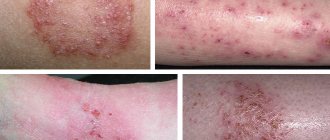
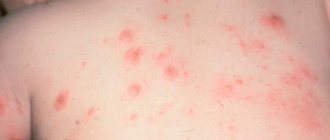
What is hand eczema
Chronic inflammation of the skin of an allergic nature is called eczema. The pathology is manifested by rashes of various types, itching on the hands. The disease is characterized by a complex and cyclical course - exacerbation is replaced by periods of remission.
Eczema is an allergic reaction of the skin to toxic poisoning, which is caused by a violation of the peripheral flow of lymph and blood.
The immune system, in response to the aggressive action of certain substances, begins to produce antibodies. They provoke an increase in the level of serotonin, histamine and lymphokines. Normally, inflammatory mediators do not affect the body, but when antigens invade, they become aggressive. Therefore, eczematous signs appear on the skin of the hands.
Classification of pathology
The disease is distinguished depending on its pathogenesis (mechanism of development). Main types of eczema:
- true (idiopathic): dyshidrotic, pruriginous, hyperkeratolytic (callosal);
- contact (professional);
- microbial: coin-shaped (numular), paratraumatic, fungal;
- seborrheic;
- atopic;
- children's: microbial, pruriginous, true, herpetiform, seborrheic.
Based on the type of rash, eczema on the hands is divided into 2 types. These include:
- Dry – a large number of dry crusts of a grayish color.
- Wet - wet rash on the palms, between the fingers. The skin turns red over the entire area of the arm.
Pathology is classified according to stages of development:
- erythematous (redness of the skin) – initial stage;
- papular (appearance of nodules);
- vesicular (formation of bubbles);
- weeping (release of serous fluid);
- crusty (drying of exudate);
- squamous (peeling of dry crusts) – the final stage.
According to the nature of the disease, it has 3 stages:
- Acute – pronounced symptoms lasting up to 2 months;
- Subacute – mild course, but symptoms persist for up to six months;
- Chronic - relapses are replaced by remission. The duration of the stage is not determined.
Diagnosis of the disease
Treatment of eczematous dermatitis is carried out exclusively by a dermatologist. Any therapy begins with diagnosing the disease. Diagnosis of eczematous dermatitis is based on the pathological history. In addition, visual signs and symptoms that the patient complains of are taken into account.
When you attend your consultation visit, your doctor will do a visual inspection of your hands. The basis of diagnosis is not only an examination of the patient, but also a survey of the patient regarding the manifestation of signs of the disease, lifestyle, type of professional activity and genetic predisposition to eczema on the hands.
Also, for a more thorough study of the etiology of the disease, a number of laboratory examinations are prescribed and a consultation with an allergist-immunologist is required.
Tests required for passing:
- General blood and urine tests
- Determination of immunoglobulin E titre level
- Allergy diagnostic tests
- Stool for the presence of helminth eggs
- Microscopy of hand skin scrapings
- Biopsy of the inflamed area
To establish an accurate diagnosis, a histological examination is performed. For eczematous dermatitis of any form, the histological picture is the same. Any changes are observed only at various stages of inflammation, which can develop with eczema on the hands.
During the acute stage of the disease, the following is observed:
- Parakeratosis in the upper layers of the skin.
- Focal spongiosis.
- Swelling of the papillary layer of skin.
In the presence of a chronic form of eczematous dermatitis, the following manifestations will occur:
- Massive hyperkeratosis
- Parakeratosis
- Acanthosis
- Perivascular infiltrate
After receiving all the results of the analysis, the dermatologist diagnoses the patient with eczematous dermatitis on the hands and prescribes full treatment for this disease. To do this, depending on the established cause of the development of eczema, such specialists as a psychotherapist, gastroenterologist, and endocrinologist can be involved in treatment.
Symptoms of the disease
Signs of pathology appear gradually. First, eczema on the fingers, palms, hands, then the disease spreads further. Symptoms depend on the type of pathology. Main features:
- redness of the skin of the hands with clear boundaries of inflammation;
- tissue swelling;
- burning and itching;
- acanthosis (thickening) of the dermis;
- formation of nodules;
- dryness or moisture of the epidermis;
- hyperthermia of the skin of the hands;
- the appearance of vesicles (bubbles with liquid);
- painful cracks, ulcers, wounds;
- insomnia, irritability.
Articles on the topic
- Scabies in humans - symptoms and manifestations, methods of treatment
- Types of dermatitis - signs and manifestations, diagnosis and treatment
- Paronychia of the finger - types of inflammation on the legs or arms, drug and surgical therapy
What does dry eczema look like?
The main difference between this type of pathology is the absence of bursting vesicles. Location: the back of the fingers and hand. The onset of the disease resembles eczematid - pink spots appear. The erythemas gradually merge and form a red plaque-like spot. Then the skin becomes dry, begins to peel, scabs and sores appear.
If left untreated, painful cracks appear, from which ichor is released. It serves as a breeding ground for pathogenic microorganisms, so purulent ulcers may appear on the fingers or hands.
Wet
This type of eczema is characterized by the formation of “serous wells” - erosions with constant fluid secretion. They have a clear border, but then unite into bright red lesions without a stratum corneum of the epithelium. The base of the erosions is edematous, and gray exudate constantly oozes from them. Wet eczema is also accompanied by burning and itching.
Symptoms and treatment of wet eczema: photos, types and initial stages of the disease on the legs
Eczema is an inflammatory skin disease of an allergic nature, characterized by a tendency to relapse and appearing in the form of burning, itching and rash on the skin in various places. Patients experience high skin sensitivity to various irritants, which explains the progression of eczema, often burdened by concomitant diseases.
The pathogenesis of the disease is similar to the mechanism of manifestation of allergic dermatitis. Often the latter is a disease that precedes the onset of eczema. The formation of eczema on the leg is one of the most common areas where it is located.
Causes of eczema on the legs
The reason for the appearance of eczema is a hereditary predisposition to impaired reactivity of the body, as well as to allergization.
The skin of those affected by eczema is usually sensitive to a variety of irritants, both internal and external. Abnormalities in the content of immune cells appear in the blood, as a result of which true eczema is mostly explained by autoimmune diseases .
Endogenous factors that influence the formation of eczema on the legs:
- Pathologies of the endocrine system (diabetes mellitus, hyperthyroidism).
- Long-term infectious diseases.
- Neurogenic (stress, vegetative-vascular dystonia, mental trauma, nervous overstrain).
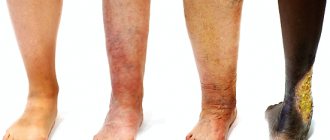
- Circulatory disorders and vascular diseases (for example, varicose veins, thrombophlebitis).
- Diseases of the intestinal and gastric tract (gastritis, colitis, pancreatitis, cholecystitis, ulcers).
Exogenous factors that lead to the appearance of eczema on the legs or relapse of the disease:
- Wearing wool or synthetic clothing.
- Abrasions, injuries, wounds, scratches.
- The effect of increased or decreased temperatures, climate change.
- Fungus on the feet.
- Exposure to chemical agents, allergens (food, air, contact).
Types and photos of eczema
Taking into account the various factors that cause the disease, the following types of eczema on the legs are distinguished:
- Microbial – formed near pyoderma, wounds, foci of inflammation.
- Idiopathic or true. Has a tendency to become a chronic disease. According to external signs, it can be wet and dry.
- Occupational eczema appears in workers in the chemical industry and other areas of production as a result of constant exposure to irritants. It can form on the skin of the legs in the absence of special clothing and protective suits.
- Mycotic – caused by infection of the skin by fungal diseases.
- Horny or callous is formed on the soles of the feet and is a keratinized layer of tissue with inflammation around it.
- Dyshidrotic. Formed on the soles of the feet, it can cause dystrophic changes in the nail plates.
- Varicose eczema often accompanies varicose veins, forming along the infected vessels of the lower extremities.
- Infantile eczema can appear anywhere on the body, usually on the arms and legs.
Symptoms of the disease
The appearance of any type of eczema is similar in basic external signs . The most common type of eczema is true.
The disease has an abrupt onset with acute symptoms, then it gradually becomes a chronic disease. Against the background of redness and swelling of the skin, small vesicles filled with clear liquid appear.
As the eczema progresses, the blisters open, creating local erosive depressions.
At this phase, this disease is called “weeping” eczema, since the contents of the vesicles slowly leak onto the skin.
As the body's defense response to this irritant increases, the vesicles dry out , forming crusts. At this stage, the skin becomes dry and severe peeling occurs. The skin on the legs begins to crack, with scabs and scales clearly visible between the cracks.
Any degree of formation may be accompanied by redness of the skin, swelling, and severe itching. The place where eczema appears on the legs is mainly the area under the knees, feet, and upper legs. The outlines of the neoplasms are uneven.
Infected areas of the skin may alternate with healthy ones.
During dyshidrotic eczema, the vesicles are inflamed and dense; due to the stratum corneum that covers the rash, there are no weeping processes.
Varicose and microbial eczema form near wounds and other skin lesions, resulting in skin redness, itching, severe swelling, as well as the appearance of lamellar crusts, ulcers and papules.
Stages of development
There are six stages of eczema:
- Papulovesicular – formation of a rash (vesicles, papules).
- Acute or erythematous - erythema and the appearance of edema.
- Weeping - opening of vesicles, pronounced moisture.
- Cortical – drying of bubbles, appearance of scabs.
- Subacute – subsidence of inflammation, dry skin, appearance of cracks and scales.
- Chronic – the skin at the sites of eczema infection remains pigmented, dry, and swollen.
Complications and consequences
With proper treatment, eczema on the legs does not leave scars or scars . In the chronic stage, external manifestations of the disease can be severe dryness of the skin, cyanosis and swelling.
Complications that can cause harm to health, as well as be a threat to life, are considered to be fungal, viral and bacterial infections that infect the inflamed area as a result of improper care or scratching.
In this case, purulent weeping formations with an unpleasant odor may appear on the skin surface, deterioration in health, headaches, and an increase in body temperature.
The most dangerous complication that can result from eczema is erythroderma . Requires hospital treatment, can affect large areas of the body and is a generalized process. Another disease that is a likely complication of eczema and requires urgent treatment is Koposi’s eczema herpetiformis.
Diagnosis of the disease
The diagnosis by an allergist or dermatologist is based on identifying factors that provoke eczema and an external examination of the patient.
Laboratory diagnostic methods consist of blood tests for immunograms, as well as biochemical and general blood tests.
Additionally, skin tests can be performed to determine allergens, as well as stool examination for helminths . If accompanying diseases are suspected, consultation with other specialists is required.
Differential diagnosis is made with the appearance of scabies, herpes virus infection, dermatitis, and in children the presence of diathesis.
Eczema on the leg: treatment
Treatment of eczema begins with the recommendations of a dermatologist, which are mandatory for patients to follow, these are:
- Room ventilation. Maintaining optimal temperature and humidity.
- Taking medications, administering serums and vaccinations.
- Careful hygiene of the skin of the feet, control of sweat.
- Adequate sleep, correction of rest and work schedules, limitation of physical and psycho-emotional stress.
- Exclusion of all possible irritants and allergens (animal hair, dust, wool and synthetic clothing, detergents, mold, pollen, chemicals).
- Hypoallergenic diet.
- Avoiding injury to contaminated areas.
Systemic treatment occurs in the following stages:
- Antihistamine and desensitizing therapy - Erius, Telfast, Kestin, Diazolin, Suprastin, Tavegil, Peritol. To avoid tolerance, it is recommended to change medications after the end of therapy.
- Sedative therapy (valerian, presen, peony root, motherwort, aminazine, mint tincture).
- To reduce sensitivity to allergens, injections of sodium thiosulfate and magnesium sulfate.
- Enterosorbents (enterosgel, polysorb).
- Laxatives and diuretics to accelerate the release of allergens from the body (duphalac, senade, furosemide).
- In case of severe disease, intravenous drip-plasma-substituting solutions (hemodesis, polydesis).
- If therapy is not effective, hormonal corticosteroids (diprospan, prednisolone) are prescribed.
- Preparations for the correction of immunity (taktivin, ruzam, dekaris).
- For diagnosed diseases of the liver and gastrointestinal tract - normalizers of intestinal microflora (bifidumbacterin, lactobacterin, linex), choleretic drugs, enzymes (festal, mezim).
Recommended physiotherapeutic procedures:
- Laser treatment.
- Ultraphonophoresis.
- Magnetotherapy.
- Electrophoresis.
- Reflexology.
- Mud therapy.
External treatment of eczema on the legs
Ointments are selected individually by the doctor, taking into account the severity of the disease and its type:
- To reduce inflammation - ichthyol, naphthalene, zinc ointments, tar.
- After inflammation subsides, use aqueous-alcohol solutions to relieve itching.
- When a bacterial or fungal infection occurs, use ointments with antimycotics and antibiotics.
- For severe eczema of the legs - corticosteroid ointments (mometasone, hydrocortisone, advantan).
Traditional treatment for eczema on the legs
At the initial stage of the disease, as well as after getting rid of the main symptoms and in the chronic stage, you can use traditional medicine:
- Stir 50 gr. honey and ground garlic (3 cloves), rub into the infected area every day.
- Grate raw potatoes, take half a glass, mix with 1 tsp. honey and apply to the affected area for two hours under a bandage.
- Grate one carrot on a fine grater, drain the juice, apply the juice to the skin of your legs under a bandage for three hours.
- Mix three tablespoons of fish oil and one spoon of tar, pour one spoon of apple cider vinegar. Use this mixture every day until symptoms subside.
- You can use 1 tbsp inside. l. corn oil twice a day and drink water with a small amount of apple cider vinegar.
- A good remedy for eczema on the legs is compresses made from fresh cabbage (a pulp of them or slightly broken leaves).
- Grind 30 gr. calendula flowers, add horseradish juice (1 spoon), the same amount of apple cider vinegar, apply to infected areas of the skin as applications.
- Lotions made from viburnum berries and currant leaves help with wet eczema.
Prevention:
- After the exacerbation is relieved, constant moisturizing of the skin is required.
- Maintaining optimal humidity and temperature in the room.
- Follow hygiene rules, but avoid prolonged and frequent contact with water.
- Using clothes made from natural materials.
- Use of washing powders, detergents, hypoallergenic cosmetics.
- Reducing stress.
- Elimination of all possible contacts with irritants, hypoallergenic diet.
Eczema on the legs is a rather serious disease, the symptoms of which constantly cause discomfort to the patient. In order to get rid of this unpleasant disease forever, it is necessary to use a combination of effective remedies for the disease.
//www.youtube.com/watch?v=5fr4vPy7hXQ
Eczema on legs
Source: //dermatolog.guru/zabolevaniya/ekzemy/ekzema-nog-na-nachalnoy-stadii-lechenie-i-foto.html
Causes of eczema
The pathology refers to diseases of neuro-allergic origin. Therefore, it is caused by a specific reaction of the skin of the hands to a certain irritant:
- poplar fluff, pollen, animal hair, mold;
- food with high allergenic properties (honey, strawberries, eggs, citrus fruits, chocolate);
- dyes, chemical compounds of various origins;
- constant contact with heavy or precious metals;
- uncontrolled use of drugs (analgesics);
- low-quality cosmetics, household chemicals, clothing fabrics.
Classification according to the location of the foci of the disease
There is also usually a classification of eczema on the hands according to the location of the lesions:
- Plaques on fingers.
- Plaques on the palms.
- Plaques on elbows.
Regardless of where the disease manifests itself, be it a rash on the inside of the arms or eczema between the fingers, treatment depends primarily on the type of disease and the specific situation of the patient.
Eczema located on the elbow
Symptoms of the disease on the hands
Eczema of the skin of the hands may differ in symptoms depending on the type of disease; if you know what eczema on the hands looks like, the type of disease is easy to determine.
Thus, the idiopathic type is expressed by the following symptoms:
- rashes in the form of bubbles and nodules, forming erosions that eventually flow into serous wells;
- skin redness and dryness - eczema on the elbows;
- severe itching;
- lichenification of the skin.
Symptoms of microbial coin type:
- the lesions are round in shape and resemble coins in appearance;
- swelling and redness of the skin;
- slight itching.
Mycotic symptoms:
- the lesions are covered with purulent and serous papules;
- there are weeping erosions;
- severe itching;
- redness of the skin.
Symptoms of dyshidrotic:
- vesicles – bubbles with a diameter of 1 to 5 mm;
- severe itching;
- bubbles can form erosions, which, when healing, remain in the form of pigment spots.
Symptoms of professional:
- the clinical picture is similar to the manifestations of the idiopathic type of the disease;
- characterized by a chronic form: remission begins when contact with the allergen ceases, exacerbation occurs when exposed to it.
The blisters crack, leaving wounds and erosions
Causes of eczema on hands
If a person is convinced that he still has eczema on his hands, the reasons should concern him first. Different types of disease are associated with different precipitating factors, so the causes and treatment are closely related.
The main cause of the idiopathic type of the disease has not yet been established. However, doctors identify a number of factors that can contribute to the development of the disease:
- genetic predisposition;
- diseases of the endocrine and digestive systems;
- vegetative-vascular dystonia;
- disorders in the mental system;
- weak immunity;
- stress.
It is with stress and lack of sleep that eczema on the hands after childbirth is usually associated.
In the chronic form of the idiopathic type of the disease, the following factors may contribute to exacerbation:
- toxic substances;
- wool;
- wrong diet;
- infectious diseases.
What exactly causes microbial coin-shaped eczema as idiopathic is currently unknown, but a number of scientists believe that the disease is caused by the presence of a chronic infection in the body. However, this still remains at the level of hypothesis.
The causes of mycotic type eczema are explained quite simply. If the skin is damaged, pathogenic fungi can enter the wound.
Considering that they are foreign to us, as are the products of their metabolism, the body begins to actively fight this. But if the immune system is impaired or weakened by another factor, it produces an excessive amount of antibodies, which ultimately cause an allergic reaction.
The root of dyshidrotic eczema remains a mystery to researchers, but a number of irritants have been proven to influence the development of the disease:
- pathologies of the endocrine and digestive systems of organs;
- weakened or impaired immunity;
- vegetative-vascular dystonia;
- genetic predisposition;
- food allergies;
- allergies to household chemicals;
- disruption of the nervous system.
Researchers believe that dyshidrotic eczema is correlated with other diseases, most notably atopic dermatitis, hay fever and asthma.
The occupational type of the disease develops under the influence of allergic sensitization, that is, with frequent repetitions of exposure to the toxin on the skin. As with other types of illness, occupational eczema is also associated with disorders of the digestive, endocrine and immune systems.
Ordinary wool can provoke an exacerbation of the disease
How to cure eczema on hands
Treatment of pathology depends on the type, cause and course of the disease and is complex. Eczema of the hands, palms and fingers is treated with the following methods:
- drug therapy;
- diet;
- physical therapy;
- folk remedies.
General drug therapy
For eczema in an adult or child, several groups of drugs are prescribed:
- Antihistamines – block the release of histamines, relieving itching. In severe cases, drugs are administered parenterally (Promethazine, Chloropyramine), in moderate cases - orally (Zodak, Citrine, Dezal). Dosage – 1 tablet 3 times a day for 2 weeks.
- Hormonal - for extensive skin lesions (Prednisolone, Dexamethasone). Corticosteroids are used for a short time (1-2 weeks) in the form of tablets or injections.
- Sorbents – for better removal of allergens (Enterosgel, Polysorb) for no longer than 10 days.
- Diuretics – 7-10 days to accelerate lymph cleansing (Furosemide).
- Means to reduce intoxication (Sodium thiosulfate, Calcium gluconate) - 10-20 injections. For microbial form - hexamethylenetetramine solution.
- Sedatives - to eliminate neurotic disorders. Sedatives of plant origin (Persen, Novopassit) for 3-4 weeks or tranquilizers in small doses for no more than 10 days (Phenazepam, Chlozepid).
- Antibacterial - for exodermatitis (microbial rash). Azithromycin, Suprax in tablets or capsules. For fungal infection - Nizoral, Fluconazole.
- Vitamins – to improve immunity (nicotinic and ascorbic acid, injections of vitamin B, oil solution E).
Local treatment of eczema
Therapy with external agents depends on the form of the disease. Groups of drugs prescribed:
- Non-hormonal creams or ointments (Elidel, Losterin) and corticosteroids (Triderm, Elokom) - relieve inflammation of the deep layers of the dermis.
- Laxative and itching agents (lead water, Burov's liquid).
- Antimicrobial – Panthenol, brilliant green, resorcinol solution.
The purpose of treatment depends on the stage of development of the disease. Means used:
- Powders made of white clay, zinc oxide - for the acute stage.
- Lotions of solutions of boric acid, tannin - for swelling, erythematous lesions of the hands.
- Boron-zinc and salicylic ointment, Lassara Paste - for chronic conditions.
Diet therapy
Diet is used to eliminate food allergens. Basic Rules:
- Eat small meals 4-6 times a day.
- Keep a food diary to identify trigger foods.
- Avoid fatty, salty, spicy foods.
- Prepare food by stewing, steaming, baking.
Eliminate some foods and make up your diet from plant-based and fermented milk foods:
| Prohibited Products | Allowed |
| Fatty meat, fish, lard, sausage, smoked products | Lamb, rabbit, turkey, offal, hake, pollock, pike perch |
| Tomatoes, garlic, beets | Greens, turnips, cucumbers, pumpkin, zucchini |
| Sweets, baked goods, honey, chocolate | Fructose, homemade marshmallow |
| Citrus fruits, pomegranate, strawberry, melon, nuts | Prunes, apples, gooseberries, watermelon, banana |
| Whole milk | Low-fat fermented milk products |
| Coffee, soda, red wine | Rosehip decoction, weak tea |
| Hot spices, marinades, mayonnaise, eggs | Buckwheat, rice, oatmeal |
Physiotherapy
Physiotherapy is used in complex treatment. Effective procedures:
- ultraviolet irradiation;
- paraffin applications;
- ozone therapy;
- mud therapy;
- dry radon baths;
- laser therapy;
- acupuncture;
- diphenhydramine inhalation.
Drug treatment
Eczema can be treated with medications, physiotherapy, and traditional methods. But the most effective treatment is drug therapy.
- If the disease is allergic in nature, it is necessary to reduce the body's susceptibility to allergens. For this, doctors prescribe a course of intravenous injections of calcium chloride, medications with magnesium, and sodium in the composition.
- For insomnia and other nervous system disorders accompanying the disease, it is recommended to undergo several sessions of hypnosis and reflexology. Also, to normalize the functioning of the nervous system, herbal-based sedatives (valerian infusion, Persen, Novopassit) are prescribed.
- To cleanse the intestines of toxic substances, Enterosgel and Polysorb are prescribed.
- To reduce the intensity of symptoms in acute eczema, antihistamines (Dezal, Zyrtec) are prescribed.
- Vitamin therapy is a mandatory measure for the treatment of any form of eczema. Doctors prescribe an oil-based solution of vitamin E, ascorbic acid, and folic acid.
- If the cause of eczema on the skin of the hands is dysbiosis or liver disease, enzyme medications (Gastenorm, Pancreatin) and probiotics (Lactobacterin) are prescribed.
- An important element of treatment is increasing immunity. For this purpose, immunostimulants are used (Hydrocortisone, Immunoglobulin, Echinacea tincture).
- Therapy for microbial eczema involves taking antibacterial drugs. If an infection of fungal origin occurs, antimycotic medications are prescribed.
Treatment with topical drugs
To alleviate the symptoms of the disease and shorten the duration of relapse, topical medications are used.
The most effective remedies are podophyllin ointment and diphenhydramine paste. If weeping wounds appear on the tips of the fingers and palms, use powders based on wheat starch. Swelling and weeping areas should be treated with lotions based on tannin and boric acid.
If there is extensive damage to the skin of the hands, including nails and hands, hormonal corticosteroid ointments (Celestoderm, Advantan) are prescribed.
Attention! You cannot choose medications at your own discretion. All medications must be prescribed by a doctor.
Physiotherapeutic procedures
Physiotherapeutic treatment plays an important role in the treatment of eczema on the hands. Dermatologists recommend taking baths with mineral water and healing mud. Ozone therapy and laser therapy are highly effective. Patients should also undergo treatment with ozokerite and ultrasound.
Diet for eczema
The frequency of meals should be at least 4 times a day. To eliminate the manifestations of eczema, you need to figure out which product is an allergen.
List of animal products that most often cause allergies:
- Fish.
- Milk (both cow's and goat's).
- Chicken.
- Eggs.
Herbal products containing allergens:
- Nuts.
- Chocolate.
- Lentils, beans, peas.
- Red, orange, yellow vegetables (strawberries, oranges, watermelons).
If after consuming a certain product the body reacts, it is necessary to completely exclude it from the diet.
Nail eczema requires special attention. With this form of the disease, cottage cheese, eggs, beans, and full-fat milk are prohibited. If the hands, fingers, or elbows are affected, nuts and citrus fruits are strictly prohibited.
Traditional medicine recipes
A popular method of treating eczema is using folk remedies at home. Here is a list of the most effective recipes:
- Salt baths. This remedy is suitable for treating eczema on the elbows and fingers. These areas are most susceptible to dryness. Pour 2 tablespoons of salt into 1 liter of hot water. After it dissolves, soak your hands in the bath for 30 minutes.
- Sea buckthorn oil. Sea buckthorn oil softens and soothes the skin. Therefore, this remedy is suitable for the treatment of dry erosion of the hands, fingers, elbows and other areas.
- Strawberries. Mash fresh berries and apply to affected areas. Strawberry pulp is most effective for eczema of the hands, palms, and fingers.
You can treat eczema with traditional methods only after consulting a dermatologist. Any folk remedy can be both useful and harmful.
How to get rid of eczema at home
To cure the disease at home, follow the recommendations:
- Follow the method of preparation and application of the recipe.
- You cannot cure eczema with folk remedies alone.
- Follow your diet.
- Use recipes for the specified types of pathology.
Treatment of eczema on the hands with folk remedies
A cure for eczema on your hands can be prepared at home. Effective recipes:
- Mix 100 g of butter (82.5%) with the same amount of birch tar. Apply the product to dry eczema 2-3 times a day for 30 minutes.
- 1 tbsp. l. apple cider vinegar and tar combined with 3 tbsp. l. fish oil. Place the ointment in a thick layer on a sterile napkin and apply a compress for 40-60 minutes.
- Combine 20 ml of freshly squeezed celandine juice with petroleum jelly until a thick consistency is formed. Leave the mixture for 15 hours. Apply the ointment to eczematous areas 2 times a day.
- 5 tbsp. l. add burdock root to 3 liters of boiling water. Simmer the broth for half an hour covered over low heat. Keep your hands in the warm broth for 15-20 minutes. The course of treatment is 2 weeks.
Traditional methods of treating eczema on the face
Traditional recipes are an effective addition to basic therapy, but are not able to cure the disease on their own.
It is important to note that in addition to the beneficial properties, traditional therapy methods have certain contraindications, which are important to consider before starting treatment. Otherwise, complications may develop.
| Recipe name | Cooking method |
| Potato compress | Grind two raw potatoes, mix with honey until smooth and thick. Apply to affected skin for 2 hours. You can also use potato juice to lubricate the rash with vesicles. |
| Propolis-based ointment | Mix 150 g of melted butter with 20 g of crushed propolis. Cook in a water bath, stirring constantly. Cool and apply on damaged skin before bed. |
| Berry compress | Grind 200 g of strawberries, mix with linseed oil (20 g). Use as a compress 2 times a day. |
Eczema on the face is a serious dermatological disease that requires timely medical attention. If the disease is advanced, it will regularly recur, cause serious complications, and be accompanied by the development of secondary infections.
Prevention and prognosis
Eczema has a chronic course, so it is impossible to completely get rid of it. But if you increase the body’s defenses and adhere to a healthy lifestyle, you can reduce the number of relapses to a minimum. The most important thing is not to let the disease get worse, and to start fighting it at the first manifestations.
To avoid the occurrence of this disease, you need to follow these recommendations:
- Always wear gloves before working with poisons or chemicals.
- Support immunity.
- Stick to proper nutrition.
- Wear clothes made from natural fabrics.
- Do wet cleaning with gloves.
- Use only high-quality cosmetics.
- Wash your hands only with soap or other means specifically designed for this purpose.
- Treat diseases of the endocrine system in a timely manner.
- If the skin on your hands becomes dry, constantly moisturize it.
- Avoid stress.
To ensure that this disease never bothers you, you need to follow the most important rule of protecting the skin of your hands from exposure to harmful substances.