Types of Throat Abscesses
Throat abscess is a general term for respiratory tract disease. That is why it is usually divided into several types.
- Peritonsillar abscess. Characterized by the development of an inflammatory process in the tonsil area.
- Retropharyngeal or retropharyngeal abscess. This process indicates suppuration of the tissue or lymph node in the retropharyngeal space.
- Peritonsillar abscess. There is damage to the fiber in the peripharyngeal space.
A throat abscess can be located in any area. Based on this, species are distinguished according to the location of the pustular formation. These include:
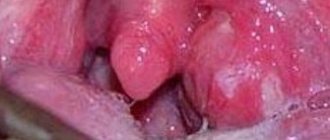
- anterior abscess. This type of disease is diagnosed most often. Infectious agents penetrate the tissue structures in the tonsil area from above. Therefore, the tonsils begin to protrude towards the uvula area;
- posterior abscess. The purulent formation is located between the affected tonsil and the back of the palatine arch;
- lower abscess. The purulent formation is located below the tonsil. Symptoms rarely make themselves felt, so it is quite difficult to identify the disease immediately;
- lateral abscess. This type of disease is much less common in practice. But it is dangerous due to the development of serious complications. The inflammatory process is located on the outside of the tonsil.
The pathological process has several stages of development. First, it all starts with the exudative-infiltrative stage. In the absence of timely treatment, it develops into abscess formation and ends with involution.
Prevention
Prevention of abscesses in young children is as follows:
- timely treatment of inflammatory diseases of the ENT organs;
- rehabilitation of carious teeth;
- treatment of foci of chronic infection in the body;
- hardening;
- massage and air baths for infants and light physical activity for preschool children.
Prevention of abscesses in adults involves caution when eating foods containing small bones and timely sanitation of carious teeth.
Diagnosis/exclusion of peritonsillar abscess (PA) at the Yauza Clinical Hospital is carried out using traditional and the most modern high-precision research methods.
- The high qualifications and extensive experience of our otolaryngologists in most cases allow us to make an accurate diagnosis already at the initial consultation based on the results of a patient interview and visual examination.
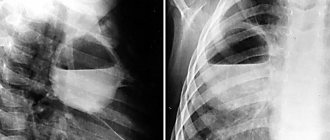
- A conversation with the patient and medical history is complemented by laboratory tests, pharyngoscopy and laryngoscopy. In some cases, the patient may be referred for an ultrasound and computed tomography scan of the neck.
- Our hospital has all the necessary diagnostic equipment, which allows us to carry out examinations in the shortest possible time and, without wasting time, proceed to treatment (conservative, surgical, combined).
- In 17% of adult patients with paratonsillitis (inflammation that precedes an abscess), the disease becomes chronic. Every tenth patient hospitalized with ENT pathology is diagnosed with peritonsillar abscess.
- With late diagnosis or lack of adequate treatment, the disease can lead to sepsis, infectious-toxic shock, purulent mediastinitis, bleeding from the vessels of the neck and other life-threatening complications
- Prevention of the development of PA, first of all, is the timely treatment of sore throat and chronic tonsillitis
Causes of an abscess in the throat
A purulent abscess in the throat is often observed in adolescence. In many situations, the cause of the pathological condition is poorly treated sore throat or pharyngitis.
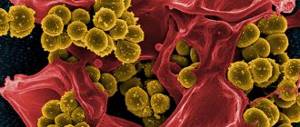
If the route of infection is tonsilogenic, then the entire infection passes into the tissue from the tonsils. The causative agents of the disease are streptococci, staphylococci, Klebsiella, Escherichia coli and Proteus.
If the treatment process was delayed or the patient interrupted the course of antibiotics, then after a slight improvement the patient’s general condition sharply worsens. When examining the throat, you can see severe swelling of the surrounding tissues.
Peritonsillar throat abscess can also appear for other reasons in the form of:
- severe hypothermia;
- decreased immune function;
- the presence of an immunodeficiency state;
- weakened immunity due to stressful situations;
- occurrence of vitamin deficiency;
- the presence of chronic tonsillitis.
In twenty percent of cases, the occurrence of paratonsillitis is not associated with a previous sore throat or pharyngitis. The inflammatory process can occur due to the ingress of infectious agents when the tonsils are injured by fish bones or rough food.
In some situations, a throat abscess occurs due to the presence of caries, pulpitis, and gum disease. In rare cases, the cause is tonsillectomy, bronchoscopy or gastroscopy.
Diagnostics
A retropharyngeal abscess is diagnosed by pharyngoscopy. An ENT doctor examines the pharynx using an optical instrument. This allows you to assess the condition of the tissues, see edema and spherical swelling - an abscess.
In addition, additional examinations are prescribed to establish an accurate diagnosis. If a retropharyngeal abscess is suspected, differential diagnosis includes:
- Throat smear - helps to conduct bacteriological studies and determine the type of pathogen.
- Clinical blood test - increased levels of ESR and leukocytes indicate purulent inflammation.
- Rhinoscopy and otoscopy are sometimes prescribed to determine the primary cause of inflammation.
To establish a diagnosis, the otolaryngologist conducts a series of studies along with a survey. The following measures are used:
- pharyngoscopy (examination of the throat) - determines redness and bulging of the mucous membrane covering the back wall of the pharynx;
- radiography and CT scan – detect purulent foci;
- palpation examination of organs - reveals enlargement of lymph nodes, hardening, swelling, and patient’s body temperature;
- a general body analysis indicates the existence of inflammation, and a throat smear can detect some irritants of the disease;
- diagnosis for syphilis, tuberculosis - performed using radiography and blood tests;
- assessment of patient complaints;
- if necessary, consult a therapist.
A diagnostic puncture may be required - in the case of suspected tumor formations or when the disease becomes chronic with a vague clinical picture to identify the causative agent of the abscess.
In this case, a retropharyngeal abscess should be distinguished from some other pathologies with similar symptoms:
- from a paratonsillar abscess (an abscess around the tonsils) – with a retropharyngeal abscess, there are no changes in the tonsils characteristic of a paratonsillar abscess;
- from edematous laryngitis - with it the laryngeal mucosa is affected over a wider area, there is no fluctuation of pus;
- from a neoplasm of the posterior wall of the pharynx - there are no signs of inflammation in the form of severe pain, redness, or elevated temperature;
- from an aneurysm of the ascending pharyngeal artery - with it the process is limited, there is no rapid increase in swelling and signs of inflammation (pain, redness, hyperthermia).
Symptoms of throat diseases
The incubation period for peritonsillar abscess ranges from two to five days.
The cause may be a sore throat, exacerbation of chronic tonsillitis, or injury to the tonsils. If the patient experiences a sharp decrease in immune strength, the disease will make itself felt within a day after the infection penetrates. Symptoms of an abscess begin to increase when the sore throat has already subsided. The patient begins to complain of a sharp painful feeling when performing swallowing functions.
Also, a throat abscess is characterized by:
- irradiation of pain to the ear area and teeth;
- trismus of muscle structures, as a result of which the patient cannot fully open the oral cavity;
- feeling of the presence of a foreign body in the throat;
- difficulties with eating, swallowing saliva;
- throwing liquid and food into the nasopharyngeal area;
- swelling and tenderness of the lymph nodes;
- development of a febrile state with a rise in temperature to forty degrees;
- the appearance of an unpleasant odor from the oral cavity;
- nasal voice;
- weakness, insomnia, poor health.
If the pustular formation is large, the patient may complain of difficulty moving the neck and head. In some cases, there is shortness of breath and difficulty breathing.
When examining the throat, swollen tissues are visible that are located near the tonsils. The tonsils are also greatly enlarged and moved slightly forward. You cannot open an abscess yourself. It may burst on its own. In this case, the patient experiences relief. But often new formations appear in the same place.
Symptoms in children and adults
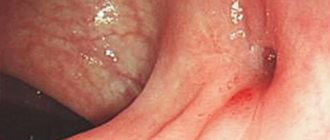
Symptoms of a retropharyngeal abscess (see photo) differ depending on the age of the patient:
Children under 1 year:
- fever;
- swelling of the neck;
- refusal to feed;
- runny nose;
- drowsiness;
- cough.
Children over 1 year:
- a sore throat;
- fever;
- stiffness in the neck;
- swallowing disorder;
- cough.
Adults:
- a sore throat;
- fever;
- swallowing disorder;
- pain in the neck;
- dyspnea.
General symptoms:
- Typically, patients complain of choking on food when swallowing, and it gets into the nose.
- If the abscess is located relatively high, nasal sounds and difficulty in nasal breathing appear.
- If the abscess penetrates down along the pharynx, the inhalation process is disrupted and wheezing appears.
- The patient's head is thrown back and tilted towards the affected side.
- The temperature rises to 39-40 ˚С.
- There may be swelling around the angle of the lower jaw and along the front surface of the neck, and drooling.
Some patients show signs of airway obstruction, and this immediately makes it possible to recognize a retropharyngeal abscess. In addition, adults experience the following external manifestations of the disease:
- swelling of the back of the throat;
- rigidity (tension) of the neck muscles, inability to tilt the head forward;
- enlarged and painful lymph nodes in the neck;
- increased body temperature;
- salivation;
- noisy, hoarse breathing;
- tilting the head to the side;
- spasm of the masticatory muscles.
In children, the following signs of a retropharyngeal abscess are more often observed:
- soreness and enlargement of the lymph nodes in the neck;
- swelling, swelling on the back wall of the pharynx (only in half of the patients);
- fever;
- noisy breathing;
- impaired movement in the neck;
- salivation;
- agitation, constant crying;
- swelling of the neck;
- lethargy;
- breathing problems;
- associated diseases - tonsillitis, pharyngitis, otitis media.
If a retropharyngeal abscess is suspected, the doctor performs pharyngoscopy - examination of the back wall of the pharynx using a special small mirror. Swelling with fluctuation is detected, that is, vibration of the walls under the influence of liquid contents. In the first days, the spherical protrusion is located on one side, and then moves to the middle of the pharynx. If there is doubt about the diagnosis, a syringe is inserted through the wall of the cavity and the purulent contents are obtained.
Treatment of throat abscess
How to treat a throat abscess? If a throat abscess occurs in childhood, treatment is carried out only in a hospital setting under the supervision of doctors. In adults, the disease is much easier to tolerate. Therefore, treatment can be carried out at home.
For mild cases, drug therapy is carried out, which includes:
- taking antibacterial agents. This will prevent infection from entering the lower respiratory tract. Patients are prescribed Amoxiclav, Flemoxin, Rovamycin, Ceftriaxone. The duration of treatment is ten days;
- throat irrigation with Lugol's solution, Miramistin, Hexoral;
- taking painkillers and anti-inflammatory medications. They allow you to relieve pain in the tonsils and lower temperature readings. Most often, patients are prescribed Nurofen, Ibuprofen, Nise, Paracetamol;
- use of antihistamines. This process will prevent tissue swelling, difficulty breathing and shortness of breath;
- the use of vitamin complexes and immunomodulatory agents. This will strengthen your immune system and allow you to recover faster from illness;
- gargling with antiseptic solutions. For such purposes, decoctions of medicinal herbs, Furacilin, Chlorhexidine, Miramistin are suitable.
If the throat abscess was caused by staphylococcus, then the patient is given immunoglobulin and autohemotherapy is performed. This treatment helps prevent the formation of a purulent cavity. It is also effective for self-opening formations.
Performing surgery
Three to four days after the development of the pathological process, the abscess should break out on its own. If this does not happen, then it is necessary to open the abscess through surgery. For such purposes, special curved clamps are used. The cutting is carried out very deeply. To prevent blood and pus from entering the respiratory tract, a hemostatic clamp is used.
During the procedure, local anesthesia is used. That is, the tissue structures are coated with Lidocaine or Dicaine. If this turns out to be ineffective, then the patient is given an additional injection inside the vein.
After cutting, the purulent contents are pumped out using tubes. Education is completely devastated. It also happens that the abscess is not completely cleared. Then the hole becomes covered with pus and fibrin. Then the patient is given drainage in the wound for three to five days.
To make the healing process faster, glucocorticosteroid drugs are injected into the affected area.
Classification
Depending on the location, retropharyngeal abscesses can be divided into the following categories:
- epipharyngeal – localized above the velum area;
- hypopharyngeal – located below the root of the tongue;
- mesopharyngeal - localized between the upper element of the velum and the root of the tongue;
- mixed.
Depending on the cause of the pathology, the following types of disease are distinguished:
- Traumatic - appear when the posterior wall of the pharynx is damaged.
- Acute - purulent lesions of the retropharyngeal lymph nodes occur after acute infections. As a rule, the inflammatory process affects the lateral nodes. This form of the disease is more common in children than in adults.
- Descending - occur as a result of the pathogen entering the retropharyngeal zone from adjacent areas. Provoking factors are otitis media, syphilitic or tuberculous spondylitis.
Read more about retropharyngeal abscess in our video:
Therapeutic measures for relapses
If the disease reappears, treatment of the throat abscess involves radical measures in the form of abscess tonsillectomy. Also, indications for the removal of tonsils are persistent tonsillitis, poor drainage of the affected area, prolonged treatment, bleeding during surgery and the development of a lateral abscess.
These manipulations are carried out using general anesthesia. If bleeding is observed, the affected vessel is sutured to the patient. In case of severe pathological process, ligation of the carotid artery is required.
If the disease is detected in the early stages, the prognosis for treatment is positive.