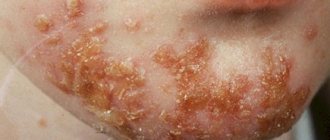
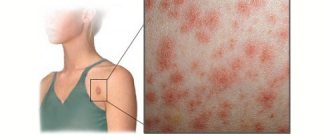
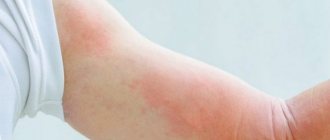
Erythrasma is a bacterial lesion of the skin caused by Corynebacterium minutissimum, and manifests itself as spots in the fold areas of the skin. Flaky spots, causing discomfort to a person, both by their appearance and their effect on the body.
In some works it is called pseudomycosis due to similar symptoms and treatment methods. Initially, this disease was classified as a mycoses, based on a study of scales, which showed similarities with fungal mycelia. But later it was discovered that the disease was actually caused by gram-positive Corynebacterium Mnutissimum. Corynebacteria do not extend beyond the stratum corneum of the epidermis, so nails and hair never suffer from them.
There are two types: generalized and interdigital erythrasma. Interdigital is the most common bacterial foot infection. It usually does not show any symptoms other than aesthetic unattractiveness. Also, interdigitation can be an early sign of type 2 diabetes. Generalized most often occurs in men with diabetes and obesity. In 75% of cases, a general appearance appears in the groin of men.
Is the disease contagious?
Erythrasma has a fairly low index of contagiousness. This means that the chance of transmission from a sick person to a healthy person is very small. However, it is still a contagious disease. People with weakened immune systems (AIDS, HIV, chemotherapy treatment, diabetes) are most susceptible to infection. Such patients are more susceptible to the disease, but the epidemiological background remains partially unresolved.
Infection occurs through contact, both through the sexual tract and through the use of the patient’s belongings, bodily contact, and walking barefoot in public pools and beaches. It is not transmitted by other methods. But you should be careful when communicating with an infected person - his saliva is also a carrier of the bacteria.
If you have been diagnosed with erythrasma, try to limit contact with other people and things in common use. Invest in multiple pairs of cotton socks and underwear to limit skin-to-surface contact options. All items that will be worn during treatment should be 1-2 sizes larger.
Symptoms
With interdigitation, cracking and chronic destruction of the spaces between the toes occur. It is asymptomatic and does not cause any subjective sensations in humans. Therefore, many patients do not even know about their disease.
Generalized is characterized by local lesions of the skin. Most often in the groin area and inner thighs. Inguinal erythrasma begins with the formation of pink, non-inflamed spots. They progress rapidly, changing their color from light brown to brown-red. Initially, the size of the lesions is only a few centimeters, but after increasing in size, the spots merge and form a large lesion. In the affected area, the skin begins to peel off, becoming smoother. In addition to visual changes in the skin, other symptoms rarely occur, but some patients complain of itching in the affected areas.
In case of complications, in addition to itching, burning sensations and pain may occur. Complications may occur:
- in people with diabetes;
- in people who are overweight;
- in case of non-compliance with hygiene standards and requirements;
- in conditions of increased sweating: hot climate, closed clothing.
Without proper diagnostics and a range of medications, a chronic course can last 10-15 years. Periods of remission and exacerbation occur cyclically. Exacerbations occur in the summer, when bacteria multiply better due to humidity and heat. Remission – in winter and autumn.
Erythrasma
Signs
The disease develops slowly and unnoticeably.
It begins with the appearance on the skin of rounded light brown or brick-red spots with clear boundaries. Their surface is covered with delicate scales. Sometimes small raised ridges form along the edges of the spots. The spots usually appear in the folds of the skin. In men, the groin area is predominantly affected, in women - the armpits, areas under the breasts and around the navel. The spaces between the fingers may also be affected. The spots gradually grow and merge with each other, forming one large lesion. In some cases, usually with inguinal erythrasma, maceration (softening, loosening of tissue) occurs along the edges of the lesion. In most cases, these spots do not cause discomfort, so only a doctor discovers them during an examination. However, sometimes the appearance of spots may be accompanied by a slight burning sensation and itching. This usually occurs in those suffering from diabetes, hyperhidrosis and obesity. In this case, erythrasma is complicated by diaper rash.
Description
For a long time, erythrasma was considered a mycosis, since the symptoms of the disease are very similar to the symptoms of many mycoses, and upon microscopy of scrapings from the lesion, specialists clearly saw long threads, very similar to fungal mycelium. However, it is now known that the causative agent of erythrasma is not fungi, but Corynebacterium minutissimum. These microorganisms are normally constantly present on human skin, without creating problems for him. However, under favorable conditions, corynebacteria begin to actively multiply and penetrate the epidermis. Bacteria produce a pigment that colors the skin. Favorable conditions for the reproduction of corynebacteria:
- high humidity and warm climate;
- soft skin;
- chronic endocrine diseases (diabetes mellitus, obesity);
- lack of personal hygiene;
- increased sweating;
- constant trauma to the skin;
- change in skin pH;
- old age.
Erythrasma is a contagious disease; Corynebacterium minutissimum can be transmitted from person to person through bed linen, towels, baths, swimming pools and sexual intercourse.
The disease can occur in a person at any age, but it is registered quite rarely in children. Men suffer from erythrasma more often than women.
Diagnostics
If you suspect erythrasma, you should consult a dermatologist. The diagnosis is made based on the results of an examination of the patient and the results of a microscopic examination of skin scrapings from the lesion. Microscopy of the scraping reveals not only long threads resembling fungal mycelium, but also coccoid cells arranged in groups or chains.
Conduct a study with a Wood's lamp. When irradiated with this lamp, the lesion glows with a reddish light. Erythrasma translated from Greek means “red coloring”. However, before irradiation with a Wood's lamp, the skin should not be treated or washed with anything, as the pigment may be washed off.
Erythrasma is differentiated from psoriasis, diaper rash, contact dermatitis, athlete's foot, rubromycosis, and lichen versicolor.
Treatment
In some cases, erythrasma goes away on its own. However, this is not always the case and in most cases treatment is still required. Typically, antibiotic ointments and sulfur-tar ointment are used for treatment. In addition, doctors recommend treating the lesion with salicylic alcohol or an alcohol solution of iodine.
For extensive skin lesions, the doctor prescribes oral antibiotics.
In addition, doctors say that physiotherapy, namely ultraviolet irradiation, has a good effect. Ultraviolet rays have an antiseptic and drying effect and help improve the patient's condition. Artificial irradiation can be replaced by tanning for 30-40 minutes in the morning and evening hours.
Also, for successful treatment, it is recommended to disinfect all the patient’s clothes, shoes and bedding.
After treatment, to prevent relapse of the disease, you need to wipe the skin folds daily with a solution of salicylic or camphor alcohol, and then apply talc or boric acid to them.
Prevention
To prevent erythrasma it is necessary:
- maintain personal hygiene;
- dry thoroughly after water procedures;
- fight excessive sweating;
- use deodorant regularly;
- monitor your weight;
- if you have chronic diseases, carefully follow all doctor’s instructions;
- refuse synthetic underwear.
© Dr. Peter
Causes of erythrasma
The causative agent is a gram-positive bacillus (Corynebacterium minutissimum). It is part of the standard microflora of human skin. But due to the influence of negative factors, it manifests pathogenic abilities. Factors that increase the risk of infection are:
- increased sweating;
- HIV, AIDS, diabetes and other diseases that weaken the human immune system;
- high humidity environment;
- problems with excess weight;
- failure to comply with hygiene standards;
- living in a hot climate;
- prolonged exposure of the skin to uncomfortable clothing or shoes;
- walking without shoes in crowded places.
Causes
The disease is caused by the pathogen Corynebacterium minutissium. The pathogen belongs to a species of corynebacteria. It is characterized by low contagiousness and pathogenicity.
It is present on the skin of every healthy person and is a saprophytic microorganism.
The following provoking factors provide pathogenic microflora with comfortable conditions for development and reproduction:
- exposure to hot and humid climates;
- change in pH of the skin;
- the phenomenon of hyperhidrosis;
- the presence of diaper rash, maceration;
- constant friction of the skin against tight underwear;
- insufficient control over personal hygiene.
This disease is contagious, patient reviews confirm this. Its transmission occurs through contact with a carrier of an active pathogen or with an object on which a living microorganism was present.
The development and reproduction of the pathogen occurs in the superficial layers of the skin on which it enters. Erythrasma in the groin in men appears after intimate intimacy with a woman on whose skin it is active.
In children, the disease manifests itself extremely rarely, but if you do not monitor the child and do not use powder to keep the skin dry, there is a risk of the disease developing.
Diagnostics
Due to the similarity between interdigital erythrasma and other diseases, many diagnostic problems arise.
Erythrosis, what is it, is a hereditary skin pathology that causes large red spots to appear. In atypical cases of pathogenesis, its lesions extend beyond the feet and palmar surface of the hands. Physical examination and history do not provide even approximate results. Therefore, erythrasma is diagnosed in two main ways:
- Wood's ultraviolet lamp. Luminescence examination causes the lesions to fluoresce a characteristic red and coral color due to porphyrin, which is produced by corynebacteria;
- Examination of scales under a microscope to exclude fungal diseases and determine the causative agent (corynebacterium).
Timely diagnosis is very important for inguinal erythrasma. In men, in addition to general symptoms, it can cause problems with the reproductive system and infertility.
Treatment of erythrasma
Without interventions, the skin will look something like the photo of erythrasma. This is not only aesthetically unsightly, but also dangerous for the body. However, there is no general agreement on the most optimal treatment for this disease. There are many restrictions for any procedure: irritation, allergic reactions. Recent studies by H. Hem and P. Prabhakar were conducted to find out the effectiveness of 2% fusidic acid and 2% clotrimazole. The overall conclusion they reached was that 2% fusidic acid was better at treating symptoms and was more effective.
Another study conducted at the beginning of 2020 by T. Grewal and F. Kahn concerned monotherapy with mapirocin ointment. Treatment of erythrasma in the groin with mapirocinin was more effective than in the treatment of lesions on smooth skin. The ointment also helped well with aggressive types of illness. How and with what to treat erythrasma depends on the location and neglect. Surgical and other treatments are not used, only conservative ones are used.
In the very first stages of infection, it is recommended to keep the affected area of skin dry and clean. Antibacterial soap or fusidic acid is suitable for this. If this does not help, and the sores begin to grow and merge into one focus, intensive treatment is required.
If the localization of lesions is on smooth skin:
- A two-week course of erythromycin 4 times a day, 0.25 g.
- A two-week course of tetracycline 4 times a day, 0.25 g.
The choice of remedy depends on the preferences of the attending physician and the patient’s tolerance.
If the lesion is in the folds, it is recommended to treat erythrasma in the groin area in men with ointments and creams:
- Apply 2% fusidic acid in the form of a cream for 14 days, 2-3 times a day.
- Rub erythromycin ointment into the lesions 2 times a day. Course – 7 days.
- 21 days, smear the lesions with bifonazole cream 2 times a day;
- Rub in iclopirox or isoconazole 2 times a day for 14 days.
Before choosing a cream/ointment, be sure to consult a dermatologist.
Treatment of erythrasma in the groin is not only the elimination of symptoms, but also the restoration of possible disorders of the reproductive and genitourinary system. Recently, it has been recommended to use Prostatilen AC. It is suitable both for monotherapy and for eliminating “male” negative consequences. This is a complete medicine that speeds up treatment.
Treatment
To prevent re-infection, it is imperative to treat personal belongings, clothing, underwear and shoes with antiseptics. Steam fabrics using an iron. If diabetes is present, you need to undergo a medical examination to assess your sugar levels and rule out complications. Topical medications based on antimicrobial and antiseptic chemical compounds are used. Tar ointment is often used twice a day. If a large lesion occurs, the doctor selects oral antimicrobial agents.
Other methods
- Physiotherapeutic procedures to improve tissue condition and destroy pathogens. Ultraviolet irradiation in therapeutic doses helps well.
- Minimally invasive treatment of excessive sweating by blocking nerve fibers.
- Other types of minimally invasive and non-invasive therapies to improve skin condition.
It is important to prevent recurrence of the disease.
Folk remedies for the treatment of erythrasma
To treat the disease, not only traditional medicine, but also various folk methods can be used.
Important information! If you notice redness of the skin, the appearance of “spotty” lesions and itching, be sure to consult a dermatologist. Prostatilen, fusidic acid and other medicinal ointments have been clinically tested, so they are most effective for treating erythrasma in men. Any fight against a disease with folk remedies can lead to complications and deterioration of the body’s condition.
To disinfect the skin and wash the affected areas, baths with medicinal herbs are used. Suitable for this:
- Dried chamomile. You need to take 400-600 grams of the plant, add it to boiling water and leave for 30-40 minutes. Pour the resulting broth into a bath of water not hotter than 38-39 degrees. Take 9-13 ablutions a day, 15 minutes each.
- St. John's wort. 3-4 tablespoons of St. John's wort per 500 mg of water, leave for a quarter of an hour. Wash every day, 2 weeks in a row, 8 minutes at a time;
- Oak bark. Chop the bark and add to boiling water (2-2.5 liters). Boil for half an hour, then strain the liquid from the solid pieces. Add the decoction to the bath.
- Sage. 600 grams per liter of water. Boil and add to hot water.
After the procedure, it is not recommended to allow contact of running water and foci of the disease for the next 6 hours. It is better to take herbal baths before bed.
Treatment of erythrasma with folk remedies proceeds faster if you use a tincture of birch buds. It is necessary to finely chop the birch buds and add alcohol in a ratio of 100 grams to 10 milligrams of alcohol. The resulting mixture is infused for 2 weeks in a dark place, after which it is filtered. The tincture is applied to the affected areas of the skin at least 3 times a day.
Preventing the return of erythrasma
There are a number of preventive measures that will prevent the disease in question from returning.
Firstly, it is necessary to begin the fight against excess weight - this applies to both nutritional correction and physical education. As soon as you manage to get rid of extra pounds, erythrasma will immediately stop.
Secondly, you need to purchase a special deodorant with the addition of aluminum at the pharmacy, since ordinary products from this category will not help get rid of the unpleasant odor and increased sweating.
Thirdly, after taking a shower or bath, you must thoroughly dry your entire body, especially the folds. Then you can wipe the problem areas with camphor alcohol - this will dry the skin.
Erythrasma is a rather unpleasant disease, but it is quite possible to cure it. But before using any medications or traditional methods, you need to see a dermatologist and undergo specific examinations - this will help you choose the right direction of therapy.
Tsygankova Yana Aleksandrovna, medical observer, therapist of the highest qualification category
18 total today
( 67 votes, average: 4.58 out of 5)
Hyperhidrosis: symptoms, causes, treatment methods
Antifungal drugs for children - review of drugs
Related Posts
Complications
If hygiene procedures are not followed, concomitant diseases or climatic conditions, patients may experience complications:
- swelling of the affected areas;
- diaper rash;
- eczema and other skin diseases;
- reproductive dysfunction.
There are also atypical complications that depend on the individual parameters of the patient. If you have several skin infections at the same time, their side effects on the body can interact, increasing several times.
Forecasting
If inguinal erythrasma treatment and diagnosis were timely and correct, then there will be no consequences. Otherwise, the disease will become chronic, with a chance of complications.
According to statistics, about 65% of people completely get rid of the disease if they correctly follow the course and dosage of prescribed medications, and also undergo prevention. If a person is not overweight or diabetic, then he has an almost 100% chance of complete recovery.
Prevention
Primary measures are based on eliminating the possible causes of the disease. It is necessary to maintain personal hygiene, thoroughly dry the skin in folds (if any), and avoid tight and synthetic clothing. For people who are obese - diet. Such actions reduce the risk of infection to several percent, even if there was contact with a sick person.
Secondary prevention is used several months (2 to 3) after treatment. Previous foci of the disease are treated with salicylic alcohol and talc. All personal clothing should be constantly disinfected, and bedding and underwear should be boiled in a soda solution.
It is also recommended to take vitamins to strengthen the immune system. The specific name of the drug and dosage can be obtained from the treating dermatologist. As a last resort, you can contact a pharmacy worker for advice.
Therapeutic measures
The purpose of therapeutic measures is to suppress the vital activity of the etiological factor - corynebacteria, as well as to restore the protective characteristics of the epidermis.
During treatment, the areas involved must be protected from external mechanical damage and, accordingly, conditions unfavorable for bacterial flora must be provided. The latter is also a preventive measure for the development of complications in the form of the addition of secondary microflora. This is facilitated by regular drying and ventilation of the damaged surface. Traditional treatment of the pathological process is local treatment with ointments with preliminary preparation of the infected surface:
- Throughout the day, the resulting spots on the skin folds are repeatedly treated with any liquid antiseptic: salicylic alcohol, 2% alcohol iodine solution, 2% alcohol or aqueous solution of aniline dye (methylene blue or fucarcin). Preparations with a drying effect also include Galmanin, Candide powders, powdered form of salicylic acid, and boric acid-based talc.
- Before applying the ointment or cream, the skin surface is cleaned of any crusts and scales that have formed, remnants of drying agents and previously used ointment preparations. It is applied in a thin (2-3 mm) layer, the classic calculation for the consumption of an ointment preparation is that one centimeter of cream squeezed out of the tube is spent on the surface of the skin, an area the size of the palm of your hand.
Before starting treatment, it is recommended to conduct a skin test, since patients often have hypersensitivity to imidazole, a drug that is used as an active ingredient in a number of medications.
The group of main therapeutic drugs for this pathology should include 2% erythromycin or 10% tar-sulfur ointment. Frequency of use – daily and twice a day rubbing into the skin for seven days.
The selection of drugs should be based on the results of the sensitivity of the microorganism to the antibiotic. In case of sensitivity to imidazole, Clotrimazole or Mycospor creams are indicated, which are rubbed once and daily for fourteen days.
When large areas are involved in the process, as well as in the case of the manifestation of a secondary infection, broad-spectrum antibiotics are added to the therapeutic agents. As additional measures, a physical procedure in the form of quartz treatment is prescribed, especially if the damaged areas are localized in places that are difficult to access for ventilation and drying (groin and abdominal folds). region).