The most common causes of scoliosis
Doctors identify several key factors in the occurrence of scoliosis:
- insufficient cushioning of the spine due to weakened or atrophied muscles;
- vitamin D deficiency;
- excessive stress on the spine;
- flat feet (due to which the load on the back is distributed unevenly);
- congenital bone defects.
At the same time, the likelihood of spinal curvature in children is much higher, since up to the age of 16 the back muscles are not strong enough and cannot fully distribute the load.
Reference : according to statistics, spinal curvature occurs 5-6 times more often in girls than in boys. This is explained by the physiology of the structure of their skeleton, as well as the slower development of muscles.
And the main cause of congenital scoliosis in most cases is vitamin D deficiency , which is responsible for the absorption of calcium and phosphorus from the small intestine and its distribution in bone tissue. Moreover, its level in children should be at least 600 - 1000 IU per day . When the consumption rate is reduced to 250 IU, the likelihood of developing scoliosis increases 10 times. The human body receives most of its vitamin D through exposure to ultraviolet rays on the skin. That is why doctors recommend taking infants for walks outside every day.
Important : the ultraviolet spectrum of rays practically does not penetrate glass. Therefore, walking with your baby on a balcony or glassed-in loggia will not be enough to replenish the vitamin D requirement.
There is also vitamin D2 (ergocalciferol ), which is also directly involved in the absorption of calcium and phosphorus. But it enters the body only with food, in particular with breast milk . That is why, in the absence of lactation, doctors always prescribe vitamin D in the form of oral drops.
And, despite the current development of medicine, doctors cannot name all the causes of spinal curvature . Therefore, there is a theory that the likelihood of the disease being manifested is also influenced by a genetic factor, that is, a predisposition to skeletal pathologies.
Causes of scoliosis of the cervical spine
The main causes of cervical scoliosis:
- dysfunction of the endocrine glands (occurs during puberty, after which active growth of the skeleton and muscles begins, but intercellular metabolism is disrupted);
- insufficiency of the muscular-ligamentous system (when the skeleton is actively developing and the muscles are weakened);
- Bone dysplasia of the cervical spine;
- syringomyelia (formation of cavities in the vertebrae or intervertebral discs);
- spinal hernia (especially often - Schmorl's hernia).
A provoking factor can also be surgical operations in the neck area. But in school-age children, curvature of the cervical spine is often caused by the wrong choice of desk. That is, when the height of the table at which the child is sitting does not correspond to his nominal height.
Doctors also claim that cervical scoliosis is often diagnosed in people with early-stage myopia (when the need to wear glasses or contact lenses does not yet arise). In this case, the patient has difficulty seeing distant objects and, in order to focus better, stretches his neck forward. This is a reflex movement, however, over time it can lead to exhaustion of the muscles of the cervical spine.
Diagnostics
Diagnosis of scoliosis in adults is extremely important. In this case, the diagnosis itself is established by appearance and characteristic symptoms. But determining the degree of deformation has significant practical significance in selecting a treatment method.
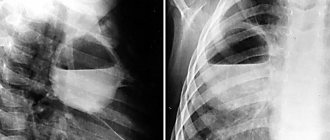
In accordance with the classification, scoliotic deformities are divided into four groups according to severity, depending on the angle of the main curvature. The angle of curvature is measured using an x-ray.
It will also be important to resolve the issue of stability or mobility of scoliotic deformity. The more mobile it is, the greater the chance of success even with conservative treatment. For accurate determination and prediction, the deformation stability index is calculated. Scoliosis in adults usually has high index values, which indicates a poor prognosis.
Causes of thoracic scoliosis
Doctors identify several main reasons for the development of scoliosis of the thoracic spine:
- back injuries;
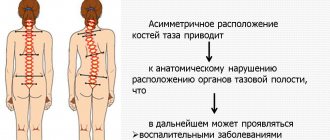
- asymmetry of the skeleton (in particular, the length of the lower limbs);
- weakening of the muscle tone of the back;
- sedentary lifestyle;
- calcium metabolism disorder;
- phosphorus deficiency;
- difficult course of pregnancy.
Doctors also emphasize that thoracic scoliosis can be an “ occupational ” disease. Most often - at dentists . This disease has also been confirmed by athletes involved in shot throwing and tennis, when the spine is exposed to an uneven load for a long time.
Symptoms
The main manifestations of scoliosis are:
- Curvature of the spinal trunk in the frontal (lateral) plane.
- Asymmetrical position of shoulders, shoulder blades, elbows.
- Distortion of the pelvic axis.
- Gait disturbance.
- Painful sensations in the back, chest, lower back.
- Fast fatiguability.
- Frequent and intense headaches.
- Various deformities of the chest bones.
- Disruption of the normal functioning of the heart, respiratory and digestive systems.
In the early stages of the disease, you can only notice a change in the curvature of the spinal trunk and an unexpressed asymmetry of the shoulder girdle and shoulder blades. As the disease progresses, new symptoms appear. In advanced cases, serious dysfunction of almost all internal organs and severe deformities of the bones of the chest, pelvis and spine appear.
Causes of scoliosis of the lumbar spine
The most common cause of lumbar scoliosis is degenerative processes of the intervertebral discs of this part of the spine. And they are conditioned by:
- received mechanical injuries to the back (in which microcracks occur in the discs or their displacement);
- overweight;
- congenital pathologies of the skeleton or muscles.
The likelihood of developing lumbar scoliosis increases significantly if there is a curvature of the spine in the thoracic region. In this case, so-called S and Z curvatures occur, that is, in several places at once.
Reference : such scoliosis at the initial stage is not accompanied by painful symptoms, which significantly complicates its timely diagnosis. Only an X-ray examination of the skeleton will help to accurately identify it with a slight curvature.
Causes of congenital scoliosis
The causes of congenital scoliosis can be:
- deficiency of vitamins D (especially dangerous for infants and children during puberty);
- formation of wedge-shaped vertebrae in a child (even during pregnancy);
- abnormal segmentation of the spine (scientists have not yet established their exact cause);
- congenital unilateral blocking of vertebral growth;
- neural tube pathologies.
Often, congenital scoliosis is diagnosed when there is a significant deficiency of vitamins in the mother’s body during pregnancy. As a rule, in such cases, pathologies are detected not only in the development of the spine, but also in the structure of the skull, upper lip, and palate.
Psychological reasons
Doctors also include a psychosomatic factor among the unobvious causes of scoliosis, and women are more susceptible to it. This is explained by the fact that constant mental discomfort or depression can provoke constant uneven muscle spasms. If this process takes only 2–3 months, then it will not lead to curvature of the spine. But if the psychological factor occurs over several years, then this significantly increases the likelihood of curvature occurring.
Classification of pathology
S-shaped type of right-sided idiopathic scoliosis III degree
Today, scoliotic diseases are classified according to several criteria:
- by reason of occurrence (origin);
- by type of spinal deformity;
- by localization of deformation;
- by the magnitude of the deviation angles;
- according to the course of the disease - rapidly and slowly progressing.
Prevention and treatment
The best option for preventing scoliosis is maintaining a healthy lifestyle, active physical activity (within reason), and a balanced diet. Periodic consultations with an orthopedist will also help prevent the onset of the disease (this is especially important for teenage children).
Scoliosis is treated using two methods:
- conservative therapy;
- surgical intervention (removal of destroyed vertebrae or atrophied muscles, restoration of nerve root conductivity).
Conservative therapy includes physical therapy, normalization of the diet and taking vitamin and mineral complexes. This will not help completely get rid of the disease, but it will completely stop its development.
Surgical solution to the problem
Definitive treatment of pathology involves surgical correction of the pathology. The operation requires preparation of the patient, stabilization of the general condition, carrying out the necessary pharmacological course of treatment, and tests to detail the diagnosis.
Indications for the operation:
- Rapid progression of the disease. After taking several x-rays, which will show rapid evolution;
- Severe curvature that disrupts the patient’s vital functions, causing disruption of the functioning of internal organs.
Types of operations performed:
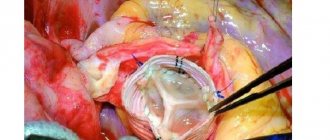
- Spinal fusion. Removal of intervertebral discs and their replacement with metal discs. As a result of this maneuver, it becomes possible to fuse the vertebrae without curvature;
- Hemivertebra removal. If there is one hemivertebra, it is possible to remove it and replace it with a metal frame, which leads to the restoration of the normal axis;
- Growing rods. Metal rods are attached to the vertebrae and every six months they are lengthened with small, light surgical interventions, thus the spine grows correctly;
- Similar to the above rods, which are attached to the ribs, because of this, neither the spine nor the chest as a whole is curved and develops normally.
Congenital disease of the spinal column becomes an obstacle to the normal development of the child and his formation as a person. To create optimal conditions for the growth and development of a child’s body, it is necessary to be registered with a family doctor in order to diagnose all pathologies in a timely manner and prescribe timely rehabilitation, pharmacological treatment and health procedures until the stage of the need to prescribe surgical intervention.
Similar:
- What treatment methods for scoliosis in adolescents are most effective at different stages?
- Causes of unfixed scoliosis, its differences from the fixed form
- General recommendations for the prevention of scoliosis in children, clinical effectiveness, physical therapy and other physiotherapeutic measures
- Symptoms and causes of left-sided scoliosis of the spine of the 1st degree
- Infantile idiopathic scoliosis
- How is ankylosing spondylitis treated, diagnostic methods, classification of the disease, causes, symptoms and complications
- Causes of development of 3rd degree scoliosis, methods of treatment, diagnosis, preventive measures, prognosis of the disease and rehabilitation