disease, in which the infected tonsils practically do not perform their functions.
Signs of decompensated form:
- frequent recurrence of relapses (more than 3 times a year);
- spread of inflammation beyond the tonsils - the tissues around them are also affected by infectious microorganisms, and general suppuration begins;
- formation of scars or other damage to the tonsils;
- persistent acute pain in the throat;
- difficulty opening the mouth;
- severe intoxication of the whole body;
- heat.
The decompensated form is a direct indication for surgical removal of the affected tonsils. Conservative therapy in this case will not bring results.
Symptoms of inflammation of the tonsils
Inflammation of the tonsils (photo) is characterized by discomfort in the throat. The first feeling is the sensation of a pain in the throat. Then a slight soreness occurs, which will gradually intensify. After this, the discomfort develops into pain. They manifest themselves especially strongly when a person swallows food. Upon examination, redness of the tonsils of the palate can be detected. In addition, they swell significantly.
Inflammation of the tonsils, the symptoms of which can be fairly easily identified, is a serious disease, the treatment of which should not be delayed. If treatment is not started on time, the patient will gradually develop breathing problems. Every day it will become more and more difficult not only to swallow food and water, but also to breathe.
You feel tired, weak, lethargic, and apathetic. These are all signs of illness. Body temperature rises. It can reach 29 degrees. The patient experiences chills and fever. You feel achy and your head starts to hurt.
Upon further examination, purulent discharge may be detected on the tonsils. The pus will be white-yellow in color. Lymph nodes in the neck and submandibular area will begin to grow. Pain will be felt upon palpation. Moreover, the lymph nodes will remain enlarged even after all other signs of the disease disappear during treatment.
In addition, the voice begins to hoarse. In some cases, you can even lose it temporarily. This is due to the fact that when the tonsils swell, they prevent the vocal cords from closing. If a sore throat is not treated, an acute form of laryngitis develops. Then the patient will begin to cough heavily.
Sore throat is an acute form of inflammatory processes in the tonsils of the palate. This disease has several types: phlegmatous, lacunar, follicular and catarrhal. The catarrhal type of sore throat is considered the mildest in the course of the disease. With the follicular type, follicles are formed - ulcers. They reach the size of a buckwheat grain. The pain will be so severe that even your ears begin to hurt. Body temperature is very high. With the phlegmatous type of the disease, an abscess develops. Body temperature rises to 40 degrees. With the lacunar type, pus will concentrate on the lacunae.
The lingual tonsil becomes inflamed quite rarely. Characteristic symptoms include pain when moving the tongue.
Adenoids are tonsils that are located in the pharynx. They can become inflamed on their own or together with the tonsils.