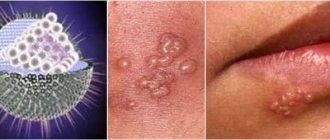
How to get rid of herpes at home
At the initial stages of skin rashes, it is recommended to start using medications. Acyclovir is a universal remedy in this case, as it also reduces the swelling that can form with herpes. If you do this in the early stages, the process of the disease itself will be somewhat easier. But you can also use improvised means and treat yourself at home with no less effectiveness.
First of all, the patient’s immunity is increased so that all the protective functions of the body are fully involved. This is facilitated by drugs that contain interferon, as well as various groups of vitamins. With their help, the process of activating the immune system will begin, and the treatment will be more effective.
It is also important to limit the contact of a carrier of the herpes virus with other people. Kissing a patient or touching an infected area is strictly prohibited. If this somehow happened, then it is strongly recommended to disinfect the hands of the pathological patient using a special product in order to eliminate the possible fact of infection.
Along with the use of all kinds of ointments, you can use various folk remedies. Before this, a mandatory consultation with a dermatologist is necessary, since, for example, if herpes occurs on the eye, it is recommended not to use traditional methods of treatment. If the doctor approves the use of a particular remedy, then you can begin therapy. Tinctures of propolis or calendula, decoctions of ginseng or rose hips, garlic and soda solution are considered popular and, most importantly, effective.
Watch your own diet, especially in spring and autumn. Pay due attention to your immunity. When it comes to treating herpes, contact a specialist to protect yourself from the possible spread of the virus not only throughout the forehead, but also to other parts of the body.
Data Jun 17 ● Comments 0 ● Views
Doctor Dmitry Sedykh
Two types of herpes infection can appear on the face - HSV and herpes zoster. The diseases have similar symptoms. Treatment of herpes on the face is carried out conservatively, using antiviral drugs, traditional medicine, and physiotherapy.
There are 6 types of herpes virus. The skin and mucous membranes are most often affected by two types - herpes simplex virus (HSV 1 or 2) and herpes zoster virus (Varicella-Zoster). The symptoms of these diseases are almost the same, but before treating herpes on the face, you need to know the type of virus. Treatment tactics for different diseases vary somewhat.
Herpes simplex virus
The most common pathogen that causes herpes infection. It affects the skin and mucous membranes. Herpes on the face is usually caused by HSV type 1. HSV is quite stable in the external environment; it dies under the influence of ultraviolet irradiation and high temperature.
Penetration of viral particles occurs through the skin and mucous membranes. The virus multiplies in epithelial cells, causing their death. Then HSV reaches the nerve ganglia along the nerve fibers, where it enters a latent state. When favorable conditions for the pathogen arise, the infection is reactivated.
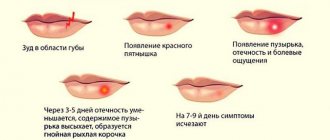
The main symptom of herpes infection on the face is a specific vesicular rash. It is represented by small grouped bubbles, inside of which there is a clear liquid. The blisters burst, forming painful and itchy erosions. Skin lesions of herpes are usually localized on the face - lips, chin, nasolabial triangle, wings of the nose. The forehead and area around the eyes are less commonly affected. The appearance of a rash on these parts of the face is considered a prognostically unfavorable sign.
Herpes simplex virus
Shingles
This form of herpes is caused by the Varicella-Zoster virus, the causative agent of chickenpox. If a person has previously had chickenpox, the pathogen is stored in the nerve ganglia. In the presence of predisposing factors, the infection reactivates in the form of herpes zoster. This name is associated with the peculiarity of the rashes - they appear along the nerve fibers, as if encircling an area of the body.
On the face, shingles is most often localized in the area of the trigeminal or facial nerve fibers - the chin, cheeks, forehead. Sometimes the appearance of rashes is observed on the scalp. People of any age get sick. The disease is characterized by initial symptoms in the form of pain along the nerve fibers. The pain can reach significant intensity.
2-3 days after the onset of pain, specific rashes appear on the face. First, small pink spots form on the skin, then in their place bubbles with transparent contents appear, as with herpes simplex. They are arranged linearly or in the form of an oval. The bubbles do not burst, but dry out, leaving a crust. After a few days, the crust disappears, leaving no scars.
A feature of the course of herpes zoster is. These are pain sensations that occur after recovery. The pain can persist for several months and is burning or aching in nature.
Shingles
Possible consequences
The Zoster virus is neurodermotropic, i.e. affects not only the skin, but also the cells of the central and peripheral nervous system. In severe cases, it can affect internal organs, affecting the autonomic ganglia of the nervous system. The most dangerous complications of herpes zoster include:
- neuralgia,
- neuropathy of the cranial and peripheral nerves,
- serous meningitis (especially in children);
- encephalitis;
- cystitis or urethritis (herpetic);
- inflammatory lesions of internal organs, etc.
There is also an opinion that the virus can cause cancer.
In 5% of patients with herpes zoster, a weakening of motor functions is observed. But the most common and unpleasant consequence is recurrent pain at the site of skin rashes. Even after traces of herpes disappear on the body, pain can persist from several months to several years. In some cases, painful sensations appear even without skin rashes. The pain is characterized by exacerbation at night, with movement, skin contact with surfaces, and temperature changes.
About pathogens
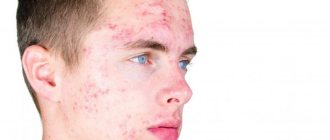
photo of herpes on face
The occurrence of facial herpes is a common clinical situation characteristic of viruses of the herpetic family.
Such pathogens are widespread in the human population and, against the background of decreased immune activity, quickly lead to the appearance of unpleasant symptoms.
The table shows what types of herpes occur on the face:
In clinical practice, there are various types of herpes on the face. In order to select the best means for therapy, the doctor needs to identify the specific type of pathogen.
It is important to note that the appearance of herpes rashes on the face in adults or children does not differ fundamentally between specific types of the virus, which makes diagnosis difficult during external examination.
Carrying out additional studies, for example, polymerase chain reaction, allows you to make an accurate diagnosis.
How does the disease progress?
Simple vesicular lichen begins quickly and causes trouble with unexpected itching and painful sensations in the area of inflammation. The area changes before our eyes, turns red, begins to itch, and the pain is peculiar, stabbing. After a few hours, blisters (with a diameter of 0.2 to 0.4 cm) appear on the inflamed area. They are located focally, in groups and are accompanied by painful sensations. A crust forms at the site where the bubbles burst. At the first signs of the disease, the temperature may rise, muscle pain may appear, and chills may be felt. Within a week the disease goes away. If the body is not strong enough, a relapse is possible and, as a rule, bubbles appear in the same place. If the rashes begin to merge and are localized on the back, abdomen or limbs, then there is a high probability that it is herpes zoster, which differs from simple herpes in symptoms and treatment methods.
Causes of development of the herpes zoster virus
First of all, it is worth saying that herpes viruses of all types quite often develop on a nervous basis:
- severe stress;
- moral pressure;
- emotional shock;
- inability to distribute psychological load;
- nervous breakdowns and tension;
- depressive states;
- dissatisfaction with the world around us and the people living in it.
These are the main psychosomatic factors that can provoke the active reproduction of herpes viruses of all types in the human body.
However, in addition to the above points, there are a number of reasons why the herpes virus type 3 begins to actively multiply in cells, causing damage to the skin on the face. They must be taken into account for the purposes of prevention, as well as to achieve positive results from the treatment of the disease, if necessary.
Childhood or old age
The development of herpes on the face is especially common in children and the elderly. This is due to a poorly developed or reduced protective function of the body (that is, the inability of the immune system to resist viruses and various infections). That is why these age categories are recommended to take vitamin complexes in tablets, capsules or drops.
Eating plenty of fruits and vegetables, either fresh or steamed, also helps boost immunity.
Poor nutrition and abuse of “junk” food
It is especially not recommended to abuse:
- salty;
- smoked;
- sharp;
- allergenic foods.
During the period of treatment, it is necessary to abandon the above delicacies, and after complete recovery, the frequency of their use should be reduced to a minimum. This will help avoid relapses in the future.
Causes
Herpes zoster is caused by reactivation of the varicella zoster virus. The main cause of herpes is a serious change in the patient’s immune status. Until this moment, the virus hides in the dorsal ganglia. Herpes zoster develops in 10% of adults who have had chickenpox. It is accompanied by neuralgia and the appearance of vesicles along the nerve trunks. The main victims of herpes on the body (3 types) are the elderly, pregnant women, and people with a reduced immune status.
A decrease in immunity can occur as a result of taking certain medications, chemotherapy, organ transplants, constant stress and overwork, cancer, and HIV infection. When talking about herpes on the body, the following reasons are distinguished: frequent hypothermia of the body, or, conversely, its overheating, for example, due to work habits, complications due to diabetes mellitus or exacerbation of certain chronic diseases.
Ophthalmic herpes zoster
The photo shows ophthalmic herpes zoster - the virus penetrates the ophthalmic branch of the trigeminal nerve, which is dangerous due to damage to the cornea. Patients may have lifelong vision damage.
People with shingles should avoid contact with people who have not been vaccinated against chickenpox and people with weakened immune systems.
Treatment
It is necessary to realize that today there is no drug that can permanently get rid of the herpes virus. The reason is its complex structure and mechanism of action, and their insensitivity to most substances of microbial origin that can suppress the growth or cause the death of this virus. Today, only Acyclovir, produced in tablets, ointments and solutions, is able to directly affect HSV-1 and stop the disease. At the initial stage, this drug can help prevent the rash from spreading throughout the body.
There are also folk remedies that are excellent if Herpevir or Anciclovir does not help the patient.
Prevention
Important! In cases of localization of simple vesicular lichen on the mucous membranes of the mouth, complete recovery occurs after 2-3 weeks. The rashes are particularly painful due to constant trauma.
In order to avoid or minimize the risk of contracting the herpes simplex virus, you need to take care of your body, carry out hardening procedures, monitor your diet, prevent overwork, do not allow yourself to be in a state of stress for a long time, and exclude the independent use of medications.
Leading dermatologists say that the key to successful prevention of HSV is constant physical exercise and increased immunity.
(
2 ratings, average: 5.00 out of 5)
Stages of herpes zoster
- A vesicular rash appears; Vesicles are small bubble-like sacs that appear on the surface of the skin
- The skin around the vesicular rash becomes red
- The rash is usually limited to one area of the body in the form of a stripe; usually one side of the body or, in some cases, the face.
- The rash breaks out into blisters and scabs, usually 7-10 days after first appearing
- The rash usually goes away in two to four weeks
About one in ten people with herpes zoster will experience a flare-up and a rash at the same time.
Good to know: if a person does not have problems with the immune system, then he is considered immunocompetent. If they have a weak or damaged immune system, they are considered immunosuppressive.
How does infection occur?
Very often, herpes zoster is accompanied by pneumonia, injuries and, in rare cases, menstruation (most often these are manifestations of genital herpes, which is classified as type 2).
The disease is unpredictable, it can be triggered by factors to which you did not attach much importance:
- You can become infected with herpes simplex by direct contact with a sick person. You did not pay attention to the rashes on your lips and kissed someone, or held the hand of a person who touched your infectious rashes a few minutes ago;
- Prolonged stay in a state of stress. During stress, the body's resistance decreases, the latent virus in the cells of the nerve ganglia is activated and causes an exacerbation;
- Prolonged exposure to the sun or hypothermia;
- Hormonal disorders (herpes simplex virus is very common in pregnant women in the 1st trimester);
- One of the reasons for HSV entering the body may be organ and tissue transplantation or artificial insemination.
There are quite a few clinical pictures of the herpes virus. The most common is herpes simplex virus type 1 or HSV-1, otherwise it is called by the place of detection - “oral” or “lip”. The most unpleasant thing is that rashes always appear at the wrong moment: on the eve of an evening, an important meeting, a meeting.
Infection occurs in the first years of a person’s life. The most typical localization is on the lips and nasolabial triangle. Under certain conditions, for example, immunodeficiency, with HSV-1, the mouth and nose are exposed, the fingers and toes are damaged, the nail fold is predominantly destroyed, and the tissues of the nervous system are modified.
Ophthalmic herpes zoster
Herpes zoster ophthalmicus is a type of shingles where the virus attacks the optic nerve and eye, causing pain and inflammation in the eye and face. If not treated quickly, it can cause permanent vision problems, including:
- Glaucoma
- Scarring of eye tissue
- Retinal necrosis, a condition in which the retina becomes inflamed
- Iritis or uveitis, inflammation of the tissues of the eye
- Cataracts
Secondary bacterial eye infections can also occur if the affected eye is affected by dry eye syndrome.
What is herpes?
Herpes is a viral disease; almost every person has encountered its pathogen at least once in their life. Infection most often occurs from person to person through contact, and the impossibility of cure is due to the introduction of the virus into the central nervous system, where it remains forever.
It can exist in a passive mode for a long time and not cause any clinical manifestations, but at the first deterioration in the immune system, the herpes pathogen begins active activity.
Herpes simplex
The herpes simplex virus is the most common; the disease it causes has the following features:
- The main manifestation is the occurrence of dermatological rashes on the sides of the nasal wings, lips or the area around the mouth.
- In the most severe situations, there is a general deterioration in condition, increased fatigue, weakness and a feeling of muscle pain.
- If the concentration of the virus in the patient’s body is too high, a strong increase in body temperature may occur.
- A number of experts believe that this virus can provoke the occurrence of aphthous stomatitis when infected in childhood, but this theory has not yet received scientific confirmation.
Herpes zoster
Most children infected with the varicella zoster virus recover from chickenpox. When re-infected in adulthood, a disease called herpes zoster occurs, contrary to the erroneous belief - these are two different diseases, despite a similar etymology and a single pathogen.
However, people who have had chickenpox develop a strong immunity to this disease. A person who has not had this disease experiences herpes zoster as an adult with extreme difficulty.
At risk are people with reduced immunity and over 50 years of age; over the years, the disease becomes more and more severe. A characteristic sign is the appearance on the body of a rash and blisters filled with liquid, which is extremely contagious. Infection of surrounding people can occur both through airborne droplets and through household contact.
Cytomegalovirus
Cytomegalovirus is another representative of herpes viruses; it was discovered only in the middle of the last century and its study is still ongoing.
Its main features are discussed below:
- Infection in adults most often occurs during kissing or unprotected sexual intercourse; children become infected through breast milk or during contact and play with peers.
- After entering the body, there follows a long incubation period , which can be several months. Due to the lack of clinical manifestations, diagnosis of the disease often always occurs late. Prolonged or severe hypothermia, severe emotional shock, or a sudden deterioration in the immune system can trigger the appearance of the first symptoms.
- Cytomegalovirus is often confused with acute respiratory diseases , since they have similar symptoms, including severe fever, headache and general malaise.
- Timely recognition and immediate treatment are required , otherwise serious complications may occur. In particular, cytomegalovirus can trigger arthritis, pneumonia or encephalitis. The consequences may be irreversible.
Symptoms
Herpes is characterized by a long asymptomatic course, however, the following clinical manifestations gradually begin to appear:
- General weakness; rapid fatigue even with little physical activity.
- Increased body temperature, false feeling of cold.
- Headache; sensations of severe pain along the nerve. In some cases, pain leads to nausea or profuse vomiting.
- Feeling pain when touching the skin near the ribs or on the back. Sometimes the pain is localized in other parts of the body.
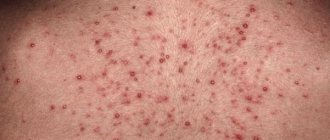
- The appearance of characteristic skin rashes, in appearance they resemble a cluster of small blisters that are grouped in certain areas of the body. Inside they are filled with clear liquid.
- Redness of the skin in the immediate vicinity of the rash, its soreness and itching or burning sensation.
- Gradual transformation of skin rashes into small ulcers that become crusty. In fact, this is always accompanied by the disappearance of the primary symptoms of herpes; discomfort continues to be felt only in the affected areas of the body.
Pain in the affected areas may continue for another month after recovery. The pigmentation remaining after the ulcers have passed lasts for 2 to 4 weeks. The clinical picture may vary in each case: sometimes the primary symptoms of herpes and pain are completely absent, or the symptoms are so severe that urgent hospitalization of the patient is required in the first days.