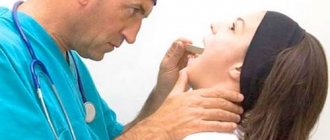
Acute, predominantly unilateral, inflammation of the peritonsillar tissue is called peritonsillar abscess (peritonsillar abscess).
Peritonsillar tissue is loose connective tissue that surrounds the palatine tonsils.
A peritonsillar abscess is located around the tonsils, and a parapharyngeal abscess is located around the pharynx.
Peritonsillar abscess is a complication of tonsillitis, especially follicular, and develops during the recovery period or a few days after suffering from tonsillitis, ARVI (acute respiratory viral infection), if local or general cooling or overheating occurs, followed by cooling against the background of an irrational lifestyle.
Sometimes the cause of paratonsillitis
There may be foreign bodies in the throat.
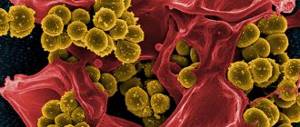
The causative agents of paratonsillar abscess are most often streptococci, staphylococci, other microorganisms are rarely found.
The infection enters the para-almond tissue from the palatine tonsil by contact, through lymphatic and blood vessels, and rarely as a result of dental disease (common caries).
Stages
- initial - exudative-infiltrative - swelling and redness;
- the height of the disease - the stage of abscess - suppuration;
- the end of the disease is the stage of reverse development - all processes are reversed.
Peritonsillar abscess is stage II of paratonsillitis
.
Based on the location of the pathological process in the paratonsillar tissue, the following forms of paratonsillar abscess are distinguished:
- anterosuperior,
- posterosuperior,
- back,
- external (lateral),
- front,
- bottom.
In children, anterosuperior and posterosuperior localizations of paratonsillar abscess are more often observed. Other localizations are rare.
Causes
Why does a peritonsillar abscess occur, and what is it? The main causative agents of paratonsillitis and paratonsillar abscess are Group A Streptococcus pyogenes and Staphylococcus aureus; Anaerobic microorganisms are also of great importance. In addition, peritonsillar abscess may have a polymicrobial etiology.
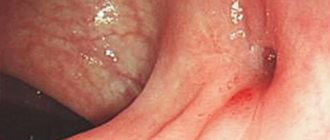
Peritonsillitis and paratonsillar abscess develop when the pathogen penetrates from the crypts of the affected palatine tonsil through its capsule into the surrounding peritonsillar tissue and intermuscular spaces. As a result, an infiltrate is formed, which, in the absence of adequate therapy, goes into the stage of purulent melting and a peritonsillar abscess is formed (see photo).
Usually, several days pass after a sore throat, the patient may even feel some relief, but then the body temperature suddenly rises again to fairly high numbers (38-39) degrees Celsius, and he feels a sharp pain in the throat when swallowing. Often the pain is localized on only one side. In the future, two outcomes of the situation are possible: either this inflammation goes away on its own under the influence of treatment, or after 3-4 days a so-called peritonsillar abscess forms.
Treatment of the disease
Phlegmonous sore throat is a serious disease that requires immediate medical intervention. In this case, treatment is carried out only in a hospital setting, since an immediate autopsy is almost always required. There is a possibility of an arbitrary breakthrough of the abscess, but this is quite rare. It is strictly forbidden to let things take their course in the hope that the problem will go away on its own. After all, the infection can enter the bloodstream and provoke the development of serious complications that threaten not only the health, but also the life of the patient.
For peritonsillar abscess, treatment is carried out under strict medical supervision. Depending on the characteristics of the course of the disease, they resort to one of the possible treatment options: surgical or conservative.
If possible, paratonsillitis is treated with medication. This is effective only when the abscess has not yet formed, but there is swelling of the mucous membrane and infiltration. Treatment of the disease should be comprehensive and include the use of the following:
- Antibacterial. Broad-spectrum antimicrobial agents are used. The main causative agent of sore throat is group A beta-hemolytic streptococcus. However, paratonsillitis can be caused by pneumococcus, staphylococcus, as well as viruses and fungi. It is best if the antibacterial drug is selected based on the results of bacteriological culture.
- Antipyretics and painkillers. An abscess is accompanied by a significant increase in body temperature, so it is necessary to use antipyretic drugs. It is preferable to use nonspecific anti-inflammatory drugs based on ibuprofen or paracetamol. This group of drugs has not only antipyretic properties, but also anti-inflammatory and analgesic properties. During the day, it is advisable to alternately use medications with different active ingredients.
- Gargling. Active rinsing with antiseptics is recommended. For this purpose, Furacilin, Chlorophyllipt and other drugs are used. With the help of washing, lacunae are mechanically cleaned of microorganisms and their toxins. You can also use folk remedies for rinsing. Infusions of chamomile, sage and other medicinal herbs have anti-inflammatory and analgesic effects.
- Detoxification therapy. The formation of an abscess is accompanied by severe intoxication of the patient’s body. Intravenous drip administration of 0.9% Sodium chloride, Ringer's solution, Reopoliglucin and other agents will help relieve symptoms and improve the condition.
- General strengthening therapy. Phlegmonous tonsillitis develops with a decrease in immunity, so efforts should be made to restore it. For this purpose, multivitamin preparations, immunomodulators and immunostimulants are used. Good results are shown by strengthening the body: hardening, physical activity, long walks in the fresh air, etc.
Classification
There are three types of peritonsillar abscess, each of which has its own distinctive features:
- Anterosuperior – occurs in 90% of cases. This is due to poor outflow of pus from the upper pole of the tonsil, which leads to its accumulation and further spread to the tissue.
- Posterior – detected in every tenth patient. It can be complicated by swelling of the larynx and, as a result, breathing problems.
- The lower one is quite rare. Its development is usually associated with an odontogenic cause. The abscess is located in the tissue behind the lower third of the palatine arch between the palatine and lingual tonsils.
Causes of the disease
The causes of inflammation of the peri-almond fiber may be:
- Streptococcal and staphylococcal infections, as well as other pathogens and bacteria.
- As a complication of trauma to the tissues of the pharynx.
- Impaired teething.
Factors contributing to the development of the disease are most often:
- decreased protective function of the immune system;
- frequent colds;
- metabolic disease;
- frequent stress;
- hypothermia;
- taking certain medications.
Symptoms of paratonsillar abscess
In the case of a paratonsillar abscess, the symptoms are very similar to those of a sore throat. The first warning sign is a severe sore throat. However, when opening the mouth, we see a swollen throat with changes similar to ulcers.
Symptoms of paratonsillar abscess most often develop in the following sequence:
- body temperature rises sharply to 38–39 °C;
- difficulty swallowing;
- sore throat is usually one-sided (but bilateral development of an abscess is possible);
- when swallowing, the pain may radiate to the ear, teeth or back of the head on the side on which the throat hurts;
- the pain intensifies sharply when you try to open your mouth;
- it is impossible to fully open the mouth due to spasms of the masticatory muscles;
- weakness, muscle pain;
- In the absence of treatment, the patient's condition quickly deteriorates, signs of microbial intoxication are observed: headache,
- nausea, dizziness, diarrhea;
- enlarged lymph nodes under the lower jaw, on the back of the head.
A peritonsillar abscess, if left untreated, can lead to very serious consequences - difficulty breathing, infection of neighboring organs, pneumonia. Therefore, if you see signs that specifically indicate an abscess, you should take immediate action.
Differential diagnosis
Differential diagnosis of paratonsillar abscess should be carried out with:
- diphtheria, especially its toxic form,
- intra-almond abscess,
- erysipelas of the throat,
- chancre,
- hemangioma,
- malignant tumors,
- aneurysm - expansion of a section of the carotid artery.
The latter disease must be especially taken into account, since surgical intervention is fatal.
The presence of pulsation in this area, as well as puncture, decide the correct diagnosis. In general, puncture should be more widely used for the differential diagnosis of peritonsillar abscess with microscopic examination of the puncture, which is of critical importance.
For intratonsilar (intratonsillar) abscess
Small inflammation is localized in the palatine tonsil. The patient complains of a sore throat and discomfort when swallowing. Pharyngoscopy reveals hyperemia and swelling of the palatine tonsil. The swelling increases in size, the contours are significantly smoothed out. 2-4 days after the onset of the disease, the site of abscess formation is clearly determined.
Often a spontaneous breakthrough of the abscess occurs, or it is opened after a puncture. The prognosis is usually favorable.
Complications
Typically, the course of a paratonsillar abscess ends in recovery, however, with the high virulence of the pathogenic flora and the weakening of the body’s defenses, such a formidable complication as phlegmon of the parapharyngeal space can develop, which is accompanied by the following disorders:
- intoxication of the body;
- the patient experiences severe salivation;
- difficulty opening the mouth;
- high body temperature;
- it becomes difficult for the patient to breathe, and he practically cannot swallow.
The transition of phlegmon into purulent mediastinitis is especially dangerous, which leads to the following consequences of a peritonsillar abscess:
- thrombophlebitis;
- bleeding of cervical vessels;
- septic processes;
- infectious-toxic shock;
- tissue necrosis.
Medical prognosis and possible complications
Peritonsillar abscess is highly treatable, subject to strict adherence to the recommendations of the attending physician and early diagnosis. Otherwise, the abscess may be complicated by phlegmon of the peripharyngeal space. The patient's condition sharply worsens, pain and swelling completely disrupt the function of swallowing food and breathing. In the absence of adequate treatment, the inflammatory process can develop into purulent mediastinitis, up to infectious-toxic shock. When the first warning symptoms appear, it is recommended to seek help from a medical facility.
How to treat a peritonsillar abscess
It should be understood that peritonsillar abscess cannot be cured at home. All drugs used to treat sore throat are ineffective. Even if the abscess is ripe and it seems to you that pus has flowed out, this is far from the case. Most of the pathological purulent contents remained deep in the soft tissues. Over time, pathological microflora will contribute to the formation of purulent masses. The pus in the abscess will accumulate until it reaches a critical mass and re-effusion occurs.
Depending on the symptoms, treatment of peritonsillar abscess is carried out using three main methods:
- Complex therapy is the most effective treatment method, which is based on a competent combination of different treatment methods.
- Conservative therapy - the use of local and general medications, physiotherapeutic procedures. Effective in early detection of inflammatory disease of the tonsils.
- Surgical treatment is a radical treatment method that involves the removal of damaged tissue.
If treatment for peritonsillar abscess is started in a timely manner, the prognosis for the outcome of the disease is favorable. Otherwise, more serious complications may develop, including sepsis. Traditional medicine is also widely used in the treatment of abscess: tonsils are rinsed with chamomile and eucalyptus decoctions, and steam inhalations are done. You also need to watch your diet. The patient is advised to eat warm and liquid food.
Treatment
To treat paratonsillar abscess, conservative (tablets) and surgical (scalpel) treatment is used.
Conservative treatment of peritonsillar abscess
consists of prescribing antibiotics, mainly intravenously, aerosols with antibiotics and antiseptics, antihistamines, and multivitamins.
Surgery
consists of opening an abscess or tonsillectomy (removal of tonsils) on the affected side. The peritonsillar abscess is opened on day 4-5. In the interval of 2-3 days before opening, the edges of the incision are separated for better emptying of the abscess.
With a paratonsillar abscess, it is first advisable to make a puncture and then open it. The abscess is cut at the site of the greatest protrusion of the mucous membrane.
Causes of the disease
The main reasons for the occurrence of an abscess in this localization are the penetration of pathogenic microorganisms into the tissues that surround the palatine tonsils. However, such a disease does not very often act as an independent pathology, that is, in both adults and children it develops against the background of other diseases.
Thus, the predisposing factors are considered to be:
- chronic or acute tonsillitis;
- relapse of sore throat;
- acute form of pharyngitis;
- damage to the upper molars by caries;
- chronic course of gingivitis;
- periostitis of the alveolar processes;
- defective removal of the tonsil, that is, a situation where surgeons leave a small area of tissue of this organ;
- wide range of injuries;
- chronic sinusitis;
- immunodeficiency states;
- the course of diabetes mellitus;
- infection of wounds located on the mucous layer of the oral cavity.
Predisposing factors may include:
- hypothermia of the body for a long time;
- poor nutrition;
- long-term abuse of bad habits;
- living in unfavorable climatic or social conditions.
In the vast majority of cases, the provocateurs are:
- streptococci;
- pneumococci;
- Klebsiella;
- fungi from the genus Candida;
- Streptococcus pyogenes;
- Staphylococcus aureus;
- Haemophilus influenzae;
- Escherichia coli.
Not the last place in the formation of an abscess is occupied by anomalies in the development of the pharynx or tonsils.
Diagnostics
Diagnosing a paratonsillar abscess usually does not cause difficulties for a doctor. It is based on typical clinical manifestations and examination results. In this case, the pharyngoscopic picture depends on the stage of the disease (asymmetry of the pharynx, the presence of protrusion of the supramyngdal region, edema and hyperemia of the affected tissues). Moreover, during the period of abscess formation, pharyngoscopy is difficult, since the patient can open his mouth only a few centimeters. The diagnosis is confirmed by characteristic changes in the blood - leukocytosis with an increase in juvenile forms, an increase in ESR.
It should be noted that an experienced specialist, despite all this data, always carries out a differential diagnosis with diphtheria, scarlet fever and a tumor process. In suspicious cases, he punctures the swelling and analyzes its contents.
Treatment[ | ]
- Opening an abscess to remove pus;
- Analgesics;
- Antibiotic therapy with clindamycin, amoxiclav, cephalosporins[5] The prescription of metronidazole in combination with benzylpenicillin is unnecessary[6];
- Draining pus with a needle or an incision is equally effective[7];
- Intravenous corticosteroids may increase the speed of recovery and relieve symptoms[2]
- It is also necessary to remember that conservative monotherapy with antibiotics is insufficient[8].