Complete blood count increased lymphocytes and monocytes
When lymphocyte and monocyte counts in the analysis are elevated, this causes concern for the patient.
Experienced doctors understand that when monocyte lymphocyte counts are elevated, this is only a consequence of some pathology. However, it is impossible to make an accurate diagnosis using a blood test alone. Therefore, it is impossible to unequivocally answer the question why, for example, monocytes are low and other blood parameters are high.
Any changes in the blood test should be perceived as an additional symptom of the disease, which is taken into account when differential diagnosis is performed and treatment is selected.
Monocytes in the blood are representatives of a young group of cells; they are sent to tissues, from where monocytes emerge as mature histiocytes and macrophages. In addition, they migrate to the mucous membranes and skin, where they first meet agents of foreign origin.
Thus, macrophages and histiocytes perform phagocytosis of the pathogen.
When monocytes become elevated, this is a sign of the presence of an agent of foreign origin in the tissues; accordingly, the monocyte level increases, since there is an increased need for macrophages.
During their delivery to the tissues, the amount in the blood also increases, which is demonstrated in tests along with an increase in leukocytes and changes in other blood parameters.
Another important indicator that is often considered together with monocytes is lymphocytes. In the body, different functions lie on the “shoulders” of these cells:
- the process of starting and stopping the immune response;
- recognition of proteins of foreign origin;
- production of immunoglobulins;
- destruction of the pathogen cell;
- storing information about it and recording it in the genetic code.
Thus, lymphocytes perform immunity work in two directions. These are cellular and humoral immunity. Very often, the analysis does not use 100 percent of only one cell.
For example, if neutrophils are low, this does not make it possible to make a diagnosis directly. It is important to consider high and low indicators together, and not separately.
That is why it is often important for doctors to see the combination of monocyte and lymphocyte levels.
Against the backdrop of an integrated approach to deciphering the analysis, you can understand what stage the pathological process is at, make a prognosis for the development of the disease, understand its causes, confirm the diagnosis and understand how impaired the immune system is.
Despite the fact that agranulocytes, neutrophil cells, lymphocytes, erythrocytes and all other representatives of the circulatory system have their own functions, in terms of task they agree on one thing. Their job is to neutralize pathogenic microorganisms.
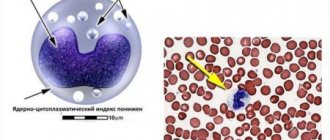
Lymphocytes and monocytes are colorless blood cells that belong to the category of leukocytes. The bone marrow is responsible for the production of monocytes, after which they absorb pathogenic bacteria.
Normally, the level of presence of monocytes as a percentage of the total number of leukocytes in the blood should be at the level of 3-11 percent. If the analysis indicates an increase in lymphocytes and monocytes, we may be talking about the presence of a tumor in its malignant form, an infection due to the work of fungi, viruses or bacteria, diseases of the intestines, heart, and blood vessels.
If monocytes are enlarged, and all other groups of cells responsible for human immunity do not show pathological changes, then it is important to check for the presence of bone marrow diseases. In this case, monocytosis is a serious disorder, and the disease itself is treated in a hospital setting.
To increase the chances of a favorable outcome, the doctor's first priority is to rule out bone marrow cancer or detect it at an early stage.
It is important to note that, regardless of the disease, monocytes and ESR are elevated throughout treatment; often the sedimentation rate and monocyte level return to normal only a few days after complete recovery, especially if extensive inflammation is present.
However, low or high monocyte levels are not always explained by the presence of pathology. Sometimes a harmless increase may occur due to the fact that lymphocytes and eosinophils have decreased.
This is possible with severe allergies.
This is due to the fact that other cells, for example, platelets and monocytes, become lower, which means the body needs to close the gap by offering compensation at the expense of others.
After two to three days, if the disease proceeds without complications, neutrophils and monocytes, platelets and other indicators will be reduced and return to normal. An increase in monocytes during the recovery period can even be considered a positive trend.
It was already noted above that doctors rarely consider absolute indicators as a sign of a disease. In most cases, we are talking about a comprehensive decoding of the analysis. In this case, different combinations are identified. The most common are the following.
A combined increase in monocytes and lymphocytes may be a sign of an acute infection of viral origin. These are not only simple respiratory diseases, but also measles, rubella or chickenpox, which are dangerous for some categories of people. In this case, neutrophils become low, and doctors usually start working with antiviral therapy.
The combination of elevated monocytes and eosinophils necessarily manifests itself if a person encounters an allergen or parasites. We are talking about chlamydia and mycoplasma. The distinctive symptom of patients in this case is a dry cough, which takes a long, painful form. However, such important clinical signs as wheezing in the lungs are absent.
The combination of monocytes and basophils also cannot be ignored. Basophils refer to cells that are among the first to respond. They rush towards the infectious focus even before everyone else starts working. Increased monocytes and basophils combined with each other can cause long-term treatment with hormonal spectrum drugs.
Moreover, against the background of increased basophils, a large number of macrophages and lymphocytes are always present. They act due to the production of serotonin, histamine and a number of other substances that enhance the inflammatory process.
When neutrophils are elevated, and along with them monocytes, it is worth checking for bacterial infections. This is how they manifest themselves in their acute stage. In this case, a reduced lymphocyte count is observed. Patients with this diagnosis are characterized by an elevated temperature, a wet cough, a runny nose with purulent discharge from the nose, and wheezing in the lungs.
It is important to note that all cells of the immune system and blood replace each other. Therefore, sudden deviations, which vary greatly in duration, must be taken very seriously. This is important to exclude malignant diseases.
When platelets are elevated, this is also a sure sign of the presence of inflammation in the body, especially if there is a combination with a monocyte increase. However, hematological diseases, cigarette abuse, the postoperative period, and endocrine diseases cannot be excluded. An increase in platelets is inevitable after removal of the spleen.
Sometimes red blood cells and monocytes are elevated. In this case, doctors usually prescribe an additional test, while monitoring the dynamics of changes in monocyte levels and indicators of other blood cells.
Separately, it is worth clarifying the erythrocyte sedimentation rate, which is always considered in conjunction with the main blood parameters. Most often, an increased level of this indicator is a signal of the presence of infectious diseases in the body.
The reasons for the increase may be an acute process of inflammatory nature, the presence in the body of chronic processes, a general reduction in the number of red blood cells against the background of anemia.
When citing other reasons for increased ESR, do not forget about teething. We are talking not only about children, but also about adults (wisdom teeth).
In addition, encounters with infection, parasites, allergies, and cancer problems lead to an increase in ESR levels.
source
Source: https://domofoniya.com/krov/obschiy-analiz-krovi-povysheny-limfotsity-monotsity/
Elevated lymphocytes and monocytes: what are they talking about?
Based on the results of blood tests, doctors are able to recognize signs of an inflammatory or pathological process in the human body. But in order to understand exactly what kind of violations have arisen, the indicators of different shaped elements are assessed. What does a condition in which lymphocytes and monocytes are elevated mean? First of all, this indicates changes in the immune response.
Therapists consider the parameters of the leukocyte series in a comprehensive manner. Particularly indicative is the ratio of two types of formed elements - lymphocytes and monocytes. The data obtained allows you to carry out the following actions:
- Clarify the stage of the inflammatory-pathological reaction;
- Identify its cause;
- Find out the prognosis of the disease;
- Understand immune disorders.
With the help of the OAC, the doctor sees what additional diagnostic procedures the patient needs to undergo to make an accurate diagnosis.
Lymphocytes and monocytes: briefly about functionality
Inside every person, immunity works like a clock. All formed elements of blood have their own functions and are aimed at destroying any microscopic enemy that penetrates the body or mutated own cells.
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=23S96rk_gt0
The immune response occurs in several ways:
- Phagocytosis . The invading pathogenic microorganism is captured by leukocyte cells and, after absorption, is destroyed with the help of enzymes. The process of phagocytosis is carried out by macrophages maturing from monocytic forms.
- Humoral response . The protective effect comes from antibodies that are produced after contact with certain types of pathogenic microbes. As soon as a foreign agent is introduced, immunocompetent cells identify it and secrete immunoglobulins with destructive properties. The main protective functions are performed by lymphocytic elements.
As you can see, lymphocytes and monocytes are responsible for the destruction of any harmful microbes. Granulocytes also carry out the immune response. In total, there are three main groups of leukocytes that perform the protective functions of the immune system. They not only destroy pathogenic agents, but also remember information about them, forming persistent, in some cases, lifelong immunity.
But in order to understand why leukocytes, lymphocytes and monocytes are elevated, it is necessary to understand their purposes and the reasons for increased production in the bone marrow. An increase in the number of blood cells is always associated with the development of a pathological process or inflammation caused by infectious invasion.
Causes of monocytosis and lymphocytosis: what provokes deviations from the norm?
If we consider each formed element separately, then their increase can be caused by a variety of factors. When the number of monocytic cells increases, they speak of monocytosis. And when the level of lymphocyte bodies increases, the condition is called lymphocytosis.
Reasons for the development of monocytosis
- Acute infectious diseases or exacerbations of chronic inflammation (tuberculosis, influenza, endocarditis, candidiasis, syphilis);
- Autoimmune disorders (sarcoidosis, rheumatoid arthritis);
- Malignant neoplasms;
- Poisoning with toxic drugs, phosphorus;
- Oncological diseases of hematopoiesis (myeloid leukemia, lymphogranulomatosis);
- Appendicitis, sepsis.
The degree of increase in parameters indicates the severity of the immune system’s response to the development of the disease. The stronger the inflammation, the more macrophages are required for phagocytosis of foreign bodies.
Reasons for the development of lymphocytosis
- Viral infection (mononucleosis, hepatitis, measles);
- Chronic lymphocytic leukemia;
- Poisoning of the body with chemicals (arsenic, lead);
- Taking medications (Levopod, Phenytoin, narcotic painkillers);
- Toxoplasmosis, leptospirosis;
- Crohn's disease;
- Endocrine diseases.
Increased lymphocyte levels are associated with a significant response to antigenic stimulation. They become larger than normal when a viral/bacterial infection occurs, as well as when cancer cells develop in the body.
High levels of leukocyte cells in the blood: how is health assessed?
Doctors look at all parameters of the OBC results, which allows them to determine the development of a particular disease. Sometimes elevated monocytic and lymphocytic body counts may not be dangerous because other values deviate downward. Against the background of reduced numbers of individual formed elements, leukocyte bodies do not cause concern and are within the acceptable norm.
For example, moderate monocytosis in the blood will not be a guide to detect serious infection or malignancy if low levels of lymphocytes and eosinophils are simultaneously observed. Such conditions most likely indicate an allergic reaction or the initial stage of a viral infection (a child is usually diagnosed with measles, chickenpox, and whooping cough).
Why is this happening? Because with the massive death of phagocytic bodies, the bone marrow quickly produces new defenders to compensate. Thus, monocytosis develops.
But after 3 days, as soon as the health status begins to stabilize, eosinophils, monocytes and lymphocytes gradually return to normal.
Most often, a slight increase in the formed elements involved in phagocytosis at the recovery stage indicates successful treatment and is a positive result.
When a simultaneous increase in monocytic and lymphocytic forms is noted, an acute virus is diagnosed. It could be ARVI, chickenpox, rubella. With monocytosis and lymphocytosis, a decrease in the level of neutrophils is observed. Such numbers usually prompt the doctor to prescribe antiviral drugs.
But the growth of neutrophil bodies with monocytosis, but a drop in the lymphocytic type, is alarming, since this usually happens with a bacterial infection of the body. As a rule, the patient's temperature rises and purulent secretion may be released.
If eosinophils increase along with monocytes, then this phenomenon indicates a parasitic infection (chlamydia, mycoplasma) or the development of allergies.
And when the numbers of three formed elements increase at once - lymphocytes, monocytes and basophils, then a pronounced inflammatory reaction occurs in the body. In this case, it is necessary to exclude the effects of taking hormonal drugs.
It is important to note that all types of microscopic immune defenders are capable of replacing each other and temporarily performing the functions of missing forms. But if a significant deviation of some parameter is observed in the blood test, then additional diagnostics should be carried out to exclude malignant tumors of the hematopoietic system.
How to restore performance in a child and an adult?
This health condition, in which there is both monocytosis and lymphocytosis, most often indicates a viral infection. Inflammation is provoked both by a common virus that causes ARVI, and by more serious pathogenic virions that infect patients with rubella, measles, and chickenpox.
Treatment of a viral infection in a child or adult patient is carried out using several groups of drugs:
- Antiviral (Oseltamivir, Tamiflu);
- Detoxification (plain water in large quantities without sugar and alcohol);
- Sorbents (activated carbon, Sorbex);
- Moisturizers for mucous membranes (Aqua-Maris, Marimer, homemade saline solution);
- Decongents for nasal swelling (Nazivin, Nazol)
- Symptomatic complex (antipyretic, analgesic, anti-inflammatory, antitussive, mucolytic, etc.).
For high fevers in children over two years of age and adults, Ibuprofen or Paracetamol can be given. The medications also relieve severe muscle pain and headaches. A child under 12 years of age should not take Acetylsalicylic acid, because it can cause complications. For example, Reye's syndrome causes liver dystrophy and affects the central nervous system.
If the treatment of ARVI helps to restore the CBC values to normal with the help of various drugs, then infections such as rubella and chickenpox are not eliminated by medications. Medicines only prevent the development of complications. Basically, drinking plenty of fluids with a solution of Regidron, Ascorutin, antispasmodic and anti-inflammatory drugs is prescribed.
Additionally, during the period of skin rashes, the child’s condition is alleviated by antiallergic components - Suprastin, Claritin. A good immunostimulant is Wobenzym, Immunal. When bacterial complications develop, antibiotics are used (Sumamed, Flemoklav).
To restore the results of the CBC to normal, it is very important to establish an accurate diagnosis. And treatment can be selected individually for each patient, depending on the age and severity of the disease.
Source: https://diagnos-med.ru/povyshennye-limfotsity-i-monotsity-o-chem-govoryat/
Elevated lymphocytes and monocytes
When lymphocyte and monocyte counts in the analysis are elevated, this causes concern for the patient. Experienced doctors understand that when monocyte lymphocyte counts are elevated, this is only a consequence of some pathology. However, it is impossible to make an accurate diagnosis using a blood test alone.
Therefore, it is impossible to unequivocally answer the question why, for example, monocytes are low and other blood parameters are high.
Any changes in the blood test should be perceived as an additional symptom of the disease, which is taken into account when differential diagnosis is performed and treatment is selected.
General information
Monocytes in the blood are representatives of a young group of cells; they are sent to tissues, from where monocytes emerge as mature histiocytes and macrophages. In addition, they migrate to the mucous membranes and skin, where they first meet agents of foreign origin.
Thus, macrophages and histiocytes perform phagocytosis of the pathogen.
When monocytes become elevated, this is a sign of the presence of an agent of foreign origin in the tissues; accordingly, the monocyte level increases, since there is an increased need for macrophages.
During their delivery to the tissues, the amount in the blood also increases, which is demonstrated in tests along with an increase in leukocytes and changes in other blood parameters.
Another important indicator that is often considered together with monocytes is lymphocytes. In the body, different functions lie on the “shoulders” of these cells:
The norm for ESR in children is 2708
- the process of starting and stopping the immune response;
- recognition of proteins of foreign origin;
- production of immunoglobulins;
- destruction of the pathogen cell;
- storing information about it and recording it in the genetic code.
Thus, lymphocytes perform immunity work in two directions.
These are cellular and humoral immunity. Very often, the analysis does not use 100 percent of only one cell. For example, if neutrophils are low, this does not make it possible to make a diagnosis directly. It is important to consider high and low indicators together, and not separately.
That is why it is often important for doctors to see the combination of monocyte and lymphocyte levels.
Against the backdrop of an integrated approach to deciphering the analysis, you can understand what stage the pathological process is at, make a prognosis for the development of the disease, understand its causes, confirm the diagnosis and understand how impaired the immune system is.
Increased lymphocytes and monocytes
Despite the fact that agranulocytes, neutrophil cells, lymphocytes, erythrocytes and all other representatives of the circulatory system have their own functions, in terms of task they agree on one thing. Their job is to neutralize pathogenic microorganisms.
Lymphocytes and monocytes are colorless blood cells that belong to the category of leukocytes. The bone marrow is responsible for the production of monocytes, after which they absorb pathogenic bacteria.
Normally, the level of presence of monocytes as a percentage of the total number of leukocytes in the blood should be at the level of 3-11 percent. If the analysis indicates an increase in lymphocytes and monocytes, we may be talking about the presence of a tumor in its malignant form, an infection due to the work of fungi, viruses or bacteria, diseases of the intestines, heart, and blood vessels.
If monocytes are enlarged, and all other groups of cells responsible for human immunity do not show pathological changes, then it is important to check for the presence of bone marrow diseases. In this case, monocytosis is a serious disorder, and the disease itself is treated in a hospital setting.
To increase the chances of a favorable outcome, the doctor's first priority is to rule out bone marrow cancer or detect it at an early stage.
It is important to note that, regardless of the disease, monocytes and ESR are elevated throughout treatment; often the sedimentation rate and monocyte level return to normal only a few days after complete recovery, especially if extensive inflammation is present.
However, low or high monocyte levels are not always explained by the presence of pathology. Sometimes a harmless increase may occur due to the fact that lymphocytes and eosinophils have decreased.
This is possible with severe allergies.
This is due to the fact that other cells, for example, platelets and monocytes, become lower, which means the body needs to close the gap by offering compensation at the expense of others.
After two to three days, if the disease proceeds without complications, neutrophils and monocytes, platelets and other indicators will be reduced and return to normal. An increase in monocytes during the recovery period can even be considered a positive trend.
Common combinations of cellular reactions
It was already noted above that doctors rarely consider absolute indicators as a sign of a disease. In most cases, we are talking about a comprehensive decoding of the analysis. In this case, different combinations are identified. The most common are the following.
A combined increase in monocytes and lymphocytes may be a sign of an acute infection of viral origin. These are not only simple respiratory diseases, but also measles, rubella or chickenpox, which are dangerous for some categories of people. In this case, neutrophils become low, and doctors usually start working with antiviral therapy.
The combination of elevated monocytes and eosinophils necessarily manifests itself if a person encounters an allergen or parasites. We are talking about chlamydia and mycoplasma. The distinctive symptom of patients in this case is a dry cough, which takes a long, painful form. However, such important clinical signs as wheezing in the lungs are absent.
The combination of monocytes and basophils also cannot be ignored. Basophils refer to cells that are among the first to respond. They rush towards the infectious focus even before everyone else starts working. Increased monocytes and basophils combined with each other can cause long-term treatment with hormonal spectrum drugs.
Moreover, against the background of increased basophils, a large number of macrophages and lymphocytes are always present. They act due to the production of serotonin, histamine and a number of other substances that enhance the inflammatory process.
Additional Variations
When neutrophils are elevated, and along with them monocytes, it is worth checking for bacterial infections. This is how they manifest themselves in their acute stage. In this case, a reduced lymphocyte count is observed. Patients with this diagnosis are characterized by an elevated temperature, a wet cough, a runny nose with purulent discharge from the nose, and wheezing in the lungs.
It is important to note that all cells of the immune system and blood replace each other. Therefore, sudden deviations, which vary greatly in duration, must be taken very seriously. This is important to exclude malignant diseases.
When platelets are elevated, this is also a sure sign of the presence of inflammation in the body, especially if there is a combination with a monocyte increase. However, hematological diseases, cigarette abuse, the postoperative period, and endocrine diseases cannot be excluded. An increase in platelets is inevitable after removal of the spleen.
Causes of increased leukocytes in the blood2873
Sometimes red blood cells and monocytes are elevated. In this case, doctors usually prescribe an additional test, while monitoring the dynamics of changes in monocyte levels and indicators of other blood cells.
Separately, it is worth clarifying the erythrocyte sedimentation rate, which is always considered in conjunction with the main blood parameters. Most often, an increased level of this indicator is a signal of the presence of infectious diseases in the body.
The reasons for the increase may be an acute process of inflammatory nature, the presence in the body of chronic processes, a general reduction in the number of red blood cells against the background of anemia.
When citing other reasons for increased ESR, do not forget about teething. We are talking not only about children, but also about adults (wisdom teeth).
In addition, encounters with infection, parasites, allergies, and cancer problems lead to an increase in ESR levels.
Source: https://1diagnos.ru/laboratornye-issledovaniya/krovi/klinicheskij/povysheny-limfotsity-i-monotsity.html
Why are basophils elevated?
Exceeding the norm has various reasons. As a rule, these are various diseases and pathological conditions, including:
- Decreased thyroid function (hypothyroidism).
- Allergic reactions.
- Chronic myeloid leukemia.
- Polycythemia vera.
- Lymphogranulomatosis.
- Acute leukemia.
- Infections of viral origin.
- Hodgkin's lymphoma.
- Myxedema.
- Crohn's disease, ulcerative colitis.
- Chronic dermatitis.
- Hemolytic anemia.
- Chronic sinusitis.
- Condition after splenectomy (removal of the spleen).
- Exposure to radioactive radiation.
- Increased estrogens.
- Taking thyreostatic drugs.
An increase in the level of basophilic granulocytes in the blood of an adult does not always indicate illness and may be normal. They may be higher than normal for physiological reasons:
- Basophils in the blood are increased in women with high estrogens. This happens in the first half of the cycle (the maximum value is reached during the ovulatory phase) and when drugs with estrogen are administered. After long-term use of estrogen, the analysis will show an increased level, so before donating blood you need to warn your doctor about all medications taken for a long time.
- The content of basophils is increased during the recovery period after infectious diseases.
- When receiving small doses of radiation, which, for example, radiologists are exposed to.
Lymphocytes and monocytes are elevated in adults - causes – All about cholesterol
Have you been struggling with CHOLESTEROL for many years without success?
Head of the Institute: “You will be amazed at how easy it is to lower your cholesterol just by taking it every day...
Read more "
An increase in monocytes in the analysis causes concern for patients. Experienced doctors know that the content of only one type of blood cell cannot make any conclusion about the state of health. There are no clear answers to the question of why some cells are increased and others are decreased.
Any changes in blood tests are used as an addition to the symptoms of the disease and are taken into account in differential diagnosis and treatment.
OUR READERS RECOMMEND!
Our readers successfully use Aterol to lower cholesterol. Seeing how popular this product is, we decided to bring it to your attention. Read more here...
To understand when and in what ways elevated levels of monocytes cause pathology in the body, we need to remember the role of these cells in supporting health.
Functions of monocytes
When aggressive substances or microorganisms enter the surface of the mucous membrane of the nasopharynx or intestine, histiocytes flock to the lesion. These are “ripe” monocytes, adapted to life in tissues. If necessary, new portions of histiocytes-macrophages are urgently prepared.
They surround bacteria, viruses, fungi, and foreign particles, draw them into the protoplasm and provide work to lysosomes to completely dissolve unnecessary molecules.
Having cleared the “battlefield” of toxins and decayed leukocytes, macrophages move on to the process of transmitting information to subsequent generations. This ensures quick recognition of “friends” and “strangers” and aims the body at defense.
Standards
The norms for women and men are practically no different. Determination of the absolute (abs.) value per 1 liter of blood is carried out by general analysis and examination of a stained smear. monocytes relative to the total amount of leukocytes is calculated as a percentage and is called the level.
Both indicators are important to evaluate the result. With a sharp fluctuation in the number of other cells included in the leukocyte formula, the level of monocytes may change (above normal or decrease). Although their absolute value will remain unchanged.
Analysis of the relationship with the age category showed an increased level in children under 6 years of age compared to the level in an adult. You can read more about the norms for the number of monocytes in a child’s blood here.
For adults, the normal absolute value is considered to be from zero to 0.08 x 109/l; for a child, from 0.05 to 1.1 x 109/l is acceptable.
In the leukocyte formula, the percentage of monocytes in children is considered normal - 2-12% after birth, in the first 2 weeks - 5-15%, in adults - 3-11%. A similar indicator during pregnancy does not exceed normal limits:
- first trimester on average 3.9%;
- second - 4.0;
- third - 4.5.
Any indicator exceeding the upper limit is called monocytosis and has its own physiological and pathological causes
When is monocytosis not dangerous?
A harmless moderate increase in monocytes can occur against the background of a decrease in lymphocytes and eosinophils. Similar situations are possible with a severe allergic reaction, in the initial stage of childhood viral acute infections (whooping cough, scarlet fever, chicken pox, measles).
Significant death of other immune cells occurs. Therefore, the body produces more phagocytes for compensatory purposes to close the gap in protection.
After 2–3 days, with an uncomplicated course of the disease, the required level of eosinophils and lymphocytes is restored. Elevated monocytes during the recovery period are even considered a positive prognostic sign.
Causes of monocytosis
The causes of monocytosis with a pathological increase usually reflect the degree of participation of one’s own immunity in anti-inflammatory activity. Elevated monocytes in the blood are detected when:
- viral infections (flu, respiratory disease, mumps, mononucleosis);
- bacterial and fungal infections (tuberculosis, syphilis, candidiasis);
- helminthic infestation in children;
- rheumatic damage to the heart and joints;
- bacterial septic endocarditis;
- enteritis, colitis of bacterial and fungal etiology;
- cases of sepsis;
- conditions after surgical treatment of appendicitis, gynecological operations;
- systemic autoimmune diseases (rheumatoid polyarthritis, sarcoidosis, lupus erythematosus);
- tumors from the blood line (lymphogranulomatosis, myeloid leukemia, thrombocytopenic purpura);
- malignant tumors.
Diagnostic value of simultaneous increase in other types of leukocytes
To make a diagnosis in a blood test, it is important to detect not only elevated monocytes, but also other cells of the leukocyte series. Together they:
- indicate the stage of the disease;
- determine the prognosis;
- confirm the type of infectious agent;
- determine the degree of loss of immunity.
Let's look at the most common reactions of blood cells.
Monocytes + lymphocytes
When monocytes and lymphocytes are elevated, an acute viral infection should be suspected: influenza, respiratory disease, measles, rubella, chickenpox. Against this background, a decrease in neutrophils is observed.
It is clear to the doctor that it is necessary to prescribe antiviral drugs.
Monocytes + eosinophils
For elevated monocytes and eosinophils, the necessary conditions are usually allergic reactions and parasitic infection (chlamydia and mycoplasma).
A distinctive symptom in patients is a long, painful dry cough in the absence of wheezing in the lungs and other clinical manifestations.
Monocytes + basophils
Basophils are fast-reacting cells; they manage to approach the source of infection while others are still “considering the information received.” If monocytes and basophils increase, it is necessary to exclude the influence of long-term treatment with hormonal agents.
The growth of basophils always accompanies an increase in macrophages and lymphocytes. They act by producing serotonin, histamine and other substances that increase inflammation.
Monocytes + neutrophils
When monocytes and neutrophils are elevated, you need to think about an acute bacterial infection. At the same time, the level of lymphocytes decreases. The patient experiences a rise in temperature, a wet cough, a runny nose with purulent discharge from the nose, and when auscultated there is a mass of wheezing in the lung tissue.
All cells of the immune system help and replace each other. Sharp and prolonged level deviations require a careful examination of the hematopoietic system to exclude malignant diseases.
Increased level of lymphocytes in the blood
Source: https://holesterin-sredstvo.ru/simptomy/limfotsity-i-monotsity-povysheny-u-vzroslogo-prichiny/
Norm of leukocytes in the blood
The normal number of lymphocytes in adults is determined by percentages; neutrophils account for about 55%. The norm in women may differ slightly from that in men, especially during pregnancy or during menstruation. An auxiliary method for detecting infection can be ESR, an indicator of a general blood test that indicates the development of inflammatory processes. The maximum value of leukocytes is considered to be 9 * 1012 / liter. An increase in the number of lymphocytes and white blood cells indicates the fight against infections. Normalization of lymphocyte levels in adults occurs as the body recovers.