Deviations in the formation of cardiac structures are caused by congenital or acquired factors. The latter prevail in clinical practice. A large diagnostic role is assigned to the genetic component, which is rarely isolated.
Myocardial deformations are considered one of the most common types of pathological process.
Left ventricular hypertrophy is an increase in the muscle mass of the walls of the main pumping chamber of the heart, which is the result of third-party abnormalities. It is not primary.
The danger of the described condition varies from one case to another. Basically, this is a sluggish pathology, without pronounced symptoms at an early stage. If there is no dynamics of the process, then even treatment is not required. Therapy is medicinal, supportive, as needed.
LVH of the heart forms at an extremely slow pace. Against the background of arterial hypertension, the period of occurrence varies from 2 to 10 years or more, which makes it possible to qualitatively examine the patient.
The main patient population is elderly people. In some cases, the condition is not considered pathological and does not require specialized care.
The mechanism of development of the anomaly
The path of formation is determined by a violation of the normal functional activity of the heart muscle. Hypertrophy is the proliferation or increase in mass of cardiac structures in the area of the left ventricle.
Appears as a result of hypertension, less often of third-party pathologies. They have one thing in common: increasing the load on normal tissues.
Excessive stimulation, inadequate to the real capabilities of the organ, leads to the work of the adaptive mechanism. To contract more actively, the heart is forced to build muscle mass.
But this is an inherently flawed way of recovery. The bulky, expanded anatomical structure is unable to function normally.
Hence the problems with myocardial contractility, the volume of blood ejection and the functioning of cardiac structures in general, hypoxia, atrophy of tissues and systems.
Multiple organ failure occurs as a natural, deadly result.
Fortunately, the process is slow. From the moment the first symptoms of hypertrophy appear to the development of generalized disorders, it takes from 7 to 15 years.
Why does the heart work “above normal”?
The term “hypertrophy” means excess tissue, enlargement of the organ; in this case, we can talk about excessive thickening of the walls of the left ventricle, which does not exclude the possibility of a simultaneous increase in the mass of the atrium and right sections.
The main “work” of the ventricles of the heart is the pumping function. They pump blood non-stop all their lives. To do this, they have 2 groups of muscle formations:
- spiral (internal and external) during contraction reduce the heart in longitudinal size, predominate in the right ventricle;
- constrictor (squeezing) - when working, they reduce the cross-section of the organ, most developed in the left.
The normal wall thickness for the left ventricle is considered to be 10–12 mm, which is 2 times larger than the right one. The relationship with the volume of the internal cavity shows the special adaptation of the right parts of the myocardium to pumping blood under conditions of low resistance, and the left parts against high pressure.
Life requires the heart to contract faster, increase the speed of blood flow and the volume of blood pumped. This is necessary under conditions of physical activity and stress. The need is regulated by the brain and hormones. Hyperfunction entails hypertrophy of the organ.
Classification
Typification is carried out on two grounds.
When assessing the characteristic anatomical changes in LVH, they call:
- Eccentric hypertrophy. It develops as a result of excess blood, its stagnation in the left ventricle, which is typical for defects of the aortic and mitral valves. The pathological process is determined by the expansion of the heart chamber, a slight increase in the muscle mass of the myocardium without direct thickening of the wall itself. Restoration is very difficult and is aimed at eliminating the root cause. Long-term course is associated with fatal complications.
- Concentric hypertrophy of the left ventricle. Inherent in hypertension. Approximately 85% of experienced patients have a history of thickening of the ventricular walls. Over the years, the process gets worse, especially if there is no proper treatment. The risk to life is determined to be 15% over a 5-year period with a developed form.
Hypertrophy in heart disease
In the compensation stage, muscle hypertrophy should be regarded as an important adaptive property of the heart. It allows the myocardium to perform intensive work for a long time. The likelihood of decompensation depends on the functional state of muscle tissue and its reserve capabilities.
The right parts of the heart suffer more from aortic valve defects and mitral stenosis. Left ventricular overload is most often associated with arterial hypertension and increased resistance (90% of cases).
During the compensation stage, the heart cavity lengthens, which is called “active dilation.” Subsequently, the chamber expands (passive dilatation). It is known from practice that hypertrophy of the left ventricular muscle well compensates for aortic valve defects and mitral regurgitation in children.
Great importance in prognosis and treatment is given to compensatory hypertrophy of the right ventricular muscle in acute left ventricular infarction. It has been established that it is the second, less adapted, ventricle that takes on an increased load in order to “help” in pumping blood. This means that coronary insufficiency, most often resulting from ischemia in the left coronary arteries, must be treated taking into account possible hypertrophy of the right ventricle.
Another mechanism for the growth of myocardial mass is observed in cardiomyopathies.
Stages of development of LVH
Another way to classify pathological changes is to stage them. The assessment is carried out based on clinical signs and the degree of functional deviations.
- First stage. Initial. Normally, the thickness of the left ventricular myocardium is 7-11 mm. As the defect develops, the wall may thicken. Another option is dilatation (stretching) of the chamber itself without increasing the wall thickness. Both options are dangerous. During the first stage, there are no symptoms, the patient is unaware of the problem. An increase in anatomical structures occurs up to 12-13 mm, no more. Compensation is full, complications occur extremely rarely. It must be borne in mind that in men the outer shell is by default 0.5-1 mm larger.
- Second stage. Moderate. The thickness of the hypertrophied wall is 13.1-14.5 mm. There are pronounced symptoms from the cardiac structures, the brain and nervous system as a whole, and the excretory tract in case of kidney damage. The risks are great. Death occurs in 20% of cases; young people tolerate deviations better, because their prognosis is not so clear.
- Third stage. In some classifications it is considered extreme, while other specialists and theorists also identify a fourth, terminal. In essence, they are one. The thickening is more than 14-15 mm, and there is a generalized dysfunction of the body. Lack of blood circulation leads to tissue hypoxia. Recovery has no prospects.
Enlargement of the left ventricle of the heart is classified by shape and severity. This combined classification is used everywhere in clinical practice.
Classification and severity
HFMD is a multifaceted pathology, as it differs in the types and severity of trophic changes. Classification of the disease allows us to establish the degree and identify a possible threat to the life and health of the patient.
Depending on the cause, LVH can be:
- physiological or working - characterized by a gradual smooth load, and does not lead to dire consequences, occurs among athletes;
- pathological or replacement – caused by pathological influences of internal and external factors.
Classification by severity:
- Severe hypotrophy - myocardial density during contraction is 25 mm.
- Moderate severity - the muscle layer increases from 21 to 24 mm.
- Moderate LVH – the myocardium increases from 15 mm.
Classification of the disease according to morphological features:
- Symmetrical. With this type of pathology, the increase in volume occurs evenly, affecting the walls of the cavity.
- Eccentric. The affected area includes the interventricular septum, less often the pathological process spreads to the side walls or the apex of the cavity.
How the pathological process, in the form of an increase in myocardial volume, affects blood circulation is distinguished:
- No obstruction. Changes in the volume of the muscle layer affect blood flow in minimal quantities
- With obstruction. The contracted ventricle compresses the aortic ostium and blocks blood flow, which aggravates hypertrophy.
Why is hypertrophy dangerous?
Complications of myocardial structure disorders pose a direct threat to human life and health:
- Stroke. Acute drop in the intensity of nutrition of cerebral structures. There is a double risk. On the one hand, persistently elevated blood pressure threatens the development of hemorrhage, that is, rupture of a blood vessel in the brain. On the other hand, the heart itself is not able to adequately provide nerve tissue. This results in an increased risk of both ischemic and hemorrhagic stroke. What comes first is the question. Patients with an eccentric form of the pathological process are at less risk.
- Heart attack. Necrosis of cardiac structures. A natural result of the inability to provide oxygen to oneself. It begins in the form of coronary artery disease, then worsens and transforms into an emergency condition.
- Cardiac arrest as a result of the development of severe arrhythmias. The electrical activity of the ventricles increases, which leads to early death in patients of all ages.
- Vascular dementia. Dementia. Reversible in the initial stages. Then, even if treatment is successful, a neurological defect is possible.
- Fainting. May cause injury.
Prevention of complications is one of the goals of therapy.
Principles of therapy for LV pathology
Treatment is carried out comprehensively, the main goal is to eliminate or minimize the factors that led to hypertrophy. The patient must reconsider his lifestyle and take the following measures:
- to refuse from bad habits;
- balance your diet (the Mediterranean diet is considered optimal);
- establish a healthy daily routine, the correct ratio of periods of sleep and wakefulness;
- minimize stress and a number of other experiences;
- organize moderate physical activity.
For LV hypertrophy, the doctor may prescribe the following medications:
- Nadolol, Propranolol, Atenolol, which belong to the group of beta-blockers;
- Disopyramide or Amiodarone for heart rhythm disturbances;
- drugs from the group of calcium channel blockers.
Failure to follow the doctor’s recommendations may result in the development of the following complications:
- progression of coronary heart disease, in which the heart does not receive the amount of oxygen and nutrients necessary for normal functioning;
- arrhythmias, that is, abnormal rhythm of the heart;
- myocardial infarction, that is, the death of some heart cells;
- sudden cardiac arrest.
All these complications most often result from atherosclerosis of the coronary vessels, congenital and acquired heart defects. And myocardial hypertrophy is one of the manifestations of these pathologies.
Left ventricular hypertrophy on ECG images
Thus, the electro- and echocardiographic method can detect pathology and its cause. These studies are carried out whenever you contact a cardiologist with complaints about the functioning of the heart. A careful and attentive attitude towards the health of yourself and your loved ones will help prolong your life.
You can learn more about the symptoms, causes and treatment of left ventricular hypertrophy from the video:
Causes
Left ventricular myocardial hypertrophy develops as a result of exposure to cardiac and vascular factors. It is extremely rare for other moments, some do not have a pathogenic background at all.
A sample list is:
Heart attack
Transported to the recent past. The result is tissue sclerosis, that is, their replacement with scar structures. Hence the increased load on the hearts, due to the need to pump blood more actively against the background of reduced resource and capacity of the myocardium.
There is a whole group of forms of the pathological process. Recovery does not make sense in the later stages. Early treatment involves lifelong medication.
Ischemic disease
Presents with the same symptoms as a heart attack. The only difference lies in the intensity of the destructive phenomena. During IHD they are slow and gradual.
Acute necrosis develops later, when the process reaches a certain critical mass. Treatment is systematic. Inpatient care is needed 1-2 times a year. Carried out as planned.
Inflammatory pathologies of cardiac structures
Myocarditis as the main type. It is predominantly of infectious origin.
Requires long, thorough recovery in a specialized hospital. Without help, destruction of muscle tissue and atria occurs.
The autoimmune type develops less frequently and has a milder course. Left ventricular hypertrophy turns out to be a complication, it is almost inevitable.
Development can be avoided only by starting therapy within 24-48 hours from the onset of the process.
Mitral valve defects
Stenosis, complete fusion, prolapse. They provide regurgitation (reverse flow) of blood into the previous chamber of the muscular organ.
A sufficient amount of liquid connective tissue is released into the aorta. Hence hypoxia and reflex intensification of cardiac activity. This is a compensatory mechanism.
Recovery is strictly surgical, in an inpatient setting. The prospects for complete cure are good if therapy is started early. The more significant the anatomical defect, the worse the prognosis.
Aortic valve defects
It covers the entrance to the largest artery, preventing blood from returning back to the ventricle. If the work is disrupted, regurgitation and stagnation of liquid connective tissue occurs. Again, the compensatory mechanism is activated. Treatment is surgical. The forecasts are identical to those in the previous case.
Cardiomegaly or bovine heart
May be a type of hypertrophic cardiomyopathy. It is hereditary, less commonly acquired.
It makes itself known by abnormal thickening of the muscle layer along its entire length.
Over time, such an organ loses its functionality. The only chance to save the patient is early transplantation.
Arterial hypertension
A persistent increase in pressure leads to an increase in the load on the left ventricle as the main structure responsible for the release of blood into the systemic circle.
Patients with experience all have hypertrophy; usually it does not manifest itself, but this is up to a certain point.
The heart of an athlete
An approximate name for the changes that occur in the cardiac structures of persons professionally engaged in physical activity.
The chambers become overfilled with blood; in order to pump more quickly, the body modifies the structure of the heart. Volume overload affects the general condition when the patient stops exercising.
There are relatively few causes of thickening of the walls of the ventricular chamber, which simplifies diagnosis.
Treatment of left ventricular myocardial hypertrophy
Treatment of the disease primarily focuses on the underlying cause that caused its development.
Eliminating Risk Factors
Since hypertension is a common cause of LVH, the main direction of its treatment is normalization of blood pressure.
For successful treatment, it is important to eliminate those factors and habits that usually lead to the development of the disease. Normalizing blood pressure is the very first and most important step. See your doctor regularly, buy a tonometer - this way you can control your blood pressure. Try to eliminate all possible sources of stress and anxiety, since excess cortisol and norepinephrine are also risk factors. Equally important in treatment is a healthy lifestyle and the elimination of bad habits.
Correction of arterial hypertension
Treatment for high blood pressure includes medications and lifestyle changes. Some of the medications that work to correct hypertension may also prevent further increase in left ventricular muscle tissue. Here are the groups of drugs prescribed for arterial hypertension:
- ACE (angiotensin-converting enzyme) inhibitors help dilate blood vessels, lower blood pressure, normalize blood flow and thus reduce the load on the heart. Examples of drugs: Enalapril (Vazotec), Captopril (Capoten), Lisinopril (Prinivil, Zestril). Medicines in this group in some cases cause an irritating cough, but the therapeutic effect is often more important. If the side effects are severe, the attending physician may choose other means.
- ARBs, or angiotensin receptor blockers, have many of the properties of ACE inhibitors, but do not cause coughing in the patient. Examples of drugs: Losartan (Cozaar), Valsartan.
- Thiazide diuretics help the kidneys get rid of excess water and sodium ions, thereby reducing total blood volume and blood pressure.
- Beta blockers reduce heart rate, lower blood pressure and prevent some of the harmful effects of stress hormones - cortisol and adrenaline, which are, although not the main factor, influencing the development of hypertension. These drugs include Bisoprolol, Carvedilol, Metoprolol, Atenolol (Tenormin).
- Calcium channel blockers prevent the entry of calcium into the cells of the heart tissue, reducing myocardial contractility, relaxing the muscle tissue of the vascular walls, having a diuretic effect and thus lowering blood pressure. Calcium antagonists include the following drugs: Nifedipine (Procardia), Verapamil (Calan, Covera, Veleran), Diltiazem (Cardizem, Tiazac).
Healthy lifestyle
Lifestyle changes can help lower your blood pressure and prevent the development of symptoms of left ventricular hypertrophy. Please note some important guidelines:
- Get rid of excess weight. Losing just 3–5 kg helps normalize blood pressure and reduces the risk of myocardial hypertrophy;
- limit the amount of salt in your diet, since its excess inevitably leads to increased blood pressure;
- do not abuse alcohol, drink it in small quantities, and also give up cigarettes;
- Exercise regularly, half an hour or an hour of moderate physical activity every day strengthens the heart without overtraining it. Walk, run, do fitness or yoga more often. If you engage in weightlifting, such as bodybuilding, or your work involves stress, consult a cardiologist, he will recommend ways to prevent hypertension and myocardial hypertrophy.
How does the disease manifest itself?
The list of symptoms is determined by the severity of the underlying process, the duration of pathological changes and some other factors.
The average list looks like this:
- Dizziness. It develops in fits and starts. Episodes can be repeated up to several times within one day. The intensity of the sign varies. From a slight discomfort to the inability to navigate in space. The cause is cerebellar ischemia of varying severity.
- Cephalgia. Dull, pressing headache. Localized in the back of the head, also the crown. Occurs sporadically. Lasts from an hour to four. In the event of a hypertensive crisis, until it is relieved.
- Discomfort in the chest. It feels like pressure, as if a stone had been placed. May indicate relatively harmless conditions or a developing heart attack.
You need to listen to the power of manifestation, does it intensify with breathing or movement? If yes, there is no need to talk about cardiac origin.
Pain that does not respond to these factors and lasts less than 10-20 minutes is of the angina type. More than that, a heart attack is suspected.
- High blood pressure numbers. The correction does not produce an effect, or it is temporary, short-term. A constant change of drugs or an increase in dosage is required (and often all together). The resistant pathological process is caused by hypertrophy and itself spurs it. A vicious cycle arises.
- Suffocation. Usually as a result of cardiac asthma. Develops against the background of a long-term deviation, as a complication. May lead to pulmonary edema. Without correction, the condition ends in the death of the patient. Has a tendency to a chronic relapsing course.
- Arrhythmias. According to the type of tachycardia, ventricular fibrillation. Less common extrasystoles. More often, “dangerous” forms arise, leading to lethal results in the short term. The manifestation intensifies against the background of physical activity. Excessive activity (assessment characteristic) leads to cardiac arrest.
- Weakness, decreased ability to work, drowsiness. It appears gradually. In severe cases, disability occurs. The patient is unable to perform even household duties, not to mention professional ones.
- Edema of the lower extremities. Develops towards evening. The symptom indicates a malfunction of the excretory tract, in particular the kidneys are affected.
- Fainting states. Repeated evidence supports a severe pathological process involving cerebral structures. A stroke is possible in the near future.
- Blue discoloration, pallor of the nasolabial triangle, skin, mucous membranes.
The clinical picture may not be complete. There must be at least 2 symptoms. In rare cases, there may be no signs.
Traditional methods of treatment
It is impossible to remodel the myocardium using folk remedies, returning it to its previous size and functions. For therapeutic purposes, well-known recommendations for lowering blood pressure, strengthening the vascular wall, and improving myocardial contractility are used.
It is better to buy plant materials in pharmacies, where quality, proper collection and drying are guaranteed.
- You can make your own drops and tincture from lily of the valley. The collected flowers are placed in a dark bottle and filled with vodka. It takes 2 weeks to insist. After straining, take no more than 15–20 drops three times a day. It is suggested to pour boiling water over the remaining pulp for an hour, then drain the water, and take the flowers within 24 hours after 3 hours, no more than twice a week.
- Garlic tincture with lemon and honey is recommended to almost all lovers of a healthy lifestyle. It helps delay the atherosclerotic process.
- A decoction of St. John's wort leaves (100 g of dry herb per 2 liters of boiling water) with honey can be stored in the refrigerator. Not indicated for people with liver disease.
People with allergies to flowers and plants should use folk remedies with caution.
Diagnostics
It is carried out by a cardiologist using instrumental, less often laboratory methods. The latter do not provide sufficient information.
List of activities in correct order:
- Collection of complaints and medical history. To objectify symptoms and record them for further analysis.
- Auscultation. Listening to heart sounds. Variations are possible. With valve defects, a sinus noise is detected, typical of regurgitation.
- Blood pressure measurement. It is consistently above normal in almost 90% of cases. Also heart rate. Tachycardia and accompanying arrhythmias are typical.
- Daily monitoring. Registration of the above indicators for 24 hours. Repeated execution is possible.
- Electrocardiography. There are specific signs, but it is prescribed to clarify the degree of preservation of the functional capabilities of the heart.
- Echocardiography. Method of visualization of cardiac structures. It is considered fundamental for the early detection of a problem or determining the nature of the defect and the prospects for its further progress. It is possible to diagnose asymmetric changes (a special coefficient is used, the problem is identified if it is more than 1.3).
- MRI as needed.
- General and biochemical blood tests according to indications.
Such techniques are usually sufficient.
What diseases does this happen in?
- Left ventricular hypertrophy occurs in young people who are constantly involved in sports. Their heart muscle works intensely during training and naturally increases its mass and volume;
- occurs in diseases associated with difficulty in the exit of blood from the left ventricle into the aorta and with an increase in vascular resistance in the body;
- this ECG sign may be the first symptom of severe heart defects - aortic stenosis and aortic insufficiency. These diseases cause deformation of the valve separating the left ventricle and the aorta. The heart works under a heavy load, but the myocardium copes with it for a long time. A sick person does not feel any discomfort for a long time;
- Left ventricular hypertrophy occurs in a serious disease – hypertrophic cardiomyopathy. This disease is manifested by severe thickening of the walls of the heart. Thickened walls “block” the exit from the left ventricle, and the heart works under load. The disease does not appear immediately; shortness of breath and swelling gradually appear. In advanced cases, this disease may be an indication for heart transplantation.
- This is one of the manifestations of heart damage due to arterial hypertension. It can also develop with a moderate but constant increase in pressure. It is precisely to stop the progression of left ventricular hypertrophy that recommendations are aimed at constantly taking medications for hypertension, even with normal pressure.
- may appear in older people with severe atherosclerosis of the heart valves. This narrows the opening from the left ventricle into the aorta.
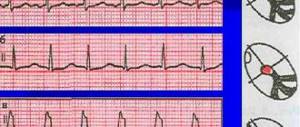
Signs on ECG
- Negative T wave in lead V5-6.
- Increased peak (amplitude) of S in V1-2.
- Positive T in V1.
- Deformation of the ST interval, its unevenness V6 is more than normal, V4 is below.
These are typical signs of left ventricular hypertrophy on an ECG, but despite the obviousness of the problem, doctors often make mistakes, mistaking the change for a variant of the physiological norm. False diagnosis of arrhythmic processes is also possible.
Decoding a cardiogram requires qualifications and a degree of professional intuition.
Treatment tactics
The basis of successful therapy is drug treatment. This is especially important for arterial hypertension. The attending cardiologist knows well how to treat left ventricular hypertrophy. The following specialist recommendations must be strictly followed:
- regular and long-term use of specially selected antihypertensive drugs;
- the use of symptomatic medications that improve the functioning of the cardiovascular system;
- lifestyle correction with the elimination of risk factors (smoking, alcohol, heavy physical labor, reduction in sports activity);
- rational nutrition with a decrease in salt in food and an increase in plant foods (vegetables and fruits);
- weight loss;
- physiotherapy.
In severe forms of the disease and a high risk of complications, surgical treatment will be required (surgery on the valve apparatus, elimination of stenosis, antiarrhythmic surgical interventions).
Left ventricular hypertrophy of the cardiac muscle is a syndrome indicating the presence of physiological or pathological reasons for the pronounced load on the heart. It is necessary to find out the main causative factor and begin effective therapy as early as possible so as not to create conditions for deadly complications.
Treatment methods
Surgical and conservative. Depends on the etiology of the process, the severity of symptoms.
Medicines:
- Beta blockers. It is recommended to give preference to Carvedilol. To relieve acute attacks of tachycardia - Anaprilin.
- Drugs to prevent cholesterol deposition: Atorvastatin, Policosanol. Antithrombic. Aspirin-Cardio.
- Antiarrhythmic. Restore normal contraction frequency. Hindin as the main one.
- Nitroglycerin for the relief of acute pain. In the event of such an episode, it is recommended to call an ambulance.
- Antihypertensives of several pharmaceutical groups: ACE inhibitors (Perindopril), calcium antagonists (Verapamil or Diltiazem).
- Mild diuretics (Veroshpiron, Spironolactone).
- Sartans. To reduce the load on the myocardium.
Surgery is prescribed for valve defects or critical narrowing of an artery.
Recovery methods involve stenting a narrowed area (artificial expansion by mechanical means in case of severe atherosclerosis) or prosthetics of affected structures that have lost their functional activity.
Lifestyle changes play a role, but not so significant. It is imperative to give up smoking and alcohol, normalize sleep, and minimize physical activity. Salt consumption is about 5-7 grams. Diet is advisable.
Attention:
Folk remedies are strictly contraindicated. It is not known how the affected cardiovascular system will react to such amateur activity.
Treatment
If the patient is identified at the stage of formation and compensation, then special treatment may not be required. Enough heart support:
- optimal physical exercise;
- work and rest schedule;
- lack of excess weight;
- proper nutrition with sufficient amounts of unsaturated fats and vitamins;
- cessation of slagging and intoxication with nicotine and alcohol.
Depending on the severity of the patient’s condition and the likely possibilities of therapeutic measures, the patient is assigned a temporary or permanent disability group, a transfer to another job, and restrictions are recommended.
In drug therapy, preference is given to an antihypertensive set of drugs for hypertension, vasodilators for symptoms of ischemia and a previous heart attack.
In order to stop the progression of overload processes in the heart muscle, the following drugs are actively recommended:
- β-blockers - to reduce the oxygen demand of cells, restore rhythm (Atenolol, Nadolol, Metoprolol);
- calcium channel blockers - actively help maintain normal blood pressure in the vessels and reduce resistance (Diltiazem, Verapamil);
- ACE inhibitors - necessary in the treatment of hypertension and heart failure (Diroton, Enalapril);
- sartans are a relatively new class of medications that allow you to reduce the mass of hypertrophied muscles (Losartan, Candesartan).
Forecast
Relatively favorable due to the long and sluggish development of the pathological change. At the same time, it is determined by the main diagnosis.
In its pure form, without treatment, complications occur in 20% of cases. Even more often in later stages.
The possibility of radical therapeutic intervention suggests a better outcome.
However, with generalized hemodynamic and dystrophic disorders, everything is much worse. There is a chance for a complete cure, but the myocardium itself will not decrease in size.
This shouldn't be scary. With complex therapy, you can live a long time, with minimal restrictions in daily activities.
Echocardiography for LV hypertrophy
In many cases, an ECG for hypertrophy is not the only way to establish the disease. A cardiologist will definitely prescribe an echocardiogram (ECHO). With its help you can establish the following signs:
- thickening of the walls of the left ventricle compared to the right;
- increase in the size and volume of the left ventricle relative to the right;
- decrease in ejection fraction indicators.
Display of LV hypertrophy on echocardiography
Traditional treatment recipes
Before using any folk recipes, you need to check with your doctor. After analyzing the stage of development of the disease, he will determine whether left ventricular hypertrophy of the heart can be cured without serious medications and surgery.
The most effective traditional medicine recipes:
- St. John's wort decoction has a calming effect and will be beneficial for the heart muscle. To prepare, you need to pour 100 grams of dry raw materials into an enamel bowl, add 2 liters of clean water and boil for 10 minutes. After this, the pan should be wrapped in a towel and left for at least an hour. Strain the infused broth through cheesecloth and add 200 milliliters of May honey. The mixture should be poured into a glass container, covered with a lid and stored in the refrigerator. Take the decoction three times a day, three tablespoons, 30 minutes before meals for 1 month.
- Drops from lily of the valley flowers . You will need a half-liter dark glass jar, fill it with fresh flowers and fill it with alcohol. Cover the whole thing with a lid and place it in a place where the sun's rays do not reach it for two weeks. After this time, pass through gauze and drink 15 drops, after dissolving in a small amount of water, three times a day before meals. The course of treatment is 2 months.
- A decoction of cornflowers is effective for headaches, in addition, it cleanses the blood. To prepare, you will need 1 tablespoon of dry cornflowers, which should be placed in a ceramic pan, add 250 milliliters of boiled water and place in a water bath for a quarter of an hour. Then, the cooled broth should be strained and taken 100 milliliters three times a day 20 minutes before meals. The course of treatment is 2 weeks.
- Hypertrophy can be treated with infusion of Adonis vernacular , but this is a poisonous plant, so it is important to follow the recommended dose exactly. You will need 1 teaspoon of herb, which you need to pour 200 milliliters of boiling water and leave under a closed lid for half an hour. Strain the infusion and take 1 tablespoon before meals three times a day.
- If you are worried about severe shortness of breath, fresh nettle will help . Fresh leaves and stems need to be chopped, separated 5 tablespoons into a jar, added the same amount of honey and placed in a place where daylight does not reach. Every day, for two weeks, the medicine must be shaken. Then heat it in a water bath until liquid and strain. Take 1 tablespoon three times a day before meals. It must be stored in the refrigerator.
- A decoction of wild rosemary helps maintain heart function. To get it you need to mix 3 tablespoons of motherwort, 2 tablespoons of wild rosemary, 2 tablespoons of dried herbs and 1 tablespoon of kidney tea. The ingredients must be placed in an airtight container. Then separate 1 tablespoon of the mixture and pour 300 milliliters of boiling water. Boil for three minutes and leave the broth for 4 hours. After this, pass through gauze and drink 100 milliliters warm three times a day half an hour before meals.
- A decoction from young shoots of blueberry bushes . To prepare it, you need to pour 1 tablespoon of raw material into a glass of water and boil for 10 minutes. It should be taken one sip in the morning at lunchtime and in the evening.
- A very healthy berry, cranberry . Grind fresh berries with sugar and store in the cold. Take one tablespoon after meals.
- Herbal tea soothes and improves health . For preparation you will need 1 teaspoon of hawthorn, fragrant rue and valerian flowers. Add 500 milliliters of boiling water to the ingredients and leave for half an hour. Then filter, divide into three portions and drink throughout the day for three months.
lechenie-narodom.ru
Classification by ECG for left ventricular hypertrophy
Author Romhilt-Estes characterizes LVH on the ECG using a five-point system. The evaluation criteria allow a complete clinical case to be examined for timely treatment of a progressive health problem:
- Branch V1: in the negative phase, the P wave, current from 0.04 s, corresponds to 3 points.
- Branch V6: presence of ST and T wave. When using glycosides, 1 point is added, in the absence of glycoside prescription - 3 points.
- Branches V5 and V6: periodicity from 0.05 s adds 1 point.
- The width of the QRS complex is greater than or equal to 0.09 s, 1 point is given.
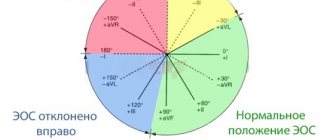
- Deviation of the EOS to the left side is 30 degrees less than or equal to 2 points.
Voltage criteria on the ECG are decisive in identifying hypertrophy. R and S from 20 mm, the height of the S tooth in branches V1 and V2 is more than 30 mm, and R in V5-V6 is from 10 mm. For the presence of each sign - a bonus of 1 point. Large deviations from the norm require re-diagnosis, and for each increase 1 point is added to the total. This is an effective diagnostic tool that provides a clear picture of progressing pathology using the ECG.