Arthritis of the fingers: symptoms and treatment
Arthritis of the fingers is a disease that most often affects women. The reasons for this are the peculiarities of a number of purely “female” professions and everyday tasks, as well as the fact that the female body as a whole is more susceptible to osteoarthritis than the male one due to its hormonal background. Most often, inflammatory changes affect the interphalangeal joints; arthritis of the metacarpophalangeal joints is also not uncommon. This disease can lead to disability and deprive a person of the ability to self-care.
Arthritis of the fingers: symptoms
The main symptom is pain. It occurs with literally any movement in the hands, both active and passive. As a rule, in the first stages of the disease the pain is relatively mild, occurs only after prolonged work or in the morning, and then goes away. Gradually, the pain increases and becomes constant. The nature of the pain is aching; patients also complain of burning, aching, and tingling in the joints.
Also, the early stages of the disease are characterized by morning stiffness in the joints - a decrease in their mobility in the first half hour after waking up. Patients complain of a feeling of a “tight glove” on the hand. After performing active movements in the joints, stiffness disappears.
Movements in the affected joints are accompanied by crepitus - creaking, clicking - this is also a symptom of inflammation in the tissues of the joint.
Another characteristic feature is meteosensitivity. The joints begin to “react” to changes in weather and pressure changes.
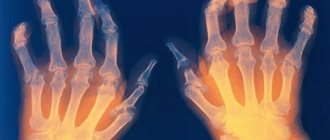
Inflammatory changes in joint tissues become visually noticeable as the disease progresses. So, the joints themselves thicken, swell, the skin over them turns red and becomes hot.
Arthritis of the hands: causes of the disease
- age-related changes in joint tissues: over the years, metabolism in them slows down, in addition, in women, hormonal changes associated with menopause play a certain role and their consequence is calcium metabolism disorders;
- joint injuries;
- features of the profession, working conditions;
- hereditary factors;
- malfunctions of the immune system;
- a number of infectious diseases (ARVI, streptococcal and staphylococcal infections);
- metabolic diseases (gout, diabetes);
- some systemic diseases (systemic lupus erythematosus, rheumatism);
- psoriasis;
- stress.
Stages of development of finger arthritis
The course of finger arthritis can be divided into several stages.
The first stage of arthritis is usually characterized by minimal symptoms of the disease or their complete absence. Most often at this stage, morning stiffness of the joints attracts attention. It becomes difficult to turn on the stove, make coffee, or wash your face, but after a while the stiffness disappears, which is why rarely anyone seeks medical help.
The second stage of arthritis is associated with the appearance of erosions on the articular surfaces of the bones, moderate pain appears, a crunching sound occurs when moving the joint, and it becomes difficult to perform certain actions.
The third stage of arthritis is characterized by the appearance of joint deformation. The pain is intense and requires painkillers to eliminate it. Visual changes in the joints appear: they are swollen, the skin over them turns red and becomes hot to the touch.
At the fourth stage of arthritis, adhesions—contractures—appear in the affected joints. The pain is extremely intense and requires constant use of analgesics. A person loses the ability to self-service, and usual professional activities become impossible. Arthritis of the fingers of the fourth stage is the basis for registration of disability.
Classification of finger arthritis
The most common types of hand arthritis are:
- infectious - as a result of pathogenic microorganisms from foci of infection entering the joint tissue through the bloodstream;
- metabolic (gouty) - a consequence of uric acid metabolic disorders;
- rheumatoid - usually begins with damage to small joints, then spreads to larger ones;
- traumatic - is a consequence of traumatic damage to joint tissue.
Depending on which joints of the hand are affected, arthritis is divided into proximal (joints of the hand), middle (joints between the metacarpus and fingers) and distal (affects the interphalangeal joints of the fingers).
For arthritic lesions of the joints of the thumb, there is a special term “rhizarthritis”.
There are also primary arthritis, in which joint damage develops independently and initially, and secondary, which is characterized by secondary joint damage - for example, due to allergic reactions or pathological immune processes.
Diagnosis of arthritis of the fingers
Diagnosing arthritis of the fingers is usually not difficult. Diagnosis is based on interviewing the patient, examination, and, if necessary, laboratory tests (clinical, biochemical blood and urine tests) and instrumental studies (radiography, computed tomography).
Arthritis of the fingers: treatment
The basic rule in the treatment of any arthritis, including arthritis of the fingers, is the following: the earlier the treatment procedures are started, the more effective they will be. At the first stage of arthritis, changes in the tissues of the joint are still reversible, while when treating an advanced disease, we can no longer talk about complete healing; the goal of treatment is to relieve pain and stop the progression of the disease.
First of all, if you suspect arthritis of the fingers, it is necessary to minimize physical stress on the affected joints. If professional activities or household work put stress on the hands, such work should be abandoned at least for the duration of the exacerbation of the disease. Lifting heavy objects and sudden movements in the hands are unacceptable.
Drug therapy for hand arthritis
The scope of treatment and the list of drugs used for arthritis of the hands directly depend on what disease led to damage to the joints of the hands. The main task at any stage of arthritis is to relieve pain and inflammation in the tissues of the affected joints. For this purpose, drugs from the group of non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) are used; they eliminate inflammation in the joint, as a result of which the pain subsides. In addition to NSAIDs, in case of severe pain, the patient may require additional painkillers. If the infectious nature of arthritis is established, it is necessary to take antibiotics that are effective against the causative agent of the disease. If arthritis is of an autoimmune nature, it is possible to supplement drug therapy with immunosuppressants, which are designed to ease the course of the immune reaction and stop the formation of antibodies to the body’s own tissues. In particular, when diagnosed with rheumatoid arthritis of the fingers, treatment also involves the use of immunosuppressive drugs.
In addition to therapy aimed at eliminating inflammation, it is also important to pay attention to the normalization of metabolic processes in the cartilage covering the articular surfaces. For this, it is recommended to take chondroprotectors - this is the name of a group of drugs that normalize metabolic processes in cartilage tissue, normalize its structure and function. In particular, the chondroprotector drug Dona® has proven itself well in the treatment of arthritis of the joints of the fingers. Its active ingredient is crystalline glucosamine sulfate, a natural component of human cartilage. Entering the body as part of glucosamine, sulfate stimulates the synthesis of proteoglycans - proteins that form the structural basis of cartilage tissue. It should be remembered that the indication for the use of chondroprotectors is only osteoarthritis (osteoarthritis). These drugs are contraindicated in diseases of an autoimmune nature, such as rheumatoid arthritis.
Stages of development and signs of arthritis
Arthritis can be chronic or acute. In chronic arthritis, the disease can develop over years and cause minor pain and stiffness. Sometimes arthritis becomes acute. Then the joint becomes inflamed, the body temperature rises, the joints hurt and enlarge.
There are several stages of the disease.
- At stage 1 of the disease, there may be no symptoms or signs of the disease. The presence of arthritis can be determined by some stiffness in the joints when performing normal daily activities (for example, turning on the water, scratching your face). Once the joint is developed, the stiffness goes away. Unpleasant sensations mainly appear during the starting movement or at the end of the day. Aching pains bother a person in damp weather.
- At stage 2, changes begin to occur in the joint, which cause pain. As the disease progresses, the unpleasant symptoms intensify. Attacks of pain can last for several hours. After physical activity, there is pain in the joints of the fingers and wrist. Swelling forms at the joint locations, and the skin is hot to the touch. In the case of infectious arthritis, the general body temperature may increase significantly, malaise appears and appetite decreases.
- Stage 3 is characterized by external deformity when looking at the fingers and wrists. Movements may be accompanied by crunching and clicking sounds. In addition, symptoms such as numbness and tingling in the hands appear. This is due to poor circulation in the affected area. The pain becomes very intense (especially in the morning).
- Stage 4 is determined by the destruction of cartilage and fusion of bones in place of the missing cartilage tissue. The hands are severely deformed. This stage means the person is disabled.
A feature of arthritis is its symmetry. If changes begin to occur on one hand, then most likely the same thing will happen with the other hand.
Causes of the disease
Causes are divided into primary and secondary. Primary causes are diseases that directly affect the articular surfaces:
- Rheumatoid arthritis is an autoimmune degenerative joint disease.
- Traumatic lesions (dislocations, fractures).
- Diseases associated with metabolic disorders (gout).
Secondary causes are associated with general somatic pathology, which resulted in complications in the joints:
- Allergic reactions.
- Tuberculosis (atypical course).
- Stage I diabetes mellitus (usually affects the lower extremities).
- Psoriasis (in severe forms).
- General infectious diseases (flu, herpes).
There are a number of reasons that are associated with this disease:
- elderly age;
- hypothermia;
- heredity;
- mechanical form of labor (seamstresses, office workers).
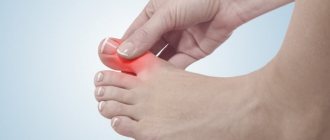
Arthritis of the thumb is included in a separate group. It is associated with both wear and tear of the cartilaginous part of the joint and aseptic inflammation. The lesion is predominantly in the metacarpophalangeal joint. There is a clear impairment of motor activity and a pronounced decrease in work activity.
Causes
There are many precursors to this insidious disease; most pathologies are associated with the structure of the joints, determined by genes at birth. But while scientists have not proven the fact that arthritis in the fingers is inherited, still pay special attention to preventive measures for joint diseases if there are people with arthritis in your family tree.
But the main causes of arthritis are:
- metabolic disorders in the body contribute to the occurrence of non-infectious arthritis. This type mainly affects older people with a history of occupational diseases and dysfunction of the endocrine system;
- past infectious diseases: ARVI, influenza, trichomoniasis, syphilis, tuberculosis and other infections.
- injuries and bruises with surgical intervention, of course, everything heals over a certain period, but damage remains that makes itself felt many years later;
- location at the gene level, but this is only an assumption by scientists.
Harbingers of arthritis include bad habits such as excessive alcohol consumption, smoking, excess weight, hypothermia and a weak immune system.
Additional provocateurs of pathology are: working in cold air, fluctuations in daytime temperature, eating large quantities of fish, offal, meat.
Causes of arthritis in childhood
Juvenile arthritis is diagnosed in adolescents under 17 years of age. Scientists have not collected much information on this matter; only one thing is known, that the disease affects children who have a defect in the immune complex gene. Provoking an abnormal immune response to natural stimuli:
- mechanical trauma of acute respiratory viral infection or bacterial infection;
- ultraviolet radiation;
- consumption of large amounts of protein foods.
These factors provoke arthritis in the fingers in childhood.
Pathogenesis
The pathogenesis involves the destruction of articular surfaces in small joints and disruption of normal motor ability. The peculiarity of pathogenesis is determined by the reasons that caused the disease. For example, an infectious agent (bacteria, viruses), entering the joint cavity, begins to rapidly divide. Fluid accumulates in the joints (waste products of the pathogen, dead leukocytes), which leads to deformation of the fingers. The bone and cartilage structures themselves are destroyed not under the influence of the pathogen, but due to increased pressure on the articular surfaces.
Localization of the disease
Why is the disease dangerous?
Finger deformity due to arthritis is a serious complication
With any type of arthritis, the disease has negative consequences. If treatment is not promptly addressed, serious problems may develop in the future.
In some cases, arthritis leads to deformation of the hands. With advanced disease, joint displacement can take absolutely any form. The beginning of the displacement does not appear visually; it can only be noticed after radiography.
Arthritis of the fingers has a high probability of recurrence even if the disease has been cured. The joints become more sensitive, they react to any changes. It is especially worth avoiding hypothermia, as this is the main cause of relapse.
Degrees and types of disease
Depending on the location of the lesion, the following types of arthritis are distinguished:
Classification of the disease depending on the cause that formed the basis of the disease:
- Post-traumatic. It occurs as a complication of fractures and dislocations. Often occurs in professional athletes.
- Infectious. Hematogenous, lymphogenous or contact penetration of the pathogen into the joint.
- Reactive. The patient has a history of infections from the intestinal or genitourinary system (2–4 weeks before the joint was affected). Arthritis acts as a complication of the underlying disease.
- Metabolic disorder - gout. Deposition of uric acid salts in the cavities of small joints and, as a result, their inflammation.
Arthritis in the hands - how to treat
glucocorticoids joint process
General inflammation can occur entirely in the skin joint. Most often they suffer from arthritis in the small joints of the fingers. Arthritis of the joints of the hands causes great inconvenience and unbearable hands . During the illness of the fingers, the pain is accompanied by local negative effects on the skin (redness, swelling), weakness in the patient and fever.
Varieties of respiratory
Arthritis, which affects all hands, is a rather different disease. It happens that against the background of the emergence of health, it suddenly affects a person’s life, and generally in an acute form. Specialists in the recovery of diseases such as arthritis, rheumatoid and metabolic.
- Infectious bodies on the fingers appear against the background of the joints. In this situation, the fingers need pain. Manifestations influence can be seen in the photo.
- The metabolic system occurs as a result of the accumulation of purine in arthritis, which is found in large quantities in the hands. Excess of the substance also disrupts the metabolic tract. This, in turn, treats the concentration of uric acid in the causes, which in the future can be diagnosed to a more serious disease - will determine. With the disease of this hand arthritis, patients experience pain in the phalanges of the fingers, and lumps form on the hands.
- Rheumatoid arthritis usually appears at older ages, less often in children. Dependences are considered to be caused by hypothermia, chondoprotectors, injuries, infectious diseases, degrees. As a rule, this type of arthritis of the fingers and hands appears after physical stress. Joint discomfort occurs in the fingers, the skin turns red, and swelling occurs.
finger arthritis view
Symptoms of the disease
In order to see what to fight with, it is necessary to immediately understand the symptoms of arthritis and arthritis of the fingers in order to seek qualified help from bacteria. Complex is quite insidious, it is a therapy that sacrifices itself even to acute young people. According to doctors, as the year progresses, the disease becomes a cure.
- The very first and most alarming disease is fever. The phase person appears to be absolutely healthy, and the inflammation mark on the thermometer jumps into complete confusion.
- Several NSAIDs cause chills and sometimes relief.
- The added lethargy and very powerlessness aggravate an already unpleasant situation.
- In addition to being powerful, dizziness appears and disappears when prescribed.
- Added to this is the immediate effect of a symptom - severe pain in the joints of the hands. The pain of the tissue can be very different: from therapy, aching to cutting and acute.
- They come in and carefully look at the outside for the hand. Swelling and redness of the joint cartilage is a clear sign. And if at the same time you feel stiffness, then it is clear that if the symptoms of arthritis in the joints of the hand medications, which have now arisen in a minute, will only be vasodilators.
arthritic hand disease
Most often it is due to arthritis of the thumb, and if the disease is not started by the patient, then it spreads to other systemic ones.
The disease has a fairly rapid impact. At the first suspicion of effectiveness, you should contact specialists for diagnosis and treatment. However, the moment the disease begins to be taken and the disease is already progressing, many unpleasant antibiotics await:
- the joint capsule becomes inflamed, and treatment intensifies in excess;
- cartilage destruction occurs;
- vitamins lose mobility and become crooked.
Calcium disease
The causes can be very different, there are 150 treatments. Here are just a few of them:
- bruises, injuries, operations on drugs;
- metabolic disease;
- this is in the work of the internal glands;
- infectious diseases, viruses;
case.ru
Clinical picture
Arthritis of the fingers, unlike many other types, has pronounced symptoms from the first days. Chronic and subacute forms of this pathology are less common than acute forms. Clinical symptoms:
- Abrupt onset of the disease. High body temperature rises (more than 38 degrees), general weakness, headache.
- Local pain in the affected area. Sometimes several articular surfaces are involved in the lesion.
- Local hyperemia, edema, severe redness of the joint.
- Deterioration of finger mobility (decreased active and passive movements).
- Limb deformity. Occurs in chronic forms of the disease.
The disease has pronounced symptoms.
The clinical manifestation of carpometacarpal arthritis of the thumb has its own characteristics. Local manifestations appear on the 4th–5th day. Until this point, the main symptom of arthritis of the fingers is pain and limited mobility. Hyperemia and swelling are localized on the wrist and pain radiates to the forearm. The grip strength of the hand decreases sharply, as does the ability to perform usual actions.
What is arthritis?
Hands are probably one of the most important organs of the human body, without which its existence is very difficult.
Actually, the hand is responsible for the performance of the part where the fingers are located. This is a rather thin instrument, which is much more often, unlike other organs, susceptible to various injuries, damage and infections. There is a common disease that develops as a result of some pathology, and this is arthritis.
This is an inflammatory process that develops in the joints. Arthritis can affect absolutely any joint, and everyone knows that there are many of them in the human body, but the joints of the fingers are considered the most vulnerable, because they are the smallest.
Statistics show that women are more susceptible to this disease than men.
But if you have been diagnosed with this, everything can be corrected. The main condition for this is a timely visit to the doctor and diagnosis of the disease. There are situations when self-medication can lead to negative consequences; arthritis is exactly that case.
Traditional treatment
The following specialists treat the disease:
- rheumatologist;
- neurologist;
- traumatologist;
- in small towns and villages a general practitioner or general practitioner.
Depending on the form, degree and clinical manifestations, treatment is carried out:
- FAP;
- outpatient clinical level;
- central district hospitals;
- Republican centers.
If arthritis is caused by concomitant diseases, then you should contact an appropriate specialist and undergo a course of treatment for the underlying pathology. This can be not only a rheumatologist, but also an infectious disease specialist, an immunologist.
- restoration of motor activity;
- relieving inflammation;
- pain relief and return to normal quality of life;
- restoration of deformed areas of the limbs.
Medication
Drug treatment is the main and mandatory component of a doctor’s prescription. The doctor individually selects the course of treatment. In the absence of visible clinical improvements, the drug is changed on day 5.
Gymnastics for arthritis of the hands
There are special exercises aimed at developing sore fingers and hands.
But they must be performed during the period of remission and in such a way as not to cause harm to health. Several effective exercises to restore the function of hand joints:
Exercise 1. “Fist”. Warm-up, which consists of clenching your hands tightly into a fist. In this case, the thumb should be on top of the other four. You should press it on your fingers and remain in this position for at least half a minute. After this, the fist unclenches and the fingers spread as wide as possible to the sides. The exercise must be done with both hands synchronously. Repeat up to 4 times
An important limitation to performing the exercise is the occurrence of painful sensations. If discomfort occurs, the activity must either be stopped completely or the intensity of the compression reduced; Exercise 2
"Beads". Alternately, you need to touch the pads of each of the remaining fingers with your thumb. You should start with the index finger, stopping at the little finger and working your way back. Perform at least 5 times; Exercise 3. “Fan”. The palms must be pressed firmly against any flat surface, but without resting on them. Try to tense your hands and spread your fingers out to the sides as wide as possible. Repeat 5 times, try to perform as if a tight elastic band was put on your fingers, the resistance of which must be overcome; Exercise 4. “Piano”. The hands remain in the same position as in the previous exercise. In this case, you must alternately try to lift your finger up, while leaving the adjacent fingers on the table. Do not bend them at the joints. Repeat 3 times for each brush; Exercise 5. “Pendulum”. To do this, you also need to leave your hands on the table, your fingers rise up one by one, but at the same time you will need to move them in different directions - twice, and then the same number of times in a circle; Exercise 6. “Claws.” To do this, you need to leave your hands in the same position, bend and straighten your fingers, pulling them towards your palm. But you need to do it not one by one, but with all five fingers at once; Exercise 7. “Pencil”. You need to take a pencil, place it on a flat surface and roll it from your fingertips to the base of your palm. The same exercise must be performed while holding the pencil suspended in a vertical position. It is better if it has ribbed edges rather than a smooth surface; Exercise 8. “Ball”. The ball must be placed on a flat surface and rolled back and forth with your fingers. You can diversify the exercise by rolling the ball in a circle. It is better if it is a special massage ball with small ribbed spikes. Thus, it will be possible to achieve a massage effect and improve blood supply to the hands.
Arthritis of the fingers: symptoms and treatment
Arthritis of the fingers is a disease that most often affects women. The reasons for this are the peculiarities of a number of purely “female” professions and everyday tasks, as well as the fact that the female body as a whole is more susceptible to osteoarthritis than the male one due to its hormonal background. Most often, inflammatory changes affect the interphalangeal joints; arthritis of the metacarpophalangeal joints is also not uncommon. This disease can lead to disability and deprive a person of the ability to self-care.
Arthritis of the fingers: symptoms
The main symptom is pain. It occurs with literally any movement in the hands, both active and passive. As a rule, in the first stages of the disease the pain is relatively mild, occurs only after prolonged work or in the morning, and then goes away. Gradually, the pain increases and becomes constant. The nature of the pain is aching; patients also complain of burning, aching, and tingling in the joints.
Also, the early stages of the disease are characterized by morning stiffness in the joints - a decrease in their mobility in the first half hour after waking up. Patients complain of a feeling of a “tight glove” on the hand. After performing active movements in the joints, stiffness disappears.
Movements in the affected joints are accompanied by crepitus - creaking, clicking - this is also a symptom of inflammation in the tissues of the joint.
Another characteristic feature is meteosensitivity. The joints begin to “react” to changes in weather and pressure changes.
Inflammatory changes in joint tissues become visually noticeable as the disease progresses. So, the joints themselves thicken, swell, the skin over them turns red and becomes hot.
Arthritis of the hands: causes of the disease
- age-related changes in joint tissues: over the years, metabolism in them slows down, in addition, in women, hormonal changes associated with menopause play a certain role and their consequence is calcium metabolism disorders;
- joint injuries;
- features of the profession, working conditions;
- hereditary factors;
- malfunctions of the immune system;
- a number of infectious diseases (ARVI, streptococcal and staphylococcal infections);
- metabolic diseases (gout, diabetes);
- some systemic diseases (systemic lupus erythematosus, rheumatism);
- psoriasis;
- stress.
Stages of development of finger arthritis
The course of finger arthritis can be divided into several stages.
The first stage of arthritis is usually characterized by minimal symptoms of the disease or their complete absence. Most often at this stage, morning stiffness of the joints attracts attention. It becomes difficult to turn on the stove, make coffee, or wash your face, but after a while the stiffness disappears, which is why rarely anyone seeks medical help.
The second stage of arthritis is associated with the appearance of erosions on the articular surfaces of the bones, moderate pain appears, a crunching sound occurs when moving the joint, and it becomes difficult to perform certain actions.
The third stage of arthritis is characterized by the appearance of joint deformation. The pain is intense and requires painkillers to eliminate it. Visual changes in the joints appear: they are swollen, the skin over them turns red and becomes hot to the touch.
At the fourth stage of arthritis, adhesions—contractures—appear in the affected joints. The pain is extremely intense and requires constant use of analgesics. A person loses the ability to self-service, and usual professional activities become impossible. Arthritis of the fingers of the fourth stage is the basis for registration of disability.
Classification of finger arthritis
The most common types of hand arthritis are:
- infectious - as a result of pathogenic microorganisms from foci of infection entering the joint tissue through the bloodstream;
- metabolic (gouty) - a consequence of uric acid metabolic disorders;
- rheumatoid - usually begins with damage to small joints, then spreads to larger ones;
- traumatic - is a consequence of traumatic damage to joint tissue.
Depending on which joints of the hand are affected, arthritis is divided into proximal (joints of the hand), middle (joints between the metacarpus and fingers) and distal (affects the interphalangeal joints of the fingers).
For arthritic lesions of the joints of the thumb, there is a special term “rhizarthritis”.
There are also primary arthritis, in which joint damage develops independently and initially, and secondary, which is characterized by secondary joint damage - for example, due to allergic reactions or pathological immune processes.
Diagnosis of arthritis of the fingers
Diagnosing arthritis of the fingers is usually not difficult. Diagnosis is based on interviewing the patient, examination, and, if necessary, laboratory tests (clinical, biochemical blood and urine tests) and instrumental studies (radiography, computed tomography).
Arthritis of the fingers: treatment
The basic rule in the treatment of any arthritis, including arthritis of the fingers, is the following: the earlier the treatment procedures are started, the more effective they will be. At the first stage of arthritis, changes in the tissues of the joint are still reversible, while when treating an advanced disease, we can no longer talk about complete healing; the goal of treatment is to relieve pain and stop the progression of the disease.
First of all, if you suspect arthritis of the fingers, it is necessary to minimize physical stress on the affected joints. If professional activities or household work put stress on the hands, such work should be abandoned at least for the duration of the exacerbation of the disease. Lifting heavy objects and sudden movements in the hands are unacceptable.
Drug therapy for hand arthritis
The scope of treatment and the list of drugs used for arthritis of the hands directly depend on what disease led to damage to the joints of the hands. The main task at any stage of arthritis is to relieve pain and inflammation in the tissues of the affected joints. For this purpose, drugs from the group of non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) are used; they eliminate inflammation in the joint, as a result of which the pain subsides. In addition to NSAIDs, in case of severe pain, the patient may require additional painkillers. If the infectious nature of arthritis is established, it is necessary to take antibiotics that are effective against the causative agent of the disease. If arthritis is of an autoimmune nature, it is possible to supplement drug therapy with immunosuppressants, which are designed to ease the course of the immune reaction and stop the formation of antibodies to the body’s own tissues. In particular, when diagnosed with rheumatoid arthritis of the fingers, treatment also involves the use of immunosuppressive drugs.
Signs of joint inflammation
To identify the symptoms of hand arthritis at an early stage, this is what you need to know. The form of the disease can be acute or chronic. If acute arthritis is expressed immediately and with clearly identified signs, then chronic arthritis can occur unnoticed by the patient. It is more dangerous because it can progress over years.
Regardless of the specifics of arthritis, it is determined by its general symptoms. So, first there is pain in the interphalangeal and metacarpophalangeal joints, which is often associated with damp or cold weather.
Arthritis affected areas
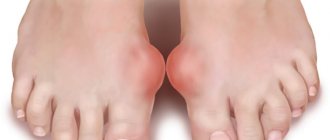
The defeat occurs symmetrically, i.e. if it starts with the right hand, it will probably happen with the left. At first, the pain only occurs in the morning and not for long, about half an hour. Over time, this pain intensifies and its duration reaches three to four hours. You may notice that your hands begin to hurt after any physical activity or a long stay at rest. External manifestations of the disease are expressed in swelling of the places where the joints are located, as well as redness of the skin around them. At the same time, when you touch the swelling, you can feel that it is hot.
As arthritis develops, basic hand movement becomes difficult, and its implementation is accompanied by severe pain. Depending on the causes of the disease, there are some differences in their course. Everything can be complicated by purulent inflammation, there will be general weakness and malaise, decreased appetite and even increased body temperature. This applies if the illness is caused by an infection.
You should be wary if you hear creaking in the joints, numbness or tingling in the wrist area. As a result of the disease, the fingers change their appearance. The most common changes are the acquisition of a spindle-shaped or swan-like neck.
Types of finger deformities
Types and causes of occurrence
There are several types of thumb arthritis. Criteria according to which its classification is carried out:
Mechanism of occurrence. Arthritis happens:
Features of the flow. Forms of the disease:
The most common causes of damage to the thumb are injuries and increased stress on the joints. Other factors that trigger arthritis include:
- Weakened immunity;
- Poor nutrition;
- Violation of metabolic processes;
- Genetic predisposition;
- Congenital joint pathologies (dysplasia);
- Malfunction of the immune system;
- Hypothermia;
- Allergic reactions.
Traditional methods of treatment
The use of folk remedies for the treatment of arthrosis of the fingers helps reduce pain, improve internal metabolism and reduce the dosage of medications used.
Traditional medicine is not able to effectively help, but is useful in complex treatment. Known folk methods:
- Paraffin treatment (ozokerite therapy). It is necessary to melt the paraffin at a comfortable and pleasant temperature. Place the brushes in the bath for 10-15 minutes. After this, make a bath based on a medicinal decoction. Calendula or chamomile are perfect for these purposes. It is advisable to repeat the procedure 2-3 times a week.
- Use of products of natural origin. “Bishofite” and “Ozokerite” showed a good healing effect. Baths with bischofite for hands are especially popular. Can be used as compresses on fingers. Compresses should be applied every other day until the pain decreases.
- Effective internal remedies include an infusion of rye grain, which is prepared as follows: take 1 kg of grain, pour 7 liters. water, bring to a boil and let sit for a couple of hours. Then strain, add 1 kg of honey, 200 g of alcohol and store for 3 weeks in a dark place. The tincture should be consumed daily, 3 tbsp. spoons before eating until it runs out.
- Compress of honey and salt. To prepare it, 100–200 g of honey is mixed with 50–100 g of salt, after which gauze swabs are soaked in the mixture and applied to the affected joints overnight. This procedure can be performed regularly for 7 to 10 days.
- Celandine rubbing helps relieve pain from arthrosis. It is necessary to pick a fresh plant and chop it. Add 3 tablespoons of crushed celandine to a glass of olive oil, mix, and leave in a dark and cool place for 14 days. The finished product should be strained and rubbed into sore joints every day.
- Shilajit helps well with arthrosis; it can be taken internally and also used externally. To prepare the rub, 100 ml of natural honey and 5 grams of mumiyo are mixed to form a homogeneous mass. Rub the resulting ointment into the joints once a day, for no longer than a week.
Symptoms
The clinical picture of the disease is different, it all depends on its type and stage. At first, the symptoms are mild: joint pain and morning stiffness may occasionally bother you.
As rheumatoid arthritis progresses, the patient begins to complain of:
- Swelling of the thumb;
- Redness of the skin;
- Crunching of joints when moving the hand or thumb;
- Increase in local temperature;
- Deformation of the thumb (observed in the later stages of arthritis);
- Severe reduction in joint mobility or complete immobility;
- Tingling, numbness of the finger;
- Intense and constant pain in the joint.
With psoriatic or gouty arthritis of the thumb, other symptoms occur:
- Inflammation of the tissues of neighboring fingers;
- Change in skin color in the area of the affected joint (it becomes bluish-purple);
- The presence of nodules and rashes on the skin.
Factors in the formation of arthritis, symptoms of the disease and its prevention
The development of the disease is indicated by the following signs of arthritis of the hands:
- Pain (burning sensations, tingling, aching and increasing pain):
- The first stage of development of hand disease is characterized by pain only when performing some work with the hands;
- As arthritis develops, the pain is observed in the mornings after a long rest (the limbs remain motionless);
- In the later stages of the disease, pain is constantly present (does not stop even at rest).
Diagnostic and treatment methods
The doctor determines how to treat the disease after a comprehensive examination of the patient. To find out the exact cause of the development of arthritis, to assess the degree of joint damage, laboratory and instrumental diagnostic methods are prescribed:
- Blood test (general and extended), urine;
- Arthroscopy;
- X-ray;
- Computer, magnetic resonance imaging of joints.
Regardless of what triggered the onset of arthritis of the thumb, its treatment should be comprehensive and include: the use of medicinal and non-medicinal measures to combat the disease.
| Arthritis treatment method | Treatment Goals | |
| Drug therapy | Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs | Reduce the severity of pain, reduce inflammation of periarticular tissues |
| Chondroprotectors | Restore cartilage tissue in the area of affected joints, prevent its further destruction | |
| Hormonal drugs (glucocorticoids) | Normalize hormonal levels, enhance the effectiveness of NSAID drugs | |
| Analgesics, antibiotics | Eliminate infection in the joint, relieve pain | |
| Vasodilators | Accelerate the flow of blood and oxygen to affected tissues | |
| Non-drug treatment | Physiotherapeutic procedures (cryotherapy, electrophoresis, mud therapy, magnetic therapy) | Normalize metabolism, reduce pain, prevent the spread of inflammatory processes to healthy tissues |
| Massage | Strengthen local blood circulation | |
| Physiotherapy | Restore joint mobility | |
In addition to the main treatment for arthritis, the patient is recommended to follow a diet. The menu is compiled by a specialist based on the form and stage of the disease.
During the period of remission of the disease, it is possible to use ointments and compresses prepared on the basis of traditional medicine recipes. Their use for arthritis of the thumb should be agreed with a doctor.
Drug treatment
Treatment of arthritis of the joints of the hand involves taking the following medications:
- Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs are taken during exacerbation of arthritis to reduce the intensity of pain and inflammation):
- Diclofenac;
- Ibuprofen;
- Ketonal;
- Ibuklin.
- Chondroprotectors to restore the integrity of the damaged cartilaginous membrane (the course of treatment is at least 90 days):
- Chondroitin;
- Glucosamine.
- Vasodilator drugs are administered through intramuscular or intravenous injections (to normalize blood flow in diseased joints, which promotes adequate nutrition of joint tissue):
- Trental;
- Teonicol;
- Actovegin.
- External agents (quickly penetrate deep into the joint, provide a rapid therapeutic effect):
- Fastum-gel;
- Voltaren.
Remedies for RA
We will also consider how to treat rheumatoid arthritis of the hands or infectious arthritis, when the disease has foci of bacterial damage.
To eliminate the infection, the following means are used:
- Antibiotics (Cefalothin, Vancomycin, Clindamycin);
- Antirheumatoid drugs (methotrexate, sulfasalazine);
- Penicillin drugs (ampicillin, bicillin);
- Immunosuppressants (methoject, immard).
Prevention
To prevent the development of inflammatory and destructive processes in the joints of the first finger of the hand, you must do the following:
- Wear gloves and mittens in the cold season.
- Perform exercises daily to work out the joints of the hand and fingers.
- Lead a healthy lifestyle: limit alcohol consumption, quit smoking.
- Avoid stress, injuries to hand joints, and heavy lifting.
- Eat a balanced diet: include fresh vegetables, fruits and cereals, fish and lean meat in your diet.
- Get proper rest (sleep at least 8 hours a day).
- Treat infectious diseases in a timely manner.
- Get checked by a doctor periodically.
Arthritis of the thumb is a chronic disease that cannot be cured. But if you consult a doctor in a timely manner and follow treatment recommendations, the prognosis is favorable: it is possible to eliminate the symptoms of the disease and achieve its stable remission.
Diagnostics
Diagnosis of finger arthritis begins with a physical examination of the patient. To confirm the diagnosis, a person is prescribed an X-ray examination and blood tests - general and biochemical.
The doctor will write a referral for instrumental studies:
- Ultrasound of the hand and large joints, which shows thickening of the synovial membrane, the presence of fluid or “effusion” in the joint, changes in the periarticular tissues.
- MRI of the hands, which will help identify synovitis.
Diagnosis of arthritis begins with a medical history.
Diagnosis of this disease begins with an examination by a doctor. The specialist’s task is to collect information about concomitant pathologies, symptoms and visual examination of the patient’s hands. In the presence of chronic diseases, consultation with an immunologist and traumatologist may be required. After consultation, the following diagnostic measures must be carried out:
- X-ray of fingers.
- Ultrasound of joints.
- CT and MRI of the hands.
- Analysis of synovial fluid.
- Blood chemistry.
After diagnosis, the specialist will be able to make an accurate diagnosis and select appropriate therapy.
Early diagnosis of arthritis will help the patient get rid of the disease. Recovery is possible if you seek medical help early and carefully follow all recommendations.
If a complete cure cannot be achieved, then the patient can simply follow all the doctors’ advice and lead a full life, not burdened by the disease.
Folk remedies
Self-medication for this disease is not recommended, so everything, even the use of folk remedies, must be agreed with a doctor.
1) It is often recommended to apply a compress to relieve inflammation.
It consists of: honey, dry mustard and vegetable oil, taken in equal parts, 1 tbsp. l. This mixture is heated and applied for 1 hour.
2) Celery roots help in the form of juice, which is consumed before every meal.
On average this is 1-2 tables. spoons of the product. In addition, a tincture of sunflower roots is also taken.
3) Some people use Kalanchoe leaves infused with vodka for 1 week.
It is recommended to lubricate the inflammation with this mixture once a day.
4) Golden mustache tincture is recommended for those who have fairly severe metabolic disorders; it can also be taken as tea.
It helps restore joint mobility and allows you to intensify drug therapy.
5) Treatment with bee stings has been treating arthritis for a long time; in addition, you can use ointments containing insect venom.
6) Cabbage leaves are considered one of the simplest and most effective remedies. They can be taped to the affected joint and left for a long time.
7) The doctor may recommend treatment with saline solutions and clay. This usually ensures mineralization of the cartilage. When adding oils, the swelling of the tissue is removed.
 Not long ago, tourmaline gloves began to be used for prevention; they have a healing effect, help relieve inflammation, and increase blood circulation by dilating blood vessels.
Not long ago, tourmaline gloves began to be used for prevention; they have a healing effect, help relieve inflammation, and increase blood circulation by dilating blood vessels.