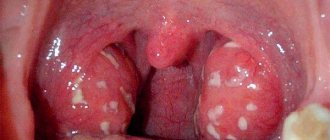
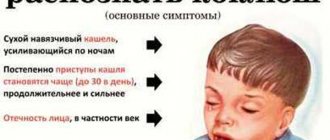
The mucous membrane of the mouth and throat should be pink, shiny, free of inclusions and foreign particles. The appearance of white, gray or yellow spots is not considered normal and indicates the onset of a disease.
Most often, these are areas of accumulation of pus formed by the body in response to microbial infection and inflammation.
- Pus in a child's throat - features
- Diagnosis of diseases when pus appears in the throat
- Treatment methods for pus in the throat
Causes of pus in the throat, symptoms of diseases, photos
Purulent formations in the throat, photo
There are several reasons for the appearance of pus:
- The most common cause is diseases of the tonsils: acute tonsillitis (follicular, lacunar), chronic tonsillitis.
- Inflammatory diseases of the sinuses: sinusitis, sinusitis.
- Diphtheria.
- Development of purulent inflammation due to a foreign object in the nose.
Pus in the throat is a frequent accompaniment of sore throat and chronic tonsillitis, however, its appearance in these ailments is accompanied by other symptoms.
Purulent plaque, photo of the throat
Acute sore throat develops over a short period of time and begins suddenly with a sore throat, poor health, and fever.
In the lacunar form, films of pus appear in the area of the depressions on the tonsils (lacunae). When rinsing or under mechanical influence (for example, with a cotton swab), the pus is easily removed.
Follicular tonsillitis is called inflammation in the follicles of the tonsils. In addition to redness and swelling of the tonsils, there is the appearance of pus, which appears in the form of small grains. These are inflamed follicles.
Over time, small abscesses can open on their own, pus flowing into the pharynx or oral cavity, which causes an unpleasant taste in the mouth and bad breath.
In acute forms of tonsillitis, the appearance of pus in the throat occurs with increased body temperature (up to 40 ° C) and impaired ability to work due to severe intoxication syndrome.
Chronic tonsillitis is the presence of an infection in the tissue of the tonsils, which can remain dormant for a long time, and with a decrease in immunity, give rise to exacerbations, manifested by inflammation and the formation of purulent plugs.
This is a consequence of previously suffered acute sore throats, which were not adequately treated and the source of infection remained.
Pus in the throat with chronic tonsillitis may appear without an increase in temperature, and the general condition may suffer slightly.
More often, the patient notices only a sore throat. Upon examination, enlarged palatine tonsils are visible, the lacunae are clogged with purulent masses, and an unpleasant odor of decomposing tissue is felt from the mouth.
Diphtheria - purulent plugs are easily confused with formations in the pharynx due to diphtheria, which are very similar in appearance. Diphtheria is considered a childhood disease and is very severe with high fever and sore throat. Gray or yellow films that resemble pus appear on the tonsils.
Type of throat with diphtheria, photo
A feature of these spots is their tight connection with the mucous membrane. With diphtheria, plaque does not disappear after rinsing and mechanical impact on them. When trying to clean the films with a spatula or improvised materials, bleeding of the mucous membrane is noted at the site of the stain.
In severe cases of the disease, films cover not only the tonsils; they can be found in any part of the mouth. The disease is dangerous due to the development of swelling of the larynx and soft tissues of the neck, which threatens respiratory arrest.
With a large number of films, there is a high probability of blockage of the larynx and disruption of normal breathing. In case of diphtheria, the child must be hospitalized urgently for specific therapy.
With inflammation of the sinuses of the skull (sinusitis), pus tends to flow into the throat. In a chronic process, the general symptoms of the disease may be mild; the patient complains only of the taste of pus in the mouth and the odor from the mouth, which is not eliminated by the use of toothpastes and rinses.
Often purulent discharge is expectorated in the form of yellow clots.
Etiology and pathogenesis
The main reason for the appearance of purulent plaque on the tonsils is a bacterial or fungal infection. Its causative agents are most often cocci, diphtheria bacillus, and microscopic fungi. Most of them belong to the group of conditional pathogens, which are included in small quantities in the composition of normocinosis of the oral cavity and do not cause harm to health. For an infectious process to develop, bacteria must multiply as much as possible and acquire pathogenic properties. This happens under the influence of provoking endogenous and exogenous factors. These include:
- Decreased immunity
- Local and systemic hypothermia,
- Diseases of the ENT organs,
- Caries, stomatitis,
- Frequent ARVI,
- Unfavorable environmental conditions,
- Hereditary predisposition.
Pus on the tonsils is a clinical manifestation of the following diseases: tonsillitis, tonsillitis, pharyngitis, laryngitis, candidiasis, stomatitis.
Children suffer from purulent inflammation of the tonsils much more often than adults. An incompletely formed children's immune system cannot fully protect the body from various microbes.
Pus in a child's throat - features
Pus in a child’s throat, examination photo
The appearance of pus in the throat of a child without previous severe symptoms can often indicate the presence of a foreign object in the nose or sinuses.
Young children love to experiment with small toys and objects by inserting them into the natural orifices of their bodies. Parents may not always notice this.
After some time, inflammation develops at the location of the foreign body, and if the mucous membrane is damaged, a secondary infection occurs with the development of purulent inflammation. This happens especially quickly if the small object has uneven or sharp edges.
Mom and dad may notice that the child has bad breath, and when examining the throat, pus can be seen on the back wall. This indicates that purulent exudate flows into the oropharynx.
If the object is located low in the nasal passage, then purulent discharge can also drain through the nose, simulating a runny nose. However, the discharge will only come from the nostril in which the object is located. For a runny nose, a one-sided flow from the nose is not typical.
Causes of pus and purulent plugs in the lacunae of the tonsils
The main reason for the appearance of pus and purulent plugs in the lacunae of the tonsils is the active activity of harmful bacteria. The cause of the disease is determined by an analysis such as a smear from the larynx. The appearance of purulent plugs is provoked by a general weakening of the immune system, diseases of the nasopharynx and oral cavity.
| Disease | Description | Symptoms |
| Angina | Tonsillitis. Occurs due to the active activity of harmful bacteria. It is divided into follicular and lacunar. Sometimes a sore throat occurs, which manifests itself in both forms at the same time. Lacunar tonsillitis is accompanied by a white coating and yellow pus. Follicular - redness of the tonsils and small pustules. |
|
| Pharyngitis | Inflammation of the back wall of the throat with the formation of purulent plugs. It occurs due to infectious infection, weak immunity, predisposition, and even due to environmental pollution. |
|
| Fungal infections | Infections of the pharyngeal mucosa with Candida fungi. Enters the body by airborne droplets. |
|
| Tonsillitis | Infectious disease of the upper respiratory tract. Infection occurs both infectiously and from chronic caries and sinusitis. |
|
The causes of purulent plugs on the tonsils are bacteria such as staphylococcus, hemolytic streptococcus, pneumococcus, and chlamydia. You can find out which bacteria caused the appearance of purulent plugs using a smear from the larynx. Most often the disease develops due to other pathologies of the respiratory tract. Infection is possible:
- By airborne droplets;
- Autoinfection.
Treatment methods for pus in the throat
Treatment is carried out only after confirmation of the diagnosis. Treatment methods should be aimed at the cause of the disease - infection. These are mostly conservative methods and may include the following:
- Antibiotic therapy. The doctor prescribes antibacterial drugs from those groups to which the causative agent of the disease is sensitive.
- In case of chronic tonsillitis, purulent plugs are removed by washing the lacunae of the tonsils. This is done with a syringe or on a special “Tonsillor” apparatus using antiseptic solutions. The method promotes rapid recovery and increases the period of remission, due to the removal of the pathogen and dead cells from the recesses of the tonsils.
- After cleansing, medications in the form of ointments and pastes are introduced into the lacunae.
- Self-rinse with antiseptics or herbal infusions.
- If a foreign object is detected in the nasal area, it is removed and medications are prescribed to heal the mucous membrane.
- Immunomodulatory drugs.
- Physiotherapy procedures that accelerate the healing process and relieve inflammation.
If purulent plugs do not respond to conservative treatment methods, surgery to remove the tonsils is prescribed - tonsillectomy.
If possible, they try to avoid surgical intervention, since the tonsils provide a filter function, neutralizing air and food. But at the same time, chronic inflammation in the throat can spread to other organs: heart, joints, kidneys.
Tonsillectomy is performed according to strict indications, when the risk of complications to internal organs exceeds all others.
Pus is a universal reaction of the body to the proliferation of harmful microbes. Bacteria, most often streptococci and staphylococci, are to blame for the occurrence and development of diseases in which pus appears in the throat.
- Causes
- Associated symptoms
- How to treat
- Prevention
- FAQ
With the help of pus, the body tries to cope with the infection and cleanse itself of bacteria.
Photo: Sources of purulent infection - staphylococcus and streptococcus
A number of upper respiratory tract diseases lead to the appearance of pus at the back of the throat. Due to the lack of sufficient outflow, inflammation spreads further into the surrounding tissues.
Ulcers in the throat (tonsils, tonsils): how to treat in adults
Since ulcers in the throat are caused by different pathogens - bacteria, viruses, fungi, the treatment in each specific case will be different. Therapeutic measures depend on the patient's diagnosis.
Drug therapy
To combat the infectious agent, therapy with various medications is used - antibiotics, antivirals, antifungals.
Antibiotics
This therapy is effective only if the infection of the body is caused by bacteria. To get rid of ulcers in the throat, use:
- Flemoxin is a penicillin antibiotic that resists bacteria such as streptococcus and staphylococcus. The active ingredient of the drug is Amoxicillin.
- Sumamed - a medicine based on Azithromycin is used to treat ulcers caused by pharyngitis, tonsillitis, scarlet fever. Broad-spectrum antibiotic from the macrolide group.
- Suprax - this antibiotic belongs to the cephalosporins. Treats purulent formations caused by pharyngitis and tonsillitis.
- Amoxiclav is a combination drug, its effectiveness is associated with the combination of the action of two components - Amoxicillin and Clavulanic acid. An analogue of Amoxiclav is Augmentin, it is more affordable.
- Cephalexin is an antibiotic from the cephalosporin group.
Antiviral drugs
The cause of the formation of ulcers in the throat may be a viral infection.
In this case, the pathology should be treated with antiviral drugs:
- Anaferon;
- Amiksin;
- Arbidol;
- Kagotselom;
- Viferon;
- Groprinosin;
- Cytovir.
Antifungal agents
These drugs will have a therapeutic effect only if the ulcers appear as a result of the activity of fungi from the genus Candida.
Such drugs are called antimycotics:
- Fluconazole - effectively treats thrush in the throat in a few days. It is better to use it in the form of lozenges and tablets.
- Ketoconazole - the drug is taken in capsules, treatment is long-term, at least 2 weeks.
- Amphotericin - used in the form of inhalations and antimycotic cream.
- Nystatin is an effective remedy with a minimum of side effects. Used in the form of tablets and ointments.
This is interesting: Topical anesthesia: indications, advantages, types of drugs, how it works
Irrigation and gargling
Antibacterial agents in the form of sprays help to quickly get rid of pain, relieve inflammation, and reduce the concentration of bacteria.
Effective sprays for adults:
- Hexoral.
- Inhalipt.
- Miramistin (can be used for children from birth, during pregnancy or lactation).
- IRS-19.
In stationary conditions, the lacunae are washed with special antiseptic solutions, and disinfectant pastes are applied.
At home, you can rinse yourself with a soda solution in the proportion of 1 tablespoon of soda per glass of water.
To consolidate the result, physiotherapeutic procedures are useful - UHF, laser, ultraviolet, ultrasound.
Antibacterial agents
Ulcers in the throat. What to do? If the cause of their appearance is bacteria (streptococci, staphylococci, Pseudomonas aeruginosa, chlamydia, shigella and others), then the otolaryngologist recommends taking broad-spectrum antibiotics. The use of antibiotics is aimed at suppressing pathogenic microflora directly at the site of inflammation.
List of effective remedies:
- Amoxicillin.
- Flucostat.
- Augmentin.
- Amoxiclav.
- Azithromycin.
- Sumamed.
To prevent the development of rheumatism, as a complication of purulent tonsillitis, and eliminate inflammation in the pharynx, experts recommend taking Ibuprofen. There is a spray for local action, the syrup is intended for children, and can be used in tablet form.
Local therapy
This type of treatment involves the use of inhalations, rinsing, irrigation, and washing with antiseptic solutions.
Inhalations
Inhalations are considered an effective means of combating ulcers. To carry them out, special devices are used - nebulizers (inhalers).
The antiseptic solutions used are effective against not only bacteria, but also viruses and fungi.
What drugs are used for inhalation:
- Bioparox is a medicine with a wide range of action. The kit includes attachments for the throat, mouth and nose.
- Dekasan - the medicine is mixed with saline in a ratio of 1 to 1. A mouthpiece is used for inhalation.
- Furacilin - a special solution is used for inhalation. The procedure is carried out 2 times a day.
- Miramistin is a complex action drug. The medicine is mixed with saline solution. Inhalations are done twice a day.
- Mineral water - it is better to take non-carbonated Essentuki or Narzan. The procedure helps eliminate laryngeal edema and restore tissue.
Rinsing and washing
For these procedures, both medications and folk remedies are used:
- Pour boiling water over equal parts of oak bark and chamomile and let it brew. Gargle with the cooled liquid several times a day;
- take the same amount of mint and sage, add water, bring to a boil and simmer over low heat for 2 - 3 minutes. You can gargle with a chilled solution every 2 hours;
- Dissolve a pinch of sea salt in a glass of heated water. Rinsing with the resulting medicine should be done up to 5 times a day;
- throat irrigation is used using Ingalipt, Miramistin, Hexoral, IRS-19;
- You can wash the affected area with Furacilin solution, Iodinol, boric acid, Chlorophyllipt (alcohol solution). For more thorough treatment of ulcers, use a syringe or syringe.
Such procedures are carried out at home and in a clinic.
Lubricating the mucous membranes of the tonsils
With lacunar angina, any lubrication of the mucous membrane is inappropriate. Only with Simanovsky-Vincent tonsillitis is contact treatment of ulcerated tonsils with antiseptic solutions permissible. Before doing this, you should consult your doctor.
Additional measures
Treatment of ulcers should be carried out comprehensively. The patient may be prescribed:
- anti-inflammatory drugs – acetylsalicylic acid, Ibuprofen;
- physiotherapeutic procedures – UHF, ultraviolet irradiation, laser and magnetic therapy, phonophoresis;
- strengthening the immune system - prescribe Immunal, vitamins B, PP, injections of aloe extract.
Trying to remove the formed purulent plug yourself is dangerous.
If we carry out such a procedure, then in compliance with certain rules:
- use a special spatula with a sterile bandage soaked in antiseptic wrapped around it;
- press on the affected area so that the plug comes out;
- Rinse your throat well with an antiseptic solution.
Today they try to remove tonsils as rarely as possible, preferring drug treatment.
If surgery is unavoidable, in adults it is performed under local anesthesia. Post-operative recovery usually lasts for a week.
How to quickly get rid of it using folk remedies
Folk remedies will help eliminate pain, inflammation, and unconventional methods help increase the period of remission in chronic forms of diseases. But if the pathology is in an acute stage, then they should be used only in combination with medications.
How to treat a throat at home:
- Add 5 g of soda and sea salt, 3-4 drops of iodine to 250 ml of warm water, use the entire portion of the medicine for rinsing, perform sessions 5-7 times a day.
- To quickly eliminate swelling and inflammation, mix 20 ml of apple cider vinegar and 200 ml of fresh beet juice. Gargle once every 3-4 hours.
- A solution of three parts water and one part lemon juice will help remove plaque and destroy pathogenic microorganisms. Gargle with the solution every 3-4 hours.
- Mix chamomile inflorescences and sage herb in equal proportions, brew 220 ml of boiling water for 10 g of the mixture, leave in a closed container for 20 minutes. Strain and gargle every 2-3 hours.
- Inhalations with essential oils - add 3-5 drops of fir or eucalyptus product to 1.5-2 liters of boiling water, breathe in steam for 7-10 minutes, perform sessions in the morning and before bed.
If the tonsils are inflamed, you should not try to remove white plaques on your own, squeeze out pus, eat hot food and drinks, or press on the tonsils.
A solution with salt, soda and iodine will help cure tonsils
Surgery
Surgical treatment is indicated in case of complications (peritonsillar abscess, cheek phlegmon) and chronic decompensated tonsillitis.
If the abscess on the back wall of the pharynx breaks out, then this is considered a favorable outcome, otherwise surgery cannot be avoided.
Removal of tonsils and opening of abscess and phlegmon is carried out in a large operating room under general anesthesia.
In the first case, the lymphoid tissue is simply excised, and in the second, multiple incisions are made to drain the pus, the area is washed with antibacterial and antiseptic solutions, and drainage tubes are left in place for some time.
Diet
Food should be liquid, not hot or spicy.
Nutrition during and after illness should help restore and strengthen the body. To do this, you should adhere to the following rules:
- Due to the fact that swallowing is difficult during the disease, food should be liquid and semi-liquid.
- Food should be warm and nutritious. The diet should include fruits and vegetables; they are rich in vitamins.
- We must not forget about animal proteins.
- Avoid salty and spicy foods.
- Drink more liquids: teas, juices, milk with honey.
This is interesting: Bad breath in adults (rotten, sour, rotten): causes, treatment in women and men
Reasons ↑
A suppuration in the throat can occur when bacteria enters there immediately before the disease.
Microbes enter through the air through close contact with an infected person through inhalation. In a dormitory, office, school, kindergarten, or home there are all conditions for the transmission of infection due to close contact between people.
Also, microbes can live indefinitely in the body and become activated due to reduced immunity. A decrease in protection occurs due to hypothermia, drafts, allergic diseases, the ingress of harmful substances along with the inhaled air, overwork, and stress.
The appearance of pus also occurs during inflammatory processes in the nose. The natural outlets from the sinuses are located in such a way that the pus flows into the throat on its own or the sick person “sucks” it and coughs it up.
Diseases in which this disease can be detected are divided into:
- purulent inflammation of the paranasal sinuses or sinusitis: sinusitis (maxillary sinusitis);
- sinusitis of other sinuses (frontal, main, ethmoidal labyrinth);
- purulent pharyngitis;
Inflammation can progress to a purulent stage with severe injuries to the bones of the facial skeleton or prolonged residence of foreign bodies in the nose and paranasal sinuses. Buttons, seeds, and pebbles are inhaled by children due to pranks and the habit of putting objects up their noses.
Sinusitis
In acute sinusitis, inflammation occurs in the right or left maxillary sinus. Pus flows from the affected side and collects in the throat.
Photo: Unilateral (left) and bilateral (right) sinusitis
If the discharge occurs through the posterior outlet or while lying down, then the pus flows into the pharynx. A sick person may complain of a pus-like taste in the mouth.
There is irritation and a feeling of something foreign, interfering. Upon examination, you can see pus flowing down the throat. A sick person may spit out pus. A similar picture occurs with purulent inflammation of other paranasal sinuses.
Video: sinusitis
Abscess
An abscess is an accumulation of pus in soft tissues, which has its own boundaries.
It occurs when the natural openings of the tonsils become blocked or difficult to empty. This may be due to scar adhesions after previous purulent throat diseases.
Severe pain occurs, it is difficult to open the mouth, the voice takes on a nasal tone. The pain in the throat is sometimes so severe that the patient cannot sleep.
Photo: Retropharyngeal abscess
Bright inflammatory redness appears in the area of the abscess. Severe swelling and bulging of the side wall lead to an asymmetrical arrangement of the arches and tongue.
If the suppuration is superficial, you may see clearing and discoloration at the site of pus formation. The appearance of a yellow spot indicates the formation of an abscess; in this place, opening and emptying of pus can occur.
When the body is weakened, typical symptoms do not occur.
The picture of the disease will not be pronounced. Sore throat does not interfere with swallowing. Redness, swelling and protrusion can only be detected by careful examination of the throat. Pus in the throat without fever should alert you.
Video: retropharyngeal abscess
Purulent pharyngitis and laryngitis
Pharyngitis is an inflammation of the pharynx.
This disease causes a sore throat, which may get worse when swallowing and be accompanied by a cough due to irritation. There is a feeling of something foreign in the throat, but coughing does not lead to relief.
When examined in the throat, redness and swelling of the walls of the pharynx and palate are visible. You can see enlarged lymphoid granules on the back of the throat that look like large grains or grains, as well as white pus in the throat.
Photo: Purulent pharyngitis
Laryngitis is an inflammation of the soft tissues of the larynx.
A hoarse voice and a dry barking cough are common manifestations of laryngitis. With swelling in the area of inflammation, breathing difficulties occur. The penetration of microbes and suppuration form pieces of pus, which the patient can cough up and the pus comes out of the throat.
Video: symptoms and treatment of pharyngitis
Reasons for the formation of ulcers
To understand why ulcers appear on the tonsils (or tonsils), you need to imagine the structure of these paired palatal formations. They consist of lymphoid tissue dotted with lacunae or crypts. This is the name given to canals with holes on the surface that open into the oral cavity. The diameter of the holes ranges from 1 to 4 mm. They become the site of accumulation of purulent masses and the formation of white ulcers on the tonsils.
Photo: structure of the tonsils
The purpose of the tonsils is to create a barrier to infection that seeks to enter the larynx, trachea, bronchi and lungs. When the onslaught of bacteria becomes too strong, symptoms of inflammation appear in the pharynx: an ulcer on the tonsil or several small ulcers, an increase in the volume of the tonsils (hypertrophy), the formation of a white coating on them, purulent accumulations in the lacunae. These accumulations scar over time and turn into plugs.
All these are symptoms of diagnoses such as chronic tonsillitis, tonsillitis, mononucleosis, diphtheria or candidiasis (stomatitis). Various microorganisms cause infections:
- adenovirus;
- streptococcus;
- staphylococcus;
- Pneumococcus;
- gonococcus;
- chlamydia;
- diphtheria bacillus;
- fungi of the genus Candida.
To get rid of suppuration, it is important to understand which pathogen caused it - the treatment regimen will depend on this. The only way to determine this is to test a swab from a sore throat
That is why it is important, without wasting time on self-medication, to quickly consult a doctor. Especially if a plaque, ulcer or abscess is noticed on the child’s tonsil. And even if the body temperature remains within normal limits and there is no acute sore throat.
https://youtube.com/watch?v=3vIEdY3FRtc
Associated symptoms ↑
In addition to local changes in the throat, patients experience a general reaction. It is associated with the spread of toxic microbial products and the response of the immune system.
Intoxication appears in the form of:
- high temperature above 380C;
- fever;
- chills;
- general weakness;
- headache.
If there is pus in the throat, inflammation of the lymph nodes located in the focal area may occur.
Those closest to the source of infection swell first. Regional filters for the throat are the lymph nodes near the angle of the lower jaw and along the side of the neck.
How to treat ↑
If pus appears in the throat, you should seek medical help.
Pus does not appear in the first days of the disease. He witnesses that the disease is out of control of the immune system and has been lasting for more than three or four days. Simple treatments and self-administration of medications can worsen the condition.
Treatment is divided into several areas:
- influence on the causative agent of the disease;
- elimination of the focus of pus;
- fight against local inflammation;
- relief of general condition.
- High fever for more than 24 hours, difficulty breathing and difficulty opening the mouth require immediate medical attention.
Medical assistance
After examination, the doctor will confirm the cause of the appearance and prescribe the necessary treatment.
Bed rest and plenty of warm drinks are required to alleviate the condition.
The choice of medications depends on the cause of the pus and the severity of the disease. To determine the type of microbe and its sensitivity to antibiotics, a study of pus may be necessary.
Treatment of pus in the throat consists of conservative and surgical methods.
Conservative method
For treatment, modern antibiotics are used that cause the death of microbes, for example semi-synthetic penicillins, for example Amoxicillin, or cephalosporins. Those drugs are prescribed to which the microorganisms that cause the disease are most sensitive.
Photo: Amoxicillin
If swallowing is difficult due to severe pain, then injections of medication are used.
The duration of the course of therapy is at least 5–7 days, it can be extended to 10. If the treatment is adequate, then on the 2–3rd day of taking the drug you will feel much better. This may make it tempting to stop taking the antibiotic.
It is important to complete the course of antibiotics prescribed by your doctor to avoid complications or recurrence of the infection.
Particular care should be taken during antibiotic therapy during pregnancy due to the side effects of drugs.
Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (containing paracetamol, ibuprofen) are given to reduce fever, reduce sore throat and fight inflammation.
Photo: Ibuprofen and Paracetamol
It is better not to use aspirin for these diseases. It can increase vascular permeability and lead to bruising and rash.
For purulent sinusitis or purulent sinusitis, vasoconstrictor drops are used in the nose to relieve swelling and remove the block from the sinus outlet. With the action of these remedies, the natural openings of the sinuses expand, and the outflow of pus from them improves.
Local warming procedures in the form of compresses, heating pads and physiotherapy can be used when there is a good outflow of pus.
Surgical method
For purulent sinusitis, the doctor can puncture the paranasal sinus with rinsing and administration of a medicinal solution. If necessary, a catheter is inserted for subsequent rinses.
Photo: Puncture for sinusitis
Treatment of abscesses is carried out according to the principle of early surgical opening. Waiting in anticipation of resorption or spontaneous emptying is dangerous due to the risk of spread of pus.
It is possible to develop a dangerous complication - laryngeal edema. In no case should you wait until the tissues soften, since extensive suppuration may already be developing in the depths.
The operation is performed under local anesthesia to preserve the pus expectoration reflex. The doctor uses an aerosol anesthetic and an injection in the area of inflammation.
Photo: Opening a retropharyngeal abscess
After opening the abscess, the patient must quickly tilt his head face down so that pus and blood do not get further into the respiratory tract. Surgical treatment is always combined with antibacterial therapy.
Video: how to make a puncture for sinusitis
How to remove pus from the throat at home
You can get rid of the discomfort of pus in your throat using home remedies.
Gargling with warm salt water or herbal infusions (chamomile, thyme). They will get rid of pus. The use of iodine and Lugol's solution is undesirable due to the cauterizing effect.
Photo: Chamomile and thyme decoctions
Warm drinks (tea, milk, compote) will reduce intoxication and chills, warm the throat, and help reduce fever.
Sucking on lozenges and wrapping a scarf around your throat will relieve a sore throat. Before starting home treatment, you need to consult a doctor to begin basic treatment.
Traditional methods of treatment
This pathology can be cured using folk remedies only in the early stages of the disease. Most often, gargling with various herbs and infusions is prescribed. We list the recipes for preparing the most effective compositions:
- Chamomile and oak bark. Mix both components in equal proportions. To obtain a healing medicine, take 25 g of the collection and add 0.8 liters of boiling water. Place on low heat for 3 minutes. Then cool and filter. You need to gargle several times a day. The procedure can be carried out conveniently using a syringe.
- Sage and mint. Both components must be taken in equal quantities. Add 1 liter of boiling water to 20 g of the obtained herbs. Put on fire for 5-10 minutes. Allow the resulting medicine to cool, and you can start irrigating your throat. It is recommended to carry out the procedure every hour.
- Sea salt. For 0.25 liters of warm water (the liquid must be filtered), take 5 g of salt. Stir everything well and begin the procedure. Repeat at least 5 times a day.
- Salt and soda. To prepare the medicinal solution you will need one teaspoon each of soda and salt and a glass of water. Mix everything well and use for gargling. It is recommended to use a syringe to thoroughly rinse the affected areas.
- Eucalyptus and calendula. Both herbs should be mixed in the same ratio. Add 1 tablespoon of the mixture to half a liter of boiling water. Wrap the glass container in a towel and leave to infuse for several hours. After filtering and gargling 5 times a day.
- Lemon, beets and honey. Grate the beets on a fine grater and squeeze out the juice through cheesecloth. For 1 serving you will need 1 tablespoon of juice, 20 ml of lemon juice and 30 ml of honey. Mix all ingredients thoroughly and add a glass of water.
Even before using a folk recipe that seems absolutely harmless, you must consult a doctor. The herbs included in the infusions can cause allergic reactions. When the first symptoms of the disease appear, you should immediately visit a doctor. Only a specialist can make an accurate diagnosis and prescribe appropriate treatment.
Prevention ↑
Microbes are transmitted from a sick person by airborne droplets.
Therefore, following simple safety rules will help you avoid getting sick.
- wash your hands often with soap;
- use a disposable mask to protect your mouth and nose;
- use personal cutlery and glass;
- avoid close contact with the patient;
- have your own toothbrush and towel;
- ventilate the premises.
To prevent the recurrence of infection, you need to eat right, increase the body's defenses and keep your living quarters clean. Walking in the fresh air, taking vitamins and hardening the body will help prevent diseases.
Frequently asked questions ↑
How long does it take to be treated?
The average treatment period for such diseases is 7–10 days. If after 2 weeks there are no signs of complete recovery, then you can think about complications or a protracted course of the disease.
When can I start doing fitness or physical education after illness?
To exclude the development of complications, for example, heart disease, joint disease, after an illness, doctors recommend resuming exercise no earlier than 10–14 days after complete recovery.
How to get rid of pus on the back of a child’s throat?
See your doctor immediately if:
- child under 1 year old;
- fever and high temperature lasts more than 24 hours;
- there is lethargy and drowsiness;
- difficulty breathing or swallowing;
- the disease is accompanied by a rash or bruises;
- it is impossible to open your mouth, there is no voice.
If a child can gargle on his own, then with frequent gargling, the throat will be freed from pus faster. If it is not possible to rinse, then use lollipops or give warm tea or milk to drink. In this case, swallowing occurs, which is acceptable for small children.
Photo: Gargling helps a child get rid of pus in the throat
When pus flows into the throat from the nose and the baby cannot blow his nose on his own, it is necessary to use a small rubber medical bulb or a special nasal aspirator.
Photo: Momert and NoseFrida nasal aspirators
After removing the discharge from the nose, you need to instill drops to reduce the amount of mucus, swelling and improve the outflow of pus.
Video: how to look at a child’s throat
Correct treatment presupposes the main thing - knowledge of the cause of the disease. You should not choose medications on your own, as many drugs have their own contraindications.
Purulent plugs in the throat occur as a result of inflammation. Their formation is caused by certain types of pathogenic microorganisms. This symptom occurs more often in children than in adults, which is explained by the immaturity of their immune system.
Pus should be distinguished from sputum, a clear secretion produced by the mucous membrane of the respiratory tract.
What does the appearance of ulcers on the tonsils with high temperature mean?
Most often, ulcers on the tonsils are accompanied by high fever. Let's find out what are the reasons for their appearance.
Sore throat - purulent plaque and sore throat
The most common reason in this case. As you know, there are many pathogens for sore throat, which is why it is the easiest to get sick with. The cause of frequent sore throats in adults and children is weakened immunity. Another name for the disease is acute tonsillitis. A sore throat can be caused by an infection of either a bacterial or viral nature. Therefore, when treating it, you must first visit a doctor in order to know exactly the source of infection.
And if a child or adult “caught” Simanovsky-Vincent’s sore throat, then in this case the disease will be especially severe. In this case, the ulcers on the tonsils are accompanied by the formation of multiple ulcers on the mucous membrane of the throat and the appearance of an acute putrid odor from the mouth.
Chronic tonsillitis
In this case, the appearance of ulcers will also be accompanied by an unpleasant odor. In addition, the situation is often aggravated by food debris stuck in the crevices of the tonsils. This organic environment becomes an excellent “home” for the existence and reproduction of pathogenic microorganisms.
This is interesting: Ultrasound and its use in dentistry: the pros and cons of the method, how dental plaque is removed
Pharyngitis and laryngitis resulting from hypothermia are also one of the reasons. Hypothermia, in general, causes the appearance of ulcers on the tonsils very often. But it can lead to the appearance of these purulent formations only in the case of low immunity.
Video: if there are pustules on the tonsils without fever
On video - ulcers on the tonsils without fever:
Adenovirus infection and infectious mononucleosis
Both diseases are caused by viruses (in the first case, adenovirus, in the second, herpes virus type 4), which are tropic to lymphatic tissues.
Adenoviral infection begins acutely, with an increase in body temperature. Later, catarrhal symptoms such as nasal congestion and rhinitis appear.
A distinctive feature of the infection is damage to the outer membranes of the eyes in the form of conjunctivitis and palatine tonsils. The tonsils increase in size, become bright red, and then become covered with whitish deposits.
During infectious mononucleosis, secondary flora often joins, so viral tonsillitis becomes mixed - viral-bacterial.
First of all, the patient’s appearance attracts attention: a significantly enlarged neck due to the reaction of the anterior, posterior cervical and submandibular lymph nodes; puffiness of the face due to hypoxia (the tonsils hypertrophy so much that they reach the uvula, completely blocking the pharynx).
During examination of the oral cavity, a purulent throat is visualized - abundant dirty gray or yellow plaque on the tonsils. The liver and spleen become larger than normal, undulating and prolonged fever is recorded, and taking penicillin antibiotics can provoke the appearance of a toxic-allergic reaction in the form of a rash.
Diphtheria
A highly contagious and dangerous infection, the most common form of which is diphtheria of the tonsils. Its distinctive features:
- hypertrophy of the tonsils;
- finely dotted white plaques in the form of cobwebs, which gradually begin to merge into islands;
- swelling of surrounding tissues, a tendency for the pathological process to quickly spread to neighboring tissues;
- painlessness and bleeding when removing plaque with a spatula;
- high fever.
The most dangerous complication of the disease in the past is true croup.
Scarlet fever in children
Pus on a child’s tonsils very often occurs as a result of scarlet fever; it is not for nothing that it is also commonly called a “childhood disease.” It mainly affects children under 10 years of age. In adults who are over 30 years old, the chances of getting sick generally tend to zero. The disease is often registered in the autumn-winter period, associated with a lack of sun, vitamins in the diet, increased concentration of children in closed, unventilated rooms, and complications of the immune system.
Scarlet fever occurs on the mucous membrane and tries to get inside the body, the causative agent of the infection, streptococcus, when it gets on the membrane of the tonsils, multiplies there and begins to produce toxins that gradually spread to the entire body and lead to rashes not only on the tongue and gray-yellow ulcers on the tonsils, which do not go away without proper treatment, but also lead to damage to all skin (face, neck, chest, arms, legs and back), to vomiting, weakness and headache.
Causes of pus in the throat
Pus is a liquid mixture of tissue areas, proteins, as well as immune system cells and microorganisms. It occurs as a result of migration of neutrophils to the site of inflammation, which leads to an influx of fluid into this area. As a result, the area of the organ or tissue swells, an abscess is formed, which after some time breaks through and its contents pour into the cavity. Only certain bacteria have the ability to cause purulent processes:
- Staphylococcus;
- Streptococci;
- Clostridia;
- Mycobacteria;
- Klebsiella, etc.
Also, in some cases, the cause may be a fungus of the genus Candida.
Pus in the throat can occur for two main reasons:
- Inflammation directly “in situ” - in the larynx, tonsils, and surrounding tissues.
- Inflammation of the sinuses or sinuses. In this case, pus enters the throat as a result of it flowing down.
Symptoms
Signs of pus in the throat can vary greatly depending on the location of the inflammation. But still characteristic symptoms can be identified:
- Heat.
- Migraine.
- Weakness, signs of general intoxication, fever.
- Cough.
- Swelling of the lymph nodes.
- Bad breath.
If the cause of inflammation is purulent plugs on the tonsils (with lacunar and follicular tonsillitis), patients note:
- Pain, sore throat, burning sensation in the throat, discomfort when swallowing.
- Changing voice tones.
- Disturbances in the gastrointestinal tract.
With complications of tonsillitis or tonsillitis, increased salivation, pain in the ear, lower back, and heart may be added to the symptoms.
Sometimes enlarged pharyngeal and nasopharyngeal tonsils (or tonsils) can cause deterioration in hearing and nasal breathing. In this case, they are called adenoids. Purulent plugs on the tonsils in this disease are detected only during an acute process or exacerbation of a chronic one. With pharyngitis, an important distinguishing feature is the localization of pus on the back wall of the throat.
With sinusitis, these symptoms may be absent, but the following signs are possible:
- Nasal congestion.
- Swelling of the eyelids and cheeks.
- Separation of pus from the nasal passages.
Signs
It is difficult to confuse tonsil plugs with some other disease. In addition to the appearance of white spots on their surface, other symptoms may appear. The first thing that worries you is severe pain, which intensifies when swallowing. Sometimes the patient even refuses to eat food. There may also be a feeling of discomfort. This symptom indicates that the plugs have reached a large size. More often it occurs in the absence of necessary treatment for a long time.
General symptoms are observed: such as sweating, chills, increased body temperature up to 40 degrees, sleep disturbance, weakness, malaise, decreased appetite, muscle pain, nausea, and in some cases even vomiting. Abscesses on the tonsils without fever appear against the background of chronic tonsillitis in remission.
Patients also complain of a sore and tingling sensation in the throat, a dry cough, and an unpleasant taste and odor from the mouth.
As a rule, pus in the throat is located in the folds of the tonsils in the form of white spots, and it is unlikely that you will be able to see them simply by opening your mouth. Only a doctor can establish the fact of their presence. It is necessary to contact him when the first symptoms appear. He will prescribe the necessary treatment.
With chronic tonsillitis, food debris begins to accumulate in the tonsil area, which becomes a favorable environment for the habitat of many microorganisms. The proliferation of diverse microflora maintains the presence of a permanent focus of infection in the tonsil area. Outwardly, this is manifested by the presence of white plugs, which can be easily removed, after which they form again. This disease requires mandatory treatment, despite the fact that there may be no other symptoms (except for the presence of plugs in the tonsils). Ulcers in the throat without fever can be due to chronic tonsillitis.
Diagnostic measures
In order to remove pus and carry out correct treatment, it is necessary to know the cause of its occurrence. To diagnose throat diseases, pharyngoscopy is performed. Using a special device, the otolaryngologist examines the cavity and the organs located there. If the focus of inflammation cannot be detected, the patient is prescribed an x-ray of the paranasal sinuses.
To select the most effective antibiotic, it is recommended to do a bacterial culture of the purulent contents. However, this study requires several days. Therefore, as the disease progresses, broad-spectrum antibiotics that are active against the most common pathogens are prescribed.
Principles of treating pus in the throat
Any therapeutic measures are divided into conservative and surgical. With a purulent-inflammatory process in the throat, both may be indicated, depending on its severity and the area of the lesion.
Conservative therapy
For purulent plugs on the tonsils or larynx, the following remedies are indicated:
- Antibiotics that specifically act against the infectious agent or have a broad spectrum of activity;
- Antiseptic and wound-healing preparations, including those made from plant materials;
- Immunomodulators;
- Painkillers and antipyretics;
- General stimulants, vitamins.
- The goals of therapy for purulent processes are to cure the disease and alleviate its course. These remedies eliminate the cause of inflammation, help the body fight infection and shorten the recovery period after the action of pathogens.
Surgical measures
This treatment is indicated for abscesses, tissue necrosis, and the presence of purulent abscesses. The simplest type of operation is opening the source of inflammation and draining the cavity. In extreme cases, a tracheostomy is performed when an abscess can cause respiratory arrest. In this case, a hole is formed in the throat to connect it with the environment. A surgical option is a tracheotomy, in which case a permanent opening is not created.
In Soviet times, punctures for sinusitis were popular in ENT practice. They were used to introduce drugs into the cavity. Today they are used only when general therapy is ineffective.
or their dead part may be indicated This usually affects the tonsils. This operation is called tonsillectomy. Typically, the indication for its implementation is paratonsillitis (a complication of tonsillitis).
Tonsillectomy
However, in this case, deletion is carried out only:
- After unsuccessful attempts to remove purulent plugs by partial resection or open an abscess;
- In severe cases;
- At risk of blood poisoning.
Modern specialists try to avoid surgery whenever possible. Doctors of the old school, on the contrary, positively assess its importance. So Professor Palchun V.T. O.
Getting rid of purulent plugs can be difficult if the process has reached a chronic stage. Then a temporary improvement is followed by a period of exacerbation, the disease either subsides or resumes again. To prevent this, it is necessary to consult a doctor when you detect the first signs of purulent inflammation and follow all his instructions. A common cause of chronic infection is the unauthorized reduction of the course of antibiotics and stopping their use after the first signs of improvement. It is necessary to treat a purulent disease using effective modern means and always under the supervision of a specialist.
How to remove pus from tonsils yourself at home
Extracted purulent plugs
If you can’t see a doctor or if purulent plugs are a common problem, you can remove the pus yourself. In the initial stages, superficial pustules can be removed by rinsing the mouth with special decoctions and infusions, which are either sold in pharmacies or can be made independently. Procedure:
- Wash your hands , treat the instruments that will be used in the process of removing purulent plugs with an antiseptic or regular alcohol.
- Prepare a mirror , spoon, bandage and antiseptic.
- To remove pus, you will need a medical spatula, but not every first aid kit has such a tool, so you can use an ordinary clean pencil or a plastic stick.
- Wrap a bandage pre-moistened in antiseptic on a prepared medical spatula or its alternative.
- If there is no medical antiseptic in the first aid kit, you can use honey and salt.
- The spoon is needed to press the tongue. It should not interfere during the procedure.
- Use a spatula to gently press on the purulent formations. If the pus does not begin to stand out, you should simply remove it with a bandage from the surface of the tonsils. The main thing is to act carefully and squeeze out the pus without damaging the mucous membrane.
- After all purulent formations have been removed, after squeezing, you need to gargle hourly to protect open wounds from harmful microbes.
Traditional recipes for sore throats with honey
Half a glass of birch buds is poured into liquid honey (about 500 ml), the mass is brought to a boil, then cooled and taken at night, a teaspoon or a tablespoon.
In 200 ml. pour in 30 ml of heated water. liquid honey and 5 ml. apple cider vinegar, mix everything, and then regularly gargle with this mixture.
Honey (about 20 g) and the same amount of butter (it should be only 82.5%!) Melt in a bathhouse, then add a little soda (on the tip of a knife) and heat the mixture until foam forms, then cool and take product 3 once a day, a teaspoon.
Sea salt solution
In case of mild sore throat, you can gargle with a mixture similar in composition to sea water.
Required ingredients:
- table salt (1 tsp);
- baking soda (0.5 tsp);
- iodine (10 drops).
The substances are mixed in warm water (an ordinary glass), and then gargled with this solution.
Fir oil for tonsillitis
Fir oil is suitable for gently lubricating the tonsils, because... has anti-inflammatory properties, but at home it is better to gargle with its solution. Initially, you need to consult your doctor.
If permitted, it is necessary to prepare fir water, i.e. Add honey (1 tsp) and a couple drops of oil to a glass of warm water. Mix everything well, and then gargle with the solution 3-4 times a day, depending on the form of the disease.
Recommendations
During the treatment of purulent tonsillitis, microbiological studies should not be neglected, and it is also necessary to rely on the opinion of the treating doctor in everything. You should not stop taking antibiotics at your own discretion or suddenly change the drug in the middle of treatment. Do not heat inflamed areas or do steam inhalations without consulting a doctor.