Hormonal balance is one of the most important conditions for the well-being of the fair sex. But overwork and life's troubles can lead to nervous breakdowns and various diseases. In this case, it is discovered that the woman’s cortisol hormone is elevated. The causes of this phenomenon must be immediately clarified and eliminated.
Cortisol is a hormone produced by the adrenal glands (their work, in turn, is regulated by the pituitary-hypothalamic system). This substance balances metabolic processes, stimulates the functioning of the immune system and brain, and promotes the formation of fetal lungs during pregnancy. The adrenal glands secrete more cortisol, and its levels in the body increase during pregnancy or in extreme situations. In other cases, hormonal imbalance is abnormal. The appearance of excess weight, infertility, and depression is a signal that it is necessary to take a cortisol test.
Norm of the hormone cortisol
Cortisol is a steroid hormone that is produced in the zona fasciculata of the adrenal cortex. Most of it in the blood is bound to a special corticosteroid-binding protein, transcortin; a small amount is bound to albumin and other plasma proteins.
Only 10% of cortisol in a free state is distributed through the general bloodstream of the body and binds to the corresponding receptors, providing physiological functions. The production of cortisol in humans follows circadian rhythms. In the evening its content in the blood is minimal, and in the morning it reaches its maximum.
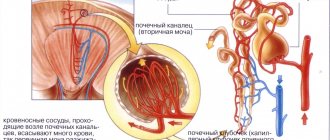
In the human body, the hormone ensures ionic homeostasis, affecting the activity of the kidneys, intestines, salivary and sweat glands. The most important target organ for cortisol is the kidney. It has its main effect by acting on the collecting ducts of the cortex - it promotes the reabsorption of sodium, and also affects the production of potassium and ammonium.
The level of corticosteroid in the blood is relatively constant - 10 mg; increased cortisol may appear in women during pregnancy. At the same time, the amount of hormone increases by 3-5 times! Also physiologically, its amount in the blood may increase during puberty. In all other cases, an increase in indicators will be a sign of pathology.
Main symptoms of elevated cortisol levels
The main symptoms of elevated cortisol levels (Cushing's syndrome) are:
Mood swings (increased irritability, depression or anxiety). This symptom is characteristic of increased levels of cortisol in the blood. If you become moody, constantly in a bad mood, or experience anxiety, then know that these symptoms are a consequence of the long-term effects of cortisol on the production of serotonin and dopamine.
Digestive problems. Elevated cortisol levels disrupt the digestive tract, reduce the production of enzymes needed to digest food, and reduce the absorption of minerals and nutrients. Stress is one of the causes of poor digestion.
Heart disease and high blood pressure. Elevated cortisol levels can be caused by a very stressful lifestyle. Too much stress can cause hypertension, which increases the risk of heart disease.
Sleep problems. Cortisol production is naturally high in the early morning as it helps us wake up energized. However, in people with elevated cortisol levels, the circadian rhythm of this hormone is altered. These people have low cortisol levels in the morning, not high ones.
Increase in body weight. Cortisol stimulates appetite and cravings for sweets and other high-calorie foods. Therefore, if you have constantly elevated cortisol levels, then most likely you will want to eat high-calorie fatty and carbohydrate foods.
Skin aging and wrinkles. Elevated cortisol levels lead to skin dehydration, which can cause you to develop wrinkles prematurely.
Reasons for the increase
There are several main etiological factors (reasons) for increased cortisol. They can be endo- and exogenous. Endogenous causes are divided into two subtypes:
ACTH-dependent form
Develops due to impaired production of ACTH. This can occur with Itsenko-Cushing's disease, syndrome of ectopic production of adrenocorticotropic hormone and taking medications containing synthetic ACTH. With Itsenko-Cushing's disease, the following changes develop in the body:
- The mechanism for regulating the function of the hypothalamic-pituitary-adrenal system and the daily production of CRH (corticoliberin) - ACTH - cortisol are disrupted;
- The “feedback” principle stops working with a simultaneous increase in ACTH and cortisol levels;
- The reaction to stress disappears - an increase in cortisol when blood sugar levels drop.
Itsenko-Cushing's disease is similar in its mechanism of action to the syndrome of ectopic ACTH production. The main difference is the source of hormone production. In the first case, the cause is a tumor of the pituitary gland, in the second, the tumor can be localized in any human organ. Most often, the malignant process will occur in the lungs - 60% of all cases, which doctors associate with smoking of patients. Less commonly, the syndrome will occur with tumors of the pancreas, intestines, and ovaries.
ACTH-independent form
It develops when the adrenal glands independently produce cortisol in excess quantities during the tumor process.
In some cases, a person's cortisol is elevated and there is no obvious source of the problem. Then you should think about functional hypercortisolism. It develops as a result of general diseases not related to the adrenal glands. The main reasons for this condition:
- Excess body weight
- Chronic liver disease (eg, cirrhosis)
- Polycystic ovary syndrome
Why is cortisol elevated and how to lower it?
Norms
Cortisol levels are determined using a blood test. The highest rate is observed in the morning, and the minimum in the evening, by 11 p.m.
The levels of this hormone in the blood change with age. Cortisol is elevated in women and men during puberty, as well as in children under 10 years of age. In adolescents aged 14-16 years, the maximum value is within the normal range - 856 nmol/l. In adults, it varies between values of 140-640 nmol/l.
Causes of elevated cortisol
In some cases, cortisol may be higher than normal. This is observed in the following pathologies and conditions:
- 1. Prolonged stress. A constant state of depression leads to an increase in the synthesis of this hormone.
- 2. Failure to comply with the daily routine.
- 3. Alcohol abuse.
- 4. Physical fatigue. As a rule, this is observed in men who experience increased stress.
- 5. Serious illnesses. Diabetes mellitus, thyroid disease, inflammation of the adrenal glands and cirrhosis of the liver can provoke an increase in cortisol.
In women, elevated cortisol may indicate polycystic ovary syndrome. The level of this hormone can jump up to 5 times during pregnancy. Since it is called a stress hormone, women often develop depression during pregnancy. Another manifestation of increased cortisol during pregnancy is stretch marks. They occur because collagen (the protein responsible for skin elasticity) becomes fragile. After delivery, cortisol levels quickly return to normal.
Symptoms
When cortisol increases in the blood, the following symptoms appear:
- unreasonable anxiety;
- dysfunction of the thyroid gland;
- insomnia;
- irritability;
- muscle pain;
- violation of metabolic processes;
- hand tremors;
- depression;
- swelling of the face and neck;
- general depression.
Women may experience excess hair growth and menstrual irregularities. This hormone can also lead to infertility. And in men, against the background of increased cortisol, libido decreases.
If these symptoms occur, you need to get tested. Timely treatment will help avoid worsening disorders. If adequate therapy is not carried out, there is a risk of the following consequences:
- muscular dystrophy;
- diabetes;
- endocrine diseases;
- mental disorders.
How to normalize hormone levels?
When diagnosing elevated cortisol, complex therapy is necessary. The patient is prescribed medication. It can vary greatly in each individual case.
The patient is prescribed products that reduce cortisol levels. This method of normalizing hormonal levels is quite effective. It is also worth making lifestyle changes. You need to get proper rest, reduce physical activity and avoid stressful situations.
Conservative treatment
Drug treatment depends on the cause of the elevated cortisol. Patients are prescribed additional examination of the adrenal glands, hypothalamus, and thyroid gland. You also need to test for other hormones and blood sugar.
Only after this is appropriate therapy established. Moreover, it will be aimed at relieving the root cause, and not at blocking cortisol.
Diet
When choosing a diet, pay attention to the fact that nutrition should help reduce excess weight, if any. Patients are advised to completely eliminate or minimize the consumption of the following foods from the daily diet:
- 1. Trans fats. Research has shown that this type of unsaturated fat can increase cortisol levels in the blood. When buying products in a store, you need to pay attention to the composition. You should not eat food that contains partially or fully hydrogenated vegetable fats. They are found in fast food, cakes, flour products, mayonnaise and sauces.
- 2. Some vegetable and cooking oils. Canola, sunflower, soybean and corn oils should be avoided as they are the product of complex chemical processing that strips them of nutritional value and fills them with toxins. These oils are destroyed under the influence of oxidative processes, which is harmful to the body. Their use disrupts hormonal balance. Olive, butter and coconut oils are recommended as a replacement - they help reduce cortisol levels in the blood.
- 3. Fruit juices. Regular consumption of fruit juices increases the risk of diabetes because it disrupts metabolism. This leads to changes in hormonal levels. But fruit in its pure form has the opposite effect. This is due to the fact that they contain fiber.
- 4. Cakes and pastries. Many sweets contain large amounts of refined sugar and are low in antioxidants. Such food stimulates the release of adrenaline and cortisol into the blood. It is because of this combination that after sweets a person feels satisfied until the sugar level drops and he wants a new portion - this is a sign of the predominance of cortisol over adrenaline.
- 5. Factory farmed beef. Such meat is not recommended, because animals are raised by feeding various genetically modified cereals, antibiotics, hormonal agents, etc.
- 6. Low-fat flavored yogurt. Natural yogurt contains a large number of probiotics - they reduce cortisol levels. But the low-fat product does not contain these beneficial bacteria, but it does contain dyes, artificial fat substitutes, and flavors.
- 7. Low fiber carbohydrates. They are otherwise called fast because they break down quickly and lead to a sharp jump in blood sugar. Increased insulin release triggers the release of cortisol. Against this background, there is a sharp drop in blood sugar. A diet containing such carbohydrates impairs digestion and causes inflammation of the gastrointestinal tract. Such products include bread, cookies, cereal flakes, crackers, that is, processed food.
- 8. Caffeine. Drinking caffeine-containing drinks does not cause a sharp increase in cortisol, but in people exposed to high levels of stress, additional stimulation of the nervous system by caffeine can provoke insomnia and irritability. And this leads to an increase in cortisol levels. With hormonal imbalance and suppressed adrenal glands, the absorption of caffeine is impaired. Therefore, if you have elevated cortisol, it is recommended to refrain from drinking this invigorating drink.
- 9. Alcohol. Alcohol-containing drinks provoke an oxidative process in the liver. Alcohol increases cortisol levels after intense exercise.
There is also such a thing as individual intolerance. Different people may have increased sensitivity to certain foods: eggs, shellfish, casein protein, grains containing gluten. If you have an allergic reaction, they should not be eaten, as this leads to stimulation of cortisol production.
To lower cortisol levels, protein foods are recommended. When the body does not receive the required amount of food, glycogen reserves are depleted. Proteins help replenish these reserves. It is advisable to use it in the morning.
You need to drink 1.5 - 2 liters of clean water per day. When dehydration occurs, the body experiences stress, which stimulates the production of cortisol. Water should be drunk immediately after waking up. Moreover, it is advisable to refrain from drinking an hour before bedtime.
The diet should contain vitamins, minerals and amino acids. One of them - glutamine - is responsible for tissue tone, reduces cortisol levels, improves protein synthesis, is involved in increasing the volume of muscle tissue, and increases immune function.
To reduce the amount of cortisol, you need to eat foods rich in vitamin C. The human body should receive 50 - 100 mg of this vitamin per day.
When there is a hormonal imbalance in the body, the amount of magnesium decreases. This trace element is very important. It helps remove excess cortisol from the body. It is recommended to use food additives - magnesium acid salts:
- citrate;
- glycinate;
- magnesium chloride;
- gluconate
Folk remedies
Among the folk remedies for lowering cortisol levels, the following plants are recommended:
- 1. Licorice. A decoction based on its root helps support the body during adrenal hypofunction. Some experts recommend it to normalize hormonal levels and with elevated cortisol. To do this, you need to take licorice root, grind it and brew it as tea. This drink is drunk in a course of 4-6 weeks, after which they take a break.
- 2. Ginkgo Biloba. The extract of this plant improves brain activity, concentration and memory. It dilates blood vessels and strengthens the walls of veins. To permanently reduce cortisol levels, you should drink ginkgo extract from the pharmacy for at least six months.
Before using traditional medicine methods, you should consult your doctor. Especially if you have to combine such therapy with the main medication.
dietary supplements
To lower cortisol levels, dietary supplements that have the following compounds can be used:
- 1. Androgenic-anabolic steroids. They improve the synthesis of protein and other nutrients, thereby reducing cortisol levels.
- 2. Growth hormone. Drugs with an anti-catabolic effect are very well known among professional athletes, as they reduce adrenocorticotropic hormone. As a result, cortisol levels decrease. Some peptide drugs (Pralmolerin, Hexarelin) have a similar effect.
- 3. Agmatine. Its anti-catabolic effect extends more to nerve cells than to muscle tissue.
- 4. Glucose. A glucose solution can greatly suppress cortisol levels.
- 5. Phosftidylserine is a cortisol blocker. It has an anti-catabolic effect and promotes increased brain activity and protein synthesis.
In addition to drugs with the above compounds, others can be used, but their anti-catabolic activity has not been confirmed by research. These include:
- Dexamethasone;
- Clenbuterol;
- Hydroxymethylbutyrate.
The presented dietary supplements are recommended to be used only after consultation with your doctor. They may not be effective and some may be harmful.
Consequences of elevated cortisol
Excess cortisol in the body leads to severe, often irreversible damage to the human body. It causes the breakdown of proteins and structural matrices of most organs and tissues, which leads to dystrophic and atrophic changes.
If cortisol is elevated for a long time, a disturbance occurs in carbohydrate metabolism: the constant production of glucose is accompanied by its breakdown in the muscles and liver. As a result, the development of steroid diabetes mellitus. Fat metabolism also gradually changes - depending on the sensitivity of receptors to steroids, in some places fat begins to be deposited in excess, in others it completely disappears.
Other symptoms of elevated cortisol levels
Pain (especially in the back) is a frequent “companion” of elevated cortisol levels.
Increased susceptibility to infection. Cortisol can weaken the activity of the immune system, so a person may get colds more often.
Facial hair on women. The appearance of “antennae” indicates a hormonal imbalance, which often occurs with elevated cortisol levels.
Purple/pink stretch marks (striae) may appear and are similar in appearance to those seen in pregnant women.
In most cases (except those caused by steroid medications), symptoms of elevated cortisol levels develop gradually. Diagnosis is often difficult because most symptoms may be due to other diseases.
Symptoms of the disease
Elevated cortisol causes the following symptoms:
- Cushingoid obesity: fat deposition in the face, neck, torso, and on the cervical vertebrae (a small hump is formed).
- Atrophy of the muscles of the limbs - arms and legs become thin and lose their original shape. Severe muscle weakness and fatigue are noted; as the disease progresses, patients have difficulty even doing basic things - getting out of a chair or bed on their own.
- The skin is dry, purple in color on the chest, back and chest. The venous pattern on the extremities is clearly visible. In the abdomen, chest, inner thighs and shoulders, ugly bluish-red stripes appear - stretch marks.
- Baldness
- Pustular skin lesions
- Sexual disorders: menstrual irregularities, infertility, miscarriage
- Emotional disorders: from mild depressive disorders to severe psychoses that require hospitalization.
- Elevated cortisol in men leads to impotence and infertility
- Arterial hypertension
- Steroid diabetes mellitus
- Cardiomyopathy – damage to the heart muscle due to protein breakdown
- Increased bone fragility – osteoporosis
- With the syndrome of ectopic ACTH production, a kind of Cushingoid obesity may be absent. in this case, severe weakness, increased skin pigmentation, puffiness of the face and signs of cancer intoxication (nausea, vomiting, weight loss) prevail.
Elevated cortisol in women: main causes and symptoms
The pace of modern life especially threatens the well-being of women. They constantly experience overload: at work, at home, in their personal lives, in communication with family and friends. Women experience troubles painfully, suffer from physical overload, as they take on much more than their nervous system and physical endurance can handle. As a result, the body reacts with stress, in which the hormone cortisol is released into the blood in large quantities.
A woman’s body can survive a one-time or slightly increased release of cortisol, but too strong nervous and physical shocks, as well as a state of constant stress over a long period, lead to very serious consequences for women’s health and even life.
Diagnosis of high cortisol in the body
Diagnosis of elevated cortisol is carried out using a set of laboratory tests:
The daily excretion in urine of cortisol and its derivatives is determined. The concentration in the blood is not particularly important, since it can jump even from stress before the injection.
A small dexamethasone test is of great diagnostic importance. It is carried out as follows: the patient's blood cortisol is measured in the morning at 7.00. At 24.00 he takes a dexamethasone tablet (4 mg) orally and the next morning the hormone level is measured again. In a healthy state, its amount in the blood is halved; with Itsenko-Cushing, there will be no suppression of hormone production.
Next, in order to differentiate Cushing's disease or an adrenal tumor, a large dexamethasone test is performed. The difference between the samples is in the dosage of dexamethasone - for a large dosage, the dosage is doubled - an 8 mg tablet. If there is a violation of the pituitary gland, a decrease in cortisol will occur; if there is disease of the adrenal glands or ectopic syndrome, the amount of the hormone will remain at the same level.
Next, magnetic resonance or computed tomography is performed to detect tumor processes.
In addition to these studies, the detection of complications of hypercortisolism is important. Therefore, accompanying laboratory diagnostics are required: Biochemical blood test (the balance of sodium, potassium and calcium ions changes);
Determination of blood sugar (a high glucose level will indicate the presence of diabetes mellitus)
X-ray of the lungs, mediastinum, thyroid gland, ultrasound examination of the abdominal cavity - are carried out in case of ectopic syndrome to detect tumors and metastases.
X-rays of bones and spine are used in severe cases to identify incipient osteoporosis.
How to reduce cortisol levels in the blood
In cases where hypersecretion of cortisol is associated with a particular disease, it is actively treated by a doctor of the appropriate profile (endocrinologist, gynecologist, hepatologist, narcologist).
If the increase in cortisol is due to functional reasons, modification of lifestyle and diet is recommended to reduce it.
In pregnant women, cortisol is increased twofold or more (there may be a fivefold increase), but this is not a pathology.
- Stick to a daily routine, devoting sufficient time for proper rest and night sleep.
- Go to bed no later than 10 pm, sleep duration should be 8-9 hours. If you have difficulty falling asleep, you should consult a doctor to select a sleeping pill.
- Bring as many positive emotions into your life as possible.
- Learn relaxation techniques and develop stress tolerance.
- Drink enough water (1.5-2 liters) throughout the day.
- Avoid drinks rich in caffeine (coffee, strong tea, cola, energy drinks) and give preference to water instead.
- Regularly include fish dishes, especially sea fish, in your diet. If this is not possible for one reason or another, you can take fish oil in capsules.
- Eliminate refined foods from the diet (white rice, pasta, confectionery, white bread).
- Avoid activities that cause a significant increase in heart rate (such as running or cycling), as they increase cortisol levels. Pilates, yoga, and swimming are recommended instead.
Video from YouTube on the topic of the article:
Education: graduated from the Tashkent State Medical Institute with a degree in general medicine in 1991. Repeatedly took advanced training courses.
Work experience: anesthesiologist-resuscitator at a city maternity complex, resuscitator at the hemodialysis department.
Found an error in the text? Select it and press Ctrl + Enter.
Our kidneys are capable of purifying three liters of blood in one minute.
Many drugs were initially marketed as medicines. Heroin, for example, was originally brought to market as a cure for children's coughs. And cocaine was recommended by doctors as an anesthesia and as a means of increasing endurance.
When we sneeze, our body stops working completely. Even the heart stops.
When lovers kiss, each of them loses 6.4 calories per minute, but at the same time they exchange almost 300 types of different bacteria.
If your liver stopped working, death would occur within 24 hours.
During operation, our brain expends an amount of energy equal to a 10-watt light bulb. So the image of a light bulb above your head at the moment an interesting thought arises is not so far from the truth.
People who eat breakfast regularly are much less likely to be obese.
Referral for treatment
Treatment for cases where cortisol is high depends on the source of the disease. For pituitary adenoma or adrenal corticosteroma, surgical excision of the tumor is performed, followed by radiation or chemotherapy.
Drug treatment includes taking medications that inhibit (suppress) the production of ACTH (diphenium, bromocriptine) and corticosteroids (chloditan).
There is also symptomatic treatment of high blood pressure, osteoporosis, insulin-resistant diabetes mellitus and mental disorders.
Diagnosis and norm in women
To check your cortisol level you need to donate blood for biochemistry
It is believed that for any human individual, regardless of age, gender, race and weight, the level of cortisol in a normal relaxed state does not exceed 10 mg. Since the level of this substance is unstable during the day, increased cortisol in women is considered to be at least 80 mg. And if the data exceeds 180 mg, then we are talking about a very high level of cortisol in the blood. This indicates the presence of severe stress, close to a state of shock, or very serious physical fatigue, even exhaustion of all strength.
Under the age of 16, the hormone level is 85-580 nmol per liter, and for adults - 138-365 nmol per liter. In pregnant women, normal levels increase up to 5 times, not being considered a pathology.
Cortisol levels are higher in the morning and tend to drop in the evening to give the body a chance to rest.
A blood test for cortisol is taken in the morning, always on an empty stomach, and the break from the last meal before the analysis should be approximately 10-12 hours. Preparation for the test begins three days before, following a diet without overeating and eating junk food, with a moderate amount of salt in the diet. Two days before the test, all medications are discontinued whenever possible, and if this cannot be done, they are notified about taking specific medications.
When preparing for the analysis, it is advisable not to be nervous or physically overtired. Half an hour before the test, the patient is advised to relax and lie down. For analysis, blood is taken from a vein, the results are transferred to the attending physician or given to the patient.
How to achieve stable hormone levels in the body
Simple rules should be followed to ensure that the hormone remains within the reference range:
- avoid stress;
- do not smoke and stop drinking alcohol;
- Monitor your diet during the day: maintain a balance of dietary fat, avoid eating simple carbohydrates;
- regularly expose your body to moderate physical activity to stimulate muscle growth;
- At the first suspicion of a hormone imbalance or health problem, consult a doctor or take tests yourself in a paid laboratory.
View gallery
Cortisol: what is it in women
If the central nervous system receives a signal about impending danger, the body raises all its forces to mobilize. The adrenal glands begin to work hard and release cortisol into the blood, which performs a protective function.
An increase in hormone levels stimulates an increase in blood pressure and an increase in glucose. This is necessary to enhance brain function in stressful situations. That is, a kind of “energy-saving mode” is activated, in which additional energy for the body begins to be drawn from the most accessible sources. They usually become muscle tissue.
What is cortisol responsible for? Main functions of the hormone:
- supports the body during periods of stress and fatigue;
- promotes the conversion of proteins into glucose (gluconeogenesis);
- takes part in protein metabolism: delays protein synthesis, accelerates its breakdown;
- activates the formation of triglycerides;
- stimulates the production of pepsin and hydrochloric acid in the stomach;
- increases glycogen deposition in the liver;
- affects the ratio of sodium and potassium in the body;
- reduces vascular permeability;
- affects the activity of the pituitary gland;
- supports immunity: reduces the number of lymphocytes, inhibits the synthesis of antibodies, γ-interferon.
Find out about the causes of discharge from the mammary glands when pressed, as well as how to get rid of negative symptoms.
Oophoritis: what is this disease and how to treat it? Read the answer at this address.
Blood test for cortisol: how to take it correctly
To determine the level of hydrocortisone, in addition to actually detecting it in the blood, a general and biochemical blood test, a study of urine collected over 24 hours (daily urine), and in some cases (rarely) a saliva test are performed.
If the increase in cortisol is due to functional reasons, lifestyle and diet modifications are recommended to reduce it.
In an adult, the concentration of hydrocortisone in the blood is 138–165 nmol/l. In different laboratories, normal values may differ, so when a result is obtained, it is assessed based on the reference values given by the laboratory that conducted the study.
When referred to the laboratory for cortisol testing, patients are given the following recommendations:
- follow a diet with a low content of table salt (no more than 2-3 g per day) for three days before blood sampling;
- limit physical activity at least 12 hours before the test.
48 hours before the upcoming study, all drugs that can affect cortisol levels (phenytoin, androgens, estrogens) are discontinued. If this is not possible, then the prescription form indicates the drug being taken and its dosage.
Blood is drawn from 6 to 9 am. Before blood is drawn, patients are placed on a couch in a quiet room and allowed to rest for at least 30 minutes, after which blood is drawn from a vein. If it is necessary to determine the daily dynamics of cortisol, repeated blood sampling is prescribed in the period from 16 to 18 hours.