Blood clot in the leg: why it is dangerous for life, symptoms, treatment, causes, diagnostic methods
There are three main pathogenetic reasons for the development of thrombosis:
- damage to the vein walls,
- disturbance of blood flow speed,
- blood composition disorder.
These are direct causes of thrombosis and blockage of blood vessels. And they are caused by a number of reasons that are considered risk factors for the development of leg thrombosis. They are divided into three groups:
- congenital,
- acquired,
- mixed.
Congenital or genetic risk factors are characteristics of a particular person’s body that increase the likelihood of developing blood clots. Factors in this group include:
- deficiency of antithrombin - a substance that inhibits the process of blood clotting;
- problems with the homeostasis system;
- congenital pathologies of the circulatory system;
- problems with the secretion and absorption of proteins C and S.
Congenital factors are the most dangerous. They are practically not diagnosed without visible manifestations and can immediately manifest themselves as problems with blood circulation.
| Risk factor | Frequency with which it occurs |
| High blood pressure (hypertension) | 75% |
| Phlebeurysm | 62% |
| Chronic obesity | 56% |
| Atherosclerosis | 44% |
| Diabetes | 37% |
| Smoking | 21% |
These figures are taken from a study by specialists from the Gomel State Medical University. In addition to these reasons, risk factors for deep vein thrombosis are:
- chronic lung disease;
- fractures in the lower leg;
- presence of a catheter in the central vein;
- liver pathologies;
- heart attack before the age of 45;
- general anesthesia;
- surgical intervention on bones;
- oncological diseases;
- use of oral contraceptives.
In this group, factors associated with blood clotting: high levels of homocysteine (an amino acid that provokes the formation of blood clots and atherosclerotic plaques) and fibrinogen (a protein dissolved in the blood plasma).
Thrombosis is a dangerous pathology characterized by the formation of blood clots in veins or arteries. The thrombus is mainly localized in the leg. It can come off at any time and lead to death. It is necessary to understand the causes of development, symptoms and diagnostic methods in order to prevent the disease.
A thrombus is a blood clot that can attach to the walls of blood vessels. The mechanism of its formation can be based on two provoking factors:
- Blood clotting disorder. It becomes viscous and thick. Blood circulation changes, blood pressure rises.
- Stagnation of blood. Occurs for a number of reasons, for example, with varicose veins, forced bed rest, prolonged stay in the same position, etc.
Thrombophlebitis develops over a long period of time. The pathological process starts when the integrity of the veins is disrupted. As a result, platelets rush to the damaged area, forming a clot.
There are a number of reasons under the influence of which blood clots form and break off in the lower extremities. These include:
- phlebeurysm;
- infectious diseases;
- congenital pathologies of veins and arteries;
- damage to the venous wall (internal, external);
- limb injuries;
- severe dehydration;
- cardiovascular diseases;
- intravascular inflammation;
- surgical manipulations on tissues and veins of the legs;
- malignant neoplasm.
The following factors are involved in the formation of a blood clot on the leg:
- smoking;
- alcohol abuse;
- sedentary lifestyle;
- excessive physical activity;
- taking certain medications;
- obesity;
- hormonal disbalance;
- menopause;
- pregnancy;
- heredity;
- age over 40 years.
The formation and separation of a blood clot in the lower extremities rarely occurs as a result of a single cause.
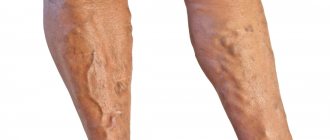
Signs of a blood clot in the leg depend on the degree of damage to the vessel. With incomplete disruption of blood flow, the symptoms of the disease are mild. Thrombosis can be acute, subacute, chronic. The latter form is characterized by the absence of clinical manifestations. A blood clot on the leg looks invisible, so the patient often has no idea that the pathological process has already started.
In the acute form, the following symptoms of leg thrombosis are observed:
- severe pain in the muscles of the lower leg, calf, less often in the thigh;
- feeling of heaviness in the limb;
- the veins in the legs hurt a lot;
- change in skin color of the affected limb (usually blue discoloration);
- pain when palpating the area where the thrombus is located;
- the leg with a blood clot is very swollen;
- muscle weakness;
- local temperature increase.
Separation occurs under the influence of strong blood flow and from a number of other negative reasons. From this moment on, the blood clot begins to wander through the arteries and veins of the body. Signs of a broken blood clot include:
- a sharp decrease in blood pressure;
- tachycardia;
- cardiopalmus;
- chest pain (with the development of a heart attack);
- numbness of the limbs, difficulty speaking (during a stroke);
- dizziness, fainting;
- fluid retention.
A blood clot can be recognized by signs of intoxication (nausea, vomiting, weakness, fever), which appear later, when structural changes in tissue are no longer reversible.
Important!
If a blood clot bursts, this condition is considered extremely dangerous, because there is a high probability of developing thromboembolism. The patient requires medical attention.
An experienced doctor can easily identify a blood clot in the leg at the initial appointment. If a pathology is suspected, a number of tests are performed in which pain manifests itself:
- Homans test;
- Lowenberg's sign;
- marching test;
- tourniquet samples.
Despite the effectiveness of the methods, the diagnosis can be confirmed or refuted after the following instrumental studies:
- Doppler ultrasound of the vessels of the lower extremities - assessment of blood movement allows you to detect a blood clot;
- X-ray contrast venography – assessment of the condition of veins and arteries after administration of a contrast agent;
- radionuclide scanning – monitoring of affected tissues during the administration of a radiopharmaceutical drug;
- MRI, CT, radiography are ineffective methods for pathology, which are used strictly according to indications.
Laboratory blood tests are not informative for thrombosis. In rare cases, changes in indicators indicating an inflammatory process are observed. Diagnostic tests help the doctor understand the location and size of the blood clot in the leg.
Treatment of thrombosis
Thrombosis of the legs is a direct indication for urgent hospitalization of the patient. The doctor determines how to treat blood clots, taking into account the general condition of the patient, the nature of the disease and the location of the clot.
It is advisable to use medications at the initial stage of pathology. A blood clot can only dissolve with long-term drug therapy.
To treat a blood clot in a vein in the leg, the following groups of drugs are used:
- Anticoagulants. They normalize the process of blood clotting, which promotes the resorption of a blood clot and prevents further formation. The most famous and accessible drug of the group is Heparin.
- Thrombolytics. These medications contain plasmin, an enzyme that has the ability to dissolve blood clots.
- Angioprotectors. The medications in this group are not able to get rid of a blood clot, but can significantly improve microcirculation.
- Blood thinning medications. This group of drugs reduces blood viscosity and prevents the formation of clots. Particularly effective in the early stages.
- Antibiotics. Used to detect an inflammatory process in the affected vascular bed.
During the treatment period, it is necessary to observe bed rest, the patient's leg is fixed in an elevated position.
If a blood clot breaks loose in the leg, this is the main indication for surgery. The operation is also performed in the following cases:
- ineffectiveness of drug therapy;
- high risk of thromboembolism;
- inflammatory process in the vein and surrounding soft tissues.
The vena cava filter is a kind of “trap” for blood formation. It is a miniature structure in the form of a nest, umbrella or hourglass. The filter is inserted into the vein to prevent blood clot migration. This type of operation does not dissolve the clot, but creates favorable conditions for further conservative treatment without complications.
Thrombectomy is another surgical method that is used to remove dangerous blood formations. Currently, such surgical intervention is performed in two ways: traditional and endovascular (without excision of the vessel). It is better to perform surgery at the first sign of a blood clot in the leg.
Important!
Surgical intervention is a last resort because... Any operation increases the risk of new blood clots.
Of course, a blood clot is dangerous. Blockage of vital arteries and veins is the most serious complication of thrombosis, often leading to death. If the pathology is not treated, blood circulation is impaired, which leads to insufficient tissue nutrition. The result is gangrene, which threatens limb amputation. If a blood clot breaks loose on your leg, the consequences may be irreversible.
The survival rate is 90%, but subject to timely treatment. After therapy, a complete cure is observed in 70-80% of all cases. The disease often recurs, so it is necessary to regularly take preventive measures to prevent the formation of blood clots.
To avoid the development of thrombosis, the following rules of prevention must be observed:
- regularly carry out a contrast shower for the limbs;
- go swimming;
- rest with your legs elevated;
- do not stay in the same position for a long time;
- perform therapeutic exercises;
- wear compression socks, tights;
- follow a diet and daily routine;
- to refuse from bad habits;
- avoid stress;
- drink plenty of fluids.
Preventive measures for thrombosis are especially relevant for patients suffering from diabetes, obesity, and varicose veins.
Blood clots in the veins of the legs are a dangerous condition. At the first signs of thrombosis of the lower extremities, you should consult a doctor. Only timely therapy and compliance with all the recommendations of the attending physician will cure the disease.
Prevention and prognosis
If thrombophlebitis is diagnosed in the initial stages and therapy is started in a timely manner, the prognosis for successful recovery and prevention of relapses is high. Thanks to drug treatment, it will be possible to control the condition and prevent the formation of blood clots. In advanced cases, surgical intervention cannot be avoided, but the operation will not eliminate the cause of the thrombosis, so there is a high probability of re-formation of blood clots.
As a preventative measure for those prone to blood clots, it is important to lead a healthy lifestyle, monitor your diet, give up bad habits, try to move more, and follow all doctor’s recommendations. With characteristic symptoms, it is dangerous to self-medicate. Only timely therapy will prevent complications and improve the prognosis for recovery.
Blood clot in the leg: symptoms and signs
If you have a blood clot in your leg, it means that there is a dangerous disorder in the body, which often does not show any signs at the very beginning of its occurrence. However, if the disease is not diagnosed in time, the risks of serious complications increase.
When adequate therapy is not carried out, clots begin to appear in the blood vessels, which leads to circulatory dysfunction. After a certain period, these clots are able to close the lumen in the vessels or break away from the vein wall. As a result of this, neighboring tissues begin to die, and a blood clot can affect the pulmonary system, heart, or other vessels.
With thrombosis (also called thrombophlebitis), unlike other diseases, there is no remission. Blood clots constantly increase, leading to a gradual deterioration of blood flow.
The tumors become larger and larger until they block the vein or break away from the walls. Then they will begin to circulate with the blood throughout the body.
Find out the most common symptoms of thrombosis, which can help you identify a blood clot in a vein:
- severe pain when moving the affected leg, which intensifies when walking;
- a rapid increase in temperature also accompanies vein thrombosis;
- red spots on the skin that appear above the affected area in the vein in the leg;
- swelling.
It is rare that the presence of a blood clot in the lower extremities can be seen visually or felt with fingers. How to identify a blood clot in the leg - symptoms and treatment for it? Places where a large blood clot has accumulated look unusual, with a bluish tint to the skin.
Possible signs
As a rule, it is easier to detect the onset of a disease if you know its first signs. With phlebothrombosis of the deep veins of the leg, the patient's temperature quickly rises, muscle swelling and severe pain appear when trying to bend the knee. Red spots may appear, which look like fresh bruises.
In case of untimely medical care (if thrombosis is diagnosed late), the skin becomes pale with a bluish tint and the subcutaneous network of veins appears. If you are careful, you can identify pathology much earlier.
During the formation of a blood clot in the deep veins of the thigh, swelling of the skin, swelling of the legs, and swelling of the saphenous veins appear, taking on the functions of the clogged ones.
There may be severe pain in the affected area, swelling of the inguinal veins, or blue discoloration of the affected limb where blood clots have formed on the legs. If the situation is neglected, the patient may develop a high temperature, which sometimes develops into fever.
Deep vein thrombosis can be classified as a disease that is especially dangerous to health. This disease appears in people who lead a sedentary lifestyle or remain in bed for a long time.
If the blood clot in the leg increases or breaks off, your health may not worsen. However, when such a clot breaks off, due to its large size, it is capable of blocking the pulmonary or hepatic arteries, and the rupture of a blood clot can cause a heart attack. This can be avoided if the disease is diagnosed in time.
Thrombophlebitis, unlike phlebothrombosis, develops close to the skin. The presence of symptoms of blood clots in the legs is easily determined by palpation. With varicose veins, due to inflammation and destruction of the walls, a large number of blockages often form.
To prevent problems associated with thrombophlebitis, regular diagnosis is necessary. Sometimes it is also possible to remove blood clots in the veins in the legs in time - most often immediately after they are identified.
If a vessel ruptures or bursts, any blood clots pose a danger, but thrombosis of the main veins poses a greater threat. A blood clot can break off at any time.
Its symptoms overlap with other diseases (fat inflammation, ruptured Baker's cyst, etc.), making it difficult to detect before the clot breaks off and travels through the bloodstream. It happens that a person does not even feel that a blood clot has broken off in his leg. In this case, only the attending physician can detect the problem.
The signs of blood clots in a person’s lower extremities largely depend on the development of thrombosis. In the early stages of the development of the disease, it is difficult to determine whether a person has a blood clot, because it may not manifest itself at all.
The same swelling or other external signs very rarely appear immediately after the appearance of thrombosis in the patient.
In the acute form of thrombosis, it is sometimes also difficult to identify symptoms and signs of the disease in a blood clot in the leg. A fairly common misconception is that acute thrombophlebitis is no different from varicose veins.
A distinctive feature of acute thrombophlebitis is a sharp increase in the patient’s temperature, whereas this is not observed with varicose veins. Sometimes people don’t even realize that the detached blood clot has already begun to wander through the bloodstream.
A dangerous case is when the patient has been diagnosed with signs of chronic thrombophlebitis. Its difference from the acute form of this disease is expressed in the expression of symptoms.
With chronic thrombophlebitis, the patient constantly feels swelling, which intensifies over a certain period of time. Chronic thrombophlebitis is characterized by a feeling of heaviness in the legs, the appearance of red spots on the skin and frequent pain in the legs.
In order to independently identify a blood clot that forms in your leg, you need to carefully examine your legs. The presence of thrombophlebitis can be determined if thickening of the veins with characteristic redness is detected.
When pressing on the surface of the veins, a person feels pain. An increase in temperature is felt in the affected area of the extremities. These are the main signs of thrombosis, by which you can suspect that you have begun to form a blood clot.
If a person feels pain when dorsiflexing the feet, this also indicates the presence of a blood clot. This method of manifesting a problem in the human body got its name as Homans' sign. Using this principle, a person can estimate the likelihood that he may develop a blood clot.
And also the fact that a blood clot has formed is indicated by general fatigue, constant malaise of the body and an increase in body temperature. For lying patients, the development of phlebothrombosis of the veins in the lower leg is typical. In such cases, treatment of thrombosis will include lifestyle correction.
If a blood clot is detected or a patient has thrombosis, you should visit a medical facility, where the doctor will examine the affected area, prescribe the necessary examination and refer you for tests.
In this way, you can find out why blood clots form in a patient. After this, a therapeutic plan for treating the patient will be drawn up.
Even at home, you can identify acute thrombosis, as well as signs of a blood clot in the leg. Leg thrombosis can be determined by knowing the following symptoms:
- Moses' sign. Using two palms, the shin is grasped. Then you need to squeeze it a little from front to back. If blood clots are present in the veins, the patient will feel discomfort in the lower leg area. Moreover, if this procedure is done from the sides, there will be no pain.
- Homans' sign. The patient needs to dorsiflex the foot. With thrombophlebitis, the patient will experience severe pain.
- Lowenberg's sign. Using a tonometer, it is necessary to influence the sore lower leg. If, with a reading of 100 mmHg, the patient experiences pain in the lower leg area, then this is a sure sign of the presence of a blood clot.
These symptoms are specific, but can help in identifying the disease. However, it is better to ask your doctor what to do if a blood clot breaks loose in your leg and what the consequences of this may be.
If the veins in your legs hurt, this could mean that the blood clot is about to break off. However, the possibility cannot be ruled out that the clot will resolve on its own. Before treating thrombosis, it is necessary to confirm or refute the diagnosis. A comprehensive examination to determine a blood clot in a leg artery includes:
- vascular examination using Doppler sonography;
- duplex scanning of arteries and veins is the most accurate way to diagnose varicose veins in modern medicine;
- general biochemical blood test;
- rheovasographic study.
Comprehensive research results will show whether the clot can resolve on its own. And it is also possible to recognize particularly advanced clots that are no longer able to dissolve even with drug therapy.
If you belong to the category of people prone to varicose veins, excess weight or a passive lifestyle, preventive measures will help relieve swelling and prevent the formation of blood clots.
Proper prevention will also eliminate dissolving clots several times faster. You just need to follow these recommendations:
- A contrast foot shower will relieve fatigue and tension from your limbs.
- The blood clot dissolves faster if the person moves more and walks barefoot.
- It would be nice to join some kind of sport - swimming or athletics.
- For preventive purposes, you can wipe your feet daily with a towel dipped in cold water.
- Learn how to massage your legs and feet yourself. Impact on acupuncture points will also have a positive effect.
- When resting, do not forget to place a bolster or pillow under your feet to ensure good blood flow from your extremities.
- Try to understand the basics of anti-varicose gymnastics so that you can practice regularly at home.
- If necessary, wear special compression stockings. It is especially effective when varicose veins only appear.
- Drink as much water as possible. This will help prevent the first signs of thrombosis. The daily norm is 1.5–2 liters.
Inflammation of blood vessels and blood clots are quite dangerous processes. If a blood clot breaks loose, the patient also faces a real threat to life. Therefore, as soon as you suspect that you are developing clots, you should not wait until the clot that has formed comes off.
Features of vein thrombosis
With thrombosis (also called thrombophlebitis), unlike other diseases, there is no remission. Blood clots constantly increase, leading to a gradual deterioration of blood flow.
The tumors become larger and larger until they block the vein or break away from the walls. Then they will begin to circulate with the blood throughout the body.
Find out the most common symptoms of thrombosis, which can help you identify a blood clot in a vein:
- severe pain when moving the affected leg, which intensifies when walking,
- a rapid increase in temperature also accompanies venous thrombosis,
- red spots on the skin that appear above the affected area in the vein in the leg,
- swelling.
It is rare that the presence of a blood clot in the lower extremities can be seen visually or felt with fingers. How to identify a blood clot in the leg - symptoms and treatment for it? Places where a large blood clot has accumulated look unusual, with a bluish tint to the skin.
Why does thrombophlebitis occur?
The disease is referred to as an inflammatory process, which can manifest itself as a complication of varicose veins of the lower extremities if it is not treated properly.
Factors contributing to the development of thrombosis:
- oncological diseases;
- long bed rest;
- hereditary predisposition;
- high blood clotting;
- constantly being in a standing or sitting position;
- advanced age or overweight;
- period of bearing a child.
Classification according to the form of thrombosis
- Migrating thrombophlebitis. It is characterized by simultaneous damage to a group of vessels. Inflamed lesions occur regularly, but can disappear after a period of time. Moreover, after they are absorbed, there are no traces left of them.
- Acute thrombophlebitis. It can develop in just a few hours, and all the symptoms will be sharply expressed.
- Chronic thrombophlebitis. The course of the disease is gradual, the development of pathology is almost imperceptible. Exacerbations occur quite rarely.
Treatment depending on the type of thrombosis
Recovery methods depend on the nature of the pathological process.
Damage to the deep veins requires primary surgical treatment if there are no other options for help. But first they try to eliminate the problem in a conservative way.
What drugs are prescribed:
- Thrombolytics to dissolve the clot. Urokinase, Streptokinase. They have a pronounced effect. But they create a lot of side effects.
- Antiplatelet agents. Heparin and its derivatives or analogues. As part of emergency assistance. Absolutely not suitable for long-term use.
- Medicines that restore blood circulation. Reopoliglyukin and others.
- Parenteral administration of solutions to restore blood fluidity. Intravenously.
Then everything depends on the results. If this is not the case, mechanical removal of blood clots is performed surgically; open or endovascular thrombectomy is practiced.
In some cases, it is practiced to install a vena cava filter, which will stop clots, but this technique is rare.
Damage to external veins or thrombophlebitis requires approximately the same measures. Only the dosages of the drugs differ.
Overall, this condition has a slightly better prognosis and is less likely to cause complications.
Among the drugs:
- Anti-inflammatory non-steroidal origin. Ketorolac, Nimesulide, Nise.
- Heparin-based products.
- Phlebotonics. Detralex, Venarus, Troxerutin and analogues. Used to restore normal venous-lymphatic outflow.
- It is possible to wear compression stockings. Surgery is also a last resort.
As for damage to the arteries of the legs, surgical correction is considered the main method. In most cases, this is the only thing that makes sense.
All other techniques are prescribed later as auxiliary ones. For example, the use of the same Heparin and its analogues.
In all cases, without exception, the pathological process requires additional treatment of the primary condition that causes thrombosis. Be it atherosclerosis, diabetes or other problems.
Without eliminating the root cause, there is no point in doing anything. This is a short term measure. The same thing will happen very soon.
If there is such a possibility, the condition needs to be normalized. Quit smoking, drinking alcohol, and maintain acceptable physical activity.
Attention:
Contrary to beliefs, thrombosis does not require long-term bed rest, rather the opposite. As soon as the patient feels able to move, this should be done.
Blood flow and metabolic processes are restored, which has a positive effect on rehabilitation.
Removing a blood clot from a leg vein or artery requires some recovery time. The total duration is 2-3 weeks.
Treatment of thrombosis
Treatment is chosen depending on each specific case. There are two main treatment options for thrombosis:
- medicinal,
- surgical
Drug treatment is the most common treatment for leg thrombosis. More often it is used independently. If surgical intervention is necessary, concomitant therapy is drug treatment. Therapy for deep vein thrombosis should solve five problems:
- decreased thrombus growth;
- exclusion of the development of pulmonary embolism;
- prevention of the development of venous gangrene by combating swelling;
- restoration of the lumen of the vessel;
- relapse prevention.
| Group of drugs | Description |
| Anticoagulants | The main group of drugs for thrombosis. Used to reduce blood clotting and prevent the development of blood clots. |
| Antiplatelet agents | A group of medications to prevent the development of blood clots. Reduces the ability of platelets and red blood cells to adhere to the endothelium of blood vessels. |
| Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs | Medicines to relieve the main symptoms of DVT: the inflammatory reaction of the venous wall and pain. |
| Phleboactive drugs | Medicines to improve venous and lymphatic blood flow. They increase the tone of the venous walls and relieve swelling. |
Antibiotics are rarely used for deep vein thrombosis. Indications for their use:
- high risk of septic complications;
- pustular skin lesions.
Direct anticoagulants directly interfere with the coagulation process, inhibiting one of its factors. The most common coagulant, heparin, interferes with the work of thrombin.
Indirect coagulants do not directly affect blood clotting factors. They inhibit the process of synthesis of substances that are involved in clotting. At the first stage of treatment for DVT, direct anticoagulants are prescribed, most often heparin. Its dose and duration of therapy depend on a number of factors, the main one of which is temporary indicators of blood clotting.
At the second stage, direct anticoagulants are replaced by indirect ones. During the transition, it is necessary to take drugs from both groups simultaneously, for three to four days. The duration of drug therapy for thrombosis is from three months to six months, since relapses of the pathology are possible during this period.
Possible consequences
Among the likely complications, the most common are:
- Stroke. As a result of the detachment of a blood clot and blockage of blood vessels in the brain.
- Heart attack. If the coronary arteries are involved. The essence of both pathological processes is the death of tissue. Nervous and muscular, respectively. The outcome in many cases is fatal.
- Gangrene. Massive cell death of the limb. Particularly characteristic of blockage of leg veins.
- Pulmonary embolism. Almost instantly leads to death without the possibility of recovery.
- Sepsis, shock with untimely assistance not against the background of necrosis of the extremities.
The result is disability or death. Depending on the developed consequences.
Is it possible to cure deep vein thrombophlebitis?
As soon as the first symptoms of the disease appear, experts suggest the use of therapeutic therapy to eliminate them. Depending on the patient's medical history, treatment can be conservative or surgical. To make the right choice, you will need to get acquainted with the characteristics of the body (below are photos and treatment).
Measures that can significantly improve the patient’s condition:
- The affected limb should be at rest. It is better for the leg to be at some elevation in relation to the whole body.
- Anticoagulants are considered first aid drugs; they actively fight blood clots and prevent new blood clots from forming. To use such drugs, you need to have hemostasis indicators on hand. Their subsequent control is mandatory. Of the medications, doctors prefer Warfarin tablets, Fraxiparin injections and Heparin in various release forms.
- To obtain a high therapeutic effect, it is assumed to use a complex of various drugs. It is necessary to prescribe the patient pain relief capsules that relieve inflammation, antioxidants, antimicrobial agents, and vitamin formulations. Solutions for improving the rheological properties of blood are helpful.
- Prescribing Pentoxifylline will improve microcirculation.
- Thrombophlebitis of the lower extremities is a complex disease, therefore, to relieve pain and improve the quality of blood clotting, it is not enough to use drugs in the form of an ointment or gel. In addition, they always take pills and injections.
- After the above manipulations, a new stage of the treatment process begins. Compression garments are selected for the patient and the presence of active movements in his life is assumed. An elastic bandage helps relieve swelling in the problem area and reduce pain. The length is adjusted to suit individual needs, and compression is selected from 23 to 32 mm. rt. Art. If a patient has thrombophlebitis in the femoral vein, then buy long stockings, they reach the inguinal folds. If you plan to constantly wear such underwear, then the model will not depend on the type of disease. In this case, experts suggest compression underwear no higher than the knee joint.
Such treatment can give good results; patients experience swelling and pain. Physical inactivity always entails the formation of new blood clots, for this reason the patient is asked to walk more.
If the patient does not have individual reactions to leeches, then hirudotherapy can cope well with the disease. After just a few sessions, relief is noted in the patient’s condition. Of course, specialists more often turn to standard procedures for help.
- Magnetic therapy – magnetic fields have a positive effect on the quality of blood composition;
- electrophoresis - a drug is delivered through the skin using an electric current;
- paraffin applications - have a therapeutic effect if there is a risk of trophic ulcer formation. The acute course of the disease does not suggest the use of this therapy;
- UHF - high frequency electric fields have a beneficial effect on the affected area. Lymph outflow is stimulated, blood circulation improves;
It is possible to perform open or endovascular surgery.
- Sewing the inferior vein. If it is not possible to implant a filter, there are a large number of blood clots, or frequent relapses, this technique is used. A profile clamp is applied to the area of the pathological area and sewn. Thus, part of the channel is blocked, leaving only a lumen for normal blood flow. Of course, the technique also has a drawback; the outflow of blood mass from the veins of the lower extremities will not be carried out as efficiently.
- Kava filters. These “traps” are placed in the vein when blood clots are actively moving through the vein. The technique has become a salvation for patients who cannot take anticoagulants. When there is no effectiveness from taking medications, the patient is implanted with a filter in the inferior vena cava. Thus, they provide a guarantee against the development of thromboembolism. Most often, the operation is performed through the inferior vena cava, but in medical practice there are cases when the filter was inserted through the superior vein.
- Plication of the inferior vena cava. It involves suturing the wall of the affected vessel using metal clips.
- Thrombectomy. Usually copes well with blood clots at an early stage of thrombosis. If the patient has already developed thrombophlebitis, then such manipulations are prohibited.
- Fogarty catheter. Its installation will allow you to remove blood clots that have formed within a week. Unfixed clots respond well to this therapy.
After any of the above operations, wearing an elastic bandage or compression stockings is required. It is strictly forbidden to remove them for the first 3 days after surgery. The risk of new clots forming in the affected area is too great.
The effect of treatment will depend on the patient’s diet, since such patients are indicated for a therapeutic diet. The diet should include enough fruits and vegetables. They contain a lot of fiber, and it helps strengthen the walls of blood vessels.
You should forget about salty and spicy foods; such dishes interfere with the natural removal of fluid from the body. Also, the volume of circulating blood can increase due to junk food, which negatively affects well-being.
To prevent the formation of new clots and help thin the blood, it is important to include foods in your diet that are rich in vitamin E. These include flaxseed oil, fish oil and seafood. You should ask your doctor questions about nutrition and permitted foods; he will give you a reminder with tips on a balanced diet.
What treatment is prescribed?
Drugs
A blood clot on the leg in unadvanced cases is treated conservatively. If thrombosis progresses and drugs are powerless, a second technique is used - surgical removal. The drug treatment regimen looks like this:
- Anticoagulants. Prevent the progression of pathology and the formation of new clots: Heparin.
- "Streptokinase";
- "Courantil";
- "Nimesulide";
Local remedies may include the use of Heparin ointment.
It is also recommended to treat blood clots with external agents, which are sold in the form of ointments and creams:
During the period of drug therapy, compression of the right or left limb is necessary. For these purposes, a rigid elastic bandage or compression stockings are used, which are fixed on the foot and above the knee. While conservative treatment is ongoing, it is important to exercise regularly, follow a diet and eat only foods approved by your doctor.
When is surgery needed?
If the negative consequences of thrombosis are inevitable or the affected vessel has burst, a decision is made on surgical treatment. The following methods are often used:
- plication of the inferior vena cava;
- thrombectomy;
- installation of a vena cava filter;
- ligation of the great saphenous vein to prevent the spread of pathology.
Return to contents
Complications
The main complication of deep vein thrombosis is postthrombophlebitis disease. It is a direct consequence of the treatment of the disease. The mechanism of its development lies in the disturbances that occur in the bloodstream after the removal of blood clots. In its place connective tissue appears, which cannot work like the natural wall of the vessel.
This leads to an increase in pressure in the blood vessels, destruction of the valves and a general disruption of blood flow. Postthrombophlebitic disease is a serious complication of DVT, which requires comprehensive drug therapy. A doctor who monitors a patient’s rehabilitation after thrombosis can quite accurately determine the onset of the disease based on the patient’s complaints and a simple examination. Therefore, completed treatment of deep vein thrombosis is the best prevention of its complications.
In the initial stages, complications are easier to stop, and their prevention gives good results.
Superficial thrombosis
Thrombophlebitis, unlike phlebothrombosis, develops close to the skin. The presence of symptoms of blood clots in the legs is easily determined by palpation. With varicose veins, due to inflammation and destruction of the walls, a large number of blockages often form.
To prevent problems associated with thrombophlebitis, regular diagnosis is necessary. Sometimes it is also possible to remove blood clots in the veins in the legs in time - most often immediately after they are identified.
If a vessel ruptures or bursts, any blood clots pose a danger, but thrombosis of the main veins poses a greater threat. A blood clot can break off at any time.
Its symptoms overlap with other diseases (fat inflammation, ruptured Baker's cyst, etc.), making it difficult to detect before the clot breaks off and travels through the bloodstream. It happens that a person does not even feel that a blood clot has broken off in his leg. In this case, only the attending physician can detect the problem.
Preventive measures
After undergoing medical therapy, the patient should not forget about caution. Now he should not wear uncomfortable shoes or clothes that put unnecessary pressure on the lower extremities. It is better to go in for sports, but not strength sports. It is especially good for overweight patients to take this measure.
The patient must understand that the presence of thrombosis implies a complete abandonment of all bad habits. Addictions can lead to disastrous consequences.
It is noted that it is good to sleep with raised legs; the limbs rest in this position. If there are no contraindications, then it is permissible to massage the problem area from time to time.
From everything written it follows that deep vein thrombosis of the lower extremities does not allow frivolity.
As with any disease, only timely and correct treatment can give favorable prognoses. If the patient does not follow medical therapy after diagnosis, then a fifth of patients will soon develop pulmonary embolism. Unfortunately, in a number of patients in this group everything ends in death.
Also, untreated thrombosis is also insidious, because the next 3 months after such treatment, there is a risk of getting pulmonary embolism. Additional pathology is diagnosed in half of such patients.
Complications of thrombophlebitis include gangrene, heart attack, and stroke.
As the patients themselves note, the therapeutic effect reaches its peak if a visit to a phlebologist was made at an early stage. They do not have time to form multiple clots, which have to be radically removed. But even advanced cases can end well.
What is the danger of a blood clot?
Even if a person knows how to recognize a blood clot in the leg,
You need to understand how dangerous this disease is, so as not to delay going to the doctor.
First of all, the patient will constantly suffer from heaviness in the lower extremities, pain, spasms, cramps, and muscle stiffness. The legs will swell and increase in size. If proper treatment is not followed soon, the pathological condition will progress and can lead to the formation of gangrene, eczema or trophic ulcers.
The most dangerous complication is thromboembolism. This is a condition when blood clots break away from the sites of formation and begin to move through the veins, vessels and arteries. This can cause blood flow to stop and lead to death. If a blood clot has broken off in the leg, you can determine this by some features:
- A sharp increase in blood pressure and pulse.
- The appearance of heart pain.
- Difficulty urinating.
- Loss of consciousness.
- Speech disturbances, lack of appetite.
Thrombosis can cause a stroke, heart attack, purulent formations or an abscess.
Rehabilitation after DVT
Rehabilitation of patients after deep vein thrombosis is needed to solve three problems:
- prevention of re-development of the disease;
- prevention of the development of postthrombophlebitis disease;
- compensation of venous outflow.
Main methods of the rehabilitation program:
- regular physical activity;
- time limit for static vertical stay of the body;
- use of compression hosiery.
Rehabilitation is an important process. If you omit it, then the risk of the disease returning in a more complex form is very high.
Doctors emphasize that without a rehabilitation program it is impossible to talk about a complete victory over deep vein thrombosis.
Clinical picture
Thrombosis of the lower extremities is dangerous because it appears suddenly, and as it develops, it often does not show symptoms and signs. Often, pathology is diagnosed accidentally during a preventive examination. To varying degrees, the manifestations of the disease are expressed in the form of the following changes:
- pain in the feet, legs, knees or thighs, worse when walking, moving or after physical activity;
- changes in skin color, which may become red or bluish;
- the surface of the skin may become glossy;
- swelling in the legs;
- heaviness in the legs;
- local or general temperature change;
- with thrombosis in the femoral part, swelling of the groin veins is possible;
- convulsions, especially at night;
- bulging of superficial vessels above the surface of the skin, even if deep lines are affected;
- the appearance of a vascular pattern.
In the early stages of the disease, symptoms may be mild. Most often they manifest themselves in a feeling of fatigue in the lower extremities, especially after physical activity or a working day. In most cases, patients attribute this to muscle overload, but in fact the problem lies in the circulatory system. Instead of pain at the onset of the disease, stabbing sensations and cramps may be observed.
To avoid blood clot rupture, if alarming symptoms occur, the patient should lie down and call an ambulance. Self-medication in this case is unacceptable, even if the leg hurts a lot.
Prevention of DVT
Preventive measures to reduce the risk of developing deep vein thrombosis are measures to improve blood flow in the lower extremities and to reduce the likelihood of blood clots.
For a person who has no history of congenital or acquired risk factors, prevention of DVT involves:
- regular physical activity;
- absence of prolonged immobilization;
- sufficient amount of liquid in the diet;
- wearing comfortable shoes;
- absence of static loads on the legs.
This list expands depending on what risk factors a person has. One of the most effective methods of prevention is the use of compression stockings. The compression that such stockings provide helps maintain adequate blood flow. As a result of the full movement of blood through the deep veins, the tendency of the blood to form blood clots is reduced.
Such stockings are widely used among people with varicose veins and those who have to fly a lot. At altitude, air pressure is lower and the pressure created by compression hosiery compensates for it.
Research shows that wearing compression stockings in-flight eliminates the risk of developing DVT and reduces swelling. At the moment, this is the most effective method of prevention for people with risk factors for DVT.
We must not forget about a healthy lifestyle. Smoking, alcohol, poor diet - all these are factors that contribute to the formation of blood clots. If they are excluded, the risk of thrombosis will decrease sharply.
Causes of hypercoagulability
Sometimes blood clots in the legs appear regardless of tissue damage as a result of hypercoagulation - pathologically increased blood clotting. This phenomenon is associated with a slowdown in blood flow and an increase in its viscosity. The main risk factors for the development of thrombosis (phlebothrombosis) include:
- Congenital pathologies of veins and arteries (insufficiency of venous valves, dysfunction of the endothelium, fistulas between vascular walls);
- Varicose veins of the legs;
- Overweight;
- History of cancer and chemotherapy;
- Hormonal imbalances caused by pathologies of the ovaries, thyroid gland, pregnancy and menopause, prolonged use of oral contraceptives;
- Previous injuries and operations on the lower extremities;
- Sedentary lifestyle, prolonged immobilization, paralysis;
- Excessive physical activity;
- Some infections (pneumonia, purulent inflammation).
Home therapy
If signs of a blood clot are detected in the lower extremities, you can additionally use traditional recipes. The most commonly used herbal infusions are:
To eliminate venous blood clots, you can use an infusion based on verbena inflorescences. Two or three tablespoons of flowers should be poured with boiling water. Take one tablespoon of the drug before each meal.- Acacia also helps get rid of blood clots. The crushed plant should be filled with diluted alcohol or vodka. The product is infused for a week in a dark and dry room. They wipe the area on the skin where the blood clot was found. You can also drink a few drops of the composition before each meal.
- A mixture of honey and onion juice demonstrates good effectiveness. Experts note that this folk recipe helps with blood clots much better than aspirin. 200 g of onion juice should be mixed with the same amount of honey. The drug is infused for two weeks. Therapy consists of several stages. Before meals, eat one tablespoon of the drug. After it ends, take a week break and then repeat the course.
In the absence of timely and adequate therapy, the patient's condition may worsen. Complications of thrombosis often lead to death. Therefore, if there is a blood clot in the leg, what to do is decided by a specialist.
Diagnosis of the disease
If you suspect vascular disease, you should contact a vascular surgeon. He will conduct an initial survey, during which he will find out the time of occurrence of disturbing symptoms, existing health problems and possible hereditary or individual predispositions. After this, both extremities will be examined, starting from the feet and ending with the groin area. This process will be accompanied by palpation to determine the possible location of the thrombus.
In this case, the doctor pays attention to external signs that suggest one or another type of thrombosis. For example, if swelling is observed only in the ankle area, this allows one to distinguish between calf thrombosis.
Swelling that does not reach the knee indicates the formation of a clot in the popliteal vessel, and swelling beyond it indicates a pathology of the femoral vein or artery.
In this case, for a preliminary diagnosis, a specialist can use some tests:
- Homens test. The patient lies down on the couch and bends his leg at the knee. The doctor carefully moves the ankle joint, and if pain is observed in the calf area, thrombosis can be confirmed.
- Lowenberg's test. A conventional tonometer cuff is placed on the patient's lower leg to measure blood pressure, after which the doctor begins to apply pressure. A healthy person begins to feel pain only at 150 mmHg. Art. and higher, and a patient with thrombosis – already at 80.
- Moses' test. The doctor alternately squeezes the patient's lower leg in the forward-backward direction, and then from the sides. If the leg begins to hurt only in the first case, we can talk about deep vein thrombosis.
In addition, the doctor may prescribe an instrumental examination to confirm the diagnosis. Most often, an ultrasound with Doppler is enough - a kind of sensor that allows you to examine the features of blood circulation.
In addition, venography may be required - a fluoroscopic examination with preliminary administration of a contrast agent to improve image clarity. Specific methods are rarely used, mainly in controversial situations.
Laboratory testing is also necessary, although it does not provide much information. A general and biochemical blood test allows you to determine its composition and other indicators, for example, coagulation, erythrocyte sedimentation rate, etc. In addition, the tests allow you to understand whether thrombosis has caused complications and whether it is associated with infectious, inflammatory or autoimmune diseases.