What is syndactyly in children
Syndactyly in children is a developmental anomaly, which is characterized by abnormal development of the fingers of the limbs, which occurs against the background of a violation of the process of their separation during the formation of the embryo. The main reasons for the formation of such a disease are genetic predisposition or the influence of a large number of unfavorable factors on the female body during gestation.
- Etiology
- Classification
- Symptoms
- Diagnostics
- Treatment
- Prevention and prognosis
This disease is characterized by specific symptoms - externally it is represented by the fusion of two or more fingers on the upper or lower extremities. Sometimes there is simultaneous involvement of the arms and legs.
Establishing the correct diagnosis is not a problem, since the pathology has a pronounced cosmetic manifestation. However, to clarify the form of the disease, instrumental examinations are necessary. Surgical methods predominate in treatment.
The International Classification of Diseases ICD-10 allocates its own meaning for such a disease - code Q70.
Classification of the disease
Treatment of syndactyly directly depends on the type of adhesion. Based on the type of fusion, there are 2 types of pathology:
- Basal cutaneous syndactalia - formed during the fusion of soft tissues.
- Bone syndactyly is formed by the fusion of bones or distal phalanges.
Depending on the length of the membranes, complete or partial fusion is diagnosed. With normal development of the fingers, a simple form of membranous syndactyly develops, but if the fingers are deformed or underdeveloped, doctors diagnose “complex syndactyly”; the ICD 10 code for this disease is indicated by the symbols Q70.
Causes of the disease
Predisposing factors for the occurrence of such pathology lie in genetics. Approximately 20% of all cases are genetic.
In cases where there is no family origin of syndactyly, the source may be a violation of the separation of the arms and legs of the fetus, which occurs under the influence of negative factors.
The laying of bones begins around the fourth or fifth week of pregnancy - in such cases, syndactyly in children will be physiological in nature. Normally, in the eighth week of gestation, the process of formation of the fetal fingers begins. This occurs against the background of intensive growth of the finger rays and a decrease in the activity of a similar process in the interdigital spaces.
The causes of syndactyly, which disrupt normal intrauterine development, are presented:
- exposure to radiation on the body of the expectant mother;
- abuse of bad habits during pregnancy - the fact that a woman will soon have a child does not in all cases affect the cessation of nicotine, alcohol and drugs;
- uncontrolled use of medications - for no apparent reason or in case of non-compliance with the acceptable dosage;
- unfavorable working conditions;
- the influence of polluted ecology;
- infectious diseases such as syphilis, influenza or tuberculosis suffered during pregnancy.
It is extremely rare that a child may be diagnosed with an acquired form of syndactyly, caused by chemical or thermal burns of the extremities. In some cases, it is not possible to determine the source of development of such an anomaly.
Causes of fused toes
The only treatment for syndactyly is surgery. Most often it is done at the age of 4-5 years. Only in complex cases, when the pathology interferes with the normal development of the foot or hand, can it be eliminated in the first year of the child’s life, but not earlier than six months of age. Most often, surgical treatment is performed on the hands, since the pathology can interfere with the normal physical and intellectual activity of the child.
And fused toes, especially in mild cases, do not manifest themselves in anything other than a cosmetic defect. Doctors believe that there is no point in having surgery in childhood. There are often cases when finger separation is carried out in an adult, for whom this cosmetic defect causes serious psychological problems.
The pathology can only be corrected through surgery.
Surgery is required if the toes are fused at the level of the bone tissue. This condition will interfere with walking and can cause gait disturbances and deformation of the foot and joints. But modern treatment methods can completely restore limb function. The effectiveness of the operation is determined not only by the appearance of the fingers - there should be no contractures, large scars, the space between the fingers must correspond to the anatomical structure. The goal of treatment is the complete restoration of all limb movements and skin sensitivity. This is especially important when separating the fingers on the hand.
The simplest operation is performed for the membranous form of syndactyly. In this case, you just need to cut the membrane between the fingers with a scalpel. Sometimes plastic surgery using tissue flaps is also required. A more complex operation with muscle and bone grafting is needed for fusion of the phalanges.
The final result largely depends on correctly carried out rehabilitation. Immobilization with a plaster splint is necessary immediately after surgery. And special gel inserts are placed between the fingers. During leg surgery, these devices must be worn for 3-4 months. During the first month of the operated limb, it is important to ensure complete rest. And after about 5-7 weeks, you need to carry out restoration procedures.
The most commonly prescribed are:
- ultraphonophoresis with Lidaza and other drugs that improve blood circulation;
- electrical stimulation of muscles helps prevent muscle atrophy and accelerates the recovery of limb function;
- applications with ozokerite improve blood circulation and prevent inflammatory reactions;
- paraffin improves the condition of joints;
- massage activates metabolic processes and blood circulation in tissues;
- Physical therapy helps restore finger function.
In addition, medications are used. At the initial stage, these are painkillers, anti-inflammatory drugs, and sometimes antibiotics. Then - means to improve blood circulation and accelerate tissue regeneration. These can be “Kontratubeks” or “Dermazin” ointments. If you do not follow the doctor's instructions, the fingers may grow together again in the same place.
The prognosis for this pathology is generally favorable. In more than 80% of diagnosed cases of syndactyly, surgery was used to restore the functions and anatomical structure of the limbs.
Fused toes, what does it mean? Is there a cure for this? Surgery is the only method of curing syndactyly: it is impossible to separate by other means. The surgeon's goal is to eliminate the cosmetic defect through surgery to restore hand function. If left untreated, syndactyly has a negative impact on the development of the limbs, and the growth of the interdigital spaces slows down.
In case of pathology of the toes, surgery is recommended only if this defect interferes with normal walking. The optimal age for surgery is 4-5 years. When the nail phalanges become fused, surgical intervention is performed at an early age - 8-12 months to prevent secondary deformation of the limbs.
Depending on the form of syndactyly and the nature of the defemation, the doctor determines the treatment method. In some cases, during the separation process, plastic surgery of the hands is performed. The skin along the entire length of the fingers is formed from flaps of the patient’s skin taken from the forearm, thighs or perineum.
We suggest you read: What helps with toenail fungus
This pathology is formed in the embryonic period, when the fetus is in the womb. It is impossible to take any action.
The causes of fused fingers are as follows:
1. Heredity.
2. Taking antibiotics during pregnancy.
3. Smoking and drinking alcohol.
4. Impact of harmful substances on a woman’s body.
5. Infectious and viral diseases of a pregnant woman, such as influenza, mumps and chicken pox.
6. Gene and chromosomal pathologies.
The fetal limbs are formed in the 4th week of pregnancy. A woman may not be aware of her situation, which increases the likelihood of negative factors affecting the child.
Classification of the disease
When making a correct diagnosis, orthopedic doctors use several classifications of such a disorder. The disease may differ in shape, extent of fusion and condition of the limbs that have undergone deformation.
Thus, according to the type of adhesions between the fingers, the disease is divided into the following forms:
- soft tissue It is divided into membranous - in which there is a thin membrane between the fingers, skin - characterized by the presence of a rather dense bridge, which consists of skin and soft tissues, terminal - when only the phalanges have undergone fusion. Membranous syndactyly in children is considered the easiest to treat;
- bone - differs in that it is observed by the formation of bone adhesions;
- mixed - in this case, signs of all forms of the disease are observed. Treatment of this type of pathology is the most difficult.
In terms of length, such a congenital anomaly can be:
- complete - this form is diagnosed when the fusion has involved the phalanges of the nails;
- incomplete – is such if the level of adhesions is limited to the distal interphalangeal joints. This type of disease is also divided into basal and terminal types.
Based on the condition of undivided toes or hands, two types of this disease are distinguished:
- simple – fingers that develop normally can be fused;
- complex - implies fusion with the presence of concomitant disorders from the tendon-ligamentous or osteoarticular apparatus.
Nevertheless, the main classification of this pathology is its division into several genetic types:
- the first type - represented by complete or moderate fusion of the membranous nature of the middle and ring fingers or the second and third toes;
- the second form is the fusion of the third and fourth fingers of the hand, which is accompanied by the simultaneous doubling of the ring finger. In addition, deformity is observed in the fourth and fifth toes, with doubling of the little toe;
- third type - is expressed by complete bilateral damage to the ring finger and little finger, the fifth finger is shortened. It is noteworthy that with this type of disease, syndactyly of the toes is not observed;
- the fourth variety has the second name syndactyly of Gaza - it is distinguished by diffuse bilateral skin fusion and polydactyly. This results in the brush being spoon-shaped. There is no lower extremity involvement;
- fifth type - represents the fusion of the metacarpal and metatarsal bones.
It should be taken into account that unilateral anomalies are diagnosed more often than bilateral ones, and syndactyly of the hand is more often diagnosed than syndactyly of the foot.
Syndactyly, classification
Syndactyly is not always an isolated defect, especially when its occurrence is hereditary. Quite often it is combined with other developmental anomalies, especially those associated with damage to the human chromosome set. Also, a pathological connection of the fingers can occur with congenital defects of the musculoskeletal system. The classification of syndactyly depends on the condition of the affected fingers, the type of fusion, as well as the extent of the existing adhesive.
The connection may take the form of a thin membrane, a skin bridge with the inclusion of soft tissue, or a dense bone formation. In this case, fusion is possible either along the entire length, or only along one or two phalanges. The complexity of syndactyly is determined by the condition of the fingers affected by the defect. They may be developed normally or have any musculoskeletal abnormalities.
Syndactyly, which primarily affects the fingers of the upper extremities, is a significant cosmetic defect. In addition, the hand’s inadequate performance of its functions also has an extremely adverse effect on the formation of the child’s personality. Syndactyly, due to the fact that the performance of differentiated movements of the fingers is severely limited or impossible, leads to secondary defects. They manifest themselves in disturbances in the psychomotor, speech and, in some cases, intellectual development of the child.
Timely treatment of this pathology allows eliminating such a congenital cosmetic defect as syndactyly, as well as eliminating its negative impact on the baby.
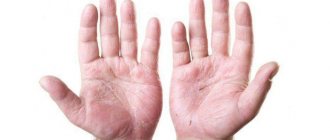
Symptoms of syndactyly in children
Symptoms of syndactyly in children photos.
Most often, with this pathology in children, fusion occurs between the middle and ring fingers and the second and third toes. It is extremely rare on the upper limbs that the ring and little fingers, thumb and index fingers will be undivided. In isolated situations, fusion of all fingers is diagnosed. With a bilateral pathology, symmetrical fusion is observed.
United fingers can be completely normal or underdeveloped, which will be expressed in:
- reduction in thickness;
- deformations;
- shortening;
- insufficient number of phalanges.
If a basal membrane is present or with a cutaneous type of syndactyly, the functioning of the hand remains normal. However, despite the fact that the child can perform a wide range of movements, he may experience problems with normal harmonious development. This means that development may be affected:
- psychomotor;
- intellectual;
- speech
Inferiority of the hand makes it difficult to study, and also greatly narrows the range of future professional activities.
Syndactyly of toes photo.
Prevention
Since syndactyly is a genetic mutation, sometimes inherited, it is impossible to prevent the formation of the mutation, except in certain cases. Thus, during the period of intrauterine development of a child, a pregnant woman should refrain from taking alcohol and potent medications that can cause disturbances in the development and growth of the upper and lower extremities of the fetus. A woman should think about the advisability of conceiving a child from a man whose ancestors suffered from similar congenital chromosomal abnormalities.
Diagnostics
Despite the fact that syndactyly of the fingers and toes is diagnosed immediately after the baby is born, to establish the type of congenital anomaly, data from instrumental examinations of the little patient are necessary.
However, the clinician needs to carry out an initial diagnosis, which can be carried out:
- pediatric orthopedist;
- neonatologist;
- pediatric surgeon.
Thus it includes:
- studying the medical history and life history of the patient’s mother both before pregnancy and during pregnancy - in some cases this may indicate the most likely predisposing factor for the occurrence of such an anomaly;
- a thorough physical examination;
- consultation with a genetics specialist - this is necessary to exclude or confirm the influence of genetic or chromosomal abnormalities.
Laboratory tests of blood, urine and feces in the presence of such a disease have no diagnostic value.
Among the instrumental diagnostic measures it is worth highlighting:
- X-ray of the hands and feet in several projections - this will help the clinician in assessing the condition of the joints and bone density, as well as in identifying the extent of fusion;
- Doppler ultrasound;
- rheovasography - a procedure for studying hemodynamics and the nature of microcirculation of the affected limb;
- angiography – is an x-ray of arterial vessels;
- electrothermometry.
Causes of pathology
Syndactyly does not always manifest itself as an independent defect: it is often combined with other diseases - genetic abnormalities of the development of the limbs (cleft hand, polyphalanx, clubhandedness).
In 60% of sick children suffering from syndactyly, other congenital pathologies of the musculoskeletal system are most often diagnosed. In 80% of cases, the cause of syndactyly is congenital pathology, which is a consequence of hereditary predisposition. In 20% of cases, the mutating gene is inherited through the male line and is familial in nature. Doctors assume that the disease is inherited as a dominant autosomal trait. There is evidence that the gene and chromosome syndrome is caused by a dominant gene that disrupts the separation of the fingers.
Genetic failure occurs in the first trimester of pregnancy. The hand and foot begin to form by the 4th week of pregnancy, and by the seventh week the fingers are completely separated. With syndactyly, this process occurs with serious disturbances.
What are the causes of fused toes and fingers, other than genetic failures? Exposure to negative factors is another cause of the disease. Alcohol intake, certain types of medications, exposure to various toxic substances, poor ecology, infectious diseases, and X-ray exposure cause all sorts of pathologies, including syndactyly. Chemical and thermal burns can also cause fused toes.
Treatment of syndactyly in children
Elimination of such congenital pathology involves surgical intervention. It is noteworthy that with syndactyly of the toes, in cases where the disease does not interfere with normal walking, surgical treatment is not carried out. In such a situation, the indication for surgery is the desire of the patient or his parents.
Treatment of syndactyly in children photo.
There are five methods by which the defect elimination procedure can be performed:
- dissection of the membrane without the use of plastic surgery;
- separation of fingers that have undergone fusion by skin grafting with regional tissues;
- separation of fingers using free skin grafting;
- dissection of fingers using combined plastic surgery;
- a multi-stage procedure involving skin, tendon, muscle and bone grafting.
The appropriate treatment method is determined individually for each patient, with clinicians taking into account the form and nature of the pathology.
The optimal age category for performing a surgical procedure is five years, but sometimes medical intervention can be carried out earlier than this period.
The postoperative period includes the application of a removable plaster splint, which provides immobilization of extended or spread fingers. The duration of this measure is approximately four months.
Fourteen days after the operation, rehabilitation therapy begins with the help of physiotherapeutic procedures. Among them it is worth highlighting:
- therapeutic massage of the hand or foot;
- exercise therapy;
- electrical stimulation of the muscles of the operated fingers;
- ultraphonophoresis;
- applications using paraffin, therapeutic mud and ozokerite.
Syndactyly
Syndactyly is a developmental anomaly of the fingers, resulting from a violation of their separation in the embryonic period. Syndactyly accounts for about half of all congenital anomalies of the upper limb and occurs with a frequency of 1 case per 2000-3000 newborns. Syndactyly of the hand or foot in a child can be an independent defect or combined with other deformities of the limbs: polyphalanxy and polydactyly, finger hypoplasia, brachydactyly, ectrodactyly, cleft hand, radial or ulnar clubhand, brachioradial synostosis, etc. 60% of children with syndactyly have concomitant congenital pathology of the musculoskeletal system (pseudoarthrosis, pathological varus or valgus position of the feet, clubfoot, etc.).
Prevention and prognosis
Due to the fact that syndactyly in children is formed during intrauterine development, there are no specific rules for prevention. Pregnant women only need to follow the rational management of pregnancy and not miss a visit to the obstetrician-gynecologist.
If one of the parents has a similar pathology in the medical history, then the couple should consult a geneticist before conceiving.
Timely surgical procedure provides a favorable prognosis, which is characterized by restoration of the normal anatomical structure and functioning of the cyst or foot.
In the absence of surgery, the pathology negatively affects the growth and development of the affected limb.
Prognosis and complications
A complication of the disease is functional inferiority of the hand, which makes it difficult to study and complicates the choice of profession. The prognosis for the congenital form of the pathology is usually favorable. The treatment methods used in modern medicine for syndactyly and pseudo-syndactyly provide good functional results.
These methods include timely surgical intervention and a set of postoperative procedures. Thanks to modern techniques, in 80% of operations it is possible to completely get rid of syndactyly, and the number of unsuccessful procedures is reduced to a minimum. During the operations, the skin, its mobility and sensitivity are completely restored.
Provided the surgeon follows the principles of modern surgical treatment, the risk of complications is minimal. Despite this, in some cases it is necessary to resort to repeated surgical intervention to correct mistakes made by the surgeon, which sometimes arise when performing complex operations.
Syndactyly: Nature's Error
Syndactyly
What does a woman in labor do when she takes her newborn in her arms? Hugs, kisses and... counts fingers. This is what our great-grandmothers and grandmothers did, and we, modern mothers, continue to do this. Normally, a baby has five fingers on each hand and foot. Normal, but sometimes not. Currently, more than 10% of children have congenital fusion of one or more fingers - syndactyly. What is the reason for this and what to do if your child is included in this number?
Syndactyly translated from Greek means “fingers together” (syndactylia: syn - together, dactylos - finger). This is a congenital complete or incomplete fusion of the fingers or toes as a result of their failure to separate during embryonic development with a violation of the cosmetic and functional state.
This pathology accounts for more than 50% of all congenital anomalies of the hands and feet. Most often there is fusion of the III and IV fingers, less often the II-III-IV-V, II-III and IV fingers. Quite often this happens on both arms or legs at the same time - bilateral syndactyly. In such cases, the fusion of the fingers is usually symmetrical.
Depending on the degree of tissue fusion, several types of syndactyly are distinguished:
- Membranous skin - there is a thin membrane between the fingers. This is the mildest type of syndactyly.
- Skin - with the presence of a thick bridge consisting of skin and underlying soft tissues, most often along the entire length of the fingers.
- Terminal - fusion is observed only at the level of the terminal phalanges.
- Bone - the bones of the phalanges of the fingers are fused. With this type of syndactyly, the fingers are usually underdeveloped, they are reduced in size and deformed.
- Combined - in this case, several forms of syndactyly occur at once. This is the most difficult type of disease to treat.
Why is that?
Syndactyly can be either an independent defect or a consequence of a hereditary factor. If one of your close relatives (up to the second knee) had fusion of the fingers, the likelihood of having a child with the same problem increases significantly. In this case, even when planning a pregnancy, future parents need to visit a geneticist. After special tests, the doctor will draw up an individual plan for preparing and managing pregnancy in order to minimize the risk of genetic inheritance of this defect.
In the absence of this factor
- Terminal - fusion is observed only at the level of the terminal phalanges.
- Bone - the bones of the phalanges of the fingers are fused. With this type of syndactyly, the fingers are usually underdeveloped, they are reduced in size and deformed.
- Combined - in this case, several forms of syndactyly occur at once. This is the most difficult type of disease to treat.
- when it is necessary to eliminate a cosmetic defect,
- in the absence or limitation of differentiated movements of the fingers, which is a big obstacle to the normal harmonious, including intellectual development of the child,
- if, as the child grows, there is a disturbance in the growth of fused fingers.
Why is that?
Syndactyly can be either an independent defect or a consequence of a hereditary factor. If one of your close relatives (up to the second knee) had fusion of the fingers, the likelihood of having a child with the same problem increases significantly. In this case, even when planning a pregnancy, future parents need to visit a geneticist. After special tests, the doctor will draw up an individual plan for preparing and managing pregnancy in order to minimize the risk of genetic inheritance of this defect.
In the absence of this factor, syndactyly is most often a consequence of disruptions in the process of intrauterine development. They can arise as a result of the action of various toxic substances on the mother’s body during pregnancy: drugs, nicotine, alcohol, unfavorable environmental conditions, work in hazardous industries.
A notorious example is the effects of the drug thalidomide, which American women were recommended to use to relieve symptoms of early toxicosis. Later it turned out that this drug often leads to congenital defects in the child’s limbs. As a result, many children with these types of problems were born in the country in a relatively short period of time. It is known that fusion of the fingers occurs due to failure to separate during their formation (at the 7-8th week of intrauterine development).
Therefore, during this period, the expectant mother should try to eliminate as much as possible the impact of adverse factors on the body. It is also necessary to take into account that toxic substances can accumulate in the body and, even if the negative factor is eliminated, they can remind themselves for a long time. For example, it has been established that congenital malformations of the limbs (including syndactyly) are much more common in women who have worked in chemical production for more than 5 years.
Work on mistakes
If the fusion is not along its entire length and there is no disturbance in the growth of the fingers, that is, the cosmetic defect is minimal, then you can refrain from surgical intervention.
The problem requires surgical intervention in the following cases:
Mild syndactyly is usually operated on after 2 years of age. For complex forms of congenital syndactyly, treatment is recommended to begin as early as 5-12 months - to prevent the progression of existing deformities and the development of secondary deformities. In the postoperative period, the limb is fixed with a plaster splint for about 1 month.
After the sutures are removed (on days 14-16), a complex of restorative treatment is prescribed, including massage of the hands, electrical stimulation of the flexors and extensors of the fingers, phonophoresis with lidase for postoperative scars, and ozokerite applications. With timely and correctly performed surgical intervention, syndactyly is completely eliminated in more than 80% of cases, and in the remaining 20%, the negative impact of syndactyly on the growth and development of the child’s limbs goes away.
Dig Deeper
Syndactyly is often a secondary defect and accompanies other skeletal developmental disorders. Up to 60% of children with syndactyly have concomitant congenital pathology of the musculoskeletal system. Therefore, if a child has any form of syndactyly (even the mildest), it is necessary to conduct a comprehensive examination as early as possible to exclude the presence of other anomalies.
Based on materials from Natalia Baurova’s article “Nature’s Mistake.”
Causes
The causes are usually genetic disorders and hereditary factors. That is, such a condition is most often transmitted along the family line.
But if such deviations were not found in the family, then it makes sense to track the characteristics of the pregnancy and the presence of unfavorable factors that could affect the fetus.
Usually these are toxic, narcotic or medicinal substances taken by the pregnant woman, stress, trauma, and so on.
The abnormal structure of the genital organs can also have an impact. Syndactyly often appears as part of the clinical picture of other congenital conditions.
Important! Syndactyly can be congenital, but cases of acquired type have also been recorded after receiving a thermal or chemical burn.
Syndactyly - therapy
Congenital pathology requires surgical treatment. Mechanism of surgical intervention:
- Plastic surgery;
- transplants;
- replacement of a skin defect;
The indication is the age and condition of the fingers. The operation can begin from twelve months. Transplants are often used. After surgery, a cast must be used.
Rehabilitation treatment after surgery includes the following:
- massage;
- electrical stimulation;
- phonophoresis;
- appliqués
A complex form of pathology should be treated in a timely manner. The principle of treatment is replacement and correction. Principles of therapy for complex forms:
- planning;
- cutting out;
- fold formation;
- disconnection;
- eliminating the defect;
- replacement
With timely treatment, the result is favorable. In most cases, results are achieved. Less often the results are negative.
The recovery period matters. It is as follows:
- tire installation;
- finger fixation;
- physiotherapy;
- massage;
- mud treatment;
- physical training
go to top
Symptoms
The symptoms of syndactyly are quite striking. First of all, we are talking about the actual fusion of the fingers, which can be complete, up to the common nail on the affected part, or partial, when one or two phalanges are fused.
In addition to the aesthetic defect, we are also talking about a violation of the functionality of the department. Lateral mobility of the joints is limited. Grasping ability also decreases. If we talk about the feet, the shock-absorbing properties of the feet are reduced.
The condition is divided into soft tissue and bone forms. in the first case, the condition is easier in the context of treatment, since the separation of the soft tissues is simpler and therefore does not require a long recovery. In the case of bone fusion, the joints suffer, and this has a greater impact on their functionality and significantly complicates the further elimination of the condition.
On the hands, fingers 3 and 4 usually undergo fusion, and on the feet, 2 and 3. Fusion of other sections occurs less frequently, and generalized forms of syndactyly, when all fingers are fused, are completely exceptional cases. Unilateral type of lesion is more common than bilateral.
The fingers may be underdeveloped or fully developed. Sometimes, during embryonic development, amniotic amputation occurs, which implies the absence of any phalanx in the affected section. With cutaneous or soft tissue syndactyly, functionality is almost not impaired.
Syndactyly - etiology
The etiology has not been studied. The factor of heredity matters. This pathology is a mutation. Inheritance affects the male population, but is rare in women.
The disease is observed later. The bones of the hand begin to form. Eighth week – formation of fingers. The following processes occur:
- the bone grows;
- tissue growth slows down
This pathology is a sign of congenitality. Concomitant pathology matters. Musculoskeletal disorders are the principle of concomitant pathology.
The pathology involves pathology of the apparatus of the hand and toes. Provoking factors in the development of this disease:
- toxins;
- medicines;
- alcohol;
- bad ecology;
- harmful substances
The consequence of this process is anomalies.
go to top