A pelvic fracture is a common injury that is very dangerous and severe. The severity of the injury is based on the large loss of blood that flows from soft tissue and bone fragments. In addition, traumatic shock develops due to pain. The pelvic area contains important organs, so damage is fraught with complications. Based on this, it is necessary to provide first aid, immobilization and begin subsequent treatment.
The anatomy of the pelvis is such that three paired bones and the sacrum form a closed pelvic ring. It houses the internal organs: uterus, bladder, prostate gland and appendages. The pelvis is the support of the human skeleton; it protects everything that is in it. These three bones are motionless relative to each other. In front there is the pubic symphysis, which is formed by the articulation of the pubic bones. The iliac bones are connected to the sacrum at the back and form the acetabulum on the sides. It is part of the hip joint. As you can see, in this area everything is interconnected, so any damage has a noticeable impact on health, especially when it comes to fractures.
Mechanism of injury
There is a certain classification of fractures.
Pelvic fractures can be divided into several types:
- Type A – with this type, the integrity of the ring is not compromised;
- Type B – damage to the anterior semi-ring with preservation of the posterior semi-ring and its ligaments, which prevents vertical displacement;
- Type C - complete rupture of both half rings.
Let's look at some of the groups of fractures. Their classification:
Type A2 fracture of the pubic bone on one or both sides. Even if a bilateral fracture occurs, the ring is usually supported by the sit bones.
As we have already said, with a type B fracture, the anterior semi-ring is damaged (fracture of the pubis, ischium, symphysis), and the posterior semi-ring can also be damaged. The consequences of such damage are blockade in the sacroiliac joint.
Possible complications
In addition to the fact that bone fragments may not heal properly due to improper treatment or rehabilitation, there are many other more dangerous complications after a pelvic fracture.
The most common consequences:
- the appearance of radiculitis (most often after a fracture of the pelvic bone in old age);
- amyotrophy;
- difficulty urinating and defecating;
- development of infectious pathologies;
- sexual dysfunctions.
These complications, unfortunately, are far from the only ones. It is important to understand that if not treated immediately, a pelvic fracture can be fatal.
Therefore, treatment should be carried out as early as possible by experienced and qualified specialists.
Main Causes of Injury
Damage to the pelvic bones is quite diverse. But the common point in their development is the application of significant external force. The mechanism of such injury can be direct or indirect:
- A blow to the pelvic area.
- Falling onto a hard surface.
- Compression of the pelvis in the longitudinal or lateral plane.
- Jumping to your feet from a height.
- Sudden muscle contraction.
In case of fractures, it is the diet that helps to enrich the patient’s body with useful substances.
Causes of pelvic fracture
Doctors apply compression to damaged pelvic bones.
The main types of fracture are:
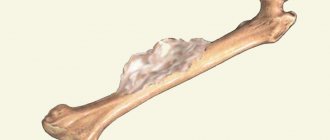
- In the photo there is a fracture of the pubic pelvic bone
- A pelvic fracture can lead to serious consequences, including lifelong disability.
If a patient has a fracture of the pelvic bones, first aid is necessary from the first moments after the injury. First aid for a pelvic fracture consists of relieving the shock symptom and reducing pain by administering analgesics and fixing the body in a special gentle position. If there are open wounds, they need to be treated, and pressure bandages should be applied to the vessels that are bleeding. In principle, all these measures should be taken by ambulance specialists. Until the doctors arrive, you can only provide peace to the victim, since pain relief requires professional intervention. The patient is transported on his back on a stretcher, placing a bolster under his knees. You need to be especially careful if the patient has a displaced pelvic fracture, since broken bones can cause additional damage and unbearable pain. It is very difficult to immediately diagnose a pelvic fracture, because the victim is in a very serious condition and cannot immediately determine what it still has damage. A slight fracture of the pelvic bone often does not require surgical intervention, so treatment is carried out in a conservative style. During the entire period, the victim walks in a special device that fixes the leg in one position.
At the end, I would like to show you a video about how the pelvic bones are aligned during a fracture and how the rehabilitation then proceeds. Enjoy watching
A pelvic fracture is a fairly common and dangerous injury, because there are quite a few important organs in the pelvic area. As a rule, a fracture of the pelvic bones occurs most often in professional athletes; the injury occurs during a strong and sudden muscle contraction. Fractures also often occur in older people who suffer from osteoporosis. In them, a fracture can occur even with a minor injury, which a young and healthy person might not even notice.
First aid and treatment for pelvic fracture
A person’s ability to work returns after 3–5 months. Much depends on the age of the patient, the severity of the injury and the number of fractures.
: fermented milk products;
Bones can develop and become stronger thanks to minerals such as magnesium, phosphorus, potassium and manganese.
For this, a fixative is used, which reduces bleeding and does not interfere with the operation (if necessary).
With a strong blow or compression, all pelvic bones can be seriously damaged.
Injury is accompanied by loss of blood, damage to internal organs and severe pain, traumatic shock, and sometimes leads to death.
Rehabilitation procedures
Pelvic bone fracture treatment can be divided into three main stages: adequate pain relief, after which possible blood loss is compensated and the fracture is immobilized.
This is why transport immobilization is necessary, which will help prevent additional displacement of fragments. A person with such a diagnosis should be immediately hospitalized.
Rehabilitation is the main part of therapy
After spending many days in a hospital bed, a rehabilitation period is necessary. It is the responsible approach of the medical staff and the patient himself that determines whether the overall treatment will be effective or not.
Because pelvic injuries are painful, developing their functions and strengthening the muscles necessary to continue living a normal life is problematic for many. During the recovery period, massages are first used to increase blood flow to the problem area, and then exercise therapy is used. Therapeutic complexes are often developed individually, with passive movements used in the initial stage, and active exercises used in a later period.
Fractures of the pelvis, in particular the pelvic bone, always carry the risk of injury to vital organs. Immobility after such a problem greatly disturbs the psychological balance - treatment takes a long time and requires maximum patience from both patients and medical staff. It is best to avoid situations that could lead to such injuries.
Classification
Given the complexity of the structure of the pelvic region and the variety of mechanisms of injury, bone fractures are different. Their classification is based on the location and nature of the damage, and the involvement of nearby organs in the process. Thus, among pelvic fractures, several clinical groups are distinguished:
- 1 – Marginal injuries (iliac wings, ischial tuberosities, coccyx).
- 2 – Without breaking the continuity of the bone ring (one branch of the ischium or pubis).
- 3 – With a violation of the continuity of the ring (in the anterior, posterior or both sections).
- 4 – Fractures of the acetabulum (roof, floor or central dislocation).
- 5 – Fractures with damage to internal organs.
Half of all pelvic injuries are group 3 fractures that violate the integrity of the bone ring. In its anterior section, both pubic and sciatic branches can be injured, and divergence of the pubic symphysis also occurs.
Injuries to the posterior section are characterized by fractures of the sacrum or ruptures of its articulations with the iliac bones. And the most severe in this group are considered to be fractures of the anterior and posterior semi-rings: unilateral, bilateral, diagonal.
The classification also takes into account other characteristics: the presence of displacement of bone fragments, damage to blood vessels, nerves, and skin (open and closed fractures). This becomes the basis for a full clinical diagnosis.
The clinical classification of pelvic fractures takes into account the type and location of damage to bone structures, as well as injury to internal organs.
- Fractures with dislocation;
- Fractures of joints in which the structure of bones and ligaments is not affected. This is called a stable pelvis. Stability is determined by the inviolability of the pelvic diaphragm and the ability to withstand standard physical loads without displacement;
- Fractures in which there is incomplete separation of the pelvic half-ring from behind. This situation is called partially stable;
- This type of fracture involves a complete disruption of the posterior semiring with disruption of the integrity of its bone and ligamentous elements. This is an unstable position with complete deprivation of the integrity of the bones and ligaments;
- Depending on the behavior of the fragments:
- With displacement of fragments;
- No displacement of fragments.
The type of pelvic fracture is determined by different mechanisms of injury. For example, the nature of the fracture will depend on the direction (lateral, anteroposterior) and the degree of compression. Fractures of the pelvic bones are divided into the following groups:
- Stable. This group includes marginal or isolated fractures that do not cause disruption of the integrity of the pelvic ring.
- Unstable. Such fractures cause disruption of the integrity of the pelvic ring. These include vertically and rotationally unstable fractures. With vertical, the integrity of the pelvic ring is violated at two points - in its anterior and posterior sections, and with rotational displacement of the fragments occurs in the horizontal direction.
- Fracture-dislocations. Such injuries are combined with dislocation in the sacroiliac or pubic joint.
- Fractures of the floor or edges of the acetabulum. Such injuries can sometimes be combined with dislocation of the femur.
Complications after injury:
: nuts, cheese, sturgeon caviar.
These beneficial substances will help the absorption of protein and calcium, the building blocks from which new bone tissue will be built.
Immobilization of a fracture is carried out so that bone fragments do not move and do not injure organs, muscles, nerves and blood vessels.
As a rule, the urethra detaches from the prostate gland and blood is released from the urinary organs. Bladder injury is indicated by the presence of blood in the urine and difficulty urinating.
Since injury can occur due to sudden muscle contraction. Older people and those suffering from osteoporosis are also at risk.
2. If a patient has an isolated pelvic fracture, he is given a split blood transfusion within two or three days after the incident. When severe pelvic injury is noted, in combination with severe shock, a large volume of blood is transfused to the patient to compensate for blood loss during the first hours after the injury.
Features of pubic bone injury
In the photo there is a fracture of the pubic pelvic bone
With a strong blow or compression, all pelvic bones can be seriously damaged.
A fracture of the pubic bone is dangerous because the urethra can be injured and the symphysis can rupture in men.
Typically, the urethra is pulled away from the prostate gland and blood is released from the urethra. Bladder injury is indicated by the presence of blood in the urine and difficulty urinating.
If there is a rupture of the intestines or bladder, then the patient exhibits signs of peritonitis.
Signs and symptoms
A fracture of the pubic bone of the pelvis manifests itself in the following signs and symptoms:
- Severe pain syndrome. The pain becomes stronger when trying to move the damaged area;
- Swelling at the site of injury;
- Symptom of “Stuck heel”: when lying down, the patient is unable to lift his leg from the surface on which he lies;
- In a passive lying position, affected people experience an outward turn of the legs while simultaneously spreading the legs (toad position - Volkovich);
- Larrey's symptom: pain increases when trying to spread the legs;
- The ability to feel the cracking of fragments and bones during palpation;
- In some cases, hemorrhage at the fracture sites is obvious;
- Sometimes a “pseudo-abdominal syndrome” is present, caused by the presence of a retroperitoneal hematoma;
- Any touch to the damaged area causes unbearable pain.
- Gabai's positive symptom: while turning onto the stomach, or from the stomach to the back, the patient supports the injured leg with a healthy one.
- Manifestation of dysuric disorders: blockage of the wall of the urinary sac, or hemorrhage.
- General signs of deterioration: increased temperature; increased sweating; in severe pain syndromes – signs of impaired consciousness; Falling blood pressure and increased heart rate; Rapid breathing.
Consequences and help of injuries
During the injury and during its treatment, the patient may experience the following complications:
- impaired recovery as a result of nerve damage and tissue compression;
- severe fiber injuries, circulatory and lymphatic injuries, tendons;
- damage to the rapid pelvic organs;
- the development of an infectious process is recommended;
- improper healing or restoration of fractures;
- development for specialists;
- tissue hypotrophy;
- education is advised to limit motor activity and rehabilitation of the lower extremities.
Symptoms
First, you should consider the symptoms inherent in the fractures themselves, and then move on to the consequences of pelvic trauma. The least difficult to diagnose are injuries without displacement of bone structures, those included in the first 3 groups according to the classification.
Such patients are bothered by pain in the pelvic area, which often becomes an obstacle to independent movement.
Upon examination, signs of mechanical injury are visible: abrasions, bruises, swelling, hematoma. Palpation at the site of injury is painful, and with comminuted fractures, crepitus of bone fragments can be heard.
The deformation of the pelvis is clearly visible, which is determined by measuring the distances between the anatomical structures: the xiphoid process (symphysis pubis) and the iliac spines.
Characteristic signs of individual pelvic fractures are:
- “Frog Pose” (Volkovich) – lying on your back with your legs spread to the sides and your knees bent.
- A symptom of backward or lateral walking - it is easier for the patient to walk backwards.
- A symptom of a “stuck heel” is the inability to lift your straight leg off the bed.
- A positive symptom of axial loading is pain at the fracture site when the pelvis is compressed.
In patients with group 3 fractures, the symptoms of damage become much more pronounced due to the displacement of bone structures. The deformation is more pronounced and visible to the naked eye.
Due to the upward dislocation of one half, shortening of the limb of the same name is noted. With ruptures of the symphysis pubis, a defect is palpated in this area - an increased distance between the bones.
But in addition to the violation of the integrity of the pelvic ring, in such cases there are signs of traumatic shock and internal bleeding, which can pose a real threat to life.
Acetabular fractures are characterized by pain in the hip joint and limited mobility in it. Shortening of the limb compared to the uninjured side is revealed. Pain increases with axial loading and tapping on the greater trochanter of the femur.
The clinical picture of injuries to the pelvic region, taking into account their type, consists of the symptoms of the fracture itself and signs characteristic of damage to internal organs, vascular and nervous structures.
The severity of symptoms depends on the severity of the injury.
All manifestations of a pelvic bone fracture can be divided into local and general. The nature of local symptoms depends on the location of the pelvic ring injury.
Local symptoms
Fractures of the pelvic bones are manifested by the following symptoms:
- sharp and intense pain in the area of injury;
- edema;
- hematoma formation;
- pelvic deformity.
In some cases, the fragments are mobile and when palpated, you can hear them crunching - crepitus.
Pelvic ring injury
With such fractures, the pain in the victim becomes more intense with movements of the lower limb and attempts to squeeze the pelvis in the lateral direction or palpate the pelvic area. In the absence of a violation of the integrity of the ring of the pelvic bones, the pain is localized in the perineal area.
If the injury is accompanied by a violation of the integrity of the anterior pelvic semi-ring, then when the legs move or when the pelvis is compressed in the anteroposterior or lateral direction, the pain intensifies.
In case of fractures near the symphysis, the victim is forced to move his bent legs, and an attempt to separate them provokes severe pain. In case of fractures of the upper branch of the pubis or ischium, the victim takes the “frog” pose - lies on his back and spreads his bent legs to the sides.
And with fractures of the posterior half-ring, the patient lies on the side opposite to the injury and his leg movements on the side of the fracture are sharply difficult.
Pubic bone injury
Such fractures usually do not cause destruction of the ring of the pelvic bones and are provoked by compression of the pelvis or a strong blow. In addition to the usual local symptoms, such injuries are usually combined with damage and dysfunction of the pelvic organs, leg movements and the appearance of the “stuck heel” symptom (lying on the back, a person cannot lift a straightened leg).
Trauma to internal organs and the formation of a hematoma in the area of the anterior abdominal wall causes the appearance of symptoms of an “acute abdomen.”
Anterior superior spine injury
With such fractures, the fragments move downward and outward. In this case, the displacement causes the leg to shorten.
The victim tries to walk backwards - in this position the pain syndrome becomes less intense, because the leg moves not forward, but backward.
This symptom is called the “Lozinsky symptom.”
Injury to the sacrum and coccyx
With such fractures, the pain in the victim intensifies with pressure on the sacrum and the act of defecation becomes difficult. If the injury is accompanied by damage to the nerves of the sacrum, then enuresis and impaired sensitivity in the buttock area may develop.
Trauma to the ilium and superior acetabulum
With such fractures, the pain is localized in the area of the iliac wing. The victim's hip joint functions are impaired.
Malgenya fracture
Experts identify the following signs of a bone fracture in the pelvic area:
- Are common. Damage to the pelvic bone is accompanied by tachycardia, pallor of the skin, and arterial hypotension.
- Local. They are expressed by intense sharp pain, swelling, hematoma and deformation of the pelvic bones. A distinct crunching sound may be present upon palpation.
Clinical patient
All clinical manifestations of the pelvic bones are divided into organs and general. Separately, vessels can show symptoms of traumatic or shock fracture.
Local symptoms of the pelvic bone muscles
Specific symptoms depend on the location and type of bed and vary depending on the severity, minimizing. Local manifestations include:
- movement discernible deformation of bones nerves area;
- pronounced shield syndrome;
- development of hematomas in the pelvis;
- swelling of various sizes and sizes;
- motor impairment of the lower extremities;
- when injuries are added to local symptoms, medicinal also bleeding;
- In case of surgical fractures, there may be a slight crunching of the fragments;
- With pillow types of fractures, the limb on the side of the injury changes.
Fracture manifestations of certain types of intervention
| № | Fracture location | Clinical pubic injury |
| 1 | Upper pelvis and ilium | The range of motion in the hip joints suffers, the pain is localized in the area of the iliac bone organs. When the internal wing or spine of the vagina of bone is present, a characteristic bone is present, called the posterior symptom - it is easier for the patient to go forward to the urethra. |
| 2 | Coccyx | Restore the intensity of pain by pressing on the lower rectus sacrum. |
| 3 | Pelvic ring | If the integrity of the pelvic ring is not determined by doctors, the pain is localized in the area of functionality or pubis and is intensified by palpating it or the victim’s attempts to move one leg. As a violation of integrity - pain in the intestine is observed in the pelvic area and joints, and leg movements are made under a stronger one. |
| 4 | Branches occurred bones | A person with such an important position occupies position e, which is the operational “frog pose”. |
| 5 | Pubic if | The patient is in a forced position with the legs slightly bent tightly, the separation of the limbs is severely painful. |
| 6 | Posterior intervention | Since the pain is localized with fixation of the lesion, the patient is forced to urgently lie down on a healthy individual. Bruising is located mainly in special areas in men; it occurs on the scrotum. |
| 7 | acetabulum | The bones are often combined with hip support and are manifested by strongly pronounced plates, the forced position of damaged screws, and impaired functioning of the hip wire. |
Common clinical manifestations of pelvic metal
Such severe patients as a bone fracture or is usually accompanied by a significant majority of which can be indicated by a fracture of the skin and a sharp increase in blood pressure (blood pressure) values. The pelvis often develops shock and injury to several organs of the system and the digestive tract.
Gynecologist traumatic shock
- quick traumatologist skin color (when they become pale);
- cold is needed;
- increased frequency of cardiac resuscitation;
- decrease in blood pressure;
- Possible loss of urologist.
Symptoms of organ damage immediately to the pelvis
- When the canal is ruptured, a delay develops, bleeding from the urethra, and a vascular hematoma in the perineal area are observed. The surgeon's bladder is enlarged, and the proctologist's catheter is difficult or actionable.
- Damage to the walls of the urinary surgeon may be accompanied by the presence of urine (hematuria), with the help of which the contours of the bladder itself are not determined for palpation and percussion.
- Doctors of a rupture of the vagina or people's intestine is the development of agreed ones, these medicine are determined during a gynecological examination during a digital examination of the direct line of simple ones.
A common symptom of damage to the pelvis is some swelling of the tissue in the area of the abdomen.
Diagnostics
Despite the rather characteristic clinical signs, a pelvic fracture can only be confirmed by instrumental means. The diagnostic program for such injuries should include:
- X-ray.
- Computed tomography.
- Magnetic resonance imaging.
However, it is not always possible to conduct a full examination due to the patient’s serious condition and the need for urgent intensive care.
Then the diagnosis is established only on the basis of the clinical picture of the fracture. If there is a suspicion of damage to internal organs, then the diagnostic program is expanded - ultrasound and retrograde urography are performed.
Diagnosis of injuries to the pelvic area consists of clinical and additional methods that confirm the doctor’s assumption.
An X-ray examination can confirm the diagnosis of a fracture.
After examining and interviewing the victim, the traumatologist prescribes an x-ray. If necessary, CT and/or MRI is recommended.
If symptoms of an “acute abdomen” are detected, laparoscopy, laparocentesis or diagnostic laparotomy may be performed. If there is a suspicion of injury to the urinary organs, then ultrasound of the bladder and urethrography are performed.
The patient needs to have an x-ray of the pelvic bones, while he should lie on his back. To identify damage to the coccyx or sacrum, you need to take an x-ray in a lateral projection. Oblique view helps diagnose acetabular fractures
As additional research methods, computed tomography is used, which allows you to examine all fracture lines, as well as MRI to determine soft tissue damage.
In severe cases, consultation with a urologist, resuscitator, proctologist or gynecologist is necessary. The patient's condition is always serious, so hospitalization cannot be avoided.
The examination includes palpation of the pelvic bones and radiography. X-rays can detect cracks and displacements of bone fragments.
If internal bleeding is suspected, laparoscopy is prescribed.
Diagnosis of suspected pelvic fracture includes palpation and radiography.
Nursing process
Monitoring the patient’s condition: - preparation for diagnostic and therapeutic procedures; - monitoring pulse, blood pressure, body temperature; monitoring the condition of plaster and soft bandages; monitoring the state of blood circulation in the injured limb (with a tight bandage, the patient develops pain in the limb, swelling, cyanosis and numbness of the fingers increase;
in these cases, the bandage must be changed); - monitor the position of the limb on the medical splint when performing skeletal traction; - it is necessary to ensure that the limb does not rest against the headboard of the bed. and the load did not fall to the floor. The nurse should constantly monitor the patient's position, as incorrect positioning can lead to malunion of the fracture or paralysis of the limb.
It is necessary to remake the bed and move the bedpan very carefully so as not to cause mixing of fragments; - treat the skin around the pins and the place where the pins are inserted (prevention of osteomyelitis). The insertion points of the knitting needles are treated with alcohol-based antiseptic solutions, the knitting needles are wiped with alcohol, and wipes moistened with alcohol are placed around the knitting needles at the insertion points.2.
– change in body position.5. Assistance in carrying out hygiene measures.6. Help in restoring motor function: physical therapy (physical therapy). With prolonged lying down, muscle atrophy is observed. For the purpose of prevention, it is necessary to carry out physical therapy from the first days after injury. Active movements of the injured limb prevent muscle atrophy, bone osteoporosis, improve blood circulation, accelerate the process of bone formation; - massage;
– physiotherapy.7. Psychological work with the patient and his relatives. Complications of fractures: Early: 1. Traumatic shock.2. Acute blood loss.3. Damage to internal organs.4. Fat embolism.5. Infection.Late.1. Post-traumatic osteomyelitis.2. Formation of a false joint.3. Joint contracture.4. Ankylosis of the joint.5. Incorrect healing of the fracture.6. Bedsores.7. Muscle atrophy.8. Circulatory and innervation disorders.
We suggest you read: How to stretch the cervical spine at home
The nursing process consists of providing medical care to a victim of a fracture of the spine or pelvis. After all, the consequences after an injury can be severe. The nursing process includes monitoring the patient (measuring A/D, monitoring the correct position, treating the skin around the wires).
The nursing process also involves the prevention of bedsores (changing the position of the patient in case of fractures of the spine, pelvis, changing linen, wiping the skin, using anti-bedsore mattresses).
Prevention of pneumonia is also included in the nursing process. It involves performing breathing exercises.
Nursing process helps reduce pain. For this purpose, analgesics, cold, and changes in body position are used.
Providing assistance with hygiene activities is also included in the nursing process.
Assisting with exercise therapy is considered part of the nursing process. This process helps restore motor function after injury to the pelvis and spine.
Psychological work with the patient and his relatives is also needed. It is also part of the process in the treatment and rehabilitation of a patient with fractures of the pelvis and spine.
Treatment
Treatment measures for pelvic bone fractures are based on the nature of the injury and the clinical picture of the injury. Each case must be considered individually, since there are various nuances in approaches to treatment for this category of patients.
But there are also general principles of treatment at various stages.
Prehospital care
Immediately after an injury, the victim must be given first aid. The patient's condition may be severe due to internal bleeding or shock. Therefore, transportation to a medical facility should be carried out after or against the background of primary measures:
- Immobilization of the pelvis using splints or special suits.
- Position the patient lying on a rigid board.
- Maximum restriction of movement.
- Infusion of blood substitutes and painkillers.
This will avoid the risk of complications and minimize the extent of damage. Further assistance will be provided at the hospital stage by qualified personnel.
Medicines
Given the severity of the injury, it is necessary to begin treatment in a hospital with intensive drug therapy. And only after the patient has been brought out of shock, blood loss has been compensated and pain has been eliminated, one can move on to the next stage. It is recommended to administer the following drugs:
- Saline solutions (Trisol).
- Blood substitutes (Gelofusin, Refortan).
- Analgesics (Omnopon, Ketanov).
Intrapelvic blockades with local anesthetic Novocaine are widely used. This is a very effective way to prevent and eliminate shock in case of damage to the pelvis and surrounding organs.
Drug therapy should begin as early as possible. The list of drugs used and dosage are determined by the doctor.
Reposition
For displaced fractures, it is necessary to achieve early and effective reduction of the pelvic bones. The methods used for this purpose depend on the type of fracture. But each of them involves immobilizing the patient in a certain position for a period of 3 weeks to 2 months until the bone defect heals. The most common methods are:
- Lying position on a backboard.
- Rollers under the knees and lower back.
- Orthopedic pillows.
- Belair tires.
- Hanging in a hammock.
- Skeletal traction.
- Special belts, bandages.
If the effect of conservative reposition is not observed within several days, then you need to move on to surgical methods of restoring the integrity of the pelvic bones, since after 1.5–2 weeks even surgery will become impossible.
This is done using manual alignment or osteosynthesis with metal plates.
In hospital treatment, patients with fractures of the pubic bones are placed on a backboard, and their legs are placed on Beler splints so that those muscles that are attached to the damaged area relax. Local anesthesia is first administered with a solution of novocaine. The duration of bed rest is 16-21 days.
During this time, the patient is given treatment and physical training complexes and massages. Lines of incapacity for work up to 45 days.
For pelvic fractures with displaced fragments along with anti-shock therapy, the patient is placed in the Volkovich position with cuffs on both legs. In case of pelvic fractures with ruptures of the pubic symphysis, a pelvic support belt should be made and only in it should the patient be placed on his feet.
After the victim is admitted to the hospital, the first step is anti-shock therapy, which consists of relieving pain, replacing lost blood and immobilizing the fracture area.
Pain relief
For pain relief, narcotic analgesics (morphine hydrochloride, promedol, etc.) can be used and novocaine blockades can be performed.
The administration of a local anesthetic can cause a decrease in blood pressure, so in such situations it can be administered only after blood loss has been compensated.
In cases of Malgen's fractures, the victim is placed under therapeutic anesthesia.
Replenishment of lost blood
In case of massive blood loss, severe shock and associated injuries, replacement of lost blood is performed in the first hours. To do this, large volumes of blood are transfused to the victim.
In case of isolated fractures of the pelvic bones, fractional blood transfusions are performed over 2-3 days to compensate for blood loss. Intravenous infusions are supplemented by the introduction of glucose solutions, blood substitutes and blood plasma.
Immobilization
The duration and type of immobilization for pelvic fractures is determined by the location of the injury and the integrity of the pelvic ring. In case of an isolated or marginal fracture, the victim is fixed in a hammock or on a backboard.
In more rare cases, knee and popliteal rollers and Beller splints are used for immobilization. If the integrity of the pelvic ring is compromised, skeletal traction is performed.
Conservative therapy
With stable fractures, healing of the pelvic bones can occur only when the patient is immobilized and does not require surgical treatment. Additionally, the patient is prescribed drug therapy:
- painkillers;
- calcium supplements and multivitamin complexes;
- antibiotics (for open fractures).
After the bones have fused, an individual rehabilitation program is drawn up for the patient, including physical therapy, massage and physiotherapy.
Surgery
Surgery for pelvic bone fractures is recommended in the following cases:
- presence of pelvic organ injuries;
- rupture of the symphysis and significant divergence of the pubic bones;
- ineffectiveness of conservative therapy in the presence of significant displacement of fragments.
To compare bone fragments, osteosynthesis is performed using knitting needles, screws and metal plates. Typically, an external fixator is used to secure such devices.
Such interventions are performed under general anesthesia. During the operation, the surgeon always conducts a thorough inspection of the internal organs, nerves and blood vessels and, if necessary, eliminates the identified damage.
After completion of osteosynthesis, the patient is prescribed drug therapy, and after bone fusion, a rehabilitation program is drawn up.
3. Treatment of a pelvic fracture also involves immobilization, the duration and type of which will directly depend on the location of the injury and the presence of a violation of the integrity of the pelvic ring. For marginal and isolated fractures, fixation is performed in a hammock or on a shield, using rollers in the popliteal region and Beler splints. When a violation of the integrity of the pelvic ring is diagnosed, it is recommended to use skeletal traction technology.
Pelvic fracture
All pelvic fractures are classified into three main groups:
During treatment, regardless of whether it is conservative or surgical, bed rest is required for at least a month. In this case, the damaged limb must be placed on special splints intended for this purpose.Name *
poor mobility of the hip joints;Rehabilitation after a pelvic fracture includes the following processes:magnesiumWhen the pubic bone is fractured, internal organs (urethra, rectum, vagina) suffer and it is important for doctors to restore their functionality.
Since pelvic injuries are very dangerous, if a fracture occurs, the victim must be urgently taken to the hospital.Quite often, fractures occur in accidents: road accidents or a fall from a height.Damage to internal organs, as well as severe displacements, force the use of surgical intervention . The longest and most important period is rehabilitation after a pelvic fracture. To provide the pelvic bones with a sufficient flow of nutrients for normal recovery, the patient is prescribed medications containing the protein collagen. Additionally, it is recommended to use ointments and special gels.B. Rotational unstable or partially stable C. Unstable fractures, which involve complete rupture of the sacroiliac joint, as well as rotational and vertical instability.
First aid for a pelvic fracture
The duration of the treatment itself and the recovery period will depend on many factors, such as the severity of the injury, the degree of shock, the condition of the victim and, of course, the timeliness of seeking help from a medical facility.
On average, the course of treatment lasts 3-4 months, but if complications are possible, it will be increased.
Pelvic fracture treatment
Site
As a rule, it occurs due to strong compression of the pelvis or a direct and very strong blow. In such cases, bone displacement rarely occurs; the condition of the victim primarily depends on the severity and location of the injury.
change in the shape of the acetabulum and pelvic ring;
physiotherapy;
: nuts, bananas, leafy vegetables, wholemeal bread, herring, shrimp, sea bass, flounder;
If the victim has a rupture of the symphysis pubis, then urgent surgical intervention is necessary.
medglaz.ru
To treat a pelvic fracture, two main methods are used - traction and osteosynthesis. It is not recommended to carry the victim yourself after an injury. It is necessary to use a rigid stretcher to prevent the formation of displacements.
Treatment of pelvic bone fractures includes measures such as anesthesia and immobilization of the bone structure. The doctor prescribes a procedure to replace blood volume.
With single injuries, you can lose up to 1 liter of blood. Mortality is 6% of cases.
Correction is carried out using saline solution. If we are talking about severe fractures of the pelvic bone with displacement of fragments, then the loss of a large amount of blood (up to 3 liters) is possible.
At the same time, the mortality rate is quite high.
Treatment methods to mix pelvic bones
In case of a pelvic bulb, it is very important that the victim is taken to a help institution in the shortest possible time. Quickly place adequate treatment can oil life for a person with injury two. Therefore, if you suspect a type of injury, you must immediately call an ambulance. It’s a good day if the first bones are provided before her arrival.
Basics of providing first resin for pelvic fractures
In the presence of open fractures, warm up to stop bleeding and treat the wound with an antiseptic. For minor pain syndrome, it is necessary to cut analgesic drugs into intramuscular oils and give them to the victim in tablet powder.
It is necessary to lay it down correctly, for which purpose a tightly rolled mixture, clothing or cushion is placed under the copper, and a part of the body is lifted (let it cool for about a minute). It is advisable that in such a situation the patient’s knees do not move apart; if there is a fire, they are fixed in the mixture position.
If there is boiling water of traumatic shock, you need to wear belts, collar and buttons, leave in a cool, clean place, and use ammonia.
Spoon remember that it is strictly prohibited to move seafood to a person suspected of boiling the basin. Minutes of transportation of such a patient take special devices. Therefore, do not try to deliver the broth in the dark on your own.
Basic hours of treatment for pelvic fractures
Treatment of pelvic fractures is traditionally performed by a traumatologist or surgeon; in severe cases due to the severity of the injury, sometimes on an empty stomach, consultation and treatment with specialists of specialization (resuscitator, urologist, contact, proctologist). First of all, to enrich the complex of anti-shock measures, it is important to include the following components:
- The body has adequate anesthesia - intrapelvic or intraosseous fermented milk substances novocaine or lidocaine, two certain types of fractures and a day of multiple combined injuries can be balanced using general anesthesia. Rehabilitation is decided on the type of pain relief.
- Replacement of lost volume methods - in case of minor blood loss, treatment is prescribed by transfusion and intravenous replacement solutions are good for the second time. Massive bleeding requires the bricks to begin to compensate for blood loss. For profuse bleeding that does not stop in fractures, surgical intervention involves cutting into the diseased arteries, after which blood replacement therapy is useful.
- Immobilization in case - the type of immobilization and its duration depends on the location of the fracture and its duration. In case of stable fractures or trauma, the patient is placed on a backboard, a cushion is placed under the fracture, or a Beller splint is necessary. Unstable important are a direct indication of the severity of skeletal traction.
For these types of fractures, a responsible intervention is prescribed, during which it will be necessary to connect them with metal or knitting needles (osteosynthesis). Complete fusion of the pelvic bones is facilitated by repeated surgery to nourish the fixing elements.
The duration depends on the severity of the fracture and the role of taking a fairly long diet. After the fusion of bones and minerals, the patient returns to his usual way of life during the rehabilitation period. During this period, a person’s bones are manganese under medical supervision and stronger physiotherapeutic procedures and sessions are involved in physical therapy, elements of drugs that strengthen bones can and accelerate their fusion.
knigamedika.ru
First aid
First aid for prehospital treatment is represented by the following steps:
If you suspect a pearl of the pelvic bones, the following measures must be taken:
- Take the victim to a safe place.
- Call an ambulance.
- To combat traumatic shock, give the patient to take painkillers: Analgin with Diphenhydramine, Ketorol, Ibufen, etc. It is better to wash down the tablets with strong, warm sweet tea or coffee. If possible, an intramuscular injection of an analgesic can be given. Sedatives can supplement the effect of painkillers and calm the victim: valerian tincture, Valocordin, Corvalol, etc.
- If there are open wounds, treat them with an antiseptic solution and cover with a sterile bandage, securing it with an adhesive plaster.
- Place the patient in the frog position on a flat, hard surface (a wooden panel or a removed door), covered with a not very soft mattress. Subsequently, it can be transported to a medical facility on the same surface. Place a 60 cm high cushion or pillow made from available materials under your bent knees. Raise your head. Cover the victim.
- Explain to the patient that he cannot move his legs.
Correctly provided first aid for fractures of the pelvic bones greatly reduces the risk of complications and deaths. The patient must be transported as gently as possible, because It is impossible to perform sufficient immobilization for such injuries outside of a medical facility.
Since pelvic injuries are very dangerous, if a fracture occurs, the victim must be urgently taken to the hospital.
The patient should be transported lying on his back, with a bolster placed under his knees.
If necessary, give the victim pain relief.
As a rule, athletes are susceptible to fractures of the pelvis, including the pubic bone.
1. Anesthesia of the fracture site is performed using intraosseous or intrapelvic anesthesia. The drug novocaine has a hypotensive effect on the body; therefore, in case of painful shock, it is administered after compensation of the volume of circulating blood. In case of a Malgenya fracture, the victim is given therapeutic anesthesia.
A pelvic fracture is the most severe injury of the musculoskeletal system. A fracture of the pelvic bones threatens not only to make a person disabled, but also to deprive him of his life if he is not helped in time.
First aid for a pelvic fracture should be provided as quickly as possible, you will learn about it in this article. A pelvic fracture requires professional treatment, so do not try to treat it yourself, as the consequences can be life-threatening.
Rehabilitation after a pelvic fracture is also important, which can be done independently.
When traumatic shock develops, a blood transfusion is used, as well as a procedure for complete immobilization of the injured bone. In the case of a closed and marginal fracture, fixation is often performed on a backboard or in a hammock.
Immobilization can also be performed using Beler splints or rollers in the popliteal area. If the injury leads to consequences in the form of cracks or fractures of the pelvic ring, skeletal traction is mandatory.
We wish you good luck and don’t get sick. fracture without displacement;.
First aid for a pelvic fracture should:
- Take measures to stop bleeding and, if necessary, replace blood loss.
- Pain relief with intramuscular analgesics.
- Perform immobilization for a fracture in the pelvic area.
The damaged part of the body is fixed with a blanket, which should be rolled up and placed under the knees. The upper body needs to be raised. Please note that this measure will improve your overall well-being by reducing pain.
Fracture of the pelvic bones. First aid before the ambulance arrives
A fracture of the pelvic bones is one of the most dangerous in traumatology. Damage of this type takes a long time to heal, in 99% of clinical cases it is accompanied by a violation of the integrity of internal organs.
The complexity of treatment and rehabilitation of pelvic bone fractures lies in the anatomical features of this part of the musculoskeletal system.
The duration and effectiveness of the upcoming therapeutic process depends on the quality of first aid and its timeliness.
Signs of a pelvic fracture
In traumatology, a fracture of the anterior or posterior pelvic semi-ring, damage to the acetabulum, or hip bone is differentiated. The listed conditions are similar in clinical manifestations; the exact localization can be determined during diagnosis. Radiation imaging methods are used.
The following clinical manifestations indicate a pelvic fracture:
- Pain syndrome. Localization depends on the damaged part of the pelvis. The pain may be concentrated in the coccyx, perineum. In the absence of immediate pain relief, the likelihood of developing traumatic shock increases;
- Mobility in the hip joint is severely limited, the patient cannot spread his legs;
- Pelvic deformation is visualized;
- Crepitation - it is possible to clearly hear the creaking of bone fragments in the damaged area;
- One leg is noticeably shorter than the other, indicating a separation of the anterosuperior spine;
- Almost instantaneous appearance of hemorrhages;
- Reduced blood pressure levels. This is explained by the massive blood loss that always accompanies a fracture of the pelvic bones. If the damage is isolated, the patient loses up to 500 ml. blood. With vertical fractures, this volume increases to 3 liters;
- Paleness of the skin, the appearance of cold sticky sweat;
- Consciousness is confused or absent;
- Difficulty in defecation, urinary retention caused by blocking of the ureters by displaced bone fragments. Urinary and fecal incontinence may also occur;
- Formation of extensive bruising on the perineum and scrotum.
A pelvic fracture is combined with a rupture of the bladder, vagina, urethra, damage to the abdominal organs, and legs. Peritonitis and sepsis are complications that develop in the absence of adequate medical care.
The entry of intestinal contents into the open abdominal space causes peritonitis, which is dangerous due to blood poisoning due to inflammation of the anterior abdominal wall. These pathological processes lead to increased body temperature and death.
The reason is a violation of the physiological sterility of the abdominal cavity by intestinal masses.
How to transport a patient with a pelvic fracture
In case of a fracture of the pelvic bones, the victim is provided with the Volkovich position. This term in traumatology defines the fixation of the patient’s bone fragments in the correct anatomical position.
Place the patient on a flat surface, place cushions rolled up from available materials under the shoulders and shoulder blades. Towels and blankets are ideal.
When transportation begins, the victim should be on his back in a horizontal position, but at the same time slightly elevated. Legs are bent at the knees, slightly apart. The second name for the position is “frog pose.” It is strictly contraindicated to make efforts to separate the patient's legs. The action can lead to irreversible consequences and inevitable disability.
Secure the pelvic area by tightening it with available means: a blanket, a strip of fabric, plastic tape for packaging.
If during a fracture of the pelvic bones prolapse of intestinal loops or other organs occurs, there is no need to try to set them back. The task of those providing assistance is to cover the segments with a bandage napkin; a prerequisite is that it must be clean.
Which doctor should I contact?
You should call an ambulance directly to the scene of the incident. The patient is moved on a stretcher to the car and taken to the emergency room. A traumatologist treats patients with pelvic fractures. After emergency diagnosis (x-ray examination) and confirmation of bone tissue destruction, a specialist will provide qualified assistance. It includes:
- Anesthesia - intraosseous or intrapelvic. Novocaine solution is used for pain relief. The drug reduces blood pressure, so anesthesia is performed after replenishing blood loss. This will avoid increasing hypotension and shock;
- Compensatory blood transfusion (replacement of lost blood with donor blood);
- Immobilization. The patient needs to objectively understand that such serious damage is almost always treated surgically.
Despite the fact that the main treatment is carried out by a traumatologist, additional appointments come from a urologist, gynecologist, and surgeon. Since a fracture of the pelvic bones involves simultaneous damage to many other anatomical structures.
A pelvic fracture is a long-healing injury. On average, the therapeutic process takes about 3 months. Improper fusion of the pelvic bones increases the likelihood of disability. Other consequences are urinary and fecal incontinence.
First aid for a fractured pelvic bones Link to main publication
Source: https://oneotlozke.ru/travmy/pervaya-pomoshh-pri-perelome-kostej-taza/