Causes of intestinal diverticulum
In most cases, the cause of the disease is a person’s low consumption of food of plant origin, for example, when a person begins to exclude fresh vegetables and fruits from his diet, replacing them with meat, as well as various flour products and a variety of baked goods. Such a diet leads to constipation, which contributes to the occurrence of diverticula.
In addition to frequent or constant constipation, the appearance of diverticula in the large intestine is also facilitated by various intestinal infections , in particular dysentery, constant intense gas formation and flatulence, frequent use of laxatives, including those related to traditional medicine. In terms of laxatives, their frequent, unreasonable and uncontrolled use for a long time plays a special role.
Meckel's diverticulum
Separately, it is worth mentioning Meckel's diverticulum, since it is the most common congenital intestinal diverticulum. Occurs in 2% of the general population. Also in 2% of cases it becomes inflamed, simulating the clinical picture of acute appendicitis.
Meckel's diverticulum is an incompletely overgrown vitelline duct through which the fetus is nourished in the womb. Located in the final section of the small intestine.
This is a true diverticulum in its structure, as it contains all layers of the intestine.
Completely repeats the clinical picture of acute appendicitis. Therefore, the operating surgeon, during an appendectomy, must examine 100 cm of the final section of the jejunum in order not to miss inflammation of Meckel’s diverticulum.
Classification of diverticula
The forms of diverticula can be different, for example, the disease can be acquired or congenital.
In the congenital form of the disease, as a rule, there are multiple formations that can be localized not only in the large intestine, but sometimes in other organs. Often such formations are part of a special condition called congenital Senta triad, when intestinal diverticula are combined with cholelithiasis, as well as with a hiatal hernia.
The most common form is the acquired form of intestinal diverticulum , which appears in almost 80% of people with age. In this case, the form of diverticulosis can be different, the formations can be false, if there are no muscle fibers in them, in the walls of the protrusion, or traction, if adhesive disease also develops
Diverticula are often formed as a result of any trauma or previous (as well as current) intestinal diseases.
The disease is also classified according to its location, distinguishing between formations in the large and small intestines. The types of the disease are divided according to its course, in particular, clinically obvious, asymptomatic and complicated forms are distinguished.
Next, we will consider the symptoms of colon diverticulum, as well as methods and methods of its treatment in adults.
What is intestinal diverticulum?
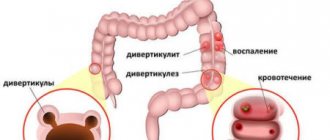
Diverticula are pouch-shaped protrusions of the intestinal wall that form in “weak” areas of the intestinal wall. There are true diverticula, which have all layers of the intestinal wall in their structure, and false ones, in which there is no muscle layer.
The diverticulum is divided into the mouth, the neck, the body and the bottom of the diverticulum. The blood supply to the diverticulum is carried out from the vessels of the submucosal layer from which thin vascular branches extend, piercing the intestinal wall and heading to the bottom of the diverticulum.
When a diverticulum forms in the projection of the fatty suspension and mesentery of the colon, it is covered on the outside with adipose tissue; when a diverticulum forms in the free edge of the intestinal wall, it is covered on the outside only with a serous membrane.
Based on the number, a single diverticulum and multiple diverticula of the colon are distinguished.
Based on the location of diverticula, right-sided, left-sided and total damage to the colon is distinguished.
Diverticulosis of right-sided localization, as a rule, is congenital in nature with a predominance of true diverticula.
With left-sided localization, diverticulosis is in most cases acquired and there is no muscle layer in the structure of diverticula.
Symptoms
In most cases, the disease does not show itself for a long time, without causing any particular inconvenience to the person and without showing any signs. Very often, the disease is discovered by chance, for example, during a general examination or diagnosis of other diseases.
With a clinically obvious form of diverticula, the patient may experience pain in the abdominal area that is vague in nature, as well as chronic diarrhea.
With a clinically obvious form of the disease, complications very often arise, which is associated with a clear disruption of the intestines and the motility of its walls, which is why there is almost constant stagnation of contents not only in the intestine itself, but also in places where there are protrusions, which contributes to a significant increase pressure inside the intestines.
An increase in pressure inside the intestine almost always leads to the appearance of high bacterial contamination , in which more than a million cells can be found in 1 ml of fluid. The rapid formation of fecal stones also occurs, and the intestinal walls in the places where the vessels pass quickly become thinner.
In the obvious clinical form of the disease, the formed protrusions of the intestinal walls usually cause pain in the abdomen, localized mainly in its left half. Most often, pain occurs at the time of defecation, and after it disappears or becomes barely noticeable, not causing serious discomfort.
An important symptom of a clinically obvious form of diverticula is stool instability, when diarrhea alternates with constipation or normal stools for no particular reason.
If you examine the feces, you will see that they are formed into balls that are surrounded by mucus. In this case, the patient complains of severe flatulence, constant bloating and frequent release of gases in a large volume.
If the stagnation of intestinal contents is long-term or permanent, then changes may occur in the walls of the organ, which in most cases are irreversible. With such factors, diverticulosis quickly develops into a more complicated form called diverticulitis. This happens due to the activation of the intestinal flora, which leads to the occurrence of an inflammatory process that quickly becomes chronic.
Diverticulitis often leads to peritonitis at the local level , and adhesions and fistulas begin to form, which connect the intestinal cavity with the skin, bladder, and in women, with the vagina. For the same reason, frequent bleeding of a recurrent nature may also occur (as a symptom).
If there is a pronounced process of inflammation in the diverticulum cavity, the result may be their perforation, as a result of which the intestinal contents begin to penetrate into the abdominal cavity and form an interintestinal abscess. The symptoms of this condition are identical to those of acute appendicitis, so they are often confused and, as a rule, a diagnostic error is discovered only during the operation, when the presence of intestinal diverticula is discovered.
Causes
Intestinal diverticula are, first of all, a social disease associated with the nutritional characteristics of modern society.
Constipation and increased gas production are the main reasons for the development of diverticula. But the reason for the latter is that buns and French fries are tastier than sauerkraut. Well, to put it in terms – “there is not enough fiber in the diet.” Fiber makes feces like neutrinos in the hadron collider, and fats and carbohydrates make like snails. When you try to squeeze this invertebrate creature out of yourself, diverticula arise.
Obesity is a factor predisposing to the development of the disease. In men with a body mass index greater than 30, pseudodiverticula (false diverticula) are found twice as often as in men with a body mass index of 20.
Diagnostics
It is not at all easy to suspect the presence of this disease in a patient, since this disease has no distinct clinical symptoms. In most cases, the presence of diverticula in the intestine is discovered randomly, for example, when a search for the causes of anemia begins and an examination is carried out to exclude possible intestinal tumors.
Diagnosis of diverticulosis, like many others affecting the digestive system, is carried out by a gastroenterologist, and if he suspects the presence of this disease, the patient is sent for some research.
Testing for diverticula includes the following procedures:
- Carrying out a general blood test, which can help identify the presence of anemia and inflammation.
- A stool test to look for possible occult blood in the stool, which can help identify possible internal bleeding.
- Bacteriological analysis of stool and a coprogram, which can be used to diagnose the presence of intestinal dysfunction, bacterial contamination and its level, as well as digestive disorders.
similar articles Digestive organs Structure and purpose of the large intestine
8 837 0
Intestines Treatment of intestinal diverticulosis, symptoms, causes
906 0
Bowel Symptoms and treatment of irritable bowel syndrome
602 0
For diagnostic purposes, irrigography using double contrast is also performed. As a result of such a study, the resulting X-ray image will show all the existing protrusions of the intestinal walls communicating with its cavity.
It is important to remember that if a patient has complicated diverticula of the large intestine, the first step is a general radiographic examination of the peritoneum and the organs located in it. Only after this is it possible to carry out irrigography.
Diagnosis of diverticulosis
Irrigoscopy:
One of the most accessible diagnostic methods is irrigoscopy, which allows one to reliably identify the location, size and number of diverticula.
! This method is not recommended for use in complicated cases due to the high risk of perforation of the inflamed diverticulum.
Colonoscopy:
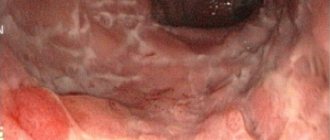
A method that allows you to visualize diverticula and identify complications is colonoscopy. With this procedure, it is possible to fairly reliably diagnose inflammatory changes in the area of the mouth of the diverticulum and detect bleeding from the diverticulum.
! This method cannot be recommended as a mandatory procedure if the patient has a clinical picture of acute surgical disease of the abdominal organs.
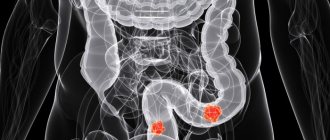
Multislice computed tomography:
The safest method for diagnosing diverticular disease, both during the latent period and when diagnosing complications, is computed tomography, which allows not only to confirm the presence of diverticula in the patient, but also to determine the nature of the complications. These include acute diverticulitis with perforation, abscess, and peritonitis.
! Despite its safety, this method is used to a limited extent due to the high cost of the study and inaccessibility due to the lack of MSCT equipment in a number of hospitals.
Ultrasonography (ultrasound of the abdominal cavity):
An effective and accessible method for diagnosing complications of diverticular disease, it allows us to identify inflammatory changes in the wall of the colon, signs of abscess and peritonitis.
Laparoscopy:
Among the invasive methods for diagnosing complications of diverticular disease, laparoscopy should be noted, which can be considered not only as a diagnostic procedure, but also of a therapeutic nature. With this method, it is possible to perform sanitation measures for local peritonitis, drainage of the abdominal cavity.
Treatment methods for diverticulosis
Treatment of intestinal diverticula, as complicated forms of this disease, occurs exclusively in inpatient settings. Only uncomplicated forms of diverticulosis can be treated at home.
When treating uncomplicated diverticulosis, the main task is to normalize stool , since this helps prevent the development of the disease and the appearance of new protrusions in the intestinal walls, as well as inflammation of intestinal diverticula.
The patient is first prescribed a special individual diet, with the obligatory consumption of wheat bran and large amounts of plant foods. To reduce the intensity of pain, the doctor may prescribe antispasmodics.
If diverticulosis progresses to diverticulitis, it is treated with antibiotics.
Drugs aimed at stopping bleeding are also used. In such situations, treatment is always prescribed individually and depends on many factors and characteristics of the disease.
If, during the examination, the presence of narrowing of the intestinal lumen or perforation of the diverticulum is revealed, then the intervention of surgeons will be necessary for treatment, and during the operation the affected areas are removed.
Drug treatment
The principle of drug treatment in the treatment of deverticulosis always depends on the severity of the disease, the general health of the patient, as well as the presence of complications.
In the asymptomatic form of the disease, which in most cases is detected completely by chance during a general examination or diagnosis of other diseases, the patient is first prescribed a special diet, which requires drinking at least 2 liters of water during the day, if there are no contraindications to such a measure for health.
With asymptomatic diverticulosis, it is necessary to limit the consumption of certain foods and increase the amount of fruits, fresh vegetables and grains in the diet.
In some cases of detection of diverticula, the doctor may prescribe antibiotics, as well as special medications, for example, Linex and its analogues. Anti-flatulence medications are also prescribed to reduce the intensity of intestinal gas production. In addition, the doctor prescribes special digestive enzymes, such as Mezim or Festal, and probiotics to the patient.
If there is an inflammatory process without complications, in which symptoms of intestinal diverticulum begin to appear, the doctor may also recommend routine outpatient treatment, provided that all instructions are strictly followed. In this case, the list of appointments will be much wider.
In addition to diet and a special drinking regime, patients with diverticulosis are prescribed:
- Antibiotic drugs with a wide spectrum of action, as well as products containing butyric and 5-aminosalicylic acid.
- Digestive enzymes designed to improve the functioning of the entire system.
- Drugs that have an antispasmodic effect , such as Spazmol, No-Shpa and its domestic analogue Drotaverin, Spazmonet.
- Drugs intended to stimulate normal intestinal function , enhancing the motility of its walls, for example, Metoclopromide, Domperidone, Pasajix, Motilium.
- Drugs that have a laxative effect . These are mainly prebiotics developed on the basis of Lactulose, in particular, Romphalac, Duphalac, Goodluck, Portalac in syrup, Lactulose Poly and LactuloseStada.
If the disease progresses during treatment, the patient is advised to undergo hospitalization and inpatient treatment.
A patient with diverticulosis is usually hospitalized in cases where, while following all the doctor’s instructions and prescriptions, the patient does not show improvement within 3 days.
In case of hospitalization, the patient is placed in a hospital, where he undergoes a full examination to adjust the prescribed treatment and select further treatment tactics. In most cases, the patient undergoes infusion therapy, which involves intravenous infusion of saline and glucose solutions. Doctors also decide whether surgery is necessary.
Folk remedies
Treatment of intestinal diverticula with folk remedies offers many recipes for the treatment of this disease, but it is important to remember that they are used only in the treatment of uncomplicated forms of the disease in the initial stages of its development. Such methods can be used during treatment only after consultation with the attending physician.
Among the traditional medicines used in the treatment of diverticulosis, the following are most often used: oatmeal jelly, herbal infusion and a mixture of wheat grains and green apples.
Let's look at each of the folk recipes in more detail.
Oatmeal jelly
Oatmeal jelly is prepared from ordinary oat flakes, which can be purchased in almost every store. This jelly allows you to normalize not only stool, but also intestinal tone. In addition, the use of this product allows the patient to get rid of pain and significantly reduce the level of flatulence.
To prepare jelly, you need to take 2.5 liters of boiled water, cool it to 50°C, pour it into a clean 3-liter jar, add 150 ml of fresh kefir and add 500 grams of regular oatmeal. The jar is covered and placed in a warm place to infuse for two days.
If signs of fermentation appear, the mixture should be strained through a colander. After straining, the grounds need to be put into a cup, pour in 1.5 liters of water, stir and strain again, then squeeze out the grounds. The liquid is poured back into the jar (mixing it with water from washing the grounds) and left for about 20 hours, until the total mass is divided into two layers.
The bottom layer of grounds is an oat concentrate necessary for making jelly. It should be carefully drained and stored in the refrigerator. To prepare jelly, take 2 glasses of water, add 10 tablespoons of the concentrated mixture, stir, bring to a boil, and then simmer over low heat until thick. Kissel should be consumed in the morning with a piece of bread.
Herbal infusion
To prepare an infusion of herbs, grind rose hips and dill in a blender. Next, you need to mix chopped dill, medicinal chamomile flowers, motherwort herb, nettle leaves, and crushed rose hips in equal parts.
To prepare the infusion, take 1 tablespoon of the mixture and pour 200 boiling water over it, then leave for 3 hours to infuse. You need to drink this infusion for 6 weeks every day during meals, 150 ml.
Mixture of wheat grains and green apples
Wheat grains (necessarily sprouted) and green apples are taken in equal parts, crushed until smooth in a blender.
The mixture should be taken for breakfast in the amount of 250 - 300 grams for one month, after which you should take a break of 4 weeks and repeat this course again.
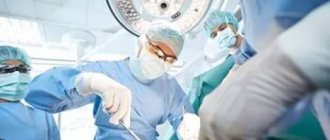
Surgical intervention
Surgical treatment of intestinal diverticulum usually becomes necessary if the patient has already had 2 attacks of diverticulosis. The operation is scheduled. If surgery is not performed in a timely manner, repeated attacks that are no longer amenable to drug therapy will lead to intestinal perforation and peritonitis in the future, which will require urgent surgery.
Very important! It is important to remember that untimely surgery after intestinal perforation and periotonitis occurs can cause the patient’s death.
In addition, surgical treatment is indicated for all patients whose age is over 40 years, after the first attack of diverticulitis.
During surgery, in most cases, surgeons remove areas of the intestine damaged by diverticula.
As a rule, surgery to remove areas of the intestine damaged by diverticula is prescribed if there are complications:
- Intestinal obstruction in a progressive form;
- Heavy or recurring bleeding;
- Perforation of the diverticulum, as a result of which the development of retroperitoneal phlegmon or peritonitis began;
- Opening the abscess, as a result of which the development of intestinal fistulas of an internal and external nature began.
The scope of surgical intervention is always individual and determined by the doctor, based on the existing characteristics of the condition and the presence of complications. The methods for carrying out such operations are also different.
It is important to remember that contacting a doctor should be timely, since adequate therapy, as well as planned surgery after an attack of diverticulosis, significantly improves the overall prognosis for the patient’s recovery.
Treatment
In the treatment of diverticulosis of the large intestine, the main importance is given to the normalization of stool and diet. It is recommended to switch to a diet high in fiber.
Treatment also involves physical activity, training the abdominal muscles is especially beneficial. Since the functioning of the intestines directly depends on their tone.
In some cases, diverticula can pose a danger in terms of the development of cancer. Then they must be removed surgically. In this case, it is not the diverticulum that is removed, but the section of the intestine on which it is located.
Also subject to surgical treatment:
- inflammation of the diverticulum – diverticulitis;
- bleeding from a diverticulum;
- diverticulum perforation;
- diffuse peritonitis.
All of the above conditions are extremely dangerous and require hospital treatment by a surgeon.
Diverticulitis is treated in a hospital. One in four patients with diverticulitis requires surgical treatment. If perforation develops in the vagina or bladder, treatment will be required by a gynecologist or urologist.
Conservative treatment of diverticulitis includes the prescription of broad-spectrum antibiotics. Dietary treatment is based on increasing the proportion of dietary fiber in the diet and reducing fat.
Diet for intestinal diverticulum
When such a disease occurs, the patient is first prescribed a special diet that requires strict adherence. The main principle of such a diet is to change the previous diet and include in it plant foods rich in fiber, since it is these foods that contribute to faster and easier passage of food mass through the organs of the gastrointestinal tract.
Recommendations for changing diet for intestinal diverticulum:
- It is necessary to include in your daily diet cereals, brown rice, a variety of legumes, as well as fresh fruits and vegetables, but without hard peels and seeds.
- You should not eat foods such as radishes, persimmons, and pineapples. They, of course, contain a large amount of essential plant fibers, but these fibers are too coarse for damaged intestines.
- It is important that the daily diet necessarily includes first courses, in particular, various soups (chicken, vegetable), a variety of freshly squeezed fruit and vegetable juices.
- It is necessary to drink clean water in sufficient quantities.
- Popcorn, all kinds of crackers, chips, as well as seeds and nuts should be excluded from the menu.
- Dairy products, like eggs, should be present in the diet, but their quantity should be limited.
- It is recommended to consume fermented milk products, for example, fresh live yoghurts, kefir, and yogurt.
It is important that food for intestinal diverticulosis is gentle, so it is best to cook food in a double boiler; you can also bake or boil food. Fried foods are prohibited.
It is necessary to consume food in small portions, chewing each piece very carefully. Meals should be separate and fractional so that the food eaten is easier to digest and better absorbed.
Characteristics of the disease
Diverticula form in the lining of the intestinal wall. In appearance they resemble a hernial protrusion. Most often, diverticula form in the intestinal area, but sometimes they can appear in the stomach and esophagus.
The disease develops due to disruption of normal peristalsis of the intestinal wall. This often happens due to errors in nutrition, as well as low physical activity. Bloating and overfilling of the intestines with gases leads to overstretching of its walls, as accumulated gas bubbles contribute to increased pressure inside the organ. This provokes the formation of diverticula. Another reason for their occurrence is weakness of the intestinal muscles.
There are 3 forms of diverticulosis:
- Asymptomatic disease.
- Diverticulosis with clinical manifestations.
- Diverticulosis with complications.
Complications and consequences
Gradually, an inflammatory process begins in the existing diverticula, which occurs due to the accumulation of feces in them and contamination with bacteria. In this case, the disease turns into diverticulitis, that is, into a complicated form. In this case, the patient develops pain in the abdomen, the temperature rises, severe flatulence appears, which greatly worries the patient, and blood and lumps of mucus are often found in the stool. As a rule, most patients consult a doctor precisely when the disease is complicated by inflammation and symptoms of this condition appear.
Diverticulitis, if left unattended, can lead to other serious complications:
- To the appearance of intestinal bleeding , in which blood clots and uncoagulated blood are found in the stool. In this case, the patient develops weakness, pale skin, and a decrease in blood pressure. In addition, there is a disturbance in stool, as well as abdominal pain when blood is released.
- To intestinal obstruction . This happens due to the narrowing of the intestinal lumens in the places where diverticula are located. Because of this, intestinal masses cannot move normally.
- To purulent inflammation of the peritoneal cavity if diverticula rupture (perforation) and intestinal contents exit into the abdominal cavity. In this case, purulent inflammation occurs, called peritonitis, which is a very dangerous condition, often leading to death.
When is surgery needed?
Surgical treatment for diverticulitis can be emergency or planned. Urgent surgery is necessary for patients whose condition is seriously life-threatening. This applies to:
- perforation (rupture) of the diverticulum into the abdominal cavity, which is accompanied by the occurrence of diffuse peritonitis;
- intestinal obstruction;
- massive bleeding.
Also, surgery (most often planned) is performed if conservative therapy does not produce a positive effect. Other indications for surgery include:
- the presence of fistulas (pathological holes);
- the formation of chronic infiltrates similar to a tumor;
- systematic relapses of the disease.
The operation is performed under general anesthesia. But the choice of intervention method is selected by the doctor depending on:
- type of complications and prevalence of the disease;
- the presence of inflammatory changes in the diverticulum itself, adjacent intestinal walls and other peritoneal tissues;
- the presence of inflammation that has arisen around the lesion, or peritonitis;
- associated health problems.
Photo: Nestor Rizhniak / Shutterstock.com
Most often, surgery involves complete removal of the affected part of the intestine. In the absence of acute inflammation, surgeons, simultaneously with intestinal resection, perform an anastomosis - connecting individual parts of the intestine to each other. However, the acute inflammatory process does not allow this to be done. In such a situation, patients undergo a colostomy (an artificial opening for the exit of intestinal contents) on the anterior abdominal wall. After normalization of the condition, repeated intervention is performed with anastomosis.
Forecast
The prognosis for diverticulosis of the small intestine is unfavorable, as it leads to serious malabsorption. The possibilities of surgical treatment are limited, since with multiple diverticula, extensive resection leads to complications.
With diverticulosis of the colon, the prognosis is favorable.
Although a lack of coarse plant fiber in the diet can lead not only to diverticulitis, but also to colon cancer, both diseases rarely occur at the same time.
data-matched-content-rows-num=”4.2″ data-matched-content-columns-num=”1.2″ data-matched-content-ui-type=”image_stacked” data-ad-format=” autorelaxed">
Drug treatment
For intestinal diverticulosis, treatment tactics are determined by the general health of the patient, the severity of the disease, and the presence of complications.
The most common and main symptoms of uncomplicated diverticulosis of the large intestine:
Use of medications
Drug therapy is aimed at eliminating the symptoms of the disease. The group of drugs for diverticulosis includes:
- Antispasmodics and prokinetics - designed to reduce pain and normalize intestinal motor function (No-spa, Spazmolgon, Motilak, Motilium).
- Anti-inflammatory drugs – Salofalk.
- Laxatives – help get rid of constipation (Regulax, Guttalax).
- Enzyme preparations - improve digestion (Mezim, Pancreatin, Creon).
- Means that normalize the composition of intestinal microflora - Todicamp-Lact, Linex.
We recommend reading: Vaccination against typhoid fever: contraindications for vaccination of adults and children
You cannot use various tablets, including homeopathic remedies and traditional medicine recipes (celandine, for example), without a doctor’s prescription.
Reasons for appearance
Congenital diverticula of the duodenum arise in places of congenital underdevelopment of the muscular membrane.
Acquired duodenal diverticula are the result of duodenal ulcer and recurrent pancreatitis.
The vascular factor plays a great role in the occurrence of diverticula: with spasm of the muscle layer, intrawall vessels are compressed with impaired microcirculation - ischemia and slowing of venous outflow, dystrophic changes develop, which subsequently become the site of formation of diverticula.
Reasons for the development of acquired diverticula:
- reduction in the content of plant fibers and fiber in the diet;
- weakening of the tissues of the intestinal wall during the aging process;
- weakening and disruption of intestinal motor function (constipation);
- adhesions in the intestines;
- significant increase in intraintestinal pressure.
Intestinal pressure can increase bile acids, stimulating intestinal function. Dietary fiber contained in bran and plant fiber has the property of lowering blood pressure.
Causes of diverticulosis
Reasons leading to the development of diverticulosis:
- Chronic constipation.
- Excess body weight.
- Flatulence and bloating.
- Past intestinal infections.
- The formation of atherosclerotic plaques in the vessels that feed the intestines.
- Maintaining a sedentary lifestyle.
- Age over 60 years.
- Complicated family history.
- Poor circulation in the intestines.
- Chronic bowel diseases.
- Poor nutrition.
Symptoms of intestinal diverticulosis
Often diverticulosis is not accompanied by any symptoms. For a long time a person does not even suspect that he has such a problem.
In other cases, pathology is manifested by such signs as:
- Abdominal pain on the left side.
- Abnormal stool, alternating diarrhea and constipation.
- Rumbling in the stomach.
- Nausea and vomiting.
Symptoms increase in severity when the diverticulum becomes inflamed. At the same time, the patient’s body temperature rises, blood appears in the stool, and abdominal bloating increases. Pain during exacerbation of pathology is concentrated in the iliac fossa on the left side. As the inflammatory response progresses, the symptoms intensify and are expressed as follows:
- Alternating diarrhea and constipation.
- Lack of appetite.
- Vomiting and nausea.
- Increased pain.
- Increase in body temperature.
- The appearance of mucus in the stool.
- Increased heart rate.
- The appearance of symptoms of peritonitis.
- Increased level of leukocytes in the blood.
- The appearance of foul-smelling gases, bloating.
- Increased urge to have bowel movements. After defecation, the patient retains a feeling of incomplete emptying of the organ.
If a person is not given help in time, the inflammation will intensify, the intestinal wall will burst and diffuse peritonitis will occur.
Types of diverticula
| View | Description | Cause |
| Congenital | Meckel's diverticulum | Ileal diverticulum occurs as a result of a violation of the reverse development of the intestinal part of the bile duct. |
| Duodenal diverticulum | Occurs in places of congenital underdevelopment of the muscle membrane | |
| Diverticulum of another location | ||
| Purchased | Pulse diverticulum | Occurs due to the effect of high intraintestinal pressure on the altered intestinal wall |
| Traction diverticulum | Develops during the adhesive process, as a result of traction on the intestinal wall from the outside | |
| False diverticulum | Formed due to protrusion of only the mucous and submucosal base through a defect in the muscular layer of the intestinal wall |
A true (congenital) formation consists of three membranes of the intestinal wall and is much less common than an acquired one.
Duodenal diverticula are classified as so-called pulsion diverticula. The pulsation is caused by contractions of the smooth muscle layer of the intestine.