Degrees of eyeball contusion according to medical classification
Depending on the severity of the changes and the prognosis for the visual analyzer, eye contusion is divided into the following 4 degrees of severity:
- Mild (minor hemorrhages under the conjunctiva, swelling of the cornea, pigment spot on the lens).
- Moderate (tears of the inner layers of the eye, hemorrhage in the anterior chamber, retinal edema, impaired contractility of the eye muscles, visual impairment up to 50%).
- Severe (tears in the sclera, iris and cornea, displacement of the lens, blood in the vitreous, detachment of the retina and rupture of the choroid, loss of vision by more than 50%).
- Extremely severe (complete loss of vision due to crushing of the structures of the eyeball, total separation of the optic nerve).
For any type of traumatic pathology, examination and treatment should begin as early as possible to prevent worsening of the intraocular situation. If the injury is extremely severe, it is impossible to save the eye.
Vision restoration - independent vision restoration without surgery
By severity of contusion injuries of the eyeball
occupy second place after perforation wounds.
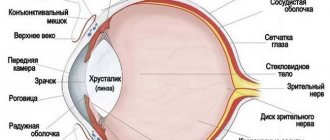
Contusions of the organ of vision are very diverse in their clinical picture - from minor hemorrhages under the conjunctiva of the eyelids to crushing of the eyeball and surrounding tissues. They can occur as a result of blunt impact of a damaging factor directly on the eye and its appendages (direct contusions) or indirectly (when affecting more or less distant parts of the body). The source of injury in the first case is bruises with a fist or any object, falls on stones, on various protruding objects, an air wave, a jet of liquid, etc. Indirect contusions
are the result of blows to the head, compression of the body, etc.
Clinical manifestations of concussion injury do not always correspond to its actual severity. In addition, even relatively mild bruises can lead to severe changes in the eyeball. Concussion injuries to the organ of vision are in some cases accompanied by closed brain injury
. Traumatic damage to eye tissue during contusion depends on two main factors: the strength and direction of the blow, as well as the characteristics of the anatomical structure of the eye. So, depending on the strength and direction of the impact, tissue damage can be insignificant, or it can be so strong that the scleral capsule ruptures. It is impossible not to take into account the patient’s age and the condition of the eye before the concussion.
Classification of eye contusion
There are three degrees of severity of concussion.
I degree
- contusions, in which there is no decrease in vision during recovery. At this degree, there are temporary reversible changes - swelling and erosion of the cornea, retinal clouding, Vossius ring, spasm of accommodation, etc.
II degree
- contusions, in which there is a persistent decrease in vision, deep erosions of the cornea, local contusion cataracts, ruptures of the pupillary sphincter, hemorrhages, etc.
III degree
- contusions, in which severe changes are observed, in which there is a possibility of volumetric enlargement of the eye due to subconjunctival rupture of the sclera, as well as a state of sharp hydrodynamic shifts. At this degree, subconjunctival ruptures of the sclera are possible; persistent ocular hypertension; deep, persistent hypotony of the eye.
Clinic
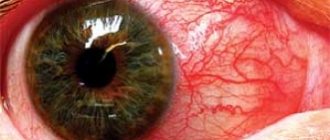
. The symptom complex in the post-concussion period is very diverse and includes not only symptoms of damage to the eyeball and its auxiliary organs, but also changes in the general condition of the patient’s body. Pain in the craniofacial region on the side of the injury, headaches at first after the injury, dizziness, mild nausea, and some changes in convergence when reading (if visual functions are preserved) are noted. These general symptoms are observed in patients only in the first days. One of the signs of eye contusion in almost all patients is an infection of the eyeball, which is observed during the first day and remains at the same level for 3-4 days, and then gradually decreases.
Contusions of the eye appendages
. In cases of mild contusions, hemorrhages of varying sizes can be observed under the eyelids and conjunctiva. Hemorrhage, which appeared immediately after the injury, arises from damaged vessels of the eyelid. Hemorrhage that appears after several hours or even days indicates damage to the deep parts of the orbit or skull. A fracture of the base of the skull is characterized by hemorrhage under the skin of the eyelids, like “spectacles,” appearing a day or later. Fresh contusional hemorrhages under the skin of the eyelids and into the conjunctiva have the appearance of sharply limited red spots of various sizes and shapes. Such hemorrhages do not require special treatment, as they gradually resolve without a trace. However, this approach is possible only after reliably excluding contusion of the eyeball and orbit.
subcutaneous emphysema can be detected by palpation by a characteristic crunch under the fingers (crepitus).
, indicating damage to the bone walls of the orbit and penetration of air from the air cavities of the nose.
Treatment
. If hemorrhage appears on the first day, cold can be recommended to narrow the blood vessels and reduce the hematoma, and then heat to speed up resorption. They do not require any other special treatment and can resolve on their own.
In case of concussions, it is necessary to monitor the patient’s condition for several days.
, since trauma associated with damage to the ethmoid sinuses can subsequently lead to the penetration of infection from the ethmoid sinuses into the cranial fossa. Serious causes can cause ptosis, which sometimes appears simultaneously with subcutaneous hemorrhage. In this case, one can think about concomitant damage to the oculomotor nerve or a rupture (stretch) of the levator eyelid. Special care for contusional ptosis is not required, but the patient should be observed by a neurologist, since the superior orbital fissure may be affected.
Severe concussions
may be accompanied by tears of the eyelids, ruptures of the conjunctiva, and even complete separation of the eyelid, and the lacrimal canaliculi are often affected. Such lesions require surgical treatment; it is carried out according to the same rules as eyelid wounds.
Retrobulbar hematoma
This condition is a manifestation of orbital contusion. Characteristic symptoms are
: exophthalmos, limited mobility of the eyeball, intraocular pressure may increase. Decreased visual function is associated with compression of the orbital part of the optic nerve. Due to a sharp increase in pressure in the orbit, reflex nausea, vomiting, and slowing of the pulse are possible. Hemorrhages are located under the skin of the eyelids and under the conjunctiva, the tactile sensitivity of the facial skin below the orbital margin is reduced.
Treatment
:
Diacarb 250 mg - 2 tablets per dose, once;
0.5% solution of timolol 2 times a day into the conjunctival sac;
osmotherapy (20% manitol solution 1-2 g/kg body weight intravenously for 45-60 minutes.
Contusions of the eyeball
Blunt injuries are accompanied by damage to various parts of the eyeball. In mild cases, epithelial damage may be observed—corneal erosion or damage to the epithelium and Bowman's capsule.
Contusions affect the eye from the front or bottom
, since it is protected from the sides by the thickened edges of the orbit. As a result of contusion, the eye sharply contracts, and intraocular pressure rises sharply. Depending on the force of the impact, either the more delicate inner membranes and parts of the eye may be damaged, or, if the force of the impact is high, the outer capsule of the eye may also be damaged.
One of the most common phenomena in eye contusion is hemorrhage into the anterior chamber and into the vitreous body.
, indicating damage to the iris, ciliary body or choroid. In the iris, one often sees it being torn off at the root (iridodialysis); at the site of separation after resorption of the hemorrhage, a black hole is noticeable, which when examined with an ophthalmoscope appears bright red; through the hole you can sometimes see the edge of the lens and fibers of the ligament of zinn. The pupil then takes on an irregular shape. In other cases, tears or radial ruptures are observed in it. Contusion of the ciliary body is indicated by a sharp and persistent ciliary infection, photophobia and pain, which are especially noticeable when touching the eye. In the case of contusions, ruptures with hemorrhages often form in the choroid; the ruptures become visible with the help of an ophthalmoscope only after the hemorrhage has resolved.
Hemorrhages, swelling and tears may also be noted in the retina. often causes retinal detachment
. The most delicate and most important part of the retina for vision is especially often affected - the area of the macula, where ruptures and hemorrhages can form during contusion.
Contusional changes in the lens
are affected either by its clouding due to rupture of the capsule, or due to separation of the ligament of Zinn by subluxation or dislocation of the lens into the vitreous body or into the anterior chamber, and in case of rupture of the sclera - under the conjunctiva. Often, eye contusions lead to secondary glaucoma.
Contusions with rupture of the outer capsule of the eyeball
are always serious in nature and very difficult. In severe cases, scleral rupture may occur, which is more common in the upper part of the eyeball and has the appearance of a crescentic wound. A scleral rupture can occur with or without a rupture of the conjunctiva, i.e., subconjunctivally. Most often, the scleral rupture has an arcuate outline, concentric to the limbus, usually 1-2 mm away from it, at a place corresponding to the position of Schlemm's canal, where the sclera is especially thin. But ruptures of the sclera are also possible in other places, often extensive and irregular in shape, where the internal parts of the eyeball can fall out. If there is intact conjunctiva above the scleral rupture and there is significant hemorrhage below it, the site of the scleral rupture is difficult to recognize before the blood is absorbed. However, a rupture, among other signs, is indicated by a sharp decrease in intraocular pressure, the presence of vitreous humor in the wound opening and its staining with pigment.
Contusional corneal edema
accompanied by a sudden deterioration in vision due to diffuse clouding. Most often, edema appears as a result of damage to the epithelium and Bowman's membrane, but it can also be a consequence of reactive hypertension of the eye.
Optic nerve damage
More often they arise due to a violation of its integrity or compression by bone fragments, foreign bodies, or a hematoma formed between the optic nerve sheaths. Symptoms of damage to the optic nerve are visual disturbances and changes in the field of vision. With significant compression, visual acuity drops to zero, while the pupil dilates; in the presence of a sympathetic reaction, there is no direct reaction to light.
Complications in the post-concussion period
are varied, among them we can distinguish ocular hypertension, hypotension, changes in the anterior part of the uveal tract.
There are two phases of hypertension - the first occurs immediately after the contusion and is the result of neurovascular changes of reflex genesis, as well as due to an increase in the secretory ability of the eye. The outflow of intraocular fluid is usually observed for 1-2 days, then gives way to hypotension
. The second stage of hypertensive changes is observed in the first weeks and months. Sometimes post-concussion glaucoma occurs 10-15 years after injury and depends on changes in the iridocorneal angle.
Hypotension after blunt eye trauma is observed somewhat less frequently than hypertension. Most often it occurs in patients with damage to the anterior segment of the eyeball - pathology of the iridocorneal angle and detachment of the ciliary body.
With persistent deep hypotension, swelling of the optic discs is observed, as well as the occurrence of myopia, which is usually associated with a decrease in the secretion of the ciliary body.
The following factors influence the course of the post-concussion period and the outcomes of blunt eye injury:
: damage to the vascular system of the eye as a whole; change in ophthalmotonus; traumatic tissue changes; hemorrhages in the cavity and tissue of the eye; inflammatory changes in the form of iritis and iridocyclitis.
When treating patients with eye contusion
in the first 1-2 weeks, the main therapy should include the use of sedatives (valerian, bromides, luminal, etc.); dehydration (place of instillation of a 2% or 3% solution of calcium chloride, 40% glucose intravenously, orally diuretics - diacarb); vascular strengthening, thrombolytic, anti-inflammatory drugs; drugs that regulate ophthalmotonus. Further treatment tactics depend on the damage to the eye tissue. So,
for corneal erosions, disinfectants and preparations that promote epithelization and regeneration are prescribed, for lens opacities - taufon, vitamin preparations;
for retinal clouding - intravenous 10% sodium chloride solution, dicinone and ascorutin orally;
for contusion of the ciliary body - painkillers, for hypertension - 0.5% solution of thymol, 0.1% solution of dexamethasone in drops 4 times a day;
for contusion rupture of the sclera - instillation of a 0.25% solution of chloramphenicol and a 20% solution of sodium sulfacyl;
for retrobulbar hematoma - Diacarb 250 mg - 2 tablets once, 0.5% solution of timolol) once a day in the conjunctival sac, osmotherapy - 20% solution of mannitol intravenously;
for damage to the iris: for mydriasis - 1% solution of pilocarpine, for miosis - 1% solution of cyclopentolate;
for contusion of the choroid - ascorutin and dicinone orally, osmotherapy - 10 ml of 10% sodium chloride solution or 40% glucose solution 20 ml intravenously;
if the lens is displaced, apply disinfectant drops (0.25% solution of chloramphenicol), if intraocular pressure increases, apply timolol 0.5% solution, inside a diacarb tablet (0.25).
Immediate surgical treatment
eye contusions are indicated only for subconjunctival ruptures of the sclera and cornea, bruises of the eyelids and conjunctiva, as well as dislocations of the lens into the anterior chamber.
—-
Article from the book: Eye diseases. Complete Guide | Perederiy V.A.
Share on social media networks
RќСЂР°РІРёС‚СЃСЏ
How to recognize an eyeball bruise? Symptoms.
To determine the degree of eye contusion and select the correct treatment, the patient is prescribed a comprehensive examination (Table 2).
Table 2 - Methods for diagnosing eye contusion
| Diagnostic methods | Type of study | Purpose of application |
| Laboratory | Analysis of urine | Assess the patient's health, determine the Rh factor and blood sugar levels. |
| General and extended blood test | ||
| Instrumental | Visometry | Determine the extent of damage. |
| Assess the effectiveness of therapy. | ||
| Predict the outcome of concussion. | ||
| Ophthalmoscopy | Examine the fundus. | |
| Determine whether there are changes in the retina and optic nerve. | ||
| Ultrasound | Assess the condition of the tissues behind the eye. | |
| Determine the degree of displacement of intraocular structures, the volume and location of hemorrhages. | ||
| X-ray (lateral and frontal projection) | Exclude a fracture of the orbital walls. | |
| To refute (confirm) the presence of foreign bodies in the eyeball and blood in the paranasal sinuses. | ||
| Computer, magnetic resonance imaging (most informative for severe contusion) | Assess the level and nature of damage to the eyes, orbit and bone structures. | |
| Identify tissue hematoma. | ||
| Determine the severity of damage to the optic nerve and extraocular muscles. | ||
| Electroretinogram | Investigate the functional state of the retina. |
READ MORE: Treatment of umbilical hernia with folk remedies in children
How to treat eye contusion is decided by the doctor, based on the results of the examination. As a rule, they resort to surgical and/or medicinal treatment. For drug therapy, the following is prescribed:
- Medicines for oral and intramuscular administration:
- glucocorticoids: Dexamethasone, Triamcinolone;
- angioprotectors: Vikasol, Dicynon;
- non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs: Diclofenac, Indomethacin;
- antihistamines: Suprastin, Tavegil;
- products containing enzymes: Fibrinolysin, Gemaza.
tranquilizers: Diazepam;
- antibacterial agents: Tobramycin, Ciprofloxacin;
mydriatics: Tropicamide, Cyclopentolate;
Eye contusion can have both mild and severe, irreversible consequences. Therefore, if you receive an injury to the organs of the visual system, you should not postpone a visit to the doctor. The sooner treatment measures are taken, the lower the risk of complications and the higher the likelihood of maintaining vision.
Treatment tactics
Treatment of victims with mild concussion can be carried out on an outpatient basis; for moderate and severe contusion, hospitalization is necessary.
For sleep disorders, anxiety and fear, as well as before surgery: Diazepam IV or IM 5-10 mg once 30-60 minutes before surgery.
In case of psychomotor agitation, the dose of diazepam is increased to 10-20 mg.
Along with systemic therapy, local treatment is carried out (in severe conditions and in the early period after injury, the frequency of administration is 6 times a day, as the severity of inflammation decreases, the interval between administrations is increased).
For contusional damage to the retina: Calf retinal polypeptides (Retinalamin) parabulbar or intramuscularly (diluted by 0.5-1 ml of 0.5% procaine solution) 5 mg 1 time / day, 10 days.
Reducing the severity of pain and hyperemia of the eye, increasing or stabilizing visual acuity, restoring normal IOP levels.
Long-term use of GCS can lead to an increase in IOP, promote the development of cataracts and the proliferation of microorganisms.
Adequate medical care starts with clarifying all the nuances of the disease. For these purposes, the following manipulations are carried out:
- X-ray of the skull, orbit. This examination not only details the extent of destruction, but also helps confirm/exclude injuries to nearby organs. CT is more effective;
- it can be treated at home if errors in the aspect of the cornea affect no more than 25% of its structure, the amount of bleeding into the anterior chamber of the damaged organ is negligible, a cloudy color of the retina is observed - but vision is normal;
- Inpatient treatment includes the following medications:
- Anti-inflammatory medications that can be administered intramuscularly, through the use of a dropper, orally. The list of such drugs is wide.
- Enzyme medications. They are often introduced into the damaged area.
- Absorbable medications. Favors the resorption of swelling and bruising.
READ MORE: Correct treatment of varicose veins with soda
For mild eye damage, medications are used. Various versions of general and local drugs of the following groups are used:
- antimicrobial;
- anti-inflammatory;
- vascular;
- mydriatic drugs;
- regenerating agents.
Treatment is selected individually for each person. Regular medical monitoring is required: in the absence of negative dynamics and with a low risk of complications, therapy can be carried out at home.
In moderate and severe forms of the pathology, it is necessary to be treated in the microsurgical department of the hospital, combining drug therapy with surgery. In case of ruptures of the internal structures of the eye and displacement of the lens, surgery is necessary to restore the anatomy of the eyeball and reduce ophthalmotonus.
The choice of combination therapy methods depends on the severity and risk of dangerous complications. It is important to carefully and consistently follow the specialist’s recommendations at all stages of therapy.
Corneal pathologies
Quite often, eye contusion leads to damage to the cornea. The main signs of such defects are erosion of varying depths and areas. In the initial period after contusion (3 days), small erosions appear; deeper ones develop within 7-8 days. Symptoms of such injuries are fear of light, spontaneous lacrimation, a feeling of a foreign body in the eye, blepharospasms. If the central zones of the cornea are subject to erosion, blurred vision occurs, and if the stroma is damaged, a noticeable decrease in visual acuity occurs.
Treatment of corneal injuries is carried out using recovery stimulants such as cornegel or solcoseryl, methylene blue with quinine. When blepharospasm occurs, a block along the temporal artery is prescribed using lidocaine. Be sure to use toxoid and disinfectant drops or ointments.
Destruction of the endothelium leads to edema in the depths of the stroma, and the penetration of purulent composition into other areas of the stroma causes opacification of the cornea in the form of stripes or latticework. Grade 3 contusion can cause the stroma to become permeated with a blood component. A clouding of a red hue occurs, which turns greenish, and then acquires a grayish tint.
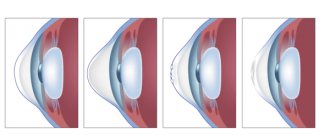
Damage to the lens
Eye contusion often leads to traumatic cataracts (clouding of the lens) or changes in the position of the lens (luxation). Cloudiness occurs due to moisture entering through tiny cracks in the capsule and appears within 5-10 days after injury. If the cracks in the anterior capsule are significant, then the fibers in the form of a swollen mass fill its volume. Sometimes they block part of the anterior chamber, which causes an increase in intraocular pressure and the occurrence of glaucoma.
Lens subluxation has the following symptoms: heterogeneity of the anterior chamber, trembling of the iris, increased intraocular pressure. Lens luxation is characterized by deformation of the anterior chamber, displacement of the iris, and the lens takes the shape of a drop filled with fat.
First aid for eye injury
The assistance that can realistically be provided in out-of-hospital conditions when receiving the illness in question should consist of the following;
- a sterile bandage (bandage, gauze) is applied to the affected area;
- You need to apply cold on top. This could be ice, wet wipes;
- if the victim has retinal clouding, antimicrobial drugs should be dripped into the eyes: saline solution of chloramphenicol, boric acid. If there are antibacterial ointments at home - for the mucous membrane of the eye, anti-hematoma - they should be used;
- If the patient notices nausea or dizziness, he should take a vertical position, placing a cushion under his head. It is allowed to take sedatives;
- To stop bleeding, it is indicative to inject Vikasol vitamin K into the muscle;
- if the pain is severe, the victim is given a painkiller and novocaine/ledocaine is added to eye drops;
- Be sure to get vaccinated against blood poisoning.
If the blow was not severe, and the victim does not experience anything drastic, this is not a reason to ignore consultations with a doctor. There are often cases when the consequences of such a concussion make themselves felt after a considerable period. In case of severe bruises, the patient must be immediately taken to the hospital, where, after examination, the doctor will prescribe one of the possible methods of treatment: at home, or in a hospital setting.