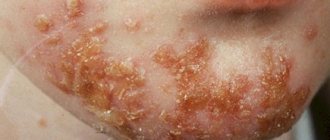
Staphylococcus from the throat 10 to 3 degrees
In addition to animals and plants, the world contains a lot of microorganisms that can be beneficial or harmful to humans. These are bacteria and viruses. And if we talk about one of the most difficult to treat and, accordingly, dangerous species, then this is Staphylococcus aureus, in Latin – Staphylococcus aureus.
General information about Staphylococcus aureus
What is this? A bacterium belonging to the class of anaerobic, that is, capable of living without air, immobile, Gram-positive. There are many types of staphylococcus, but the golden one is the most dangerous. They didn't call it that because of its color. Aureus - because when sown in a nutrient medium, a colony of bacteria gives a yellow-golden color.
You might immediately think that the microorganism is rare, but in fact, it can be found everywhere. The bacterium lives on human skin and mucous membranes and thrives in the environment: on furniture, toys, dishes, money.
This is explained by the high resistance of the microorganism to antiseptics, detergents, even boiling (it dies only after 10 minutes), and freezing. Not afraid of staphylococcus and alcohol, hydrogen peroxide. The only available product that can kill bacteria is ordinary Zelenka.
Staphylococcus aureus is most often found in the nose.
However, despite its prevalence, this microorganism rarely causes diseases, even living on the human body. In order for inflammation to develop, a decrease in immunity is necessary. Only in this case will bacteria begin to be active and cause a variety of diseases of the skin and mucous membranes.
The danger of Staphylococcus aureus is that it is resistant to penicillin antibiotics due to the production of lidase and penicillinase, enzymes that destroy proteins. These same substances melt the skin and mucous membranes, helping bacteria enter the body.
In addition, staphylococcus produces endotoxin, which causes intoxication, food poisoning and infectious-toxic shock in humans - a dangerous condition that is extremely difficult to treat.
It is worth adding to this the lack of permanent immunity to such bacteria. That is, having had an infection, a person still runs the risk of getting sick again.
Norm indicators of Staphylococcus aureus
As mentioned above, bacteria are everywhere. But if staphylococcus has been detected, this is not yet a reason to panic; there are certain standards for its content on the skin, mucous membranes, and objects.
Many people begin to worry when they receive test results: Staphylococcus aureus 10 in 4, or, for example, Staphylococcus aureus 10 in 3.
To understand, you need to understand the principles of determining the number of microorganisms in a biomaterial.
There are 4 degrees of bacterial growth:
- – weak growth;
- – growth of up to 10 colonies of one species;
- – growth from 10 to 100 colonies;
- – growth of more than 100 colonies;
It is clear that the greater the degree, the higher the number of bacteria, and accordingly, the more active the pathological process. The first two degrees indicate the presence of bacteria in the biomaterial, the third indicates that the disease has begun, stage 4 staphylococcus is already a pronounced pathology.
How to decipher seeding data? Each organ has its own standards. So, Staphylococcus aureus 10 to 6 degrees is the upper limit of normal. A detected microorganism in the nose, pharynx or throat, or stool cultures does not yet pose a danger.
That is, if tests show Staphylococcus aureus 10 in grade 5 or lower, there is no reason to particularly panic. Treatment may be required, but the doctor decides in each specific case, taking into account many nuances.
Of course, the lower the number, the better, but if staphylococcus 10 to 3 degrees is detected, this is a variant of the norm.
Risk factors
In order for Staphylococcus aureus to become active, the reasons must be compelling, since immunity itself does not decrease. Provoking factors are the following conditions:
- hypovitaminosis, vitamin deficiency;
- eating disorders;
- other infectious diseases;
- taking antibiotics;
- taking hormonal medications;
- dysbiosis.
These are the causes that provoke the development of infection in adults and children over one year old. But most often staphylococcus is detected in infants. Moreover, the highest risk of getting staphylococcus is in newborns, since in the hospital (and maternity hospital is no exception) a large amount of Staphylococcus aureus is always detected, which is not surprising, given the resistance of the bacterium to antiseptics.
If the newborn is born prematurely or is born immature, the likelihood of infection increases even more. A relatively effective prevention of this is early breastfeeding and refusal of artificial feeding.
What diseases may occur
In both adults and children, regardless of age, Staphylococcus aureus causes many diseases. The infection affects the skin and mucous membranes, but can enter the wound and internal organs.
Symptoms of Staphylococcus aureus characteristic of all types of infection: fever and severe intoxication, which is manifested by weakness, poor appetite, and nausea. That is, if inflammation occurs on the skin, even a small one, but it is accompanied by a high temperature and a clear deterioration in well-being, a staphylococcal infection can be suspected.
Skin diseases
They are the most common, because bacteria live on the skin, and when immunity decreases, it is the body’s integument that becomes the main target, especially if there is a wound, any rashes, and so on. The bacterium can cause the following pathologies:
Phlegmon is a purulent process that develops in fatty tissue, and most often it is triggered by Staphylococcus aureus. In addition to the general symptoms, swelling and soreness of the affected area appears. Phlegmons do not have clear boundaries, and without treatment they can spread to other tissues: muscles, bones, and so on. In addition, the development of sepsis is possible.
Source: https://parazitoved.ru/parazity/stafilokokk-iz-zeva-10-v-3-stepeni.html
Properties of Staphylococcus aureus
Pathogenic staphylococcus synthesizes and secretes many substances that allow this type of microbe to survive in the human body and damage its organs and tissues.
Enterotoxins
Staphylococci, contaminating food products (meat, milk), release enterotoxins, which, when entering the human body, cause food poisoning. Enterotoxins are resistant to high temperatures and human digestive juices.
Exotoxins
Staphylococci produce a number of exotoxins. Exotoxins have the following properties:
- damage the membrane of red blood cells, causing their hemolysis;
- damage leukocytes;
- damage the skin of newborns (Ritter's disease), the skin of children and adults (bullous impetigo);
- cause toxic shock syndrome.
Enzymes
Staphylococci secrete a number of enzymes with multidirectional effects:
- facilitate the adhesion of microbes to human tissues and the penetration of the pathogen deep into the tissues, damaging them;
— destroy the sebaceous plugs of hair follicles, which contributes to the penetration of infection deep into the tissues;
READ ALSO: Scalp fungus, mycosis of the scalp
- cause the coagulation of areas of blood plasma around microbes, which, like a cocoon, envelops staphylococcus, protecting it;
- protect the microbial population from the action of antibiotics.
Allergenic components
Toxins and microbial cell components have strong allergenic properties, which contributes to even greater skin damage.
Breeding factor
Staphylococci contain substances that promote the proliferation of microbes in phagocytes - cells that protect humans from microbes.
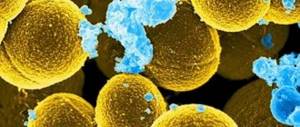
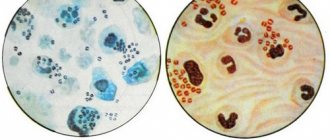
Rice. 3. The photo shows a cluster of Staphylococcus aureus.
Staphylococcus aureus: content standards and caused pathologies – All microbes
Staphylococcus is a conditionally pathogenic flora. This microorganism remains on the human body almost all the time. In moderate quantities it does not pose a clear threat to human health and life. If the number of staphylococci is normal, then there is no need to worry.
When favorable conditions arise, the number of microorganisms increases sharply. Most often this is observed with a decrease in immunity, which occurs during an acute or chronic disease.
From this article you will learn about the features of the development of the disease, its diagnosis and test indicators.
Routes of infection
Staphylococcus is resistant to external factors, it is not afraid of the scorching sun, frost, exposure to drugs containing alcohol, and so on. A very fast route of transmission from one person to another.
The pathogenic microorganism can be in the body of an animal, child or adult. Staphylococcus in infants' stool is normal for most children of this age.
Main routes of transmission:
- everyday way, when using personal funds of a sick person.
- airborne droplet path,
- through poorly processed medical instruments;
- airborne dust method, a huge amount of staphylococcus is in the dust that a person inhales.
Types of tests for staphylococcus
If a staphylococcal infection is suspected, the doctor recommends certain tests.
Timely identification of pathogenic bacteria increases the effectiveness of drug therapy and protects against complications.
Let's look at the most common types of analyzes.
Blood analysis. Most often, a general blood test is used, which shows the amount of leukocytes and staphylococci. It is necessary to visit the laboratory in the morning, on an empty stomach.
ATTENTION! It is not recommended to take antibiotics or antiviral drugs for several days before the test. They may cause incorrect test results.
Analysis of urine . A few days before the test, it is not recommended to use diuretics. Before donation, it is necessary to carry out hygienic procedures to clean the genitals.
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=ARu6i7bxOWY
It is better to purchase a sterile container from a pharmacy. If this is not possible, first scald the jar with boiling water. An average portion of urine is required for analysis. The container is filled to half.
Stool analysis . The collected biological material is examined by sowing to identify the nutrient medium. It is not recommended to take laxatives before donating stool.
The collection container must be sterile or treated with boiling water.
It is strictly forbidden to take material from the toilet, as there may be other microbes there.
Analysis of material from mucous membranes . The material can be taken from the mouth, nose, lower eyelid. If the analysis is taken from the throat, then you should not brush your teeth or eat food before the collection. It is recommended to drink plenty of plain or mineral water. The analysis will quickly show the excess or norm of staphylococcus in a throat smear.
Urogenital smear. A man should not urinate for several hours before collecting material. Women hand over the material 3 days before the onset of menstruation or three days after.
Skin scraping. The analysis is carried out if there is a wound on the skin. The skin around the wound is first treated with an antiseptic solution and dried blood is removed.
Tests will help identify the disease that caused staphylococcus. If the norm of staphylococcus content in the body is not exceeded, then the person is healthy.
Tests are prescribed during a routine medical examination of medical workers, food industry workers, and salespeople. Strict adherence to the recommendations for taking the analysis will give the most accurate results. Only after receiving the results can the doctor prescribe the most effective drug therapy.
How to submit biological material for analysis correctly
It is not recommended to take antibiotics 2 months before the test. The most suitable time for collecting biological material is early in the morning, on an empty stomach.
If the material will be collected directly by the patient himself, then it is important to do the procedure correctly. It is convenient to take a swab from the mucous membrane of the nose and throat with a cotton swab or swab.
Before the procedure, the doctor will give some explanations on how to properly prepare for the procedure. Staphylococcus aureus is normal in adults - I really want to hear from the attending physician.
Staphylococcal infection can stay in the body for years and cause certain diseases. It is very important to get tested in the early stages so that treatment is timely.
As a rule, taking tests for staphylococcus is practically painless and does not require any overwhelming preparation.
All types of tests for staphylococcus are painless and quite simple. However, you should very strictly follow the recommendations for preparing for the study in order to get the right result.
What the results mean: indicator norms
What is the norm of staphylococcus in adults? Was staphylococcus detected within the acceptable range in the analysis? These and many other questions worry people with suspected staphylococcus.
You can get a blood test or scraping of the mucous membrane the next day. The examination of feces and urine is somewhat delayed up to several days.
The result can be one of two things: positive or negative. A positive result means that there is a staphylococcal infection in the body.
A person without medical education will not be able to determine the presence of a disease based on certain signs. If a person often suffers from all kinds of respiratory diseases, inflammations, and so on for a long time, then it is recommended to get tested.
To date, there is no identical scheme or table for assessing the normal status of Staphylococcus aureus in feces in an infant.
Experts have different opinions. Some consider 10 CFU per 1 gram of feces normal. Others, even 100 CFU per 1 gram does not pose a danger to the body.
The norm for Staphylococcus aureus in the throat of children is 104. This is the maximum value for those children who have reached one year of age. For infants the figure is slightly lower.
The norm for staphylococcus in adults is 102 or 103 degrees CFU/ml. The normal level of Staphylococcus aureus in the nose does not pose any threat.
An important step is monitoring the development of staphylococcal infection. If there is a strong increase in indicators, this means that the infection is developing and needs to be treated. With moderate fluctuations, you should not worry, because the condition should be normal.
Activation of staphylococcal infection occurs when the body's protective functions decrease. Therefore, it is very important to follow preventive measures. The most important thing is a healthy lifestyle.
Daily consumption of fresh vegetables and fruits in sufficient quantities. They saturate the body with essential vitamins and microelements, strengthening the immune system.
IMPORTANT! Any respiratory disease that occurs must be treated, without hoping that it will go away on its own.
Taking medications that strengthen the immune system during exacerbation of respiratory diseases. Mandatory hand washing with soap after coming home.
Carrying out wet cleaning of the premises, ventilation and maintaining order. Hardening procedures that have a positive effect on the body.
Conclusion
Staphylococcus, as a rule, is found in the body of every person. It is impossible to become infected with a staphylococcal infection from a patient. The bacterium has a pathogenic effect on the body only when health deteriorates and immunity decreases.
The body's protective functions deteriorate with any respiratory disease. It is necessary to carefully monitor your health, promptly and correctly treat emerging diseases.
An important point is to observe the rules of personal hygiene. With the right approach, the staphylococcus living in your body will not bother you.
Source:
Staphylococcus aureus in feces: danger, treatment and prognosis
Staphylococcus aureus (in the study form it is designated as Staphylococcus aureus) is one of the many opportunistic cocci. Found in the stool of a healthy person. The disease (staphylococcal infection) develops only when there is a significant number of microbial cells and a significant weakening of the immune system.
Pathogen danger
Staphylococcus aureus is found on the surface of human skin and mucous membranes, as well as in biological fluids (feces, urine).
In most cases, Staphylococcus aureus is discovered accidentally during a routine examination. A person does not feel such a symbiosis with the microbe, that is, there are no clinical symptoms.
In such a situation, treatment is not required, since the microorganism does not have a damaging effect on human organs and tissues - there is no disease.
When the immune system is weakened (congenital or acquired immunodeficiency, long-term infectious diseases, chronic endocrine pathology), conditions arise under which Staphylococcus aureus actively multiplies, penetrates tissues, and produces pathogenicity factors (enzymes and toxins). As a result of the colonization of microorganisms with the bloodstream, the formation of purulent-inflammatory foci in the internal organs occurs. This condition is called staph infection .
Depending on the location of the pathological process, the following forms of staphylococcal infection are distinguished:
- osteomyelitis (inflammation of bone tissue);
- purulent foci in the skin, subcutaneous fat (cellulitis, abscess, furunculosis);
- bursitis or synovitis (joint damage);
- pneumonia, bronchitis, pleurisy;
- enterocolitis and enteritis (inflammation of the intestines);
- damage to brain tissue (meningoencephalitis and meningitis);
- blood poisoning (staphylococcal sepsis).
Any of the above conditions is a serious test for the human body, since with staphylococcal infection local changes are combined with severe general intoxication.
It is possible for the acute form of the disease to transform into a chronic form - with periodic exacerbations and remission. Damage to brain tissue, pulmonary and septic conditions do not always have a favorable prognosis - without adequate treatment, the death of the patient cannot be ruled out.
Do you have intestinal diseases? — Take the online test!
Pathways of transmission and growth of bacteria
Staphylococcus aureus is widespread in nature and on objects surrounding humans. This microbial agent is resistant to environmental factors, so it is not possible to talk about its complete destruction.
Staphylococcus aureus is transmitted in the following ways:
- food – when consuming “contaminated” products;
- contact – through direct communication with an infected person or when using common household items (dishes, towels);
- aerosol (through the air);
- artificial (in the process of medical manipulations in any health care facility).
It is impossible to avoid contact with Staphylococcus aureus; it is important to prevent the development of an infectious process. The growth and reproduction of staphylococcus is promoted by:
- immunodeficiency (acquired and congenital);
- unbalanced diet (with excess carbohydrates);
- chronic pathology;
- repeated infectious processes of another etiology;
- bad habits.
Simple and clear points reduce the likelihood of developing a staphylococcal infection:
- balanced diet;
- compliance with the work and rest regime;
- timely treatment of chronic diseases (achieving long-term remission).
Norms for content in feces
The concept of the norm for the content of Staphylococcus aureus in feces for a non-specialist may look somewhat ambiguous.
- In a normal stool examination (bacteriological), this microorganism may not be detected - this is a negative answer, the best possible option.
- Another option is a positive answer, that is, Staphylococcus aureus was found in the patient’s feces.
A positive result of bacteriological examination of stool without clinical manifestations of the disease is not the basis for diagnosis and subsequent treatment.
Symptoms of the disease
Clinical manifestations of staphylococcal infection are determined by the predominant localization of the pathological process. When Staphylococcus aureus affects the digestive canal, the following is noted:
- prolonged nausea combined with repeated vomiting;
- lack of appetite and aversion to any food;
- diffuse abdominal pain;
- loose stools often mixed with mucus and streaks of blood.
Gastroenterocolitis of staphylococcal etiology is characterized by a long course and slow recovery of the patient. Staphylococcal gastroenterocolitis is especially severe in preschool children, as well as in premature babies. It is these patients who are most likely to develop a generalized staphylococcal infection - sepsis.
Treatment
If a person has Staphylococcus aureus in the stool, but there are no signs of dysfunction of the digestive canal, then treatment is not necessary. This condition is regarded only as the fact of the presence of Staphylococcus aureus in the intestine as a representative of opportunistic flora.
Therapy for staphylococcal infections, including those localized in the digestive canal, is necessary when a person’s general condition changes and characteristic clinical symptoms appear.
Doctors practice an integrated approach, including dietary nutrition, antibacterial agents and other medications.
Source: https://leprozori.ru/mocha/zolotistyj-stafilokokk-normy-soderzhaniya-i-vyzyvaemye-patologii.html