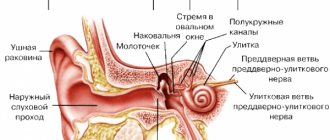
What is stye on the eye?
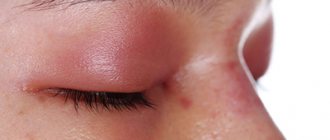
This is an inflammation of the eyelash bulbs, meibomian lobules or sebaceous glands. Ophthalmologists distinguish between internal and external neoplasms. External barley is an acute inflammatory process in the sebaceous gland. The edge of the upper eyelid thickens, turns red and swells. The degree of pain varies depending on how swollen the eyelid is. Sometimes it swells so much that a person cannot open the swollen eye.
After several days, a center of inflammation with a whitish head of a purulent core appears in the edematous focus. After a few more days, the abscess opens, and the person experiences significant relief. How long does this eye disease last? The eyelid usually heals within a week. A small scar remains at the site of the abscess, which then disappears without a trace.
Internal styes are similar in symptoms to external neoplasms. The difference is that the process of suppuration develops deep in the tissue, and a purulent capsule forms close to the conjunctiva. If the lesion of stye on the upper eyelid opens spontaneously, then pus pours into the palpebral fissure. Sometimes the inflammation does not have time to fester and goes away on its own. Then the swelling subsides in a matter of days.
Symptoms
The disease begins with itching, the sensation of a foreign body in the eye. Soon pain joins the itching, and the following signs appear:
- the eyelid swells, then the conjunctiva;
- the tissues around the neoplasm become denser;
- the skin becomes inflamed;
- the eye swims, narrowing the field of vision.
Soon the yellowish head of the purulent rod is visible. The center of the edema in the upper eyelid becomes like a grain of barley - hence the name of the disease. Often the abscess opens on its own: the external one - outward, the internal one - into the conjunctiva. There may be more than one barley. With multiple development of the disease, headache, fever, and swollen lymph nodes may appear. Under the mask of stye, other eye diseases are often hidden, which are treated differently, so differential diagnosis is important.
Causes of inflammation of the upper eyelid
What causes stye on the eye? Many blame the cold weather, believing that the illness is caused by severe hypothermia. However, this is far from the only reason: often the disease occurs after violation of hygiene requirements; eyelids should not be touched with hands, especially with unwashed hands. Barley can appear with a sharp weakening of the immune system. Low quality cosmetics also cause eyelid disease. In teenagers, stye on the eyelid is not uncommon, since rapid hormonal changes occur in their bodies. Sometimes hereditary predisposition also plays a role.
Is stye contagious?
Ophthalmologists do not have a single scientific opinion on this matter. A person with such a disease does not need isolation. However, since barley is a purulent infection, there is a risk of infection. It is especially great in people with weak immunity, in patients with blepharitis, conjunctivitis or demodicosis. If you have barley on the upper eyelid, relatives or friends should not be allowed to come into contact with sources of pus.
Stye inside the eye
Internal stye on the eye or meibomitis is an inflammatory process of the meibomian glands located on the back of the edge of the upper or lower eyelids. Treatment of such a disease at home is complicated by the inaccessibility of the abscess, but the lack of contact with the external environment facilitates the course of the acute process. Like external stye, internal inflammation causes severe discomfort in the patient, which intensifies when the abscess is exposed to the surface of the eyeball.
Pain with stye
In everyday life, barley is an acute purulent inflammation of the eyelash bulb and the sebaceous gland around the hair follicle. The disease is caused by staphylococcus, and people with reduced immunity often suffer from styes.
First, pain is felt when pressing, and then redness and swelling of the eyelid occurs. The swelling increases, which sometimes causes the palpebral fissure to decrease. After a few days, an abscess with a yellow head forms on the eyelid. Inflammation may be accompanied by signs of malaise: fever, swollen lymph nodes, headache.
As soon as the abscess opens on its own, the pain gradually disappears and health improves. You should not try to squeeze out the pus; this can lead to phlegmon, abscess and even meningitis.
Pain in the lower eyelid occurs due to stye
Sometimes several affected areas form on the eyelid, which merge with each other. An abscess may appear on the inside of the eyelid, this indicates inflammation of the sebaceous glands at the edges of the eyelid, this disease is called meibomitis. With this form of stye, the symptoms of the disease are less acute, and pus breaks into the conjunctival sac.
Why does the lower eyelid hurt?
If you have stye, you should not apply heat or apply compresses to the sore eye. It is necessary to use antibacterial eye ointments Hydrocortisone, Floxal, as well as Levomycetin and Tsipromed drops. If the abscess does not mature for a long time, UHF therapy helps; it is carried out in the absence of elevated temperature.
What treatment is prescribed?
Effective medications
Inflammation of the eyelid of a bacterial-infectious nature is treated conservatively. Depending on the established diagnosis, the doctor selects the optimal treatment regimen, which helps eliminate the root cause of the pathology and accompanying symptoms in the shortest possible time. An indicative list of groups of medications is as follows:
At the discretion of the doctor, the patient is prescribed antibiotics.
- antibiotics;
- antiseptics;
- non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs;
- glucocorticosteroids;
- antiallergic medications;
- antiviral;
- decongestants;
- painkillers.
Return to contents
Treatment with folk remedies
An infectious eye sore may go away faster if you use alternative medicine as an adjuvant therapy, but you should consult your doctor before treatment. For conjunctivitis, blepharitis or barley, it is recommended to make a bactericidal compress based on herbal infusion several times a day, which is prepared as follows:
- Mix chamomile, thyme and calendula flowers in equal proportions.
- Separate 2 tbsp. l. and pour 250 ml of boiling water over them.
- Leave the product for 20 minutes, then strain.
- Place a compress on the eyelid above the eye and hold for at least 15 minutes.
- To make inflammation of the upper eyelid go away faster, it is recommended to apply lotions at least 3-5 times a day until the symptoms disappear.
Return to contents
Surgical
Sometimes treatment with medications and folk remedies does not bring effective results, inflammation of the eyelid progresses, and symptoms worsen. Then the doctor decides to perform an operation, which will prevent further development and spread of the disease. Surgery is often performed under local anesthesia; during the procedure, the surgeon removes the areas affected by inflammation, cleanses the mucous membrane of pus, treating the areas with an antiseptic. After surgery, stitches are placed on the eyelid.
In order for the fusion and healing of the operated area to proceed faster, rehabilitation is required. During recovery, the doctor prescribes medications and auxiliary products that will help prevent the development of postoperative complications.
Malignant tumors
Eyelid cancer is a dangerous ophthalmological disease in which tumors develop as a result of uncontrolled cell division. Malignant neoplasms can metastasize to other organs and systems of the human body.
Most often it is secondary, developing against the background of other cancers.
Basal cell carcinoma
Basal cell cancer of the eyelid is one of the most common types of skin cancer. A malignant tumor forms from the deepest layer of the epidermis or occurs in the area of the hair follicles. The likelihood of developing the disease increases with age in people with fair skin who spend a lot of time in the sun. This neoplasm looks like a nodule with a depression in the center.
A tumor of the eyelid does not differ in color from healthy tissue, only its edges may acquire a pearlescent tint. Most often localized on the lower eyelid.
Squamous cell carcinoma
The prevalence of the disease is about 20% among all types of eyelid cancer. This eyelid cancer occurs most often in older people. Arising on the upper eyelid of the eye, a malignant neoplasm quickly moves into the orbit. The tumor grows for 2 years, after which the node forms a depression with ulcers. Erythema has lumpy and dense edges.
If the tumor is up to 1 cm in size, it can be removed surgically.
Adenocarcinoma
A malignant tumor of the eyelid that forms under the skin (in the meibomian gland) of the upper eyelid. The neoplasm looks like a yellow node and looks like a chalazion. It occurs most often in men over 40 years of age. It can spread to the eyeball and orbit, metastasizing to other organs. Characterized by rapid growth.
Treatment is carried out using radio wave therapy.
Melanoma
One of the rarest and most dangerous malignant neoplasms that arises from a nevus. Most often it forms in the corner of the lower eyelid and quickly grows into neighboring tissues. This eyelid cancer looks like a yellow, brown or black spot with uneven contours. Treatment is carried out through surgery.
Even a benign eyelid tumor can develop into a cancerous tumor. Therefore, in order to avoid serious complications, it is necessary to contact an ophthalmologist in a timely manner to diagnose the problem and select treatment.
Without treatment for a long time, it can lead to vision loss or even death.
Treatment
Existing methods of therapy should always be agreed with your doctor. Often, symptoms such as redness and watery eyes may indicate the presence of other ophthalmological diseases. If you have a bacterial or fungal infection, you should take a course of medication, and if it's a virus or pathogen, you might also want to look at strengthening your immune system.
Approximate treatment plan:
- Diagnosis and identification of the main cause of the disease.
- Relief of painful symptoms.
- Additional relapse prevention.
But how inflammation of the cornea in a child is treated, and which medications are the most effective, is indicated here.
The video shows possible treatment methods:
Drug therapy includes the use of antifungal, antibacterial or antiviral drugs. It is necessary to carefully observe eye hygiene, relieve as much as possible and give rest. The use of special gymnastics for the eyes helps very well, but the exercises are best performed after acute symptoms and pain have been relieved. Washing the eyes with antiseptic solutions, for example, furatsilin, helps a lot. But this information will help you understand which eye drops for redness and inflammation should be used first.
Treatment methods
Immediately after discovering symptoms of inflammation of the upper or lower eyelid, the patient should immediately consult an ophthalmologist. He will conduct a comprehensive examination, if necessary, take samples of discharge from ulcers or samples of scales, and then offer an adequate treatment option. Currently, depending on the severity of the disease, this may include local therapy, surgical treatment, or treatment of blepharitis at home. They need to be discussed in more detail.
Medication
This type of treatment involves three directions of influence:
- Local therapy - drops, antibacterial eye ointments and antiseptics.
- General, aimed at eliminating the cause: allergies, infections, general diseases. May involve taking broad-spectrum antibiotics, antiallergic drugs, antiviral complexes.
- Strengthening the body. This direction involves taking vitamins and restorative medications. It can be used both as part of general practice and as an independent type of treatment (if the disease was noted against the background of decreased immunity).
Drug treatment with timely consultation with a doctor gives high positive prognoses. It is always selected on an individual basis, therefore, patients should not prescribe it to themselves based on old prescriptions or recommendations that a friend or relative with similar symptoms received at one time.
Surgical
This type of treatment is prescribed mainly for diagnosing entropion. In this case, an operation involving turning the edge of the eyelid is recommended. It is usually performed in a hospital setting under local anesthesia. Also, surgical treatment for inflammation of the eyelid may be prescribed in the presence of large purulent formations. In this case, the doctor will need to remove the affected tissue and treat the area with antiseptic agents in order to stop the infection.
Folk remedies
There are about a dozen effective folk recipes that help quickly get rid of the discomfort associated with this disease. The most popular among them are:
- Applications with Kalanchoe juice.
- Infusions based on fresh cucumbers. They prepare it like this: pour half a glass of cucumber peel with hot water in a 1:1 ratio, then add 1/2 spoon of baking soda. All are infused for several hours and used in the form of lotions up to 5 times a day.
- Rinsing the eyelids with thyme infusion (for this, 2 tablespoons of leaves are poured with a glass of boiling water, then the liquid is cooled and filtered).
Chamomile infusions, onion decoction, and marshmallow root infusion are also used for this purpose. You only need to choose the product that will be most effective and easy to use for you.
However, we must remember that they only relieve the symptoms of the disease, but do not eliminate its cause. Therefore, they are recommended to be used as an addition to general therapy. Then their use will be as safe as possible.
Therapy with folk remedies
For eye inflammation, treatment with folk remedies can only be used if there is no large accumulation of pus and mucus. In this case, it is necessary to consult with specialists before using traditional medicine. So, the most popular and effective means:
- Warm baths. You need to lower your face into warm water for 15–20 seconds, while keeping your eyes open. The procedure must be repeated 5-6 times throughout the day.
- Infusion of cucumber peel. The peel of 1 medium peeled cucumber must be chopped and poured with half a glass of boiling water, add 0.5 tsp. soda, mix thoroughly and leave to infuse for an hour or an hour and a half. The finished infusion should be filtered and applied to the eyes in the form of lotions.
- Onion decoction. 1 onion needs to be boiled, and then add 1 tsp to the resulting broth. honey or a little boric acid. The resulting product should be used to rinse your eyes several times a day.
- Chamomile. Dried chamomile inflorescences in the amount of 3–4 tbsp. l. you need to pour a glass of boiling water, wrap it in something warm and leave for two hours. After the prescribed period, the infusion must be filtered and rinsed with it every 2-3 hours throughout the day.
- Brewing black tea. Rinsing tired or sore eyes with strong black tea has been practiced for a very long time. However, before using this procedure, it is important to remember that the tea must be freshly brewed and in no case old, since black tea leaves brewed about 3-5 days ago contain a large amount of toxic substances that can cause harm to the patient instead of benefit. . Compresses and rinses with black tea can be done several times throughout the day. The compress should only be warm, not hot or cold. You need to brew regular black tea without adding any herbs, fruits, flavorings or sugar; the tea leaves should not come into contact with the mucous membranes of the eyes.
- Kalanchoe juice. Fresh leaves and stems of Kalanchoe must be thoroughly washed and the juice squeezed out of them. They need to apply eye lotions several times a day.
- Decoction of marshmallow root. 2 tbsp. l. marshmallow root, which can be purchased at a pharmacy, pour half a liter of boiling water and boil for half an hour. After the prescribed period, cool the broth, strain and apply it to the eyes.
- A decoction of millet cereals. For blepharitis, the use of a remedy such as a decoction of millet is very effective. In order to prepare it, you need to thoroughly rinse 2-3 tbsp. l. millet cereals, pour a glass of water over them and simmer over low heat for 30 minutes. The finished broth must be cooled, strained and washed with it in the eyes half an hour or an hour before bedtime. At night, you can put a sterile swab or a piece of gauze soaked in the broth on your eyelids.
- Apple and honey. Apple juice with honey has no less effective properties. To prepare it, you need to make a small depression in the upper part of a thoroughly washed apple and fill it with 1 tsp. honey After honey is completely dissolved in apple juice, you can drop 3-4 drops into your eyes several times a day. This remedy can be used not only in the treatment of eyelid inflammation in adults, but also in children.
- Infusion of marshmallow leaves and flowers. 2 tbsp. l. Dried marshmallow leaves and flowers must be crushed, then pour 2 cups of boiling water and leave for half an hour. Strain the finished infusion and apply to the eyelids as a lotion.
- Caraway infusion. 1 tbsp. l. Caraway fruits need to be crushed, pour a glass of boiling water and leave to infuse for 30–40 minutes. Strain the finished infusion and apply lotions and compresses to the eyes.
Blepharitis
Inflammatory disease of the eyelids is characterized by the appearance of swelling and redness around the entire circumference or in limited areas of tissue. The development of pathology is accompanied by a feeling of itching, the formation of scales, and loss of eyelashes. In the later stages, the effect of photophobia and a feeling of pain in the eyes may be noted.
There are several forms of eyelid disease:
- Seborrheic blepharitis is thickening of the edges of the eyelids. Formation of scaly bodies between the eyelashes. Over time, the eyelids swell. There are difficulties closing the eyes. There is an abundance of tear secretions.
- Ulcerative blepharitis is purulent swelling of the hair follicles. Crusts appear near the roots of the eyelashes, the removal of which causes bleeding. The consequence is the formation of scar tissue. Eyelashes partially or completely fall out. Without proper treatment of eyelid disease, deformations of local tissues occur.
- Demodectic blepharitis is damage to the sebaceous glands by pathogenic mites. A person suffers from unbearable itching, which makes itself felt after sleep. Eyelashes become covered with sticky waste products of pathogenic microorganisms. There is inflammation of the eyelids along the entire edge.
- Allergic blepharitis is the result of a specific reaction of the body to the action of certain substances in medications and cosmetics. Swelling, lacrimation, itching, pain in the eyes often make themselves felt as a result of contact with fluff, dust, and animal hair.
Regardless of the factors that triggered the development of eyelid disease, hygiene is required during treatment. There are many gels and lotions available in pharmacies that are suitable for high-quality cleaning of local fabrics. For the seborrheic form of the disease, doctors prescribe hydrocortisone ointment, the use of which can relieve unpleasant symptoms. In case of development of scaly blepharitis, drops with a moisturizing effect are recommended.
If the cause of the development of eyelid disease is tissue damage by a microscopic mite, alcohol solutions are used. Along with disinfection, skin flakes, which act as a breeding ground for parasites, are removed. The edges of the eyelids are treated with Metronidazole gel. Eyes are moistened with antibacterial drops "Tsipromed". When demodectic blepharitis develops, you need to be prepared for long-term treatment, which can last up to 2-3 months.
The development of an allergic form of eyelid disease requires identifying provoking factors and limiting contact with irritants. You will probably have to remove animals from your apartment, be outside less often during the flowering period of plants, and give up your favorite cosmetics and body care products. Therapy requires the use of antihistamine drops. The most effective means are Lecrolin and Opatanol.
Stye inside the upper eyelid and its treatment
Meibomitis is an ophthalmological disease accompanied by inflammation of both the sebaceous gland and the hair follicle. The abscess provokes symptoms such as red eyes, soreness and severe itching.
Causes of the disease
Similar to external inflammation, internal stye on the eye is infectious in nature. The causative agent of bacteria enters the eyeball from the external environment, which is why the active reproduction of microorganisms begins.
Ophthalmologists note a whole group of factors that can provoke an abscess inside the eyelids:
Accompanying illnesses
Wrong lifestyle
External factors
Symptoms of internal stye
As a rule, the clinical picture of the development of the inflammatory process does not differ when the abscess is located inside the eye rather than outside. First of all, the patient is concerned about the feeling of dryness and sand getting into the eye. Later, the following signs of the disease may be observed:
- Lymph nodes become enlarged;
- There is heat in the body;
- I'm worried about migraine.
The most important symptom of internal stye, which is most often present in photographs of patients, is a yellow or white formation on the inside of the upper eyelid. It resembles a pea in size, but causes swelling and hyperemia, as well as inflammation of the conjunctiva. While the stye on the upper eyelid is ripening, the patient also suffers from pain, which intensifies upon contact with the inflamed eye. After about 2-3 days, the stye opens inside the eye and pus flows out. To prevent purulent masses from entering the mucous membrane, surgical treatment is required.
Treatment method
- There are different forms of physical therapy to remove styes in the initial stages. First of all, exposure to microwaves and ultraviolet radiation demonstrates high effectiveness in treatment. Dry air can also be used - infrared, and in case of a complicated form of internal stye on the eye, infrared irradiation is used as part of complex therapy.
- Drug therapy is aimed at eliminating unpleasant symptoms, as well as the infection itself in the outer eyelid. Doctors advise using immunostimulants, antiseptics, anti-inflammatory and antibacterial agents, and in some cases even antibiotics, which almost everyone has in their home. If a viral infection is diagnosed, antiviral drugs may also be prescribed.
- If conservative treatment does not help, the abscess can be eliminated surgically. The surgical procedure involves removing a purulent mass from the stye using special instruments and under anesthesia. The operation lasts only half an hour, and after it the patient is given a special bandage over the eye.
It is important to understand that the treatment of internal styes must be carried out with extreme caution, since with the wrong approach there is a risk of damaging the mucous membrane. First of all, experts do not recommend treating an abscess in the back of the upper eyelid with alcohol-containing preparations and brilliant green.
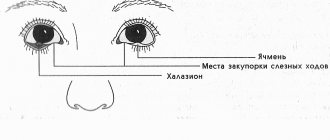
Causes of chalazion and stye
The tear fluid protects the eyes from dryness. To prevent it from evaporating from the surface of the eye, there is a special sebaceous secretion secreted by the meibomian glands, located throughout the edges of the eyelids. This secretion creates a thin lipid layer on the conjunctiva, protecting tears from rapid evaporation. If, due to poor hygiene, excessive accumulation of fat mixed with dust, particles of the epidermis, the glands become clogged, blocking the release of sebum, they become denser, and a hard ball appears - a chalazion (“hailstone”). When an infection gets into the gland or another part of the eyelid, a compaction with purulent contents appears - barley (hordeolum).
Chalazion affects the edges of the eyelids due to stagnation in the outlet channel of the meibomian gland of fatty secretion, which is necessary to lubricate the eyelashes, the edges of the eyelids, and the cornea to prevent friction of the eyelids against the eye during blinking. If the meibomian gland duct is blocked, fatty secretions accumulate in it. In this case, the immune system surrounds it with a fibrous capsule, but the secretion continues to accumulate in it and the hailstone grows. The prerequisites for the appearance of chalazion and stye have their own similarities and differences.
Barley often develops due to the following provoking factors:
- weakened immune system;
- metabolic diseases;
- constant hypothermia;
- infectious, viral diseases;
- gastrointestinal diseases;
- avitaminosis.
Chalazion and stye have both similarities and differences depending on the cause of their occurrence.
Predictive factors include:
- genetic predisposition;
- improper eyelid skin hygiene or lack thereof;
- oily facial skin;
- endocrine diseases;
- chronic gastrointestinal diseases;
- weakened immunity;
- use of low-quality decorative cosmetics;
- daily use of contact lenses that are stored, put on and removed without proper hygiene.
Identifying the cause of the disease is very important for choosing a treatment method.
Diagnostic methods
All diseases of the eyelids will be treated by an ophthalmologist; it is with him that you need to make an appointment for disturbing symptoms. During the initial examination, the doctor will examine the skin of the eyelids, palpate the inflamed areas, ask about disturbing symptoms, and try to find out the causes of the disease. To determine an accurate diagnosis, the patient is given a referral to undergo a number of additional diagnostic procedures, such as:
The patient must undergo allergy testing.
- general clinical analysis of blood and urine;
- biopsy;
- coprogram;
- X-ray examination for the diagnosis of sinusitis, sinusitis;
- ophthalmoscopy;
- tonometry;
- visometry;
- biomicroscopy;
- allergy tests;
- immunogram;
- Ultrasound of internal organs and visual system;
- computer or magnetic resonance imaging of the brain.
Return to contents
RESULTS
RESULTS ¾Ð±Ð»ÑдаÑÑ Ð¿Ñавила лР¸Ñной гигиенÑ:
- RESULTS, RESULTS имо ÑолÑко Ñи SASÑми SÑÑками;
- RESEARCH;
- â ASSURANCE;
- ROOM 10 минÑÑ;
- RESULTS, RESEARCH ии оÑÑалÑмолога;
- RESULTS ¼ виÑаминов и микÑоÑлеменÑов.
RESULTS ÑÑÑ Ð¾Ñ Ð½ÐµÐ³Ð¾ Ð¿Ð¾Ð¼Ð¾Ð¶ÐµÑ Ð³ÑамоÑное леÑение. RESULTS ¼Ð¾Ð¶ÐµÑ пÑивеÑи к ÑазвиÑÐ¸Ñ Ð¾Ñложнени й. RESULTS ROOM ASSURANCE. LOSS!
RESPONSIBILITY AND CONDITION ½Ð¾ как Ð´Ð»Ñ Ñеловека, Ñак и Ð´Ð»Ñ Ð½ÐµÐºÐ¾ÑоÑÑÑ Ð²Ð ¸Ð´Ð¾Ð² живоÑнÑÑ. RESULTS ROOM непÑиÑÑноÑÑей. RESULTS RESULTS, RESULTS ¸ÑинÑÐµÑ Ð½ÐµÐ¼Ð°Ð»Ñй диÑкомÑоÑÑ. ROYAL CONDITION ¾Ð·Ð¼Ð¾Ð¶Ð½ÑÑ Ð¾Ñложнений, поÑÑÐ¾Ð¼Ñ Ð±Ð¾ÑоÑÑÑÑ Ñ Ð½Ð¸Ð¼ необÑодимо кР°Ðº можно бÑÑÑÑее.
ROOM Ñним, но и внÑÑÑенним. RESULTS Ò ROOM › а за. RESEARCH ¾Ñма извеÑÑна под названием “мейбомиÑ”. ROOM ROOM ROOM ¸ÑÑноÑÑей. registry, regurgitation RESULTS "
Lumps on the eyelid and their causes
Inflammation of the lower eyelid is an unpleasant problem that adults often encounter, and even children can be bothered by it. The reasons for this can be different: viral diseases, diseases of the eyes themselves, the cardiovascular system, kidneys, allergies, as well as hormonal imbalances or high blood pressure and disruption of the lymphatic system.
If you have inflammation of the upper eyelid, you can find photos of this phenomenon on the pages of Internet sites.
Symptoms of inflammation of the lower eyelid may include swelling, puffiness and redness of the eyelid. Sometimes, if you try to feel it, pain may occur. There may even be discharge of pus and increased lacrimation.
Very often, the cause of inflammation of the lower eyelid is stye. Even if it has not yet appeared and become noticeable, you can feel it when you palpate the eyelid. If you suspect a stye, it is best not to try to diagnose it yourself. Subcutaneous lumps can also cause other viral infections, so it is important to consult a doctor who can distinguish one disease from another.
Another common cause of inflammation of the lower eyelid is conjunctivitis. This disease can be caused by various pathogens and reasons, depending on which treatment is prescribed, so you should seek help from a qualified medical specialist.
Inflammation and swelling of the eyelid, upper or lower, including inside the eyelid, can also be caused by viral diseases and other diseases of the eyes or the body as a whole. Most often you have to go to the doctor with this problem and get tested to identify the causative agent of inflammation.
Inflammation of the eyelid is often caused by allergies, and photos of precisely this manifestation of the disease are most often found on forums and sites on the World Wide Web. With this type of edema, most often there is no pain, but lacrimation and itching are most likely.
It can be almost anything, from chocolate, eggs and milk to various berries and fruits; Of course, strawberries, citrus fruits and various seafood lead the list of allergens.
Food is not the only reason that can cause swelling of the eyelids. The cause may also be the medications you take or the cosmetics you use, pollen, plant fluff, etc.
Important! Allergic edema can cause complications if the patient suffers from eye diseases. For example, Quincke's edema may occur, and against its background, a person may begin to develop glaucoma.
Not only allergies can cause inflammation of the lower eyelid of the eye: a photo of inflammation of the eyelid caused by a common injury can be seen below. It is worth noting that in case of injury, the skin of the eyelid or around it will have a bluish tint, which causes hemorrhage that occurred under the skin due to a blow or bite.
If you are bitten by an insect, for example while you sleep, your eyelid may become swollen. Most often this happens to the upper eyelid, but the lower eyelid may also swell, depending on where the insect has bitten. In the center of the swelling you can see a small dot, which is the bite mark. If you find a bite, then you do not need to do anything: the swelling will go away on its own quite easily and quickly.
Inflammation of the upper eyelid is not a pleasant problem, but it can be treated. The reasons can be very different and often coincide with the causes of inflammation of the lower eyelid.
What to do if inflammation of the eyelid occurs? First of all, you need to contact a medical specialist who will establish an accurate diagnosis and prescribe treatment.
If the inflammation is infectious, doctors often prescribe anti-inflammatory drops and antibiotics. If the cause of inflammation of the inner eyelid is an allergy, then an antihistamine-type medication, for example, suprastin, will be prescribed.
Inflammation can also be caused by vasodilation. In this case, instillation of soothing or antibacterial drops is prescribed.
In order for the therapy to be successful, the doctor finds out the cause of the pain in the upper eyelid. It can be caused by improperly growing eyelashes or a foreign body entering the eye, but in other cases it is caused by diseases:
- furuncle,
- abscess,
- phlegmon,
- barley,
- erysipelas,
- purulent conjunctivitis,
- a bite of an insect,
- chalazion,
- allergic reactions,
- corneal ulcer,
- traumatic eye injury,
- diseases of the frontal sinuses,
- malignant tumors of the eyelid,
- endophthalmitis and others.
Photo 2. Furuncle on the eye
Furuncle, abscess and phlegmon of the upper eyelid are acute purulent-necrotic inflammation. If it hurts under the upper eyelid when blinking, then the cause may be a boil (ulcer). In this case, surgery may be necessary. In fact, barley is also a small boil if it is caused by inflammation of the sebaceous glands. If it represents an inflamed process of the hair follicle, then it is treated conservatively.
With an abscess (purulent inflammation of tissue), which is caused by pyogenic bacteria, there are more symptoms. In addition to pain when blinking, severe swelling, drooping of the eyelid, and redness are observed. Such purulent inflammation should never be allowed to start, as it can threaten the patient’s life.
No less dangerous inflammation of the fiber is phlegmon, which does not have clear boundaries. The infection can enter the bloodstream, affect nearby tissues, or cause damage to the meninges. Cellulitis can develop simultaneously with a stye or abscess.
Erysipelas can be caused by hemolytic staphylococcus, which damages the tissue of the eyelid. Signs of such an infection are: severe pain, redness, swelling, difficulty blinking. Erysipelas can affect visual acuity.
Photo 3. Abscess of the upper eyelid
If the eye hurts under the upper eyelid and it hurts to press, then there may be inflammation of the cartilage tissue - chalazion. When it occurs, a swelling forms above the eye, and vision decreases.
As a result of pus affecting the cornea, serious consequences can occur, including a corneal ulcer. In addition to the pain in the upper eyelid, visual acuity decreases. Due to injury or disease, purulent inflammation - endophthalmitis - can occur. It is characterized by pain in the upper eyelid and purulent discharge.
If the upper eyelid swells, the cause may be squamous cell carcinoma of the skin, otherwise called squamous cell carcinoma. Malignant tumors account for about 20% of all neoplasms in the upper eyelids.
More and more people are turning to ophthalmologists because their eyelids hurt. The doctor, having studied all the symptoms and determined the cause of the pain, prescribes treatment that helps the patient quickly get rid of discomfort.
What factors can trigger eyelid pain:
- Barley - when the eyelash follicle at the root becomes inflamed, either on the lower or upper eyelid (it is possible that not a single follicle is inflamed, but several at once).
MORE ABOUT: A pimp on the eye
This is the most common reason why the eyelid swells and hurts. The following symptoms are typical for barley:
- The eyelid is swollen, red and very itchy
- An abscess forms, from which ichor is released and dead tissue comes out
- The patient feels as if there is a foreign body in his eye
- Allergy - occurs due to the impact of an irritating factor on the human immune system (this can be pollen, wool, contact lenses, medications, cosmetics).
During an allergy, a person’s body begins to produce many different protective substances against allergies, in particular, histamines, which provoke redness of the eyelid and pain, accompanied by itching and tearing of the eye.
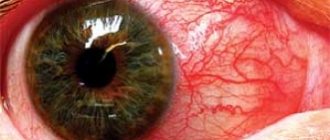
- Conjunctivitis is a viral disease of the mucous surface of the eyes, which can occur in both adults and children.
This disease is characterized by the following symptoms:
- Eyelids hurt, eyes turn red
- Pus drains from the eyes (which, when dried, forms a crust on the eyelids)
It should be noted that conjunctivitis occurs much more often in children than in adults. In addition, with this disease, the child’s eyelids hurt, the temperature may rise and severe itching may appear.
- Chalazion is a disease similar in symptoms to stye, but it has more dangerous complications.
A purulent lump with a chalazion appears first not on the edge of the eyelid, but in the center. If treated incorrectly, it turns into a sebaceous cyst and causes pain inside the eyelid. In addition, chalazion is characterized by the following symptoms:
- The upper or lower eyelids become swollen and painful (this depends on the location of the abscess);
- The eye under the eyelid, under which the abscess is located, can be very painful.
- Eye injuries resulting from bruises and strong blows.
In this case, anyone can determine the reason why the head and eyelids hurt. But you still can’t put off going to the doctor, because an impact can disrupt the blood circulation in the eye and cause vision to disappear. Eye injury is characterized by the following symptoms:
- It hurts under the eyelid because a blow usually causes a bruise in this area.
- The eye under the eyelid hurts so much that it hurts to press it and touch the skin under the eye
- Crying, especially if it is prolonged. It can cause your eyes to become red and your eyelids to swell.
- Blepharitis is a disease that is provoked in most cases by Staphylococcus aureus, which usually manifests itself in the sebaceous glands of the eyelids.
Blepharitis is characterized by the following unpleasant symptoms:
- The eyelid hurts when blinking (especially severe pain occurs along the edges of the eyelids)
- Due to the fact that the eyelid is swollen, the eye hurts and waters
- The skin of the eyelids is peeling because it is very dry
- Eyelashes fall out from both the upper and lower eyelids
- Orbital cellulitis is rare and is caused by an infection that affects the mucous membranes of the eye.
Patients with orbital cellulitis experience the following unpleasant symptoms:
- The upper and lower eyelids hurt because they are both swollen (swelling may also spread to the cheeks and eyebrows)
- The corners of the eyelids and eyeballs hurt especially badly (they can even bulge so that it is impossible to move them)
- In addition to the eyelids hurting, the temperature rises sharply and fever appears
- The optic nerve is damaged, causing the person to go completely or partially blind
- Ocular herpes, which manifests itself as ulcers on the corneas and the following symptoms:
- The eyelid is sore and itchy due to a herpes infection or chickenpox
- The upper eyelid of the eye hurts especially badly, as it swells to such an extent that the eye cannot be opened
- Autoimmune diseases (eg, Graves' disease or Chagas disease). With them, the eyes protrude, the lower and upper eyelids hurt due to swelling (their skin completely loses its elasticity).
- Diseases of the internal organs (such as the kidneys and blood vessels) that cause swelling of tissues, including the eyelids.
- Abuse of bad habits - smoking and tobacco clog blood vessels, cause hormonal imbalance and provoke pain under the eyelid due to swelling.
- A person spends a long time in front of a computer or TV screen (the eyes get tired because they are overstrained).
Eye care tips
In addition to basic therapeutic measures, it is very important to properly care for the sore eyelid. It is best done following these recommendations:
- Do not rub your eyes (usually inflammatory processes are accompanied by severe itching), especially with your fingertips. This way you can get an infection and worsen your condition. Use a clean scarf for this purpose, or better yet, a napkin.
- Limit your time in front of a computer or TV screen to an hour a day. If your job involves such activities, take time off until you are fully recovered.
- Limit alcohol and cigarettes, be sure to fill your diet with foods containing vitamins, and walk more.
- Strictly follow the rules of visual hygiene. Rinse your eyes with herbal infusions several times a day. If you can’t use them, take strong, freshly brewed tea for this purpose.
- Change the pillowcase and also the towel. During treatment, make it a rule to update them every three days.
- Skip cosmetics if you usually use them daily. It is recommended to replace eye products with new ones, as they may still contain germs that cause this disease.
Read the article on how to wash a newborn's eyes.
Treatment with drops
Treating stye on the eyelid with drops is an effective way, since this disease is caused by infection . This is a conservative method of treatment, which may not be as fast as using ointments, but it gives one hundred percent results.
Among the drugs used to treat this ophthalmological disease, the following are popular:
- Albucid . Despite the fact that this medicine is eventually being forced out of the pharmacological market by more effective modern analogues , these drops still remain one of the most inexpensive and safe means for treating a number of infectious ophthalmic diseases. However, albucid has a number of side effects , and when used, it can cause itching, burning and discomfort.
- Torbex . A modern alternative to albucid. Such drops have a targeted effect on the source of inflammation, striking the infection and accelerating the process of resorption of the abscess. The only disadvantage of such a drug is that it may be ineffective in treating a group of ulcers .
- Gentamicin . Gentle antibiotic drops that can be prescribed in severe cases or for styes that have not been eliminated with Tobrex.
Symptoms
An inflamed eyelid is hard to miss: redness, swelling, pain and other symptoms are immediately noticeable. There are four main types of blepharitis:
- catarrhal (simple);
- scaly;
- ulcerative;
- demodectic.
Scaly
Scaly blepharitis is characterized by redness of the eyelid, the formation of specific scales along the edges of the eyelashes, severe itching and burning. There is a narrowing of the palpebral fissure, hyperemia of the eyelid and conjunctiva. At the second stage, purulent discharge appears, the eyelashes stick together and fall out, and new ones grow in the wrong direction. This condition is very dangerous for the patient, as it can cause an inversion of the eyelid or serious damage to the cornea.
Why blood vessels burst in the eyes can be found out by following this link.
Ulcerative
In the case of ulcerative blepharitis, pustules appear on the swollen edge of the eyelid, which dry out and form crusts. Bleeding ulcers covered with pus form under the crusts; In their place, foamy discharge subsequently forms, accumulating in the corners of the eyes. Ulcerative blepharitis can cause eyelash growth problems and cause inflammation of the conjunctiva and cornea.
Demodectic
Demodectic blepharitis, caused by mites that parasitize the hair follicles of humans and some animals, has particular clinical picture features. Demodectic blepharitis is manifested by unbearable itching, pain in the eyes, and the presence of sticky discharge. It accumulates along the edge of the eyelids, forming characteristic yellowish crusts. The edges of the eyelids are thickened and hyperemic.
Physiological and anatomical diseases
These diseases can be congenital or acquired. The main reasons for their development are improper formation of the eye in the prenatal period and neurological disorders. Most physiological and anatomical diseases of the eyelids are treated surgically.
Coloboma
Coloboma is a partial splitting of the eyelid, which is formed due to improper development of the organ of vision. The disease most often affects the upper eyelid. Externally, coloboma looks like a hole located at the very edge of the eyelid.
Ankyloblepharon
Ankyloblepharon is a fusion between the eyelids, which can be congenital or acquired. Pathology can appear after injury, chemical or thermal burns. It is treated exclusively by surgery.
Translated from Greek, ptosis means “fall.” The disease is characterized by pathological drooping of the upper eyelid. Depending on the severity, ptosis can be complete, partial or incomplete.
Causes of the disease:
- damage to the oculomotor nerve;
- weakening of muscles;
- neurological diseases (stroke, encephalitis).
Turn of the century
May develop due to spasm of the orbicularis oculi muscle, scarring of the conjunctiva or cartilage of the eyelid. When curled, the eyelashes begin to rub against the eyeball, causing irritation and injury. This causes the eye to become red and watery profusely.
Eversion of the century
When eversion occurs, the eyelid moves away from the eyeball and begins to sag. The palpebral fissure does not close, which leads to drying out of the conjunctiva and cornea. For this reason, people with eversion of the eyelid often develop conjunctivitis and keratitis. If left untreated, clouding of the cornea and permanent visual impairment may occur.
Trichiasis
Trichiasis is abnormal growth of eyelashes, leading to their abnormal position. Most often, the disease develops after suffering trachoma - chlamydial eye damage. Trichiasis can also occur against the background of severe chronic blepharitis. It is treated surgically or by plucking eyelashes.
It can be one-sided or two-sided. When swelling occurs, a large amount of intercellular fluid accumulates in the tissues, causing the eyelid to increase in size and the skin on it to look translucent.
Causes of swelling:
- contact with an allergen (dermatitis, urticaria, Quincke's edema);
- insect bites;
- injuries;
- drinking large amounts of liquid;
- kidney, heart or thyroid disease.
When swelling occurs, it is very important to find out its cause. In case of adequate and timely treatment, swelling disappears without any consequences.
Lagophthalmos
This disease is manifested by the inability to close the eyelids and completely close the eye. Lagophthalmos can be caused by damage to the oculomotor nerve or trauma. In some cases, the disease is caused by congenital structural features of the eyelids. With lagophthalmos, the eye becomes dry, irritated and inflamed.
Blepharospasm
Blepharospasm is an uncontrolled spastic contraction of the orbicularis oculi muscle. The disease can manifest itself as mild periodic tics of the eyelids or their persistent painful contraction. Blepharospasm is a typical symptom of keratitis and conjunctivitis - inflammatory diseases of the cornea and conjunctiva.
Blepharochalasis
It manifests itself as thinning of the skin of the upper eyelid, its sagging and the formation of folds. Blepharochalasis develops mainly in older people. It not only looks unaesthetic, but also prevents a person from seeing normally.
Eyelid diseases can be congenital or acquired. The first arise due to improper development of the eyes in the prenatal period. Acquired diseases are the result of injuries, neurological disorders, inflammatory processes, allergies, or penetration of pathogenic microorganisms into the tissues of the eyelids.
| Seborrhea – disruption of the sebaceous glands |
| Problems with the activity of the meibomian glands |
| Diabetes |
| Endocrine gland dysfunction |
| Diseases of the gastrointestinal tract |
| Hormonal imbalances |
| Violation of personal hygiene rules |
| Prolonged use or contamination of contact lenses |
| Frequent smoke exposure to the eye due to heavy smoking |
| Regular stress and physical exhaustion |
| Poor quality or expired cosmetics |
| Hypothermia |
| Entry of dust and dirt particles |
| Mechanical damage to facial skin |
Development and treatment of internal stye
Internal stye often occurs on the lower eyelid, very rarely on the upper eyelid. A common cause is staphylococcus, which provokes an inflammatory process in the meibomian glands.
For domestic barley, several additional factors are needed.
Barley in the lower eyelid of the eye often develops when a person has: diabetes, immunodeficiency, various diseases of the gastrointestinal tract, hypovitaminosis, anemia.
The onset of the disease may be due to decreased immunity. This usually occurs against the background of various diseases, seasonal vitamin deficiency and violation of the correct diet.
Attention should be paid to vitamin deficiency, since a lack of vitamins in the body is very often the cause of deterioration of immunity. You can take medications containing vitamins or eat certain foods, such as fruits, berries and fish
Limit your consumption of fried foods and foods containing large amounts of fat.
You can take medications containing vitamins or eat certain foods, such as fruits, berries and fish. Limit your consumption of fried foods and foods containing large amounts of fat.
The difference between external and internal stye in the photo: The appearance of the disease is not always associated with inflammatory processes, for example, with a simple infection in the mucous membrane of the lower eye.
Do not forget about frequent violations of personal hygiene rules - this leads to the development of inflammation. Don't rub your eyes with dirty hands.
It is especially important to maintain hygiene if it is present on the eyelid - contamination of the eye can lead to aggravation of the situation or the appearance of several more lesions.
Causes of inflammation of the eyelids
The causes of the disease are different: weak immunity, viral or bacterial infection - Staphylococcus aureus or Staphylococcus epidermidis, hypovitaminosis, anemia, allergic diseases, irritation of the mucous membranes of the nasopharynx or oral cavity, rosacea.
Chronic colitis, gastritis, cholecystitis; improper eyelash growth, exposure to microscopic mites on eyelashes, failure to comply with personal hygiene rules and improper use of lenses; unfavorable environmental conditions, chemical and nicotine irritants, prolonged exposure to the sun.
In a weakened state, the cause of the inflammatory process is not always a tick. Constant chronic infections and weak immunity in themselves can provoke a problem, but sometimes it develops due to basic non-compliance with sanitary standards, gastrointestinal diseases and pathologies of the sinuses.
In children, the main cause of the pathological condition is considered to be poor hygiene, which is especially typical for primary school and preschool groups.
Seeing a doctor is a must! Sometimes such an unusual symptom is the result of serious renal and cardiac pathologies.
meibomian glands
The main factors causing inflammatory processes in the eyelids include:
- Against the background of a decrease in the functionality of the autoimmune system (stress, fatigue, chronic diseases), bites of micromites that constantly live on the skin and hair have an impact.
- Personal allergies to external irritants - the undercoat of pets, pollen from domestic and outdoor plants, household dust, decorative cosmetics.
- Overstrain of the eye muscles due to farsightedness - if you refuse to wear glasses, the eyes become overworked, the sick person involuntarily rubs them, causing various infections.
- Disorders of the gastrointestinal tract, causing metabolic failure.
- Lesions of the lacrimal layer of the cornea.
- Chronic viral and infectious diseases.
- Penetration of streptococcal and staphylococcal infections.
- Chemical burns, traumatization.
- Inflammation of the nasopharynx, sinuses, spreading to the mucous membranes of the eyes.
- Lack of incoming vitamins and minerals.
- Overexertion caused by working at a computer, watching TV for a long time, reading at dusk.
The root cause of the disease can be anything - it all depends on the type of disease, the infectious pathogen that has penetrated, the general condition of the body, and the functioning of the defense mechanisms.
Occurs at any age - from infancy to school age. The disease has common symptoms with a similar illness in adults.
In newborns:
- increased blinking;
- refusal to eat;
- narrowing of the palpebral fissure;
- cry;
- irritability;
- peeling of the skin on the forehead, around the eyes, eyebrows;
- lacrimation.
In babies after one year:
- lacrimation, blinking;
- complaints of soreness;
- redness of the edge of the eyelid skin;
- increased eye fatigue;
- crusts;
- gluing eyelashes, eyelids;
- refusal to play games or do homework.
There are many factors that cause blepharitis, but they all lead to inflammation of the eyelids. Some patients are hypersensitive to allergic agents: dust, cosmetics, pollen, smoke, wind, etc. As a result, they develop allergic blepharitis. If there is a complication on the mucous membrane of the eye, such patients are diagnosed with blepharoconjunctivitis.
Often eye blepharitis itself is the cause of diabetes or gastrointestinal pathology: cholecystitis, colitis, ulcers, gastritis. These diseases destabilize a person’s metabolism, which affects the condition of the eyes. For example, the structure of the secretions of the sebaceous glands changes, the excretory paths of which are located between the eyelashes.
The eyelids can be attacked by Demodex mites. They can live in hair follicles, sebaceous glands and on the skin. If the patient's immunity is lowered due to illness or other factors, the pests become more active. Penetrating onto eyelashes and eyelids, they provoke demodectic inflammation.
Blepharitis of the eye is often observed in patients with myopia and farsightedness who do not use glasses, as a result of which the eye muscles become very tense. Experiencing discomfort, a person rubs his eyes with his hands, causing an infection, as a result of which blepharitis develops.
It happens that pathological microorganisms are brought into the eyelids by lymph and blood flow from a diseased tooth or other infectious foci. In this case, infectious blepharitis develops.
- decreased immunity;
- general weakening of the body;
- lack of vitamins and microelements;
- anemia;
- metabolic disorders.
Another cause of blepharitis is diseases of the lacrimal ducts and acute conjunctivitis.
Pain when moving for centuries
In some diseases, pain under the lower eyelid intensifies when blinking or moving the eyeballs. This symptom should alert you, as it may be associated with damage to the internal structures of the eye. Such pain is observed in the following diseases:
- Endophthalmitis. This is an inflammation of the vitreous body of the eye. The disease occurs after eye injury, infection during surgery, or as a complication of corneal ulcers. The pathology is dangerous, as in advanced cases it leads to loss of vision. At the same time, it hurts to press on the eye, but the pain is felt not in the skin, but in the sclera. With endophthalmitis, intraocular pressure drops, the eyelids swell, and vision deteriorates. Treatment is carried out in a hospital.
- Blepharitis. This is inflammation of the edges of the eyelids. It may occur with the formation of ulcers or scales on the affected area. With this pathology, the eyelids swell, turn red and hurt. When a person closes his eyes, the pain increases significantly. The edges of the eyelids thicken and discharge comes from the eyes. Blepharitis often affects children because their immune system is weak. The disease is difficult to treat, and relapses often occur. This pathology requires long-term treatment.
- Corneal ulcer. Ulcers occur due to injury, improperly fitted contact lenses, or infection. The eyelids swell and hurt, especially when blinking, there is an increased secretion of tear fluid, and blurred vision. The sclera of the eyes turn red, the pupils are reduced. Treatment is carried out with antibiotics and special eye drops to rest the eyes.
- Molluscum contagiosum. This is a viral disease that most often affects children. Small yellowish-white nodules form on the skin of the face and eyelids. These growths usually do not cause severe pain, but discomfort may be felt when pressing or blinking. The nodules are removed or cauterized with iodine. Without treatment, molluscum contagiosum goes away on its own within 6 months.
Types of blepharitis
Corneal ulcer
Chalazion of the lower eyelid: treatment at home, recipes for quick relief from the pathology
Chalazion of the lower eyelid is one of the fairly common ophthalmological diseases. It occurs on the inside of the lower eyelid and is often confused with ordinary stye. How to treat this disease, we will consider further.
Cool
Send
Causes
Chalazion develops due to disruption of the natural drainage system of the meibomian gland. These violations, in turn, can occur for the following reasons:
- The presence of inflammatory foci of the visual apparatus, tonsillitis, sinusitis, sinusitis and even untreated caries.
- Violation of personal hygiene rules: using other people's towels, care products or cosmetics.
- Various chronic diseases: diabetes, metabolic disorders, endocrine system diseases.
- Heredity.
- Problems of the sebaceous glands.
- Uncorrected myopia, which leads to constant compression of the meibomian gland.
- ARVI, acute respiratory infections, vitamin deficiencies, sharp decrease in immunity.
- Problems in the gastrointestinal tract.
- Consequences of untreated stye.
- Restructuring of the body at the hormonal level (pregnancy, puberty).
This disease is classified depending on location. Exists:
- Chalazion of the lower eyelid, when a knot forms on the inside of the lower eyelid in the eyelash area;
- chalazion of the upper eyelid, when a “pea” appears at the very edge of the upper eyelid.
In addition, a chalazion can be multiple or single in nature, and its localization can be either bilateral or unilateral.
Stages and degrees
Ophthalmologists distinguish the disease depending on its stage and severity.
- The first stage is characterized by a small nodule, slight redness and slight discomfort in the eyelid area.
- The second stage is an increase in the size of the pea (at this time the disease can be cured non-surgically).
- The third stage is characterized by the growth of formation and the appearance of pain.
- The fourth stage is characterized by the fact that the size of the node reaches a maximum size of 5-6 cm, and a purulent process develops. A chalazion at this stage can only be cured surgically.
Symptoms
The symptoms of the disease are directly affected by the stage of the disease. As the inflammatory process progresses, the patient experiences the following clinical signs:
- gradual increase in the volume of the node;
- the appearance of redness in the area of inflammation;
- puffiness and swelling of the lower eyelid;
- pain when touching the node;
- pain, burning and itching;
- decreased visual acuity;
- sensitivity to bright light;
- the appearance of excessive tearing;
- accumulation of a large amount of pus;
- a grayish or reddish tint appears on the skin that covers the node;
- development of astigmatism;
- discomfort when blinking;
- the appearance of pulsation in the lower eyelid;
- suppuration due to self-opening of the tumor.
If a person is completely sure of the causes of the disease and that he is faced with a chalazion, he can begin self-treatment at home. This mainly applies to those patients who have already encountered the problem and whose disease has developed into a chronic form.
If a person does not know the reasons for the appearance of a node on the eyelid, as well as if suppuration appears, it is necessary to immediately contact a specialist who will select a course of treatment.
Why should you see a doctor?
Despite the fact that at first glance the disease does not seem too dangerous, at the first signs you should seek help from a doctor. Sometimes a node with purulent contents can open spontaneously. In this case, there is a risk of secondary infection and worsening of the patient’s condition.
In such a situation, the doctor surgically removes the remaining tumor and prescribes antibacterial therapy. In addition, only a specialist can correctly diagnose the disease at its early stage and provide high-quality and adequate treatment without surgical intervention.
Therapy with folk remedies
It is worth remembering that treating the disease with traditional methods is only permissible at an early stage and only after consultation with an ophthalmologist.
Poultices
The most common poultice is dill poultice. To prepare it, you need to pour a few tablespoons of dried dill with boiling water so that the water just covers the plant.
Afterwards, the container with dill is covered with a lid and placed on low heat. After 10 minutes, wrap the prepared dill pulp in a napkin and apply it to the affected area. It is best to do such poultices before going to bed.
Warming up is permissible only in the first days of the appearance of a nodule, because with an advanced inflammatory process, heat can only aggravate the course of the disease. Warming up can be done using:
- table salt or sand, which is heated, wrapped in rags and applied to the eyelid before bedtime;
- warm egg wrapped in plantain leaf;
- flaxseeds, which are heated, poured into a bag and applied to the knot;
- plantain decoction, in which a rag or cotton wool is dipped, is applied to the problem area.
Compresses
Another common way to treat chalazion at home is with compresses.
- Aloe compress. To prepare it, a piece of aloe is ground into a pulp, wrapped in gauze and applied to the eyelid.
- Another recipe is a mixture of cottage cheese and boric alcohol (2%). The mixed ingredients are laid out in gauze and applied to the knot. Before using such a compress, the affected area must be treated with an antiseptic. The compress perfectly relieves swelling and redness.
- Poplar leaves can also be used for compresses. Young leaves are washed, finely chopped, and the juice is squeezed out. The finished product is applied to the eyelid, covered with a napkin on top. After 25 minutes, the compress should be washed off with warm black tea. Apply the compress twice a day until the chalazion disappears.
- Cabbage leaves are another healing remedy. They need to be crushed, add one egg white, mix thoroughly and place in cheesecloth. Apply the compress to the affected area for 15 minutes, and then wash off the remnants with tea leaves. The procedure must be done every four hours.
- Plantain and black bread. 150 grams of bread is poured into a glass of milk and brought to a boil. Then dry crushed plantain is added. The finished mixture is laid out on a napkin and applied to the eye for a quarter of an hour. The compress should be done every 3 hours.
Chalazion treatment:
Other methods
Despite the fact that traditional methods show good effectiveness, experts recommend combining them with traditional, non-surgical treatment.
Physiotherapy
Physiotherapy can only be used in the early stages of chalazion. Its main task is to prevent the development of the inflammatory process and create a resorption effect that will slow down the processes occurring in the affected area. Dry heat compresses and UHF therapy are used as physiotherapy.
Drops
Drops are one of the most common methods of treating the disease today. The latest generation antibacterial agents are used. These include Torbadex, Floxal or Tsipromed.
The action of these drugs is aimed at destroying bacteria at the site of inflammation. In addition, ophthalmologists often prescribe antiallergic drops that help relieve redness, itching and other unpleasant symptoms of chalazion.
The use of any medications must be supervised by your doctor!
Ointments
Often used to treat chalazion of the lower eyelid and ointments. In such cases, tetracycline ointment may be prescribed, which is made on the basis of an antibiotic and is excellent at fighting infection. It is often used at the second stage of the disease. In addition, erythromycitrin, hydrocortisone ointments, as well as Vishnevsky ointment are also prescribed.
The latter is an excellent antiseptic, which has a positive effect on the treatment of chalazion, accelerates the process of maturation and bursting of the node, and also perfectly disinfects the infectious focus.
Prevention
To prevent the development of chalazion of the lower eyelid, it is enough to follow simple rules:
- harden the body, thereby increasing immunity;
- provide proper nutrition;
- treat ophthalmological diseases in a timely manner;
- adhere to the rules for using contact lenses;
- don’t forget to wash off your makeup;
- observe the rules of personal hygiene;
- Regularly monitor your health and under no circumstances self-medicate any diseases.
Conclusion
Despite the fact that chalazion of the lower eyelid is not considered a dangerous disease, ignoring it can lead to the development of serious complications and health consequences. That is why it is necessary to start treating it at the earliest stages. With proper therapy and subsequent compliance with all rules of prevention, you can minimize the risk of relapse of the disease.
, please select a piece of text and press Ctrl+Enter.
Source: https://proglaza.net/lechenie/narodnye-metody/halyazion-nizhnego-veka
Symptoms
In the vast majority of cases, inflammation of the eyelid is accompanied by the following characteristic manifestations:
- pain in the damaged area;
- narrowing of the palpebral fissure;
- changes in skin color;
- swelling;
- slight increase in body temperature;
- increased tear production, especially in the wind or in bright light;
- itching and other discomfort;
- the formation of scales at the edge of the damaged eyelid;
- in rare cases - the formation of ulcers;
- release of a clear secretion when pressing on the inflamed area.
This article will tell you how to avoid eye discomfort when wearing contact lenses.
The set of symptoms characteristic of it, as well as the intensity of their manifestation, directly depend on the cause of the disease and the general condition of the body. However, whatever they are, if such characteristic signs of inflammation of the eyelid appear, especially with the formation of scales, a person should immediately consult a specialist and undergo a comprehensive examination.
How to quickly treat internal stye?
At an early stage of the disease, doctors advise following the following tips:
- Provide a warm, dry environment for the affected eye. It is best to warm the eyelids with a lamp with a blue light spectrum or UHF. Wet dressings are not recommended to avoid the spread of infection.
- Instill drops that will kill bacteria. These may be the drugs "Floxal" or "Tsiprolet". For the same purposes, ointments that have an additional anti-inflammatory effect are suitable: “Tetracycline”, “Hydrocortisone”, “Tobradex”. These drugs can be recognized from photographs on the Internet.
If the barley has already ripened, you need to resort to additional measures:
- Avoid using cosmetics and contact lenses for a while. Rinse your eyes daily with filtered water and wash your hands often with soap.
- A medical professional should treat the eyelid with a disinfection solution to help avoid burns to the eye shell.
- According to the recommendations of the attending physician, you can also resort to drip infusion of solutions of penicillin or erythromycin, albucid, hormonal drops with hydrocortisone.
- The inside of the eyelid can be lubricated with ointments containing antibiotics or sulfonamides, as well as yellow mercury ointment.
When treating styes on the inside of the lower and upper eyelids at home, you can also resort to traditional medicine, but only after consultation with a doctor. In addition to pharmaceuticals, it is worth recommending a lotion made from aloe leaves or calendula flowers. However, it is still not worth actively engaging in independent treatment, since the spread of infection can lead to serious consequences requiring surgical intervention. Timely contact with a specialist and professional therapy will help get rid of internal stye within a few days.
Fungal diseases
Actinomycosis. The causative agent is radiata fungi (actinomycetes). A dense, painless nodule appears in the outer or inner corner of the eyelid, which then softens, forming an intradermal infiltrate.
A breakthrough of the infiltrate leaves a long-term non-healing fistula, secreting pus with tangles of fungal threads. Treatment includes the use of antibiotics and actinolysate. Conducting radiotherapy, opening the abscess and curettage it.
Candidiasis (candidiasis) is a disease caused by yeast-like fungi of the genus Candida. When affected, swelling of the skin of the eyelids, hyperemia, and rashes of small pustules are observed.
Treatment includes lubricating the lesions with a solution of brilliant green prepared in water, using nystatin ointment and taking nystatin orally.
Trichophytosis (ringworm). The disease occurs as folliculitis and is caused by fungi of the genus Trichophyton. It is customary to distinguish between superficial and deep trichophytosis. At the same time, the edges of the eyelids are hyperemic and swollen, contain pustules, in yellowish crusts. In some areas of the eyelids there are no eyelashes, in others they are broken off. There is a coating of spores on the eyelashes.
The process may be accompanied by conjunctivitis or keratoconjunctivitis. As healing occurs, scars appear.
During treatment, the affected areas of the skin are wiped with an alcohol solution of iodine or methylene blue. Griseofulvin is prescribed orally.
Inflammatory diseases
Inflammatory lesions of the eyelids occur due to the penetration of pathogenic microorganisms into their tissue. Most often people with weakened immune systems, diabetes and chronic diseases of the gastrointestinal tract get sick. Diseases of the eyelids are treated conservatively (with the help of medications) or surgically.
Blepharitis
Blepharitis is an acute or chronic inflammation of the eyelid margins caused by pathogenic bacteria, fungi or mites. The disease is accompanied by itching and discomfort in the eye area. In this case, the edges of the eyelids turn red or become covered with wounds, and purulent crusts are deposited on the eyelashes. Blepharitis is more common in people with farsightedness and astigmatism who refuse to wear glasses.
Types of blepharitis:
To treat blepharitis, eye drops and ointments with antibiotics (Tobrex, Floxal, Normax) are used. Additionally, doctors may prescribe corticosteroids (Hydrocortisone ointment, Tobradex). These drugs have a powerful anti-inflammatory effect and speed up recovery.
Demodicosis
One of the most common eyelid diseases in humans. It has a chronic course and mild symptoms, which makes it difficult to diagnose. To confirm the diagnosis, laboratory testing of 3-4 eyelashes obtained from a sick person is required. Demodicosis is treated with special anti-mite drugs: Stop Demodex, Glycodem.
Abscess of the century
It is a local accumulation of pus in the thickness of the eyelid. It manifests itself as severe pain and severe swelling in the eye area. The skin becomes very red and hot. When palpated, a dense, painful formation is revealed in the thickness of the eyelid.
To treat an abscess, systemic antibiotics and desensitizing agents are used. The place is prescribed dry heat and disinfectant drops. If fluctuation occurs, the abscess is opened surgically.
Barley
Barley is an acute inflammation of the hair follicle of the eyelash or one of the glands located in the thickness of the lower or upper eyelid. It manifests itself as severe pain, swelling and discomfort in the eye area. Unlike an abscess, a stye is located along the edge of the eyelid and is opened without outside help.
In the first 2-3 days, the progression of the disease can be stopped using dry heat, 70% ethyl alcohol and antibiotics. With timely treatment, the stye can completely disappear without opening. Read more about barley →
Chalazion
A chalazion is a painless, dense formation in the thickness of the eyelid, which is formed due to blockage of the ducts of the sebaceous glands. Unlike barley, the disease has a chronic course. With chalazion there is no swelling, pain or redness of the skin.
In the initial stages, the disease is treated with dry heat, massage and eye drops with corticosteroids (Maxidex, Pharmadex, Dexamethasone). If conservative therapy is ineffective, injection of steroids is indicated. A small amount of Diprospam is injected into the chalazion cavity. If the drug does not help, surgery is performed.
Inflammation of the upper eyelid
Inflammation of the upper eyelid occurs as a consequence of chronic and viral diseases, dysfunction of the endocrine system and gastrointestinal tract, decreased protective functions of the body, exposure to bacterial infections, allergies, demodicosis or molluscum contagiosum. Poor hygiene, all kinds of eye injuries, and vitamin deficiency can also lead to the disease.
Due to the constant irritation of the eye, it is especially susceptible to inflammation and infection, sometimes with severe consequences. Constantly rubbing the eyelashes on the cornea can cause small cracks in which bacteria can invade and cause corneal ulcers.
As a result, scarring can be difficult, making untreated entropy a serious threat. Since entropy is easy to see with the naked eye, diagnosis by a trained ophthalmologist or general practitioner should not be too much of a problem. It only becomes more complex when it comes to investigating the causes. Using a slit lamp and microscope, the ophthalmologist can look closely at the cornea and connective tissue to look for possible triggers for entropy.
Symptoms of inflammation of the upper eyelid, as well as methods of its treatment, are similar to those listed above for the lower eyelid.
Inflammation of the eyelid is an inflammatory process of various etiologies, occurring on the upper, lower eyelids or affecting both eyelids. Symptoms of inflammation of the eyelid are different: itching, redness, swelling. The main causes of eyelid inflammation are stye (inflammation of the meibomian glands of the eyelid edge), eyelid abscess (eyelid abscess), blepharitis (inflammation of the eyelid edge), and herpetic infection.
Treatment for entropy depends on its cause, but almost always requires a complete surgical procedure. In the case of age-related, as well as spastic entropy, there are many different approaches to surgical correction of impaired magic. It is very common to use several zugnachten on the affected eyelid, causing it to slowly turn outward again. Another popular method is horizontal division of the inner eyelid. Threads are pulled through the resulting column, which turn off the lid.
In this case, another intervention is necessary. Until then, the wound is first protected for 24 hours with a bandage and then treated with eye ointment. For example, contact lenses can protect the eye from eyelash friction, or the eyelid can be pulled forward using a tape that tightens the edge of the eyelid.
Barley is an acute purulent inflammatory process of the hair follicle of the eyelash or the sebaceous gland, the duct of which flows into its follicle. The main cause of the disease is Staphylococcus aureus. Barley is also called meibomite - a purulent staphylococcal inflammatory process of the meibomian glands. Barley can be single or multiple. There may be development of inflammation of both the upper and lower eyelids, one or both eyes.
Since it is unfortunately impossible to prevent aging and its accompanying symptoms, age-related entropion cannot be prevented, but it can already be prevented by scar tissue caused by scar tissue. As a precaution, ophthalmologists should be consulted for minor eye injuries to prevent scarring of the connective tissue and hence entropion at an early stage.
Entropion is very unpleasant, but fortunately it is almost always curable. Early detection is very important to avoid permanent negative effects on vision. Inflammation of the eyelid margin may manifest itself with slight swelling and redness. Eyelid hygiene is very important.
Symptoms of inflammation of the eyelid with meibomitis:
- Swelling, redness;
- Swelling of the eyelid;
- Pain on palpation;
- Purulent discharge from the apex of the swelling.
With such inflammation of the eyelid, treatment is reduced to local cauterization of the inflamed area of the eyelid with 70% ethyl alcohol or brilliant green solution.
An abscess of the eyelid is an abscess caused by infection in the wound surfaces of the skin of the eyelid. Often this inflammation of the eyelid is a consequence of the spread of a purulent process from barley. Another common cause of inflammation of the upper eyelid (also lower) is purulent processes occurring in the surrounding tissues - paranasal sinuses, orbit. The most common causative agent of eyelid abscess is staphylococcus.
Symptom of inflammation of the eyelid with an abscess:
- Enlargement of the eyelid, swelling of its area;
- Redness of the eyelid;
- Acquisition of a yellowish tint by the conjunctiva;
- Pain in the eye area, eyelid;
- Severe headaches.
With such inflammation of the eyelid, treatment involves the use of antibiotics, elimination of the main cause of the development of the abscess, and physiotherapeutic treatment. In extreme cases, purulent melting requires surgical intervention.
Herpetic inflammation of the eyelid is caused by the simple herpes virus (Herpes Simplex) and the herpes zoster virus (Herpes Zoster). The disease affects both the upper and lower eyelids; blisters filled with watery contents form on the skin of the eyelids. During the course of the disease, the contents of the vesicles become cloudy, the vesicles open, after which the affected areas of the eyelid heal, becoming covered with epithelium. The course of the disease is complicated by severe itching; when the vesicles are mechanically damaged, the virus spreads and further tissue damage occurs. The inflammatory process is accompanied by moderate pain. Viral herpes infection is recurrent.
Blepharitis is the most common cause of inflammatory processes in the eyelid.
Inflammation of the lower eyelid
Inflammation of the lower eyelid occurs both as an independent disease and as a symptom accompanying other diseases. Its first manifestations are:
Non-standard methods of treatment
However, the most common cause of entropy is age. Age increases the likelihood of entropy quickly because the eyelid muscles become weaker and often fail to maintain them, and the eyelids cannot be held in place properly. In general, internal eyelid return is not a particularly dangerous condition and therefore does not necessarily need to be treated by a doctor. However, inward movement of the eyelids can lead to unpleasant discomfort and pain in the eyes. Therefore, if we are talking about complaints that reduce the quality of life of the victim, this should be done in any case, treatment.
- Severe redness of the edge of the eyelid;
- Swelling of the eyelid;
- Formation of small grayish-yellow scales along the ciliary edge of the eyelid;
- Feeling of heaviness of eyelids;
- Loss of eyelashes;
- Watery eyes.
Subsequently, the edge of the eyelid becomes covered with purulent crusts, in place of which bleeding ulcers form.
In case of inflammation of the lower eyelid, careful hygiene of the affected areas, refusal to wear lenses, avoiding contact with unwashed hands, compresses from medicinal herbs and a set of measures aimed at generally strengthening the immune system are recommended.
An examination by a doctor should be carried out even if the disease is not congenital, but was acquired during life. This may be another underlying condition that also needs to be treated. As a rule, you can contact an ophthalmologist. A visit to the ophthalmologist should be done when it comes to the sensation of a foreign body in the eye, although there is no foreign body. Even reddish and watery eyes are typical symptoms of the inner eyelid and should be examined.
Entropy symptoms are mainly caused by the appearance of eyelashes on the cornea. Thus, there is often a sensation of a foreign body in the eye, which in jargon is called trichiasis and is usually perceived by those affected as extremely disturbing. It can also cause the eye to become red and increase the flow of tears, often accompanied by severe itching.