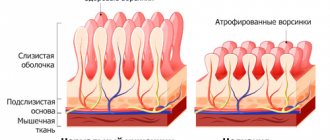
Under the influence of certain negative factors, an inflammatory process may begin to develop, and foci of dystrophy or muscle spasms may appear. All this will influence what type of intestinal colitis develops in your case; it can be catarrhal, atrophic, spastic or atonic. Atrophic colitis of the intestine is characterized by the development of the inflammatory process and atrophy of its mucous membrane.
If treatment is not carried out, concomitant diseases such as atopic dermatitis, allergies may appear, the functioning of the endocrine system is disrupted, which leads to weight gain. If you do not pay attention to chronic intestinal colitis and its symptoms, this leads to dilation of the pelvic veins, as a result of which hemorrhoids, intestinal colic develop, and from time to time constipation and profuse diarrhea occur.
You need to know how to treat chronic intestinal colitis, so you need to seek qualified medical help in a timely manner. In most of these patients, in addition to the indicated pathology, chronic gastritis, duodenitis, and enteritis usually develop. If you continue to delay the necessary treatment, there is a high risk of developing ulcerative colitis; malignant tumors can develop in the intestines and polyps can grow.
What is colitis?
This disease is a consequence of the spread of the inflammatory process in the large intestine. Inflammation affects the intestinal mucosa. The process may involve either the entire colon or only a separate part of it. Chronic intestinal colitis occurs. Symptoms and treatment will depend on the spread of the inflammatory process and the involvement of other parts.
There are situations when problems in the form of inflammation begin simultaneously in the large and small intestines, then we can talk about a pathology such as enterocolitis.
Classification
There are several classifications of chronic manifestations of colitis, differing in different characteristics. First of all, the nature of the clinical course plays an important role, therefore a period of exacerbation and a stage of remission are distinguished. According to the nature of the damage to the colon, there are:
- segmental, in which a specific part of the intestine is chronically affected;
- total, which is characterized by damage to the entire intestine.
The disease can have varying degrees of severity.
Depending on the severity of the disease, mild, moderate and severe stages are distinguished. Often, motor or digestive functioning is impaired along with this. In turn, motor function can be chronically impaired in the form of hyperdynamic, hypodynamic or mixed type. During the period of impaired digestive function, the patient experiences purulent formations or the fermentation process begins, leading to dyspepsia.
The nature of morphological changes also plays an important role. According to this parameter there are:
- chronic catarrhal form;
- ulcerative type of colitis;
- erosive appearance;
- atrophic form;
- mixed species.
Types of disease
Symptoms and treatment of intestinal colitis will directly depend on the form and type of disease. In medical circles, the following types of colitis are currently distinguished:
- Chronic. It differs from other forms in its sluggish course, exacerbations occur periodically, they can be provoked by antibiotics, dietary errors or frequent stressful situations.
- Ulcerative colitis usually ends with the appearance of ulcerative-necrotic disorders of the mucous membrane. Until now, the nature and causes of this form have been little studied, but it is believed that allergic reactions can cause it. If you exclude allergenic foods from the diet, the patient’s condition improves significantly.
- Acute colitis will not allow itself to be ignored. Its manifestations always have a pronounced character. Often the culprits are staphylococci, salmonella and other microorganisms.
- The atrophic form of colitis is an inflammation of the colon. It is divided into atonic and spastic depending on the causing factors.
- Spastic colitis is also called spasmodic, as severe cramps, abdominal pain, and stool disorders occur. Doctors are of the opinion that provocateurs are stress, fatigue and nervous tension.
- Erosive colitis is considered the initial stage of the development of ulcerative colitis, because the inflammatory process leads to the formation of ulcers.
- It’s called superficial because all processes take place in the upper layer.
- Catarrhal colitis is the initial manifestation of the disease. With strong immunity, the symptoms of the disease disappear on their own and no special treatment is required.
Only a doctor can determine the type of disease and prescribe therapy.
Symptoms of intestinal inflammation
Medicine distinguishes several types of intestinal colitis. Each of them differs in its etiology, pathogenesis, symptoms, and diagnosis. A detailed study of all these aspects is a task for doctors. The average citizen needs to have at least a basic understanding of the manifestations of these diseases in order to know when to seek medical help. In the list below you will find common symptoms common to all types of intestinal colitis:
- Discomfort/pain in the lower abdomen . This kind of manifestation accompanies intestinal colitis in 90% of cases. Exacerbation of pain is observed after therapeutic procedures, eating, and exposure to mechanical factors (shaking in transport, running, walking, etc.).
- Tenesmus (false urge to defecate). This symptom may indicate a number of gastrointestinal diseases. In this regard, colitis is distinguished by the rare occurrence of tenesmus - no more than two or three times a day. If the inflammatory process is localized in the sigmoid or rectum, the urge becomes more painful. As a rule, they occur at night and end with the release of small volumes of feces. In some cases, blood/mucus/pus may be present.
- Disorder (unstable stool). This symptom cannot be considered the main one, however, if other signs are present, it can indicate intestinal colitis with a high degree of accuracy. The main difference between the stool in this disease and all other cases is the admixture of greenish or colorless streaks of mucus and/or drops of dark blood.
- Heaviness in the stomach.
- Flatulence.
- Bloating.
To determine the type of disease more specifically, you need to pay attention to characteristic signs and symptoms. Some of them are not so easy to detect, however, with careful monitoring of the state of health, it is still possible to make a preliminary diagnosis with a high degree of accuracy. After reviewing the table below, you will learn how inflammation of the colon manifests itself in different forms.
| Chronic colitis |
|
| Spastic colitis |
|
| Ischemic colitis |
|
| Catarrhal colitis |
|
Symptoms of colitis
Any form of the disease, if you do not pay due attention to its treatment, can become chronic. In this case, you can be sure that questions such as “symptoms, causes and treatment of intestinal colitis” will become constant companions of a person.
A frequent accompaniment of chronic colitis is dull, aching and cramping pain, which usually occurs in the lower or lateral abdomen. The pain may become worse after eating or before going to the toilet.
Other obvious symptoms of chronic colitis include:
- Discharge of mucus with stool.
- Blood streaks may appear.
- Sheep feces
- Constipation and diarrhea alternate.
- General weakness.
- Attacks of nausea and vomiting may occur.
- Body temperature periodically rises.
- Blood pressure jumps in the direction of increase.
- An unpleasant belching appears.
- Bloating.
- A bitter taste may appear in the mouth.
- If the disease lasts for a long time, the patient loses weight.
These are the symptoms of chronic intestinal colitis, and treatment should only be prescribed by a doctor, taking into account the general condition.
Causes
Exacerbation of chronic colitis can occur for a variety of reasons. The main and most common include:
- The presence in the body of any pathogenic microorganisms that provoke the development of infectious inflammation. These may be intestinal pathogens, especially if their presence was detected quite late or the treatment was not completed. Viral agents can contribute to the development of the disease, especially against the background of weakened immunity.
- Infection with parasitic worms, i.e. the presence of worms, they change the state of the flora in the intestines.
- The presence and development of opportunistic microorganisms in the large intestine.
- Endogenous or exogenous intoxication of the body. For example, disruption of the functioning of organs such as the liver and kidneys.
- For cancer due to exposure to ionizing radiation.
- Prolonged and uncontrolled use of antibiotics.
- Congenital metabolic disorders.
- Enzyme deficiency.
- Food allergies, inability to digest certain food groups.
- Damage to the thermal portion of the abdominal aorta.
- Chronic inflammation of connective tissues.
The reasons for the development of intestinal colitis can be very diverse, from infectious pathogens to ischemic factors. Based on this, chronic colitis can be classified as follows:
- infectious;
- nutritional;
- toxic;
- ischemic;
- allergic;
- ray;
- combined.
Causes of colitis development
A variety of factors can provoke an inflammatory process in the large intestine. For example, the acute form of the disease can be caused by:
- Intestinal infection.
- Taking antibiotics or other medications.
- Error in nutrition.
- Eating spicy food.
- Alcohol.
- Dysbacteriosis.
If the disease already has a chronic form, then an exacerbation can be provoked by:
- Impaired blood supply to the intestinal walls.
- Allergy to certain foods.
- Poor nutrition.
- Helminths.
- Intoxication of the body.
- Consumption of low-quality products.
- Contains a large number of preservatives in food.
All these reasons can easily cause intestinal colitis. We will discuss the symptoms and how to treat this disease below.
Factors contributing to the occurrence of colitis
Any weakening of the immune system or stressful situations contribute to the proliferation of pathogenic microflora, disruption of the normal functioning of all human organs and systems, and therefore can favor the appearance of inflammation in the colon. The most common causes of colitis are:
- Uncontrolled and improper use of medications, most often antibiotics, which lead to disruption of the intestinal microflora biocenosis, dysbiosis and, as a consequence, inflammation of the intestinal mucosa;
- Entry of an infectious agent into the body (most often streptococcus, staphylococcus, salmonella);
- Incorrect, irregular or inadequate nutrition;
- Excessive alcohol consumption, smoking, and other stress factors lead to weakened immunity, which means they contribute to the development of colitis;
- Working with various chemicals in hazardous industries;
- Diseases of the cardiovascular system;
- Diseases of other calvings of the digestive tract contribute to the development of this disease.
Diagnosis of the disease
After a visit to the doctor, the patient will be prescribed some tests that will allow a more accurate diagnosis:
- Stool analysis. It will show whether the intestines are working properly and whether there is an intestinal infection in the body.
- A general blood test is necessary to diagnose the patient’s general condition, and will also allow you to see the number of leukocytes and red blood cells. Their content can indicate the presence or absence of an inflammatory process, as well as the level of hemoglobin, which also affects general well-being.
- The doctor may prescribe an ultrasound examination of the intestinal cavity.
After all the tests and research, a diagnosis is made and a course of treatment is prescribed.
Diagnostics
At an appointment with a doctor (generalist, gastroenterologist), you need to outline your complaints in detail and indicate when they appeared. After a general examination, depending on the indications, the specialist will prescribe additional studies:
- coprogram (stool examination);
- general and biochemical blood test;
- colonoscopy;
- X-ray of the intestine with contrast (irrigoscopy);
- computed tomography;
- ultrasonography.
A biopsy of the intestinal mucosa is necessary if an autoimmune process is suspected, for example, with Crohn's disease. The manipulation is performed during a colonoscopy. If a neoplasm is detected, they proceed in the same way - a histological examination of the tissue is carried out.
Colitis therapy
Chronic colitis requires an integrated approach to its treatment. To cope with this disease, you must follow all the doctor’s recommendations.
Therapy may include the following areas:
- Drug treatment.
- Dieting.
- The use of folk remedies.
It must be remembered that only in combination these methods will help cope with the disease and the patient will no longer be bothered by chronic intestinal colitis, the symptoms and signs of this disease will disappear.
Consequences and preventive measures
In case of exacerbation and severity of symptoms, it is necessary to call a doctor and “move” to the hospital for further treatment. If you ignore the body’s “signals” for help, the following serious complications and diseases may develop:
- kidney inflammation - nephritis;
- intoxication in the body;
- disturbance of water balance, dehydration of the body;
- disruption between blood flow to the heart and its outflow;
- decrease in the content of chlorine minerals in the blood plasma;
Treatment is comprehensive, taking into account all current and accompanying symptoms of the disease. In the absence of clearly defined signs, serious measures must be taken to recover the patient, otherwise the following consequences may occur:
- malignant neoplasms;
- purulent inflammation of the portal vein and its branches;
- abscesses, accumulation of pus and inflammation in the liver.
To avoid complications and serious health problems, timely treatment is necessary, as well as preventive measures:
- strict compliance with prescribed nutrition, adherence to diet;
- visits to doctors, regular medical examinations by a dentist, family doctor, gastroenterologist;
- maintaining a healthy lifestyle;
- timely consumption of food (breakfast cannot be ignored);
- Compliance with basic hygiene rules (washing hands);
- avoiding the intake of raw water and thoroughly washing vegetables and fruits before consumption;
- use of personal household items.
It is very important to know and understand how to treat chronic colitis, but the most important thing is not to get carried away with self-medication, but still seek the help of qualified specialists. Hospitalization should not be avoided in severe stages and acute manifestations of the disease. In a hospital setting, relief and improvement in health occurs much faster than at home.
Treatment of chronic colitis with drugs
If the exacerbation is caused by an intestinal infection, the doctor will definitely prescribe antibiotics. The choice of drug will depend on the type of pathogen.
The following groups of drugs are most often used in the treatment of chronic colitis:
- Antispasmodic drugs, for example "No-Shpa".
- Intestinal antiseptics, these include “Furazolidone”, “Enterosgel”, “Smecta”.
- Adsorbents, for example activated carbon, Laktofiltrum.
- Antidiarrheals: Loperamide, Imodium.
- Anti-inflammatory drugs, such as Sulfasalazine.
In severe situations, the doctor may prescribe glucocorticoid hormones. There are situations when drug treatment does not bring results and the patient only gets worse, then surgery is performed to remove a section of the colon.
Against colitis on your own
We looked at what colitis is (symptoms and treatment). Diet for colitis, however, should occupy one of the main places in the treatment of this disease.
If you visit a gastroenterologist, for this disease he will advise you to adhere to the fourth dietary table. His general recommendations are:
- It is not recommended to consume freshly squeezed juices; it is better to replace them with fresh fruits.
- Avoid meat, especially pork and beef.
- It is not recommended to eat bran bread during treatment.
- Remove fried foods from your diet.
- It is forbidden to eat fresh vegetable salads.
- During therapy, food should be at room temperature, avoiding too cold or hot.
- Eliminate hot spices and seasonings from your diet.
- In small quantities, you can include chicken and lamb in the menu.
- It is better to eat vegetables not raw, but to steam them.
- Limit the consumption of animal fats; a little butter is allowed.
- When treating colitis, food should be of a delicate consistency.
- After waking up, before breakfast, you need to drink a glass of water, preferably boiled.
We looked at what chronic intestinal colitis is, symptoms and treatment. Diet in therapy should be an important step. Only then can you expect positive results.
Treatment
During treatment, you will need to follow a diet.
For patients with inflamed intestines, there is a special treatment complex. Non-ulcerative inactive colitis should not be treated independently to avoid complications. First of all, an important point is the diet for chronic intestinal colitis. Patients with this disease are prescribed the 4th treatment table. Concentrated juices, fried foods, fatty meats, and bran breads are removed from the dietary menu. To achieve a speedy recovery, the patient needs to take the basic diet, which includes puree soup, boiled chicken (without skin), and lamb. Porridges and soups are cooked only with milk, vegetables are ground, and fruits are baked.
If you have colitis, you need to eat five meals a day, and the portions should be small. Every morning on an empty stomach the patient drinks a glass of warm boiled water. Food should be not hot, warm, so as not to burn the inflamed mucous membrane.
Drug treatment can have different manifestations, it all depends on the causes of the disease. When a patient is diagnosed with acute infectious colitis, the doctor recommends taking antibiotics. In addition, to improve intestinal function and combat dysbiosis, Hilak Forte, activated carbon, Lactrofiltrum, and Regidron saline solution are prescribed.
Help of traditional medicine in treatment
There are always recipes in the healers' bins to get rid of many diseases. You already know how important the role of a proper diet is if chronic colitis exhibits symptoms. And treatment with folk remedies cannot be left aside; it may well help. Here are some recipes:
- Pour 10 grams of quince seeds into 1 liter of water and leave for 8-10 hours. It is recommended to take 100 ml 3-4 times a day.
- 1 tsp. pour a glass of hot milk over chicory, leave for half an hour and drink a quarter glass 4 times a day.
- Take 3 tablespoons of blueberry berries and leaves and brew in 600 ml of boiling water, leave for 8 hours and take a glass 3 times a day.
- 2 tbsp. Infuse 1 liter of sage in 400 ml of boiling water and drink half a glass before each meal.
- For 1 part alder cones, take 5 parts water, leave for 14 days in the dark. Take half a teaspoon 4 times a day.
- Oats can be used for treatment. Pour 100 grams of flakes with cold water and leave for 3 hours, then add a liter of hot water and cook until it thickens. This jelly should be taken before meals.
- If chronic intestinal colitis acutely manifests symptoms, treatment with alcohol tincture of propolis can help; it is carried out as follows: take 30 drops of 10% tincture half an hour before meals. You can dilute the drops in water or milk.
These recipes will be a good help in the drug treatment of colitis.
Treatment options
Treatment of colitis involves not only drug therapy, but also adherence to a strict diet. Nutrition is about reducing the load on the intestines. Acceptable and prohibited products are presented in the table.
| Authorized products | What needs to be excluded |
| Pearl barley and rice porridge | Bran |
| Cauliflower | Marinades and smoked dishes |
| Pears, peaches, as well as berries such as blueberries, lingonberries and, of course, currants | Seeds (sunflower and pumpkin) |
| In small quantities cottage cheese (as low fat as possible) and cheese | Salt and sweets |
| Eggs. No more than one per day. It must be hard boiled | Legumes |
| Sugar. No more than two teaspoons per day | Acidic foods, including fruits |
| Butter. 20 g throughout the day | Peanut |
| Cocoa, black tea, jelly and berry infusions | Raw vegetables, fruits |
| Baking, today's baking bread, pasta |
Drug treatment for colitis is as follows:
- Taking antimicrobial agents and antibiotics, for example, Alpha Normix, Enterofuril or Tsifran. They are used for infectious etiology of the disease. The course of therapy with such medications does not exceed five days.
- Use of anthelmintic medications. They are prescribed if the cause of colitis is parasites.
Patients are prohibited from eating sunflower seeds.
- Relief from pain. The doctor prescribes antispasmodics (Papaverine or No-shpa). Sometimes the use of anticholinergic medications is required.
- Treatment of concomitant diseases.
- Elimination of stool disorders. To relieve the patient of constipation, cleansing enemas are used. Elimination of diarrhea is carried out by other means - astringents (oak bark, white clay).
- Normalization of microflora. Probiotics may be prescribed, for example Linex, enzymes, enterosorbents (Enterosgel, Filtrum).
Ulcerative colitis is more difficult to treat. Treatment usually takes a long time and is not cheap. Medicines are not only expensive, but also have many adverse reactions. Therefore, they can be purchased strictly as prescribed by doctors. These medications are produced in various forms - rectal suppositories, tablets, enemas (Mesacol, Salofalk, Mezavant).
Treatment of acute radiation colitis is carried out using intravenous administration of the drug Prednisolone. Salofalk, Mesalazine or Sulfasalazine are also prescribed.
You will learn more about colitis from the video:
Herbal remedies against chronic colitis
We looked at chronic intestinal colitis, symptoms and treatment with diet and medication. But there are also some medicinal herbs, infusions and decoctions of which will help overcome the disease.
Recipe 1
Take in equal proportions serpentine (root), rhizome of erect cinquefoil, rhizome of burnet, St. John's wort, flowers of calendula and chamomile, and yarrow. Prepare an infusion from a teaspoon of the mixture and 0.5 liters of water and drink warm before meals 3 times a day.
Recipe 2
You can prepare a cocktail from medicinal herbs, or rather, from tinctures. You need to take 20 ml of tincture of peony, hawthorn, mint, calendula, motherwort, 30 ml of valerian and 5 ml of belladonna. A single dosage per dose is from 1 to 8 drops 10 minutes before meals 3-4 times a day.
Recipe 3
If the disease is accompanied by constipation, then the medicinal herbal mixture must be supplemented with oregano, dill seeds, buckthorn bark and immortelle flowers.
Thus, we have studied in detail how symptoms of chronic intestinal colitis manifest. And treatment with diet, medications and traditional methods was also considered. It remains to be seen what ineffective therapy or an undertreated disease can lead to.
Consequences of colitis
If an exacerbation of chronic colitis has begun and the symptoms are too vivid, then treatment is best carried out in a hospital setting. Any form of colitis, if therapy is not taken seriously and all specialist recommendations are not followed, can lead to serious complications.
If the acute form of the disease is not treated, the patient can expect:
- Nephritis.
- Dysglycemic syndrome.
- Cardiovascular failure.
- Intoxication of the whole body.
- Dehydration.
- Hypochloremia.
If chronic colitis of the large intestine clearly shows symptoms, treatment should be serious and comprehensive, otherwise everything may end in even more serious consequences, for example:
- Degeneration into oncology.
- Liver or intramural abscess.
- Intestinal polyps.
- Pancreatitis.
- Pylephlebitis of the portal vein.
Everyone is familiar with these pathologies and knows about their seriousness, so denying timely treatment is simply stupid and frivolous in relation to your health.
Carrying out treatment
With the development of this pathology, peristalsis and secretion are disrupted, therefore the process of removing feces from the body is disrupted. When feces decompose and are not removed from the body in time, chronic poisoning occurs, so it is imperative to treat chronic intestinal colitis.
The treatment process for this disease consists of two stages: first, the symptoms of exacerbation of chronic colitis are relieved, after which therapy is carried out, which allows the period of remission to continue. If an exacerbation develops, treatment must be carried out in a medical facility, since at home it is almost impossible to ensure effective removal of waste and toxins from the body, and it will be difficult to choose the right diet.
The best cure for the development of chronic colitis is to follow a diet; meals should be fractional. To do this, the entire daily amount of food must be divided into 6 equal parts, which are taken after a certain time; in this case, sleep time is not taken into account.
When compiling a diet, it is necessary to take into account that the ratio of proteins, fats and carbohydrates in it is 1: 1: 4. In the acute stage, it is recommended to reduce the amount of carbohydrates by 4 times in the first 3 days.
It is necessary to exclude fresh bread, meat can only be boiled or steamed, vegetables are consumed in the form of soups, you cannot drink coffee, tea, or eat fatty or fried foods.
Medicines are used mainly during the period of exacerbation, with the development of an allergic or enzymatic form of the disease; medications for long-term use may be prescribed.
Medicines used to treat chronic colitis:
- antimicrobial and antibacterial drugs, for example Loperamide, Furazolidone;
- antispasmodics, such as tablets “Noshpa” or “Duspatalin”, and in severe cases they can inject intramuscularly “Platifillin”;
- if there is pathology of the gallbladder, then choleretic drugs are used, for example “Allohol”, “Hofitol”;
- to improve the regenerative processes of damaged tissues, it is necessary to take nicotinic acid and B vitamins;
- In order to normalize the process of food digestion and assimilation, enzymatic preparations are prescribed, such as Mezim, Panzinorm and others.
Other drugs may be prescribed depending on the symptoms of the disease. To reduce the formation of gases and to remove toxins from the body, activated carbon, Smecta, is usually used. If there is constipation, to facilitate the removal of feces, laxatives such as magnesium sulfate, Senade, and drugs that help stimulate intestinal motility, such as Docusate, are used.
Disease prevention
It is much easier to prevent the development of inflammatory processes in the large intestine than to suffer from the consequences for a long time. Prevention of colitis is as follows:
- Treat the acute form of the disease in a timely manner.
- Stick to a diet.
- Visit the dentist regularly to examine the oral cavity and timely sanitation.
- Lead a healthy lifestyle.
- Try to eliminate foods containing chemical additives from your diet.
- Eat regular meals, preferably at least 3 times a day, and take most of your meals during breakfast.
- To develop intestinal microflora, eat more fresh vegetables and fruits.
- Stop drinking alcoholic beverages.
Since colitis is most often caused by parasitic or infectious diseases, to prevent the inflammatory process in the large intestine it is necessary to follow the most common rules of hygiene:
- Wash your hands more often and thoroughly.
- Drink only boiled water.
- Do not eat vegetables and fruits without first peeling and washing them thoroughly.
- When swimming, do not swallow water.
- Get rid of bad habits, such as biting nails or any other objects.
- Be careful with close contacts with people you don’t know: don’t drink from the same bottle, don’t eat with the same spoon.
If you follow these simple recommendations, chronic colitis will not show symptoms and treatment will not be required.
Prevention
To prevent colitis from manifesting itself chronically, you need to remember to prevent diseases of the gastrointestinal tract. Inactive colitis can be counteracted by eating a balanced diet consisting of healthy foods containing a minimum of fats and spices, which can cause aggravation. Spicy or smoked food only harms the body.
A person should see a gastroenterologist once a year, and this is especially true for patients who have already had cases of inflammation. Healthy people are recommended to lead an active lifestyle and avoid drinking alcohol and smoking.