Birth trauma is a deterioration in the body functions of a newborn due to adverse events that occurred at birth. Currently, the incidence of birth injuries has decreased due to improved quality of obstetric care and perinatal diagnosis. Statistics on birth injuries vary from country to country, with an average of about 5% of children suffering from varying degrees of injury. Damage can occur during fetal development, during labor and after birth, especially in babies requiring intensive care. Birth injuries are different.
Birth injuries of the vulva and vagina
Vulvar tissue is most often disrupted during childbirth near the labia minora or clitoris. Violations manifest themselves in the form of cracks and tears. If a tear occurs in the clitoral area, women in labor experience severe bleeding because blood vessels are damaged.
Treatment of an injured vulva involves applying a special suture with thin catgut. When stitching up wounds near the clitoris, it is imperative to insert a urine catheter into the urethra. Sutures should be placed very carefully so as not to provoke severe bleeding.
Vaginal injuries are very often found in combination with ruptures of the perineum and cervix. Vaginal lesions occur deep in the layers, but the mucous membrane itself is not damaged. At the site of vascular damage, hematomas are formed that can reach enormous sizes. Diagnosing a vaginal rupture is not at all difficult, because during a gynecological examination, a hematoma cannot go unnoticed. If the hematoma is small, then after some time it can resolve on its own, but a strong rupture in the walls must be closed with a continuous suture. Sometimes the bleeding is so severe that surgery becomes simply impossible. In order to stop the outpouring of blood, the hematoma is opened, emptied and sutures are placed on the vessels, and, if necessary, on the tissues. To treat large hematomas, drainage in the form of a rubber strip is sometimes used.
Classification
Birth injuries due to their occurrence can be divided into two types:
- hypoxic;
- mechanical.
Hypoxic birth injuries are caused by a complete cessation of oxygen supply and prolonged restrictions, as a result of which excess carbon dioxide accumulates in the baby’s body.
These include:
- oppression syndrome;
- agitation syndrome;
- intracranial hemorrhages.
The depression syndrome is expressed in the form of absence or weakening of basic reflexes, lethargy of the baby, and hypotension.
On agitation syndrome is characterized by excessive restlessness of the baby, shallow sleep, spontaneous active movements, muscle hypertension, convulsions, and increased reflexes.
Intracranial hemorrhages occur during prolonged hypoxic conditions. They are characterized by symptoms of agitation syndrome. To make a diagnosis, the fundus of the eye, which is closely related to brain activity, is additionally examined.
Birth injuries can be divided into four types based on their effect on certain organs:
- damage to the skin and muscles;
- bone damage;
- damage to the central and peripheral nervous system
- abdominal organ damage
Injuries to the skin and muscles are the easiest. They manifest themselves as superficial skin lesions. Damage to the muscles of the cervico-brachial girdle and the occurrence of torticollis is a more severe injury. Typically, these injuries do not require special treatment and go away within a few days (except for torticollis).
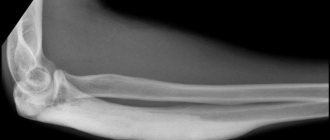
Bone damage includes cracks and fractures that occur due to erroneous actions of obstetricians or a large fetus. More often, injuries occur during severe labor and the bones of the collarbone, shoulder and hip are affected. A clavicle fracture is more common.
Typically, this type of injury is easy to diagnose, since tissue swelling is observed in this area and the child practically does not make active movements of the injured limb and reacts painfully to passive movements. To establish an accurate diagnosis, you need to take an x-ray. Treatment consists of fixing the affected limb in a stationary position for 5-10 days and placing the child on the other side.
Damage to the nervous system includes damage to the peripheral nervous system, intracerebral hemorrhage, and spinal cord injury. These injuries are the most severe in their consequences on the baby’s life.
Among them are often highlighted:
- facial paralysis;
- paralysis of the laryngeal nerves;
- spinal cord damage.
Facial nerve paralysis , often unilateral, manifests itself in facial asymmetry when a newborn cries. Paralysis is expressed in incomplete closure of the eye on one side, drooping of the corner of the mouth, and complicated grasping of the chest. It usually goes away on its own within a few months; it is necessary to monitor the hygiene of the affected eye and ensure the application of a sterile bandage with antiseptic agents.
There is also damage to the nerves of the larynx , expressed in impaired swallowing function and hoarse cry of the baby. Diagnosed using laryngoscopy to rule out other diseases. Recovers within 4-6 weeks.
Spinal cord injuries often lead to stillbirth due to the baby's inability to breathe on his own. Surviving children are usually weak and sickly. To speed up the recovery of paralyzed muscles, injections of vitamins B1 and B12 are prescribed.
Internal organ injuries are the most rare and are mainly associated with obstetric intervention. Most often they represent a rupture of the liver, spleen or adrenal glands, which manifests itself in the form of abdominal bleeding. Diagnosis is quite difficult, since bleeding may not appear externally. If you notice bluish skin and abdominal distension, or your baby is restless, seek help immediately. Only after examining the abdominal cavity using X-rays or ultrasound can a diagnosis be made.
Birth injuries of the perineum
Vulvar tissue is most often disrupted during childbirth near the labia minora or clitoris. Violations manifest themselves in the form of cracks and tears. If a tear occurs in the clitoral area, women in labor experience severe bleeding because blood vessels are damaged.
Treatment of an injured vulva involves applying a special suture with thin catgut. When stitching up wounds near the clitoris, it is imperative to insert a urine catheter into the urethra. Sutures should be placed very carefully so as not to provoke severe bleeding.
Vaginal injuries are very often found in combination with ruptures of the perineum and cervix. Vaginal lesions occur deep in the layers, but the mucous membrane itself is not damaged. At the site of vascular damage, hematomas are formed that can reach enormous sizes. Diagnosing a vaginal rupture is not at all difficult, because during a gynecological examination, a hematoma cannot go unnoticed. If the hematoma is small, then after some time it can resolve on its own, but a strong rupture in the walls must be closed with a continuous suture. Sometimes the bleeding is so severe that surgery becomes simply impossible. In order to stop the outpouring of blood, the hematoma is opened, emptied and sutures are placed on the vessels, and, if necessary, on the tissues. To treat large hematomas, drainage in the form of a rubber strip is sometimes used.
Birth injuries of the uterus
Uterine rupture is a complex injury that can cause the death of the mother. Severe consequences are caused by blood loss and shock, and therefore always require emergency surgical intervention. Fortunately, such damage is quite rare - up to 0.1% of the total number of births performed. The rehabilitation period takes a long time, as purulent complications can develop. If the uterus ruptures, the child has no chance of survival, so such an injury becomes the cause of fetal death.
Risk group for possible uterine rupture:
- women with scars after a previous cesarean section, induced abortion and uterine perforation;
- pregnant women who have already given birth several times, had an abortion and suffered from complications after pregnancy and abortion;
- women with a discrepancy between the size of the fetus and the pelvis;
- the presence of multiple births or polyhydramnios, transverse position of the fetus;
- abnormal course of pregnancy, prescription of labor stimulation.
The symptoms of uterine rupture directly depend on the reasons that caused the damage, the stage of injury, and concomitant diseases of the internal organs of the expectant mother. Complications can result from gestosis, physical and moral exhaustion of the mother's body, and chronic infectious diseases. The first symptoms are painful contractions, uncharacteristic dilatation of the uterus, swelling of the cervix, difficulty urinating, and pain in the vaginal cavity. At the first gusts of contraction, the uterus becomes convulsive in nature, and bloody discharge from the vagina appears, which is uncharacteristic of the birth process. When a rupture occurs, the woman experiences severe sharp pain in the lower abdomen. After this, women in labor experience apathy, and the pain shock they experience causes the cessation of labor. Uterine rupture can be easily diagnosed by the appearance and general condition of the mother's body: pallor, rapid heartbeat, sweating, nausea and possible vomiting. After a uterine rupture, the fetus is located in the abdominal cavity, and its heart stops beating. Bleeding from ruptures can be very severe, its abundance depends on the size and location of the birth injury.
If specialists have been able to establish a real threat of a woman receiving a uterine injury during childbirth, they prescribe immediate delivery: a cesarean section or a special operation aimed at destroying the fetus. When medical personnel are faced with the question “whose life should they save: the woman in labor or the fetus?”, they always choose the woman’s life. After injury to the uterus during childbirth, hemostasis is immediately performed. Interventions for birth injuries to the uterus may include supravaginal removal or even hysterectomy. These are extreme measures that doctors take in emergency situations. For young patients with small damage and absence of infectious infection, the uterus is sutured. All procedures related to the restoration of the uterus are carried out in parallel with blood transfusions, since it is necessary to restore the amount of lost blood as quickly as possible.
Cervical rupture occurs in many women in labor, according to some data, about 60%. There are two types of these birth injuries: violent and spontaneous.
Depending on the depth of the damage received, all cervical injuries are divided into three stages:
- The depth of the gap does not reach 2 cm;
- The damage exceeds 2 cm, although it does not reach the vaginal vault;
- The injury reaches the vaginal vaults, and sometimes can spread to them.
Most often, cervical rupture occurs in its left lateral part. The first symptoms indicating a birth injury to the cervix are postpartum bleeding from the vaginal cavity and contraction of the uterus itself. The blood flowing from the genital area is bright scarlet in color. Discharge can flow continuously in a small stream, sometimes along with clots. But nbsp; medical practice knows cases when a cervical breakthrough was not accompanied by bleeding at all. If the resulting birth injury was so severe that damage to the uterine arteries occurred, massive blood loss is observed, and patients experience severe pain shock. If the injury is not diagnosed in a timely manner, complications may develop in the form of postpartum injuries, dysplasia, parametritis, etc.
To diagnose a cervical rupture, specialists perform a postpartum examination using a speculum. A repeat examination is carried out after the swelling has subsided and the uterine tissue has returned to a state of rest - 6-48 hours after the birth of the child. If ruptures are found during the examination, they are immediately stitched up or surgery is scheduled until two days after the end of the birth process.
The development of medicine and the training of highly qualified specialists have led to a significant reduction in the number of mechanical uterine ruptures. Uterine ruptures of a violent nature are becoming less and less common, but, unfortunately, cases of uterine rupture due to cicatricial changes in its walls are increasing. This is due to the high number of cesarean sections, abortions and plastic surgery interventions.
Birth injuries resulting in damage to the central and peripheral nervous systems
During the evolution of mammals and humans, Mother Nature did everything to minimize the problem of trauma during childbirth. The bones of the skull in newborn children “move”; their articulation is not as rigid as in adults. There are fontanelles, the seams are elastic.
When the head moves through the birth canal, the skull in children experiences large mechanical loads and pressure, but its shape seems to adapt and thus resists them. The passage of the head is the most critical moment of childbirth! There are often simple types of trauma that should not cause serious concern:
- A birth tumor is the most harmless case. This is just a slight swelling on the face that will go away on its own in a few days. The reason for the formation is tissue compression.
- Edema on the crown or subaponeurotic hemorrhage is of a similar nature and also does not require special treatment.
Cephalohematoma
It is very difficult to diagnose immediately after birth, usually within the first days. It is observed in only 3-5 cases per 1000 newborns. This is a hemorrhage under the periosteum, resulting from rupture of blood vessels during deformation of the skull passing through the narrow birth canal. Usually from 50 to 140 ml of blood is poured out, sometimes more; cephalohematoma is most often observed on the bones of the crown. The tumor is elastic to the touch, and over the course of several weeks it gradually resolves. If this does not happen, the hematoma hardens, which can cause deformation of the skull bones.
Dangerous complications can be expressed in the suppuration of cephalohematoma, blood loss can cause anemia.
In severe cases of suppuration, antibiotics are used, blood suction is used, and surgery is performed. In uncomplicated cases, the resorption process is stimulated with vitamin K, and potassium gluconate is prescribed.
Intracranial injuries in children
In 70% of cases, the causes of damage to the central nervous system are intracranial injuries, this is one of the causes of death in newborn children. Medicine claims that the main causes of birth intracranial injuries in children are intrauterine oxygen deprivation (hypoxia) or asphyxia during childbirth.
Changes in the functional properties of blood vessels, cerebral edema, hemorrhages are observed, and natural mechanisms for regulating intracranial pressure are disrupted. All these disorders are complemented and intensified by mechanical compression of the skull during the passage of the birth canal, or by errors or excessive efforts during obstetric manipulations.
Treatment depends on the severity and type of intracranial injury: surgery is performed, artificial ventilation is activated (if necessary), drug therapy is prescribed to stabilize hemostasis, metabolism and prevent convulsions and swelling.
The list of diseases of the central nervous system of children as a result of intracranial injuries is quite extensive. Often intracranial injuries cause cerebral palsy (CP), mental and physical development retardation, mental retardation, epilepsy, paralysis, and muscle atrophy. It is necessary to take immediate measures in the first days of the baby’s life in order to stop serious consequences. Unfortunately, intracranial injuries often lead to death...
Other birth injuries
- Uterine inversion develops due to improper postpartum period, often causing painful shock. This birth trauma can manifest itself in two forms: partial and complete. Therapy for inversion consists of immediately eliminating the state of shock and straightening the uterus. This procedure takes place under general anesthesia.
- Stretches and tears of the pelvic joints: observed in women with softened pelvic joints and a large fetus. Ruptures are accompanied by stretching and separation of the bones, which leads to damage to the pelvic organs. This type of injury is accompanied by severe pain, especially when spreading the legs. Often, women with sprains may have impaired gait and coordination of movements. When diagnosing an injury, it is necessary to undergo examination by a traumatologist. The doctor often conducts an examination by palpation and prescribes x-rays of the pelvic joints. Therapy for injury involves complete rest for the patient, tight bandaging and constant wearing of support corsets. If the symphysis pubis was damaged during the rupture, then surgery is necessary.
- Urogenic and rectal-vaginal fistulas: appear when the fetal head remains in one position for a long time. The head can press on tissue and thereby disrupt blood circulation, which contributes to the development of necrosis. Sometimes fistulas can form due to damage to the tissues of the bladder or rectum during surgery.
Common Causes of Maternal Birth Injuries
The formation of birth injuries has a number of causes, which are divided into 2 groups: mechanical and histopathic.
The mechanical group includes interference with the natural process of childbirth and the use of forceps, the use of vacuum extraction, manual separation of the placenta, and improper stimulation of labor. The use of such radical methods provokes complications during pregnancy: post-maturity of the child in the womb or premature birth, incorrect positioning of the fetus, narrow maternal pelvis, etc.
The histopathic group is based on an analysis of the woman’s gynecological parameters. Uterine ruptures can be caused by operations that the mother has undergone in the past: cesarean section during a previous pregnancy, abortion, metroplasty. All of the above manipulations leave a scar on the uterus, which reduces the ability of the myometrium to contract during labor.
Women with anatomical abnormalities of the genital organs are at risk: septum inside the uterus, hypoplasia, bicornus, rigidity, etc. They provoke the manifestation of birth injuries and diseases suffered during pregnancy: hydatidiform mole, colpitis, chorionepithelioma.
Statistics show that ruptures of the perineum, vagina and cervix are more common in women who give birth for the first time. This is about 20% of the total number of births. Uterine ruptures are much less common - 0.05%. The main reason for such birth trauma is the difficult course of pregnancy and unqualified assistance from an obstetrician-gynecologist.
The soft tissues of the birth canal of a woman in labor are most often damaged by the large size of the fetus, the narrow pelvis of the mother, inflammatory processes of the internal genital organs, during rapid labor and the use of obstetric forceps.
4mama
How to protect yourself and your baby during childbirth? There is no clear answer to this question. The main recommendations given to a pregnant woman are aimed at preserving the health of the baby and her own. A healthy lifestyle, moderate physical activity, weight control, timely visits to the doctor - a set of measures that prepares a woman in advance for a successful birth. Injuries to a newborn baby Various situations can lead to injuries during childbirth, for example, a discrepancy between the size of the baby's head (the largest part) and the size of the woman's pelvis, prolonged or, conversely, rapid labor. Those at risk for developing birth injuries include premature babies, as well as children who have suffered intrauterine hypoxia (oxygen deficiency) or asphyxia during childbirth. Some obstetric aids, such as the application of forceps or a vacuum extractor, unfortunately, can also cause certain injuries to the baby. Damage to soft tissues Prolonged standing of the baby in the birth canal can lead to the formation of a birth tumor. This is a potentially harmless condition that resolves on its own in the first 2-3 days of the baby’s life. A birth tumor has the appearance of a swelling of soft tissues and is located in the so-called presenting part of the fetus - that is, in the place that first passes the birth canal. Thus, a birth tumor can be localized on the head, face, buttocks and even the external genitalia. Cephalohematoma, or subperiosteal hemorrhage, is a deeper injury. It is localized in the presenting part of the head, more often in the projection of one bone. Cephalohematoma is often “covered” by a birth tumor, so it is not always possible to diagnose it in the first day of a baby’s life. Cephalohematoma always worries specialists! There are situations of ongoing hemorrhage under the periosteum, which leads to anemia in the child. Treatment tactics are agreed upon with the surgeon. Most often, the hematoma is evacuated by puncture (puncture). Soft tissue injuries also include abrasions, hemorrhages in the skin and subcutaneous tissue, which resolve on their own, requiring only antiseptic treatment and observation. Among muscle tissue injuries, the most common is tearing of fibers or complete rupture of the sternocleidomastoid muscle (“sternocleidomastoid” muscle), with the formation of a hematoma. Significant muscle damage can lead to acquired torticollis! Treatment tactics depend on the degree of damage and consist either of conservative measures (fixation of the head in the desired position, exercise therapy, physiotherapy) or surgical treatment. Bone tissue injuries This type of birth injury includes cracks and fractures of bones. According to statistics, fractures of the clavicle, humerus and femur occur more often. A fracture of the collarbone is manifested by the baby's anxiety and crying when feeling the injury site, and limited movements in the arm on the side of the injury. The doctor, by feeling the collarbone, can determine the compaction at the fracture site. When the humerus or femur is fractured, there is a sharp restriction of movements in the limb and a painful reaction of the baby to palpation and touch. The final answer is given by x-ray diagnostics. In treatment, it is important to compare the fragments and immobilize the limb. In most cases, the prognosis for this type of injury is favorable. Damage to internal organs and the central nervous system This type of birth injury is potentially very severe. In case of severe injury to internal organs, the newborn’s well-being suffers, lethargy and severe pallor are observed. In terms of diagnosis, instrumental research methods are often required: ultrasound, x-ray, computed tomography (CT). The most severe injuries include damage to the structures of the central nervous system. At risk are premature babies, children who have suffered severe intrauterine infection and hypoxia (oxygen deficiency). Such injuries are potentially life-threatening to the child. When making a diagnosis, data from neurosonography (ultrasound of brain structures) and other instrumental diagnostic methods are taken into account. It is important! The creation of perinatal centers on the basis of maternity hospitals and, in general, an increase in the level of medical care for newborn children has made it possible to significantly reduce the level of injuries during childbirth. An important condition for a successful delivery is the mother’s attention to her own health, timely visit to the doctor for examination and implementation of recommendations! Injuries to mothers During labor, the female body can also suffer. One of the purposes of maternity benefits is to protect the woman’s tissues: the cervix, perineum, etc. from injuries during the birth of the baby. An important step is making a fundamental decision - whether a woman can give birth on her own or whether a cesarean section is necessary. During independent childbirth, the doctor and midwife assess the degree of dilatation of the cervix, the intensity of contractions and help the woman decide when and with what force to push. Despite the provision of assistance, injuries to the mother's body still occur. These include injuries to the perineum (ruptures, tears, hematomas), vagina and cervix. Injury to bone tissue—the pelvic ring—occurs extremely rarely. It is important! How to avoid trauma during childbirth? Listen to advice! A large weight gain will not benefit the baby and will complicate the course of labor. Sometimes a woman is recommended to go to the maternity hospital in advance, for so-called prenatal preparation; you should not ignore this recommendation! During the birth process, the midwife holds the baby's head at the right moments, preventing it from injuring the maternal tissues. The woman in labor is given clear instructions: to push, not to push, to breathe correctly, etc. If necessary (overstretching of the perineal tissue), dissection is performed - episotomy. Subsequently, such wounds heal faster.
Prevention of birth injuries
It is very difficult to prevent birth injuries, but if you carefully monitor your health and promptly treat the resulting inflammatory processes in the vaginal cavity, the risks of injury during the birth process are significantly reduced.
Many doctors advise pregnant women to regularly massage the perineum, which increases the elasticity of its tissues and will help avoid future ruptures and cracks. You can start using massage treatments regardless of the stage of pregnancy, but always after a warm shower. To improve the effect of the procedure, you should use natural olive, sunflower, and wheat oils. Apply a small amount of massage oil to the perineum, labia and carefully insert an oiled finger into the vagina to a depth of no more than three centimeters. Then we lightly press on the vaginal wall adjacent to the surface of the rectum and dynamically repeat the movements for five minutes. You can apply massage every five days.
No matter how hard a pregnant woman tries to protect herself and her baby from birth injuries, the main responsibility lies with the obstetrician-gynecologists who deliver the baby. Specialists must monitor the successful progress of the birth process and, in case of any complications that arise, must maintain the rapid movement of the fetal head. The actions of medical staff, according to obstetric instructions, help prevent perineal breakthroughs. The use of the “perineal protection” technique will help preserve the tissues of the organs and perineum of the mother in labor.
An integrated approach will help prevent birth injuries to the mother and the born baby, then an easy birth will be guaranteed.
Types of birth injuries[ | ]
Birth trauma is divided into spontaneous
, which occurs during normal labor (complicated and uncomplicated), and
obstetric
, caused by the physical actions of the obstetrician (forceps, traction, aids, hand pressure on the fundus of the uterus in order to move the head faster, various manipulations).
There is also the concept of maternal birth trauma
.
The main types of birth injury: birth injury of the skull and brain, spine[5], internal organs (liver, spleen, adrenal glands, etc.), various skeletal bones (clavicle, femur, etc.), brachial plexus, etc.
The most common are birth traumatic injuries of the skull and brain, which not only can lead to death, but are also accompanied by damage to the central nervous system, leading to disability and delayed neuropsychic development.