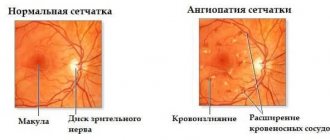
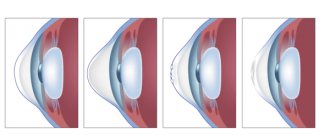
The visual system has a complex structure, in which the retina occupies a special place. This is the inner layer of the eye that provides the perception of light impulses. It establishes a relationship between the optical system and certain parts of vision located in the brain. This process makes it possible to receive, process and send information received through the operation of the visual system.
When the blood circulation of the eye apparatus is impaired, retinal dystrophy develops. Pathology is more often diagnosed in old age. If the patient is not provided with timely treatment, retinal dystrophy rapidly develops, affecting the photoreceptors. As a result, a person cannot see objects located far from him and is not able to fully perceive the entire spectrum of colors.
What is retinal dystrophy?
Retinal dystrophy refers to a disease in which the thin nervous tissue of the organ of vision is destroyed. This process is accompanied by serious trials for a person; the functions of the eye begin to gradually fade away. Degeneration of the retina leads to degeneration of its central part, called the macula. It is an extremely important element. If the macula works well, then the person is able to:
- read;
- see everything that is at close range;
- recognize colors;
- write.
Retinal structure diagram
Macular degeneration of the retina involves damage to the cells of the macula. It is not completely known what causes this disease. Scientists highlight age-related changes. Most often it occurs in older people. In tissues with age, decay products of material metabolism accumulate. Visual cells may lack nutrition as a result of:
- intoxication;
- impaired blood circulation;
- infections.
Retinal degeneration can develop due to existing myopia, during which pressure on the membrane of the eyes increases. There are other causes of retinal dystrophy.
Factors that trigger the mechanism of its development:
- excess body weight;
- diabetes;
- hypertension;
- cigarette abuse.
There are cases when the disease develops at a young age against the background of diseases of the heart, blood vessels, thyroid gland and injuries. There are cases when retinal dystrophy develops during pregnancy. Stress, excessive exposure to ultraviolet rays and heredity are also factors that increase the risk of this disease.
Causes of the disease
The main role in the progression of this disease belongs to hereditary predisposition. Typically, it is because of this etiological factor that progression of retinal dystrophy in children is observed.
In addition, the following reasons can provoke the progression of the disease:
- visual impairment such as myopia;
- infectious diseases of the body;
- deviations from normal human body weight;
- diabetes;
- alcohol and nicotine abuse;
- high blood pressure;
- various circulatory disorders;
- heart problems;
- prolonged direct exposure to sunlight on the eyes;
- pregnancy;
- poisoning;
- exposure to stressful situations;
- removal of half or all of the thyroid gland;
- unbalanced diet, as a result of which the body lacks vitamins and nutrients;
- variety of eye injuries.
Consequences of retinal dystrophy
If a person who has dystrophic changes in the retina of the eyes does not seek medical help in a timely manner, but carries out treatment at home on his own, he may face serious problems in the future.
Diagram of retinal detachment
A complication of the disease is often detachment of the visual organ. The worst that awaits is loss of vision, which will not return even after surgery. But still, complete blindness as a result of this disease develops infrequently. The prognosis for the dry form is more favorable than for the wet form.
At-risk groups
Dystrophy is most often observed in elderly patients. The risk group includes people diagnosed with myopia, as well as with blood vessel diseases, hypertension and diabetes. A predisposition to this pathology is inherited, as a result of which children of patients with retinal dystrophy are recommended to have fundus examinations more often.
According to statistics, this disease is more often observed in people with white skin and blue eyes, and men get sick less often than women.
Signs of illness
The dry form of the disease develops at the initial stage and is the most common. 90% of the entire population suffers from this type of disease. In these cases, a person gradually loses central vision, but most often he does not attach due importance to such a change. It is very important at this time to visit an ophthalmologist for a preventive examination, during which a specialist will be able to identify the disease and its form.
Scheme of forms of macular degeneration
Early symptoms of retinal dystrophy include that the clarity of vision decreases gradually. There is a slow progression of the disease; over time, images begin to be perceived in a distorted form. If the dry form is not identified at an early stage, wet macular degeneration will develop in its place. Its development occurs much more rapidly than dry. A person with retinal dystrophy may have the following symptoms:
- no peripheral vision;
- images are bent and straight lines are distorted;
- at night and when lighting decreases, vision deteriorates;
- flashes of light, flies and colored spots appear before the eyes;
- color perception is distorted;
- Contrast sensitivity of vision is completely lost or reduced;
- visible objects bifurcate.
The severe wet form is quite difficult to cure; vision deteriorates quickly. Degeneration progresses and new, brittle and very dry blood vessels begin to form. This leads to hemorrhage and yellow accumulations are formed. With macular degeneration, the eyes quickly become tired. This age-related degeneration is common in people over 50 years of age. This condition often leads to the development of central retinal dystrophy.
But it should be noted that in a patient suffering from chorioretinal retinal dystrophy, peripheral vision is normal. However, if there is no central vision, then a person is not able to clearly perceive the objects around him.
People who show signs of this type of illness cannot drive or read. The type and severity of chorioretinal retinal dystrophy affects how quickly it progresses. Macular age-related degeneration is always bilateral. The wet form develops in one eye and the dry form in the other.
Classification of the disease
Retinal dystrophy is a general concept that includes various types and types of pathology. Dystrophy is divided into two types:
- Congenital – genetically determined, inherited. The first signs of the disease appear at an early age, up to 15-20 years, and increase as the patient grows older.
- Acquired – which is a complication of any disease. Most often, acquired dystrophy develops in old or senile age.
ARTICLES ON THE TOPIC:
- What causes a retinal tear? Consequences, symptoms and treatment of the disease
- What causes a macular hole in the retina: all about the symptoms and treatment of the pathology
- How dangerous is the disease peripheral retinal dystrophy of the fundus?
Peripheral
Peripheral vitreochorioretinal dystrophy is a consequence of eye trauma. The impetus for its development is congenital or acquired myopia, or myopia. Retinal dystrophy is a consequence of the formation of adhesions of the vitreous body to the retina, which provoke ruptures and tissue destruction.
The disease causes impairment of peripheral vision, which makes it difficult for the patient to orient himself in space. A subtype of peripheral dystrophy is frost-like degeneration, which provokes the appearance of pathological formations on the retina that look like snow. Central vision is not affected in this type.
Abiotrophy
Tapetoretinal abiotrophy is a hereditary pigmentary degeneration of the retina. Affects the rods responsible for peripheral black-and-white twilight vision.
Patients find it difficult to navigate in poor lighting. Retinal damage begins in the periphery and moves toward the central optic nerve. The process takes decades and develops, as a rule, in both eyes at once, less often in one.
Central
Central dystrophy is recognized as an senile pathology, since it mainly develops after 40-50 years. In the early stages, patients feel a decrease in visual acuity when looking into the distance and viewing a picture close up. One of the obvious symptoms of this type of pathology is the curvature of straight lines.
The most common subtype of pathology is macular degeneration - a chronic, rapidly progressive lesion of the central zone of the retina (macula) and choroid. Pathology affects cells and intercellular space. Macular degeneration is the main cause of irreversible vision loss and blindness in old age.
For men aged 20-25 years, another type of pathology is characteristic - central chorioretinal dystrophy. A subtype of the disease develops due to the accumulation of effusion from the vessels under the retina. The effusion interferes with the nutrition and metabolism in the retina, and its gradual detachment occurs.
Laser treatment
Nowadays, the most effective treatment method is laser surgery. Many people wonder whether it is possible to restore their previous vision with a laser. It must be borne in mind that this is not possible. The laser helps stop the progression of the disease, as well as minimize the risk of retinal detachment.
This method is considered the most effective due to the least trauma. The surgeon does not open the eyeball, so the operation is completely bloodless. Cauterization with a laser beam occurs as a result of non-contact exposure to the affected area, where tissue gluing and sealing occurs under the influence of thermal energy.
The laser helps distinguish between affected and healthy tissues. As a result, the treated area is limited. Thanks to this method, dystrophy is stopped. Laser intervention is carried out quickly. During the rehabilitation period, it is necessary to carry out special gymnastics for the eyes and instill drops prescribed by the doctor for quite a long time. In this way, retinal dystrophy has to be treated if the disease has gone too far.
Treatment with folk remedies for this disease can only be carried out in combination with traditional therapy. Alternative medicine drugs in some cases help to stop the progression of the disease and significantly improve a person’s condition.
It is necessary to understand that the treatment of retinal dystrophy with folk remedies and medications has contraindications. Therefore, before you start using various traditional methods, you should definitely consult with an ophthalmologist.
Diagnostic methods
The patient's examination begins with an examination by an ophthalmologist, who makes an initial diagnosis. To identify the condition of the retina and assess the rate of progression of pathology. A comprehensive examination is carried out using the following methods:
- Perimetry – assessment of the patient’s visual field. Detects disturbances in peripheral vision.
- Visometry – assessment of visual acuity.
- Refractometry is the study of the refractive power of the retina.
- Adaptometry – assessment of visual function in dark conditions.
- Fluorescein angiography is a study of capillaries and vessels covering the fundus, choroid and anterior parts of the eye. Before the examination, a fluorescent substance is injected into the vessels.
- Biomicroscopy - examination of the central parts of the fundus and tissues of the eyeball.
- Optical coherence tomography of the retina - measuring the thickness and assessing the degree of retinal detachment.
A comprehensive examination using several methods allows you to identify signs of pathology in the early stages.
Treatment with medications
After it becomes clear what retinal dystrophy is, the patient wants to know how such a pathology is treated. Before prescribing treatment, a comprehensive diagnosis is carried out. Only an ophthalmologist knows how to treat retinal dystrophy, and you should contact him immediately after discovering the disease. A highly specialized specialist will use all kinds of methods.
At the initial stage, for the treatment of the retina, special medications are prescribed, which ensure a complex effect on the affected organ. The retina in this situation is weak, so medications help strengthen and dilate the blood vessels of the eyes.
For retinal dystrophy, the doctor prescribes treatment individually, and develops a specific medication regimen. In most cases, patients with this serious diagnosis need to repeat the course several times a year.
Treatment of retinal dystrophy is carried out with medications that have the following properties:
- vasoconstrictor;
- sealing the walls of blood vessels;
- blood thinners.
A patient suffering from this disease needs to take microelements (zinc, beta-carotene and Omega-3 fatty acids) and vitamin preparations. One should not forget about taking such medications even in the earliest stages of the disease and regardless of what medications are being treated.
In case of age-related degeneration of the organ of vision, great attention must be paid to such a substance as lutein. This special pigment, which is very effective for this disease, is found in plants. It is distinguished by its antioxidant properties and ability to absorb light.
Lutein is contained in specialized vitamin complexes. They help protect the eyes from excess radiation, which causes great harm to the organ during illness. When diagnosing the wet form, the patient will be prescribed medications containing inhibitors.
Etiology and mechanism of development
The main reasons for the development of the disease are age-related changes in blood supply and metabolism. Degenerative eye diseases are a consequence of poor functioning of the aging human vascular system. However, according to medical statistics, in recent decades the disease has become noticeably “younger”. In a child, the disease develops due to a hereditary predisposition.
Experts believe that the development of dystrophy is influenced by the following factors that cause disruption of the blood vessels of the eye:
- weakened immunity;
- smoking and alcohol abuse;
- malnutrition, vitamin deficiency;
- pregnancy;
- viral infections;
- chronic pathologies: diabetes, pathologies of the cardiovascular and endocrine systems, hypertension;
- obesity;
- intoxication of the body;
- injuries and eye surgeries.
A serious factor that has a negative impact on the body, and in particular on the eyes, is the unfavorable environmental situation. Under the influence of harmful substances, vascular failure occurs, which affects the retina of the eyes.
Experts distinguish two stages of pathology:
Dry form (grade 1 dystrophy) - characterized by the accumulation of cellular metabolic products between blood vessels and on the retina. Neoplasms are yellow tubercles (drusen) that are deposited under the retina. The dry form is slow. At an early stage, a small number of drusen form in the eye, which do not reduce visual acuity. As the pathology progresses, their number increases, and spots appear in the patient’s eyes, interfering with vision.
- The wet form (grade 2 exudative dystrophy) is diagnosed in 10% of patients suffering from dystrophy. It develops as a complication of the dry form that occurs without treatment. The wet form causes small blood vessels to grow under the retina. The walls of the overgrown vessels are thin. They are easily damaged, causing numerous hemorrhages in the eye tissue. As a result of the accumulation of exudate under the retina, ruptures and detachment occur.
IMPORTANT! The wet form of dystrophy develops quickly, is difficult to treat, and gradually the patient experiences partial or complete loss of vision.
Physiotherapeutic treatment
Along with drug treatment, doctors use all kinds of physiotherapeutic methods. With this addition, the doses of drugs used are reduced. Often the development of the disease is stopped. The main physical methods include:
- Laser therapy. Promotes retinal stimulation.
- Magnetic therapy. Helps reduce pressure inside the eye, speed up recovery, and increase the size of retinal vessels.
- Electrophoresis. In this case, the procedure is carried out using certain medications.
- Ultrasound. Thanks to its use, metabolism and microcirculation are improved.
The ophthalmologist selects a specific method, based on the real situation, the type of disease and its course. If retinal degeneration cannot be cured with medication and physiological methods, surgical intervention is performed.
Prognosis and possible complications
With timely treatment, the prognosis is favorable. With the help of modern methods, it is possible to effectively restore lost vision. The course of the disease largely depends on the morphological type of the disease. Degeneration of the “cobblestone pavement” type occurs more favorably.
REFERENCE! The cobblestone pavement that an ophthalmologist sees when examining the fundus of the eye is just a beautiful name for round accumulations of pigment.
If you do not consult a doctor in a timely manner, retinal detachment and complete loss of vision may develop.
Preventive actions
People who have been diagnosed with this should regularly take preventive measures after completing the course of therapy. Such patients should absolutely not be allowed to overstrain their visual organs. This applies to reading, during which it is necessary to take breaks so that the eyes can rest. Prevention of retinal dystrophy also includes the following measures:
- measured time spent on the computer, TV and books;
- abstaining from taking hot baths and showers;
- refusal to lift heavy objects and increased physical activity.
Such people should provide themselves with proper lighting and systematically perform special eye exercises. When going outside, you must wear sunglasses, thanks to which the retina of the eye will be protected from the influence of ultraviolet rays. To prevent oxidation of cells in the eyes, which in most cases leads to dystrophy, it is necessary that healthy foods be present in the diet. Proper nutrition involves eating foods rich in antioxidants.
If a person has destruction of the retina, then taking vitamins is considered mandatory, especially A, E and group B. They contribute to the normal functioning of this organ. Thanks to the vitamins contained in fresh vegetables, fruits, nuts, and grains, tissue nutrition improves, and their continued use stops degenerative changes. The patient must completely abstain from alcoholic beverages and cigarettes. All this must be done in the presence of any type of eye dystrophy to avoid the development of atrophy.
It should be noted that such a dangerous disease cannot be prevented, because it is associated with withering of the body. But regular ophthalmological examination will help to detect the problem in time and carry out surgical treatment.