A malignant tumor of the retina (retinoblastoma) is a cancer that is most often detected in childhood. This condition is often congenital, but diagnosing it in newborns is quite difficult. Most often, this disease is detected at the age of two years. Almost all cases of retinoblastoma (up to 98%) are detected in patients under five years of age.
This malignant neoplasm occurs in all countries, approximately one case of retinoblastoma is registered per 20 thousand newborns. Boys and girls get sick equally often. Most often the tumor is unilateral, but in 20-30% of cases there is bilateral eye damage (the diagnosis of the tumor occurs at an earlier age).
Feature of the disease
The eye has a complex structure. The small eyeball contains protection from external negative factors, an optical system for clear perception of objects, and a structure that perceives light waves. This is a hereditary disease in children, which is formed from the cells of the retina of the eye. The tumor grows from the retinal pigment epithelium and provokes:
- loss of vision;
- spread of secondary lesions to the brain and other organs;
- increased intraocular pressure.
Retinoblastoma mainly appears in the first 2 years of a child’s life. Currently, the incidence of this disease is 1 case per 10-13 thousand newborns.
Signs of retinoblastoma of the eye
Although retinal tumors have several characteristic warning signs, they are very difficult to spot in children. So,
Loss of vision will be one of the first signs, which is difficult to diagnose. Children under 2 years of age may not notice a decrease in visual acuity. This period is characterized by loss of visual fields and blurred images.
Cat's eye syndrome (white pupillary reflex) is one of the first symptoms. It is most often noticed by parents. From a certain angle, it seems that the baby’s eye (or eyes) sparkled “like a cat’s.” Sometimes there is a feeling that the eye has turned white; the swelling is noticeable through the pupil. This symptom appears quite early, the tumor is clearly visible during an ophthalmological examination. Timely diagnosis allows us to give good prognosis for vision preservation.
Strabismus is also one of the first symptoms of a retinal tumor. This sign is easy to notice and often detection of retinoblastoma occurs during examination regarding complaints of childhood strabismus.
Other symptoms. In later stages, the tumor affects the ENT organs and the nervous system. These specialists issue a referral to an ophthalmologist. In the later stages of the disease, the child becomes lethargic, gets tired quickly (a sign of intoxication), and complains of severe headaches.
Types and forms
According to the prevalence of retinoblastoma in children, this disease is divided into types such as endophytic and exophytic. The endophytic type of pathology refers to intraocular. When malignant cells grow, the eyeball is completely affected. In this case, intraocular pressure increases slightly, the retina detaches and glaucoma forms.
The exophytic type of disease is characterized by the spread of malignant cells beyond the eyeball. At the same time, they cover the mucous membranes, sclera and blood vessels. Moving through the visual cells, malignant neoplasms metastasize to the nervous system and lymph nodes.
According to the clinical course of the disease, several stages are distinguished. The resting stage is characterized by the absence of pronounced clinical symptoms. Parents may only notice a small white spot that has formed. As it progresses, binocular vision is lost, and the child's eye begins to squint.
The stage of glaucoma is characterized by more pronounced symptoms. The child begins to be afraid of the light, and his eyes water. At this stage, the iris is affected. The outflow of intraocular fluid is disrupted, pressure increases, and very severe pain is felt. Glaucoma begins to develop.
The germination stage is considered the most dangerous, since the patient experiences protrusion of the eyeball. Cancer cells begin to metastasize into the soft tissues located in the eye area. The final stage is characterized by the spread of malignant neoplasms to other organs. Cancer cells are carried along with the blood to the meninges, lymph nodes and optic nerves. The patient experiences severe weakness and other signs of pathology.
Why does eye cancer occur?
Retinoblastoma in children is a dangerous oncology, and parents may wonder why this form of cancer develops? The main factor is genetic predisposition.
In other cases (60% of all situations), when there is no history of this type of cancer in the family, only one visual organ is affected. They are less likely to develop the same type of cancer in the other eye. This pathology is called unilateral retinoblastoma.
Children who have hereditary retinoblastoma have a high probability that the symptoms of oncology will soon spread to the second eye. For this reason, doctors recommend regular examinations of the healthy eye for 28 months, every two to four months.
After the patient has completed treatment, it is recommended to take special preventive measures in order to avoid relapse of the disease. It is recommended to carry out measures until the child turns five years old.
Causes
Retinoblastoma in children can be hereditary or acquired. The hereditary form of the disease is genetic in nature. Mostly, parents who had retinoblastoma in childhood have children born with the same disease. This form develops rapidly and is accompanied by other disorders and pathologies.
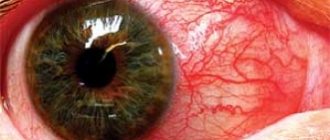
A malignant tumor of the retina can occur as a result of the negative impact of environmental factors and consumption of genetically modified foods. This form of the disease often affects only one eye. This tumor appears at an older age, but is much easier to treat. This pathology can be one of the causes of red eyes in a child. It is by this sign that the presence of the disease can be determined.
Etiology and pathogenesis
The etiology of retinoblastoma is still unknown.
Risk factors for the development of sporadic congenital tumors include the advanced age of the mother and father, and the father's long-term work in metallurgy. Unilateral retinoblastomas usually develop as a result of somatic mutations affecting only the retinal cells. Bilateral neoplasms are often the result of mutations in germ cell chromosomes. Hereditary forms of retinoblastoma are observed in approximately 40-50% of patients. Healthy parents who have one child with retinoblastoma have a 6% chance of developing the tumor in subsequent children. In cases where several children in a family are sick, the risk of developing blastoma in subsequent children increases to 50%.
More than half of children born with this tumor are born to parents who had retinoblastoma in childhood.
Main symptoms
Among the main symptoms of retinoblastoma in children are the following:
- white spot on the pupil;
- decreased vision;
- photophobia;
- lacrimation;
- changes in the mucous membrane of the eye.
Pain in the area of the visual organs may also be observed, and intraocular pressure increases as a result of the outflow of fluid. This leads to the formation of secondary glaucoma. When a pathology develops in a baby, one pupil is larger than the other, which should definitely alert parents.
The germination stage is accompanied by a slight displacement of the eyeball forward. This is due to the tumor growing into the paranasal sinuses, located between the membranes of the brain. If a child has red eyes, the reasons for this may be related to the development of retinoblastoma. In this case, you should definitely see an ophthalmologist, since in the initial stages it is much easier to get rid of the existing disease.
The metastasis stage is characterized by the fact that metastases spread to other organs, in particular the liver, brain, and bones. At the same time, the patient’s well-being significantly worsens. Common symptoms include symptoms of intoxication, severe weakness and headache.
Symptoms
The clinical picture among children is largely determined by the size of the tumors and their location. A characteristic sign of the pathology is leukocoria, which is popularly called cat's eye syndrome. Its manifestation can be noticed if the tumor has grown to a fairly large size or with retinal dissection. In this case, the tumor protrudes beyond the lens and can be easily seen through the pupil.
Depending on the stage of the pathology, the symptoms in each case are different:
- Stage T1 (rest) - there are no obvious signs here yet, but during the examination you can notice leukocoria, or cat's eye (as noted above), which is due to the tumor being visible through the pupil. Patients may also experience strabismus and loss of full stereoscopic vision.
- Stage T2 (glaucoma) - a good photo specialist of retinoblastoma in children can detect all the signs of an inflammatory process in the membranes of the eye (mucous, iris, vascular), which is accompanied by their redness. In addition, lacrimation and photophobia are observed. And due to the fact that the outflow of internal fluid is impaired, pressure in the eye increases, which, in turn, leads to pain.
- Stage T3 (sprouting) - in this case, the tumor has already acquired extensive dimensions, and the eyeball begins to protrude forward, beyond the orbit. In addition, the tumor affected the surrounding tissues, the paranasal sinuses, including the space between the soft and arachnoid membranes of the brain. Not only does this pose a danger in terms of vision loss, but there is also a threat to the patient's life.
- Stage T4 (metastasis) – repeated foci of retinoblastoma tumor can be in the liver, bone tissue, spinal column or brain. The spread of metastases occurs through the circulatory and lymphatic systems of the body, the optic nerve, and brain tissue. In this case, there are many more symptoms: severe intoxication, weakness, and the appearance of vomiting and headache.
Often, the presence of a tumor can be determined even before the tumor leaves the orbital area. Therefore, the most important thing here is to carry out diagnosis in a timely manner.
Carrying out diagnostics
If your baby has one pupil larger than the other, strabismus, or decreased vision, this may be a sign of retinoblastoma. In this case, you should definitely contact an ophthalmologist for an examination. For diagnosis, an examination of the fundus of the eye is performed, since with ophthalmoscopy the neoplasm can be seen quite easily.
Children whose parents have suffered the same disease must be registered at the dispensary, since there is a high risk of hereditary transmission of the pathology. To clarify the diagnosis and determine the extent of the disease, it is necessary to conduct a number of diagnostic studies, in particular, such as:
- tomography of the affected area;
- brain biopsy;
- ultrasound diagnostics of the abdominal cavity to detect metastases;
- X-rays of light;
- blood and urine tests.
Due to the fact that children with retinoblastia often have pathologies and disturbances in the functioning of internal organs and systems, additional consultation with an ENT specialist and a neurologist may be required.
Symptoms
Where is the tumor located in retinoblastoma, look in the picture:
As tumor formation progresses, the following visible signs appear:
- Lightening 1 or 2 eyes in flash photos. If one of your family members notices this effect, you should immediately contact an ophthalmologist for diagnosis. Leukocoria - light spots in the pupils. In a normal state, the flash will make vision in red light, but not in brightened light. This means that the tumor has begun to block blood vessels and capillaries. In addition, this symptom can also manifest itself in a darkened room. This factor does not always indicate the presence of a problem, so you need to visit a doctor.
When can you suspect retinoblastoma in a child? See how the pathology manifests itself in the photo:
- Deterioration in the quality of vision. The most obvious symptom of the malignant development of a retinal tumor is a failure in the functionality of the rods and cones or their deformation due to the overlap of the tumor. The prognosis may have a disappointing result if you do not intervene in time. The child will most likely lose his sight.
- Deviation of the visual axes is strabismus, which manifests itself in childhood. It is necessary to understand that such a violation does not necessarily indicate oncology. Analyze your baby's daily routine, diet and bad habits. Perhaps behind the sidelong glance is watching TV at a distance of less than a meter or drawing pictures while lying with your head on the table.
- Pain syndromes, discomfort and lacrimation are secondary symptoms.
- Inflammatory processes, conjunctivitis, photophobia. If the child’s eyes are constantly red, and at certain moments have a light tint, it is necessary to urgently contact an ophthalmologist, and then an oncologist.
When the formation reaches a significant size, it tends to spread cancer cells to nearby vital organs, affecting them and causing serious inflammatory processes. Sometimes diagnostic x-rays reveal lightened spots in areas of the brain.
Signs of symptomatic manifestations of cancer in the brain include the following:
- Severe pain in the temples, on the back of the head or over the entire surface of the head. Conventional medications are not able to relieve pain.
- Manifestation of nausea and vomiting.
- Loss of consciousness, fainting.
- Epileptic seizures.
- Cramps.
- Poor memory, loss of concentration.
- Numbness of certain areas of the body.
- Malfunction of the vestibular apparatus.
- Impaired hearing, voice, vision, and breathing.
The formation of secondary cancerous foci of development in the brain is an extremely negative sign, which reduces the likelihood of recovery by 70 percent or more.
Also, metastases are most often fixed on:
- Bone tissue.
- Spinal cord.
- Liver.
When additional tumors appear in the body, the chance of survival decreases by 60%.
Features of treatment
Treatment of retinoblastoma depends primarily on the stage of the disease. Often the following is used for therapy:
- chemotherapy;
- radiation therapy;
- surgical intervention;
- cryotherapy;
- laser coagulation;
- thermotherapy.
If you start treatment in a timely manner and select the most effective therapy, you can maintain normal vision and health of the child. For bilateral lesions, techniques are selected separately for each eye.
The Institute of Eye Diseases provides complex therapy, which involves the use of several different techniques. Typically, tumor treatment begins with radiation therapy, since retinoblastoma cancer cells are characterized by a very high degree of sensitivity to the effects of radio rays. This technique is quite effective, but side effects include the formation of cataracts and secondary bone tumors. With localized radiation therapy, the risk of side effects is significantly reduced.
At the Institute of Eye Diseases, ophthalmologists prefer to use conservative treatment methods. If the tumor is less than 7 mm in size and is located in the anterior region of the eye, then cryotherapy is prescribed. If the tumor is located in the posterior sections and is less than 4 mm in size, then photocoagulation is indicated. When carrying out thermotherapy, infrared radiation and ultrasound rays are directed to the affected area.
In case of significant growth of tumor tissue, the addition of secondary glaucoma, and the impossibility of maintaining vision, an operation is performed to remove the eye, followed by the use of special artificial prostheses. When metastases form in the area of the optic nerves, the only method of treatment is chemotherapy in combination with the use of cytostatics.
Diagnosis of retinoblastoma
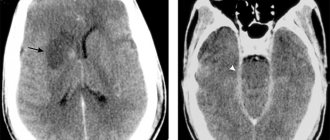
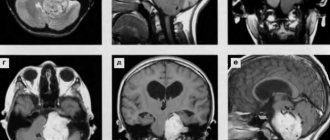
The diagnosis of a tumor is made on the basis of a computed tomography (CT) scan or a head scan using nuclear magnetic resonance (MRI). These methods are the most diagnostically valuable, since they make it possible to establish not only the presence of a tumor, but also how widespread it is and affects neighboring tissues, i.e. its stage, which is important for developing subsequent treatment tactics for retinoblastoma.
Ultrasound of the eye and chest, and osteoscintigraphy are also used - the latter to detect possible metastases. For this purpose, a lumbar puncture is performed, followed by a laboratory study of the cerebrospinal fluid. All these diagnostic tests in young children are performed under general anesthesia.
An important method for diagnosing retinoblastoma, which makes it possible to establish the cellular composition of the tumor, is a biopsy; in this case, it is performed during surgery to remove the tumor.
Surgical intervention
Retinoblastoma must undergo surgery. However, maintaining normal vision in the affected eye is not always possible. At the Fedorov Eye Microsurgery Clinic, treatment is provided using modern techniques that can quickly eliminate the existing problem and improve vision.
For small tumors, thermotherapy is used. This technique involves targeted exposure to high temperatures. Cryotherapy gives very good results when treating a small tumor that forms in the anterior part of the retina. The procedure involves freezing the tumor tissue using a special probe that is applied to the outer surface of the sclera.
In addition, in the presence of a small tumor, photocoagulation is prescribed. The operation is based on the destruction of blood vessels that feed vascular cancer cells. A laser beam is used for this.
The Fedorov Eye Microsurgery Clinic also provides laser treatment, which helps to quickly and effectively eliminate the existing problem in a minimally invasive way.
If retinoblastoma has spread significantly from the retina to other parts of the eye, the eyeball is completely removed, followed by implantation of an artificial lens. One of the most important aspects of the operation is to excise the optic nerve as deeply as possible.
If the tumor has spread beyond the eye, then the tumor is removed along with the bone walls of the orbit. After removal, prosthetics are performed.
Pathology treatment methods
Depending on the stage of retinoblastoma, an appropriate course of treatment is prescribed, and in a comprehensive manner. But here it is worth considering a number of factors. First of all, it is necessary to find out the area of coverage of the tumor in neighboring tissues, whether there are metastases in the body, etc.
Typically, comprehensive treatment includes the following:
- Surgical intervention.
- Radiation therapy.
- Chemotherapy.
Usually, you can get rid of the tumor through surgery, which is the main treatment for retinoblastoma. Previously, enucleation of the eye was carried out for this purpose, but now, thanks to modern innovative medical solutions, other effective methods have become available.
Chemotherapy
In combination with surgery, chemotherapy treatment can be carried out, which guarantees 80-90% cure. Chemotherapy is required for:
- significant intraocular damage;
- optic nerve invasion;
- orbital lesions;
- regional metastases.
Retinoblastoma is very sensitive to chemotherapy. Several cytostatics can be used for treatment at once. The best results can be obtained by combining drugs such as Carboplatin, Vepesid, Vincristine.
Chemotherapy can reduce the size of the tumor, which is why this technique is recommended before surgery. In addition, this technique is intended for systemic therapy in advanced cases.
Causes of the disease
In most cases, retinoblastoma is caused by a genetic factor. The hereditary type of oncology is often bilateral and progresses quite quickly. Over time, the tumor begins to dissipate and penetrate into nearby tissues. The reasons for the formation of accidental retinoblastoma have not been fully established, but there are several favorable etiological factors:
- the child’s consumption of large amounts of foods high in GMOs;
- polluted living environment;
- age of parents.
Other techniques
Treatment of a malignant neoplasm is carried out under the supervision of an ophthalmologist, oncologist and ophthalmic surgeon. The tumor is sensitive to X-ray radiation. Treatment is carried out in several sessions, and the dosage is selected by the radiologist purely individually.
Irradiation of a tumor is carried out remotely, when the X-ray source is located at some distance from the pathological focus. The contact method involves the use of applications of radioactive substances that are applied directly to the eyeball. However, in this case, the risk of complications increases, in particular, such as inflammation of the cornea, ulcers, and clouding of the lens.
The introduction of antitumor drugs into the body helps prevent the spread of a malignant neoplasm and reduce its size. Medications are injected directly into the tumor area or used as intravenous infusions. During treatment, anesthesia and a special table are used to secure the patient.
Features of radiation therapy
If there is even the slightest opportunity to preserve the organ of vision, then radiotherapy is applied to the affected eye. Due to the fact that the tumor is able to actively respond to X-ray radiation, this method of treatment is fully justified. In this case, the retina, vitreous body and the anterior segment of the optic nerve (at least 1 cm) must be in the area of influence of the device.
Thanks to special protective screens, clouding of the lens can be avoided, thus reducing the danger of this method of treating retinoblastoma. This, in turn, minimizes the harmful effects of therapy on the body.
And if we take into account that the patients, as a rule, are young children, then such an operation is performed using general anesthesia with the child fixed on a special table.
Eye prostheses
If the eyeball was removed during the operation, the child is taught to wear an artificial prosthesis. Its constant presence is required in order to prevent facial deformation as the child grows. In addition, the absence of a prosthesis can lead to eyelashes curling inside the eye socket, which leads to irritation of the mucous membrane.
A temporary prosthesis is inserted 6 days after surgery to remove the eyeball. After the swelling of the eye sac goes away, the child is given a permanent prosthesis. Prosthetics has 3 purposes at once, namely:
- cosmetic;
- functional;
- psychological.
Modern materials and technologies make it possible to produce prosthetics that are practically indistinguishable from real eyes. Prosthetic models skillfully imitate the movements of your own eyeball.
To make the resemblance to a healthy eye even more pronounced, a lens is placed on the surface of the prosthesis, which exactly repeats the shape, size and color of a healthy iris. Thanks to this, the child will not feel disabled.
Treatment of the disease
Currently, treatment of retinoblastoma in children is carried out in several ways:
- surgical intervention;
- laser therapy;
- cryodestruction;
- chemotherapy.
The basis of medical intervention is enucleation - this is the most common method of removing malignant tumors. Indications for implementation may include severe tumor growth, glaucoma, blindness and inability to restore vision. Already two months after such an operation, eye prosthetics can be performed.
Radiation treatment, the main purpose of which is to preserve vision. Often, such elimination of retinoblastoma is carried out in conjunction with cryotherapy. The operation is carried out with the introduction of an anesthetic, since the patients are mainly children under three years of age. Thanks to this, it is possible to achieve the best results in preserving the eye and restoring vision. In addition, the latest treatment methods include photocoagulation and thermotherapy, during which the tumor is exposed to ultrasound or infrared radiation.
Chemotherapy for retinoblastoma is used only in cases of distant metastasis of oncology.
With early diagnosis and proper treatment, it is possible to achieve the most favorable prognosis for the child’s recovery, since it is possible to save the cancer-prone eye and completely restore vision. The prognosis is less favorable in children with complicated course of the disease. Usually in such cases ocular prosthetics is performed.
What to do?
If you think you have Retinoblastoma
and the symptoms characteristic of this disease, then doctors can help you: an ophthalmologist, an oncologist.
Source
Did you like the article? Share with friends on social networks:
Possible complications
Complications occur when the disease becomes very aggressive, is not diagnosed in a timely manner, or is not treated correctly. With strong growth of retinoblastoma into the orbit, the risk of metastases increases significantly. The main complication of malignant neoplasm is relapse after therapy.
A tumor growing inside the eye can spread beyond the visual organs. Cancer often travels through the optic nerve and into the brain. This complication can lead to the death of the child. In some cases, the cancer travels through the walls of the eye and spreads to other internal organs throughout the body. If there are complications, there is a high risk of death, which is why diagnosis and treatment must be carried out in a timely manner.
The main thing about retinoblastoma
Retinoblastoma is a malignant tumor consisting of cells of the neuroectoderm of the retina. The disease affects the retina, choroid and orbit. Retinal tumors grow very quickly, metastases penetrate the brain through the optic nerve, from where they enter the bone marrow and tubular bones through the blood.
Stages of development of retinoblastoma according to the TNM system:
- The tumor occupies 25% of the fundus (T1).
- The neoplasm occupies 25-50% of the retinal surface (T2).
- Covers more than half of the retina and extends beyond it, but the intraocular location is preserved (T3).
- The tumor extends beyond the orbit (T4).
- Metastases in regional lymph nodes (N1).
- Metastases in the brain, bones and internal organs (MI).
Retinoblastomas account for 2-4% of all cases of malignant tumors in patients under 15 years of age. The tumor develops mainly in children under 5 years of age, most patients are children aged 2-3 years. The risk of occurrence does not depend on gender.
This tumor is a typical hereditary cancer. Many people who have had retinoblastoma have children with a similar diagnosis. The likelihood of a second child developing a tumor when retinoblastoma was diagnosed in the first is 6%. If there are several sick children in one family, the risk increases to 50%. Despite its malignant nature, the disease is curable. Timely treatment ensures survival of the vast majority of patients.
Prognosis and prevention
Timely diagnosis of retinoblastoma at the initial stage makes it possible to achieve complete cure using photocoagulation, cryotherapy or radiation therapy. All these techniques are organ-preserving and less traumatic. Surgical removal of the eyes also guarantees a complete cure, but causes discomfort and leaves a cosmetic defect. The prognosis is unfavorable in the presence of complications such as:
- extrascleral spread of the tumor;
- tumor growth deep into the optic nerve;
- involvement of the choroidal membranes in the pathological process.
Prevention is very important, as this will prevent subsequent long-term treatment and the occurrence of dangerous complications. Families with a history of hereditary retinoblastoma should consult a geneticist. It is important to undergo examinations by an ophthalmologist, as this will help identify the disease in the initial stages of development in the child and preserve vision.
Retinoblastoma is a very dangerous cancer. The earlier the diagnosis is made, the more favorable the outcome of treatment and preservation of vision.
Treatment methods
Today, close attention is paid to organ-preserving techniques. In addition to local and systemic chemotherapy, radiation therapy, if indicated, the following are used:
- photocoagulation (removal of a tumor by exposing it to a powerful light flux);
- cryodestruction (destruction of the tumor by cold);
- laser destruction (tumor removal with laser).
Principles of organ-preserving therapy in the treatment of retinoblastoma
- Patients from group A receive only local treatment (laser coagulation, cryodestruction, diathermocoagulation).
- Patients from group B were given 6 courses of two-component chemotherapy (polychemotherapy), as well as additionally one of the local treatment methods (laser destruction, cryodestruction, brachytherapy).
- Those who belong to groups C and D are prescribed 6 courses of PCT, consisting of three components. Treatment is supplemented with local chemotherapy and, if necessary, physical methods of tumor destruction.
Patients from group E are indicated for enucleation (that is, removal of the eyeball, which also involves cutting the external eye muscles and the optic nerve). Within 5-7 days after surgery, ocular prosthetics are performed. The selection of a permanent prosthesis is carried out within 1.5 months after surgery.
Enucleation of the eye has clear indications:
- the patient must belong to group E according to the Amsterdam ABC classification;
- bilateral form of the disease, irreversible loss of function of one eye;
- the inability to assess the extent of eye damage due to cataracts or vitreous hemorrhage after conservative treatment;
- If the damage to both eyes has gone too far and there is no chance of restoring vision, bilateral enucleation is performed (both eyes are removed).
Surgical treatment is combined with PCT, irradiation, laser destruction, etc.
PCT (conservative therapy) after enucleation
Indicated in the following cases:
- tumor growth into the optic nerve and extrabulbar spread;
- large or multiple tumor nodes, tumor localization in the peripapillary zone, intraocular dissemination (spread) of the process into the iris, vitreous body, etc., involvement of the choroid and optic nerve in the malignant process.
If there is a retrolaminar spread of the formation, then PCT is supplemented with radiation treatment. If the tumor extends to the optic nerve resection line and/or extrascleral spread occurs, these patients are considered to be at high risk. They are shown external beam radiation therapy in combination with PCT, and then high-dose PCT followed by autotransplantation (transplantation of their own) peripheral blood stem cells.
We suggest that you familiarize yourself with several of the most commonly used PCT regimens that are indicated for this disease:
- "Cyclophosphamide" at a dosage of 400 mg/m2 per day. If the child's weight is less than 12 kg, then the dosage is calculated as 13 mg per kg of weight per day. Days 1-5, intravenously, drip. “Carboplatin” at a dosage of 500 mg/m2. If the child’s weight is up to 12 kg, then it is calculated as 12 mg per kg of weight per day. Day 5, intravenously, drip. "Etoposide" at a dosage of 100 mg/m2 per day. If the patient's weight is up to 12 kg, then 3.3 mg per kg of weight per day. Days 1-5, intravenously, drip.
- “Vincristine” at a dosage of 1.5 mg/m2, day 1, intravenously, infusion (injection). “Cyclophosphamide” at a dosage of 1.2 g/m2, day 1, intravenously, drip. “Doxorubicin” at a dosage of 45 mg/m2, day 1, intravenously, drip.
- “Vincristine” at a dosage of 1.5 mg/m2, day 1, intravenously, in a stream. “Carboplatin” at a dosage of 500 mg/m2, day 1, intravenously, drip. "Etoposide" at a dosage of 100 mg/m2, days 1-3, intravenously, drip.
- "Carboplatin" at a dosage of 560 mg/m2. For children under 3 years of age, it is calculated as 18.6 mg per kg of weight. Day 1, intravenously, by drip. Vincristine at a dosage of 1.5 mg/m2. For children under 3 years of age, it is calculated as 0.05 mg per kg of weight. Day 1, intravenous, stream.
Types of pathology
There are a wide variety of forms and stages of manifestation of pathology. In this case, the classification consists of several factors.
So, depending on the causes of the tumor, pathology can be considered:
Based on the coverage area, retinoblastoma also has the following forms:
The growth pattern of the tumor is also taken into account, which can be:
As for the stages of the disease, the TNM system is taken into account. In this case, the Latin letter T implies the following:
If the letter N is present in the designation, this indicates that the pathology has affected nearby lymph nodes:
The last letter M indicates the appearance of metastases in distant areas in the body:
Retinoblastoma refers to a type of tumor in which the altered cells are significantly different from the healthy surrounding tissue. But such neoplasms are more aggressive in nature and have accelerated growth. As for metastasis, repeated foci of pathology affect not only the spinal cord, brain, but also the bone structure.