The knee joints are one of the largest joints in the human body; they perform the most important musculoskeletal function. If the knee joint is damaged for any reason, the person becomes incapacitated because he is deprived of the ability to walk.
[contents]
Pain and impaired motor activity of the joint can occur due to injury or inflammation, in the latter case they speak of arthritis of the knee joint. Knee arthritis is a serious disease that often causes disability, so it should be treated as early as possible.
Causes
Diagnosis of joint diseases is fraught with some difficulties, since the inflammatory process develops gradually, accompanied by slow degeneration of cartilage tissue. Nonspecific symptoms indicate the disease at the time of its manifestation, but there are dozens of possible reasons for its development: post-traumatic, infectious, autoimmune, parasitic, etc. Even a simple rubella vaccine can provoke arthritis. Therefore, it is extremely difficult to make a clear and comprehensive etiological classification, and the cause of arthritis of the knee joint is determined individually after differential diagnosis.
| Type of relay protection | Cause | |
| P | Osteoarthritis | genetic predisposition, metabolic disorders |
| Rheumatoid | idiopathic etiology with possible autoimmune pathogenesis | |
| Gouty | metabolic disorder causing deposition of uric acid salts in the joints | |
| Still's disease | hereditary causes, but there is evidence of the influence of viruses and bacteria on the course of the disease | |
| IN | "Lupus" | damage occurs to all structures and organs where there is connective tissue |
| Scleroderma | pathogenesis similar to lupus arthritis, but the epidermis is predominantly affected | |
| Enteropathic | degeneration of cartilage tissue is associated with inflammation in the intestines (ulcers, colitis, dysentery, celiac disease, etc.) | |
| Tuberculous | arthritis is a complication of tuberculosis, although joint pain may increase even after treatment of the underlying disease | |
| Reactive | develops as a consequence of infectious diseases, mainly intestinal (salmonellosis, shigellosis) and urogenital (chlamydia, gonorrhea) | |
| Hemochromatic | joint degeneration occurs due to abnormal accumulation of iron in the body |
Designations in the table:
- (P) - primary arthritis;
- (B) - secondary arthritis.
The division of arthritis into primary and secondary is very arbitrary, since it is possible to find cause-and-effect relationships between the manifestations of certain diseases, but their exact etiological mechanisms have not been fully established. For example, in hemochromatosis, arthritis is caused by the accumulation of iron in tissues and joints, but what exactly causes this anomaly is not known for certain.
In most cases, the main cause of arthritis of the knee joint is injury with infection in the synovial area. If there is a genetic predisposition to this disease, it can develop under the influence of trigger factors.
Etiology:
- Infectious
- Autoimmune
- Post-traumatic
- Idiopathic
- Bacterial staphylococcus;
- streptococci;
- gram-negative bacteria;
- gonococci;
- hemophilus influenzae, etc.
- parvoviruses;
- schistosomiasis;
Leaving aside the specific etiology, we can identify the following factors against the background of which the knee joint develops:
- old age and associated metabolic disorders;
- weakened immunity and the presence of chronic diseases;
- injuries and severe hypothermia;
- professional factor;
- hormonal disorders associated with diabetes and obesity;
- transmission of severe infectious diseases;
- sedentary lifestyle.
Studies have shown that a sedentary lifestyle causes joints to “rust”, that is, rapid atrophy of cartilage tissue occurs. Therefore, to prevent arthritis, daily exercise or regular visits to the pool are simply necessary.
Kinds
Gonit can be classified according to various signs, which in the medical history determine the diagnosis. Doctors identify the following characteristic types of knee arthritis.
According to the location of the source of inflammation
| capsular (synovial, synovitis) | bone (dry) | |||
| degeneration of the osteochondral structures of the joint occurs | |||
By the nature of the effusion
- serous
- purulent
- serous-purulent
According to the microflora of effusion
| aseptic | septic | |||
| There is no pathogenic microflora, the synovial fluid is sterile | pathogenic microorganisms are present in the exudate sample | |||
This classification determines the time periods of the disease. For example, the focus of inflammation may initially be capsular, but as the disease progresses it can become dry and vice versa.
Causes of knee arthritis
Arthritis of the knee joint can occur for a huge number of reasons; the disease is often provoked by the impact on the patient’s body of several negative factors at once. Let's look at the most common causes of knee arthritis:
- knee injuries;
- increased load on the knees, including obesity;
- metabolic disease;
- infectious diseases;
- allergies, most often to medications, vaccines;
- endocrine pathologies;
- autoimmune pathologies;
- passive lifestyle.
It is difficult to determine the exact cause of the disease, since it progresses gradually. From the onset of pathology, several weeks may pass before the patient feels pain and consults a specialist.
Stages
A more significant classification is the division according to the nature of the inflammatory process. As the disease progresses, arthritis goes through three stages:
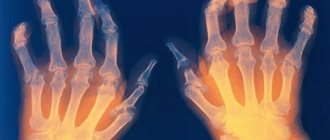
- acute (initial) - characterized by severe sharp pain that is localized in one knee. Most often it occurs as a result of injury or against the background of an acute infectious disease. The pain is usually short-term and wave-like, and is felt mainly in the morning and when the weather changes. During this period, narrowing of the joint space and other structural changes are practically invisible on x-rays. It is very important to completely cure the inflammatory process, otherwise it will begin to progress slowly;
- subacute is an intermediate period between the acute and chronic forms, which is accompanied by a protracted inflammatory process and gradual degradation of cartilage. During this period, pain is felt constantly, but the symptoms are not as severe as with acute arthritis of the knee joint. The person feels constant discomfort and stiffness, and the picture shows erosion of cartilage tissue, thickening of the joint capsule and narrowing of the gap;
- chronic is a stage of long-term inflammation, in which the patient feels constant discomfort in the area of the affected joint, and remission only periodically occurs. Cartilage degeneration becomes more pronounced than in the subacute phase. The image clearly shows fibrous growths, deposits of salts and osteophytes in the joint capsule. At this stage, the need for endoprosthetics becomes only a matter of time.
Acute arthritis of the knee joint
Arthritis of the knee joint is divided into acute and chronic. The acute form of the pathology is characterized by severe symptoms: severe pain, swelling, increased local temperature, and general weakness. The chronic form of the disease is a complication of an untreated acute form of arthritis.
With chronic arthritis of the knee joint, the patient is bothered by mild aching pain, which usually occurs during physical activity and at the end of the working day. Chronic arthritis is characterized by periodic exacerbations, especially during the cold season. If left untreated, chronic arthritis can lead to cartilage destruction and disability.
Arthritis develops gradually, so the disease is divided into 3 stages:
- At the first stage, the inflammatory process in the joint cavity is just forming; most patients do not feel pain at this time.
- At the second stage, the disease progresses; in the infectious form, an abscess forms, pain and inflammation become severe.
- Arthritis of the knee joint grade 3 is the most difficult to treat. At the last stage, cartilage tissue is destroyed, the knee completely loses motor function, and the patient becomes disabled.
To avoid disability, you should consult a doctor for any pain in the knee joint, especially if it occurs for no apparent reason and continues to bother you for more than a few days.
Symptoms and signs
Recognizing the symptoms of acute arthritis of the knee joint is quite simple - it is an attack of severe pain and swelling, painful on palpation. The development of the chronic form occurs gradually and is manifested by barely noticeable pain, mainly after physical activity and “in the weather.” The following symptoms of driving can be distinguished.
| Feature groups | Description |
| Articular |
|
| Are common |
|
| Structural |
|
Each type of arthritis has its own characteristic features, by which the cause of its development can be determined. For example, doctors identify the following specific signs of arthritis of the knee joint according to the etiology of the disease:
- rheumatoid - unlike other types, this type of drive is characterized by severe intoxication. In addition to local pain in the knee, nausea, low-grade fever up to 38°C, malaise, dizziness and rapid weight loss are clearly evident. Lack of timely treatment leads to irreversible joint deformation;
- gouty - with this disease, pain occurs after the action of a provoking factor, for example, stress, consumption of alcohol or protein foods. Attacks are always acute, but short-lived. Gouty arthritis never leads to contractures and deformation of the knee joint. However, over time, tophi can form in the knee area - mobile dense formations;
- lupus and scleroderma - this arthritis differs in that it is manifested only by pain, while other “standard” symptoms (swelling, pain, redness, hyperthermia) are not observed. The only possible sign of such a pathology is dry skin and signs of internal hemorrhages (small red “stars” and “strings”);
- tuberculosis - the development of the inflammatory tuberculosis process in the knee occurs within 2–7 years. At first, there is only slight swelling and a general feeling of malaise. Pain, if it occurs, is very weak, so patients do not pay attention to it. Gradually, the activity of the infection increases, leading to all the typical manifestations of driving;
- psoriatic - joint pain often precedes the development of the acute phase of psoriasis. Therefore, if you are prone to this disease, it is necessary to carefully examine your nails and skin for the presence of characteristic nodules if there is causeless pain in the knee.
Despite the nonspecificity of the symptoms of knee arthritis, the etiological treatment is always different. Therefore, a qualitative analysis of the complete clinical picture plays a very important role in differential diagnosis.
Diagnostics
Differential diagnosis of arthritis of the knee joint always begins with a study of the patient's medical history and characteristics of his current clinical picture. The second stage is visualization of destructive changes in the knee, which allows us to determine the degree of inflammation and the reversibility of deformations occurring in the joint. Most often, X-rays are used as the cheapest type of instrumental diagnostics, but if necessary, CT or MRI are also performed.
X-rays are often sufficient to understand the severity of symptoms and prescribe “local” treatment for arthritis of the knee joints. However, to determine the cause of the disease, a laboratory examination is necessary (the last column presents critical indicators indicating the progression of arthritis).
| Analyzes | Options | Critical indicator | ||
| General blood analysis | ESR | > 20 mm/hour | ||
| leukocytes | > 9*109/l with normal arthritis | |||
| < 4*109/l for systemic arthritis | ||||
| hemoglobin | < 120 g/l | |||
| red blood cells | women | < 3.7*1012/l | ||
| men | < 4.5*1012/l | |||
| Blood biochemistry | uric acid | > 5.8 mg/dl (for gout) | ||
| creatinine | > 110 µmol/l | for systemic arthritis | ||
| urea | > 7.5 mmol/l | |||
| C-reactive protein | > 5 mg/l | |||
| General urine analysis | presence of blood, glucose or protein | > 0.14 g/l (with systemic arthritis, when kidney function is impaired) | ||
| Serology | rheumatoid factor | > 10 U/ml (for rheumatoid and systemic arthritis) | ||
In addition to general tests, a scraping of the patient’s urethra is taken to determine the presence of genitourinary infections, and a puncture is also made to study the microflora of the exudate. Examination of the joint fluid makes it possible to establish tuberculous arthritis using microscopic and fluorescent methods. However, culture is considered the most reliable diagnostic method. It is at least 90% accurate, but takes about 3 months to complete.
An important point is the difference between arthritis and arthrosis of the knee joint. Although the clinical picture is similar, these diseases still have some differences.
| Arthritis | Arthrosis | |
| Inflammation | generalized (affects both joints and internal organs) | local (only cartilage and joints are affected) |
| Main group of patients | people of any age | mostly over 60 years old |
| Pain | constant, periodically intensifying | periodic (intensifies with movement) |
| Limited mobility | in all directions | only in one direction |
With arthrosis, a characteristic crunching and clicking sound in the joint is often heard during movement. With arthritis, this symptom is observed less frequently.
Drug treatment
Medical opinions are mixed about whether knee arthritis can be cured. Post-traumatic inflammation can be treated, while allergic or autoimmune arthritis can only be stopped and slowed down. However, the patient’s quality of life depends on the correctness of the prescribed treatment. Therefore, complex therapy involves the use of the following drugs:
- non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs. These medications constitute the symptomatic treatment of knee arthritis. They eliminate pain and prolong remission. The mechanism of action is based on inhibition of the production of enzymes that stimulate inflammatory reactions. All used NSAIDs can be divided into two groups according to the type of active substance:
- non-selective (Diclofenac, Indomethacin, Ibuprofen) - they contain a high concentration of acids, which is why they often cause adverse reactions from the gastrointestinal tract. People with a low blood clotting factor and a tendency to digestive diseases should take such drugs only under the supervision of a doctor. At the initial stage, when the disease is characterized only by local inflammation, local remedies are prescribed: ointments, gels and compresses;
- selective (“Arkoxia”, “Denebol”, “Celebrex”) - their active substances are bases that do not have a harmful effect on the digestive tract. However, there is a danger of developing cardiovascular complications. However, these drugs represent a new generation of drugs that have much fewer contraindications and side effects with the same effectiveness as non-selective NSAIDs;
- basic drugs. Now in the treatment of any type of arthritis, great attention is paid to the action of chondroprotectors. Great hopes are placed on preparations of chondroitin, glucosamine and hyaluronic acid. Recent studies show that they actually stop the degeneration of cartilage tissue and eliminate the inflammatory process. Such medications for knee arthritis are aimed at stimulating the natural mechanisms of protection and restoration of cartilage tissue.
However, with the development of the rheumatoid form, it is necessary to use completely different drugs that can suppress the aggressive action of the immune system that causes inflammatory processes:
- quinolines - the patient must take them constantly, and daily in the first year of therapy. If the dynamics are positive, it is allowed to take pills every other day and even take breaks for up to 3 months;
- Salazol drugs - these drugs are gradually being phased out as they have been replaced by more effective and safe drugs. A significant disadvantage of salazal preparations is the increased risk of stone formation in the kidneys and bladder;
- D-penicillamine is a powerful immunosuppressant that is now rarely used due to the high risk of complications such as nephritis, alveolitis, dermatitis and cytopenia;
- cytostatics (Methotrexate, Cyclosporine) are the so-called “gold standard” for drug treatment of rheumatoid arthritis of the knee joints. These drugs suppress immune inflammation very well and cause fewer complications. However, treatment is carried out only under the supervision of a doctor, since it is necessary to constantly screen the condition of the liver and blood counts.
In 1929, it was proposed to inject gold salts into the patient to treat rheumatoid arthritis. However, the effectiveness of this treatment has not been confirmed, and an allergy to the drug occurred in every fourth patient.
The choice of the basic drug is determined by the diagnostic results and the type of arthritis:
- rheumatoid → immunosuppressants, cytostatics and glucocorticosteroids;
- gouty → diet and drugs that reduce uric acid levels;
- tuberculosis → anti-tuberculosis drugs that should be taken for up to 2 years;
- reactive → antibiotics, antiviral or antiparasitic drugs depending on the cause of the infection; with such arthritis, it is necessary to increase general immunity to fight pathogens, therefore immunostimulants are prescribed: Methyluracil, Tactivin, Levamisole.
Chondroprotectors are considered universal means of treating joints, therefore they are recommended for use in any form of arthritis.
Treatment methods
The standard treatment for knee arthritis, like other affected joints, is non-steroidal anti-inflammatory medications. The most popular non-steroidal drugs are:
- Almiral;
- Nimesulide;
- Olfen;
- Revmoxicam.
The listed drugs help to quickly cope with inflammation and reduce pain in the joints. Nonsteroidal medications are used in cases where the inflammatory process lasts for a long time without proper treatment.
If the diagnosis of the disease was made at an early stage, then anti-inflammatory ointments and gels will help cope with the disease. Therapy with these drugs is possible only for mild arthritis. Most often, for arthritis of the knee joint, the following are prescribed for treatment:
- Histalgon;
- Finalgon;
- Apisatron.
Anti-inflammatory gels and ointments are also used in complex treatment together with injections and other medications. This is due to the fact that most often the use of gels helps only for a short period of time; pain and swelling return after some time.
In case of exacerbation of pain, the knees should be kept at rest. It is best to stay in bed and not worsen the condition of the joints with physical activity.
Compresses will help partially relieve swelling, as they also improve blood circulation in the injured knee by warming it. There are many traditional methods of compresses that will help relieve pain in the joints.
You should not treat yourself, you may harm yourself.
In order to know how to treat arthritis of the knee joint, you must immediately see a doctor when primary symptoms appear. After a complete examination, you will be prescribed a comprehensive treatment, depending on the degree and type of pathology.
Traditional treatment is mainly prescribed tablets, injections and therapeutic exercises. The issue of treatment must be approached seriously and all signs must be taken into account individually, since much depends on the general condition of the body.
Traditional therapy
To treat arthritis of the knee joint, anti-inflammatory drugs, which include hormonal substances and ascorbic acid, are mainly used.
If the disease is caused by an infectious process, then in this case doctors prescribe antibiotics. For other reasons, treatment is prescribed depending on the presence of identified diseases.
For external use, doctors prescribe ointments, creams and various compresses, which are aimed at reducing pain, reducing swelling and improving blood circulation in the knee, and these drugs also warm it.
If the case is much more serious, then the drugs are administered intravenously, using injections into the joint cavity itself. In such cases, drugs that contain hormones and anti-inflammatory substances are used.
When the disease worsens, it is necessary to create peace and warmth for the sick person. Bed rest is recommended.
During the course of treatment, it is necessary to carefully approach nutrition and follow the recommended diet, which includes:
- Fresh vegetables and fruits.
- Fish, preferably fatty, omega-3 fatty acids are very beneficial for joint cartilage.
- Also, if possible, you should eat seafood that contains chondroitin - this is a component aimed at nourishing cartilage. This includes squid, shrimp, and mussels.
Advice! You should not overuse salty foods and spicy seasonings.
In addition to all of the above, massage and manual therapy are prescribed as treatments for arthritis. Do not forget that for greater effect it is necessary to undergo complex treatment.
Can arthritis be cured? A conservative (medicinal) method of treating the knee joint is aimed at combating symptoms; therapy does not allow the disease to develop into acute forms. The surgical method is used only in cases of severe deformation and destruction of cartilage tissue.
Operation
There are only two types of surgery for this disease - arthroscopy or complete removal of the joint with its further prosthetics. Surgeries can be performed using a laser.
Arthroscopy
Despite the fact that this method has collected a huge amount of positive feedback in the fight against diseases of the knee joints, it is not very effective for arthritis.
But still, it is used to relieve symptoms. The arthroscope can easily overcome limited mobility or instability of the knee.
It can also be used to flush the joint cavity, which significantly reduces inflammatory processes. But this procedure is recommended only to get rid of the symptom of joint stiffness.
The procedure is also effective in flushing out infection inside the knee without requiring a large surgical incision. The photo shows access points for minimally invasive surgery.
For reference! The arthroscopic chondroplasty technique is used to polish the rough surface of the tissue, and during manipulations, a hole is made in the kneecap, which is then filled with cartilage tissue.
Such operations do not require special training and are performed in an outpatient clinic. In cases of osteochondral deformity, the damage can be treated with a microfracture technique in order to stimulate the regeneration of cartilage tissue that fills the defect area.
But still, arthroscopy is most often used as a preparatory diagnosis for partial or complete joint replacement.
Endoprosthetics
When arthritis of the knee joint is diagnosed, treatment includes the following set of measures:
- elimination of the inflammatory reaction;
- blocking pain syndrome;
- normalization of metabolism and blood supply to tissues;
- increasing immune defense;
- optimization of nutrition and normalization of one’s own weight; restoration of mobility of the joint and limb as a whole;
- preventive measures to prevent relapses of exacerbation.
The doctor prescribes various treatments for arthritis of the knee joint: medications (local and systemic), physiotherapeutic procedures, massage, acupuncture, exercise therapy. As a last resort, surgical treatment is used.
Ibuprofen
Surgery
If a stage comes when drugs for the treatment of arthritis of the knee joint become ineffective, the doctor recommends surgery. Depending on the severity of the disease and the degree of deformation of the joint, it is possible to perform the following surgical measures:
- removal of inflamed and necrotic areas of the joint;
- excision of fibrous plaques;
- replantation of the synovial membrane;
- transplantation of cartilage structures;
- removal of osteophytes;
- washing the joint;
- alignment of menisci;
- removal of part of the joint to relieve pressure on it.
Whenever possible, surgeons try to limit themselves to arthroscopy, an operation performed through miniature incisions. This surgery is characterized by fewer complications and a short recovery period.
Nutrition for knee arthritis
The patient’s nutrition plays an important role in the treatment of knee arthritis, especially when it comes to gouty arthritis. With gout, the patient is prohibited from eating foods that contain purines - these are substances that provoke an increase in the concentration of uric acid in the blood. These products include fish, meat, and beans.
Stress arthritis of the knee joint and its other types require a balanced and proper diet. Patients are strictly prohibited from gaining excess weight, as the knee suffers greatly from this. If the patient is already obese, he needs to try to lose excess weight.
To cure arthritis of the feet and knees, you need to eat fresh vegetables, eat low-fat dairy products, cereals, and lean meat in small quantities. Patients are advised to reduce the amount of salt consumed to 2 grams per day, and to exclude foods with pure sugar from the diet.
It is forbidden to eat fatty, fried, smoked, too spicy, salty and sweet foods. Patients with knee arthritis should eat only freshly prepared meals from natural products, without dyes or preservatives. It is forbidden to eat ready-made food from the store, fast food, or semi-finished products.
Other means
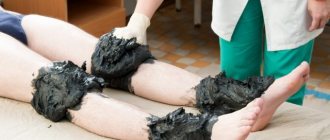
Considering the duration and high risks of complications with classical drug and surgical therapy, the question of how to treat arthritis of the knee joint with non-traditional means is becoming increasingly urgent. You should pay attention to physiotherapy, since procedures such as massage, acupuncture, quartz treatment, phonophoresis, clay and paraffin applications, rubbing, magnetic and infrared effects are very effective.
Speaking about traditional medicine, we can highlight the following most effective methods for treating arthritis of the knees and other joints:
- baths - to prepare medicinal baths you can use oats, pine needles, birch leaves, bran or an alkaline solution. They must be taken daily for 10 days. After a two-week break, you can repeat the course if necessary. You can also take dry baths by simply immersing your sore knee in a box of sand for half an hour. Procedures must be performed until pain is completely eliminated;
- ointments - for their preparation you should use turpentine, birch buds, mustard, paraffin, elecampane or pine (fir) oil. Homemade creams relieve pain well, but they should be used for at least 2 weeks;
- Mustard plasters - this long-known folk remedy perfectly relieves inflammation, but has some contraindications. Therefore, you should consult your doctor before use;
- compresses - to relieve pain and improve knee mobility, you can make compresses with chalk, honey, cabbage and potatoes. Traditional healers also recommend vinegar and alcohol compresses, but they have a warming effect, which is undesirable in the acute phase of arthritis;
- tinctures and decoctions - for problems with joints, herbalists advise treatment with herbal teas and tincture of walnut shells. You can make tinctures with celery, birch buds and lingonberry leaves. Another recipe involves eating fresh cherries with homemade milk in the morning and evening.
Treatment of knee arthritis
Arthritis of the knee joint is a whole complex of pathologies that require various therapies, so only a doctor can correctly diagnose, study the symptoms and prescribe treatment. If you have knee pain, you should consult a therapist as soon as possible, the doctor will conduct an examination and, if necessary, send the patient to a specialist. Children's arthritis of the knee joint should be treated immediately by an orthopedist.
The doctor will conduct an examination and prescribe blood and urine tests for the patient, X-rays, ultrasound, MRI and other studies, depending on the possible cause of inflammation. In case of a purulent form, the doctor must prescribe a puncture of the joint, with the help of which the type of pathogen can be identified, as well as cleanse the joints of pus.
Only a doctor can tell you how to treat knee arthritis correctly, because first you need to make an accurate diagnosis. But we can say that the treatment of knee arthritis is always complex and long-term, the patient is prescribed medications, physiotherapy, exercise therapy and massage, and the patient’s nutrition also plays an important role in the therapy.
Treatment of any type of arthritis begins with immobilization of the knee joint. The doctor prescribes wearing a fixing bandage, bandage or orthosis, in severe cases a splint or plaster. All of these bracing techniques help limit or eliminate movement in the knee to stop it from deteriorating and speed up healing.
Drug treatment
The most important part of therapy is drug treatment. The doctor prescribes tablets and injections for arthritis of the knee joint individually, taking into account the type of pathology, stage of the disease and the age of the patient.
In the complex treatment of arthritis, doctors prescribe the following groups of drugs:
- Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs help relieve pain and inflammation, such drugs include Ibuprofen, Diclofenac, Nimesulide, etc. Such drugs are taken orally in the form of tablets and intramuscular injections; also, for knee arthritis, it is recommended to use ointments with a non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drug to quickly get rid of pain.
- In advanced cases, steroid hormones are prescribed, such drugs include hydrocotrisone.
- Antibiotics, antiviral and antifungal medications are prescribed for infections.
- For gout, medications that reduce uric acid levels are indicated.
- For psoriatic arthritis, appropriate medications are prescribed, as well as sedatives.
- Rheumatoid arthritis of the knee requires taking special basic medications, these include cytostatics and immunosuppressants.
- Allergic arthritis requires taking antihistamines.
- Vitamins and chondroprotectors are indicated for restoring cartilage tissue and strengthening general immunity.
Physiotherapy for knee arthritis
In addition to taking medication, patients with knee arthritis are required to attend physical therapy. Such procedures help to significantly speed up the healing process, activate all body systems, improve tissue nutrition and speed up their regeneration.
Physiotherapy treats arthritis of the left and right knee joints in patients of all ages, even young children. The doctor chooses the procedure individually; it can be magnetic therapy, laser or ultrasound treatment, electrophoresis with drugs, as well as treatment with paraffin and mineral water, and other methods of physiotherapy.
Massage for knee arthritis
Another excellent therapeutic method for treating arthritis is massage. Regular therapeutic massage will help improve blood circulation in the knee joint, strengthen muscles and speed up recovery.
During an exacerbation, the massage should be light so as not to injure the knee. It is recommended to rub the skin above and below the joint to improve the flow and outflow of blood; you can lightly rub the joint itself. For the best effect, it is recommended to apply medicinal ointment to the knee, but first you must consult with your doctor.
Physical therapy for knee arthritis
After the exacerbation has resolved, when signs of inflammation and pain have disappeared, the patient is prescribed physical therapy. Exercises should be performed every day, gradually increasing the load. Exercise therapy is necessary to develop the joint, strengthen the muscles and improve blood circulation in the tissues.
If, after prolonged immobilization, the patient immediately begins to load the sore knee, then relapse of the disease cannot be avoided. By gradually increasing the load and training the muscles, the risk of injury and relapse of arthritis will be minimized.
Gymnastics for knee arthritis
There are several different exercise routines for treating knee arthritis. State clinics usually offer a general set of exercises that can effectively develop joints. Popov's gymnastics for the treatment of knee arthritis is intended for daily training of patients who have already returned to active walking.
It is best if a specialist selects a set of exercises, taking into account the patient’s physical capabilities. Here are some examples of exercises that will be effective for knee arthritis:
- You need to stand up straight, straighten your back, and lean on the back of the chair with one hand. Raise your right and left knees alternately up so that an angle of 90 degrees is formed, hold for a few seconds and slowly return to the starting position.
- Remain in the starting position as in the first exercise. Pull your knee to your chest, helping with your hand, try to keep your back straight. Repeat the exercise on the other leg.
- Lie on your back, raise your legs up, performing the “bicycle” exercise.
- Lying on your back, pull both knees towards your stomach, staying in this position for a few seconds.
- Lie on your stomach, bend your left leg at the knee and pull your foot towards your buttock, helping yourself with your hands.
- Lying on your stomach, bend your knees and perform circular movements with your ankle joints to the right and left.
- Sit on a chair, straighten your back, bend your knees and place it in front of you. Alternately straighten and lift each leg, holding it at the top for 5 seconds, then slowly lower it.
For arthritis of the knee joint, all exercises should be performed smoothly, avoiding excessive load on the joint. It is forbidden to run, jump, or perform too active movements until the joint is completely restored. Professional athletes are allowed to increase their loads by doctors individually.
Prognosis and prevention
To improve your general condition and prevent arthritis, you must follow simple rules:
- control weight;
- avoid excessive physical activity, but exercise regularly;
- maintain a balanced diet;
- give up alcohol and tobacco;
- control your posture and organize yourself a comfortable workplace.
KNEES HURT - causes and treatment. Knee pain - meniscus, arthrosis of the knee joint, arthritis.
The prognosis for arthritis is conditionally unfavorable. Local inflammation can be cured, but systemic articular pathology will still progress. This will lead to immobilization of the joint and disability of the patient. However, therapy can improve the patient's quality of life.